Abstract
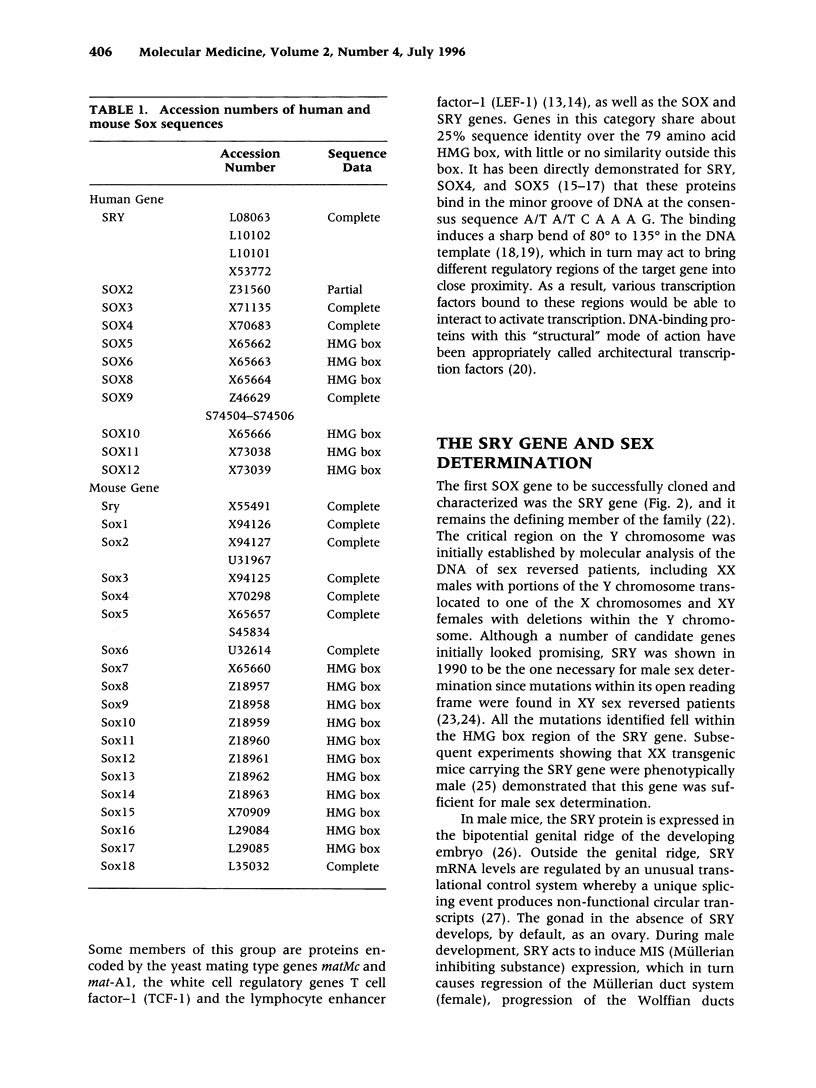
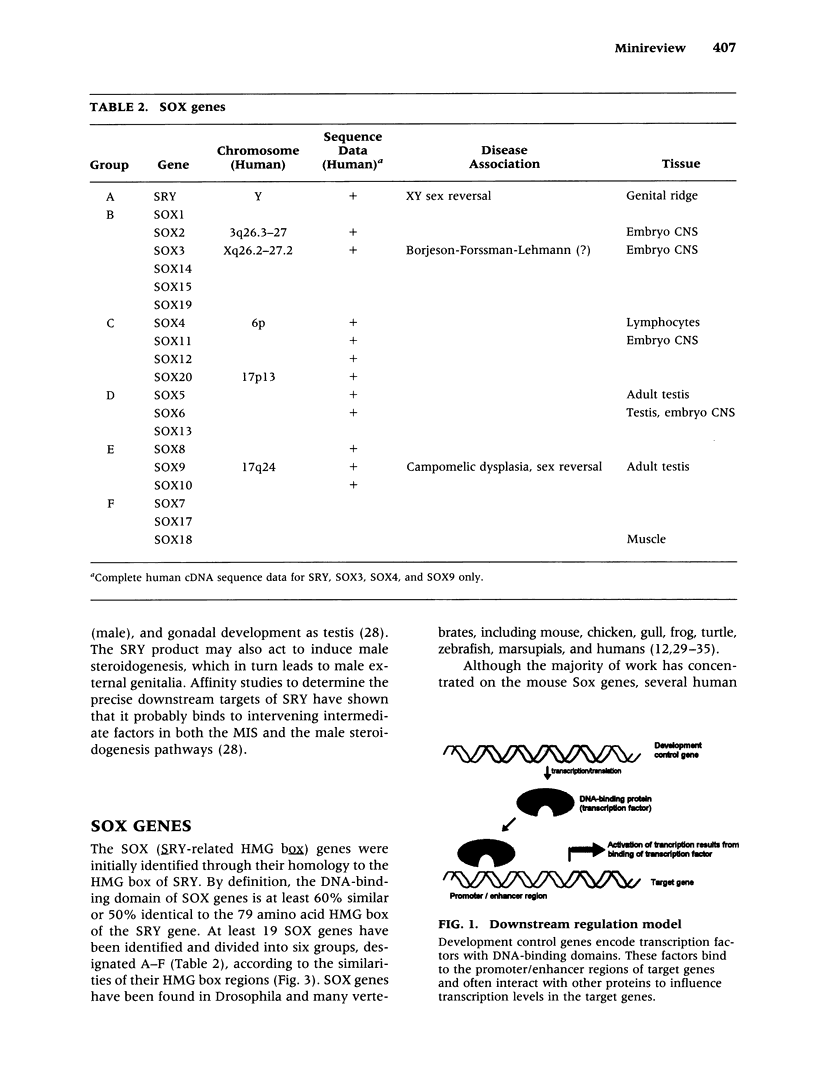
Development in higher organisms involves complex genetic regulation at the molecular level. The emerging picture of development control includes several families of master regulatory genes which can affect the expression of down-stream target genes in developmental cascade pathways. One new family of such development regulators is the SOX gene family. The SOX genes are named for a shared motif called the SRY box a region homologous to the DNA-binding domain of SRY, the mammalian sex determining gene. Like SRY, SOX genes play important roles in chordate development. At least a dozen human SOX genes have been identified and partially characterized (Tables 1 and 2). Mutations in SOX9 have recently been linked to campomelic dysplasia and autosomal sex reversal, and other SOX genes may also be associated with human disease.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Behlke M. A., Bogan J. S., Beer-Romero P., Page D. C. Evidence that the SRY protein is encoded by a single exon on the human Y chromosome. Genomics. 1993 Sep;17(3):736–739. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busch S. J., Sassone-Corsi P. Dimers, leucine zippers and DNA-binding domains. Trends Genet. 1990 Feb;6(2):36–40. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90071-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capel B., Swain A., Nicolis S., Hacker A., Walter M., Koopman P., Goodfellow P., Lovell-Badge R. Circular transcripts of the testis-determining gene Sry in adult mouse testis. Cell. 1993 Jun 4;73(5):1019–1030. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90279-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chardard D., Chesnel A., Gozé C., Dournon C., Berta P. Pw Sox-1: the first member of the Sox gene family in Urodeles. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jul 25;21(15):3576–3576. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.15.3576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clépet C., Schafer A. J., Sinclair A. H., Palmer M. S., Lovell-Badge R., Goodfellow P. N. The human SRY transcript. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Dec;2(12):2007–2012. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.12.2007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collignon J., Sockanathan S., Hacker A., Cohen-Tannoudji M., Norris D., Rastan S., Stevanovic M., Goodfellow P. N., Lovell-Badge R. A comparison of the properties of Sox-3 with Sry and two related genes, Sox-1 and Sox-2. Development. 1996 Feb;122(2):509–520. doi: 10.1242/dev.122.2.509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor F., Cary P. D., Read C. M., Preston N. S., Driscoll P. C., Denny P., Crane-Robinson C., Ashworth A. DNA binding and bending properties of the post-meiotically expressed Sry-related protein Sox-5. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Aug 25;22(16):3339–3346. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.16.3339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor F., Wright E., Denny P., Koopman P., Ashworth A. The Sry-related HMG box-containing gene Sox6 is expressed in the adult testis and developing nervous system of the mouse. Nucleic Acids Res. 1995 Sep 11;23(17):3365–3372. doi: 10.1093/nar/23.17.3365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coriat A. M., Müller U., Harry J. L., Uwanogho D., Sharpe P. T. PCR amplification of SRY-related gene sequences reveals evolutionary conservation of the SRY-box motif. PCR Methods Appl. 1993 Feb;2(3):218–222. doi: 10.1101/gr.2.3.218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denny P., Swift S., Brand N., Dabhade N., Barton P., Ashworth A. A conserved family of genes related to the testis determining gene, SRY. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jun 11;20(11):2887–2887. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.11.2887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denny P., Swift S., Connor F., Ashworth A. An SRY-related gene expressed during spermatogenesis in the mouse encodes a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein. EMBO J. 1992 Oct;11(10):3705–3712. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05455.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn T. L., Mynett-Johnson L., Wright E. M., Hosking B. M., Koopman P. A., Muscat G. E. Sequence and expression of Sox-18 encoding a new HMG-box transcription factor. Gene. 1995 Aug 19;161(2):223–225. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(95)00280-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk K., Rötzschke O., Rammensee H. G. Cellular peptide composition governed by major histocompatibility complex class I molecules. Nature. 1990 Nov 15;348(6298):248–251. doi: 10.1038/348248a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farr C. J., Easty D. J., Ragoussis J., Collignon J., Lovell-Badge R., Goodfellow P. N. Characterization and mapping of the human SOX4 gene. Mamm Genome. 1993;4(10):577–584. doi: 10.1007/BF00361388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari S., Harley V. R., Pontiggia A., Goodfellow P. N., Lovell-Badge R., Bianchi M. E. SRY, like HMG1, recognizes sharp angles in DNA. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(12):4497–4506. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05551.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster J. W., Dominguez-Steglich M. A., Guioli S., Kwok C., Weller P. A., Stevanović M., Weissenbach J., Mansour S., Young I. D., Goodfellow P. N. Campomelic dysplasia and autosomal sex reversal caused by mutations in an SRY-related gene. Nature. 1994 Dec 8;372(6506):525–530. doi: 10.1038/372525a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster J. W., Graves J. A. An SRY-related sequence on the marsupial X chromosome: implications for the evolution of the mammalian testis-determining gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 1;91(5):1927–1931. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.5.1927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gozé C., Poulat F., Berta P. Partial cloning of SOX-11 and SOX-12, two new human SOX genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jun 25;21(12):2943–2943. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.12.2943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths R. The isolation of conserved DNA sequences related to the human sex-determining region Y gene from the lesser black-backed gull (Larus fuscus). Proc Biol Sci. 1991 May 22;244(1310):123–128. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1991.0060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Giese K., Pagel J. HMG domain proteins: architectural elements in the assembly of nucleoprotein structures. Trends Genet. 1994 Mar;10(3):94–100. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(94)90232-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubbay J., Collignon J., Koopman P., Capel B., Economou A., Münsterberg A., Vivian N., Goodfellow P., Lovell-Badge R. A gene mapping to the sex-determining region of the mouse Y chromosome is a member of a novel family of embryonically expressed genes. Nature. 1990 Jul 19;346(6281):245–250. doi: 10.1038/346245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hacker A., Capel B., Goodfellow P., Lovell-Badge R. Expression of Sry, the mouse sex determining gene. Development. 1995 Jun;121(6):1603–1614. doi: 10.1242/dev.121.6.1603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halder G., Callaerts P., Gehring W. J. New perspectives on eye evolution. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1995 Oct;5(5):602–609. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(95)80029-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haqq C. M., King C. Y., Ukiyama E., Falsafi S., Haqq T. N., Donahoe P. K., Weiss M. A. Molecular basis of mammalian sexual determination: activation of Müllerian inhibiting substance gene expression by SRY. Science. 1994 Dec 2;266(5190):1494–1500. doi: 10.1126/science.7985018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harley V. R., Lovell-Badge R., Goodfellow P. N. Definition of a consensus DNA binding site for SRY. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Apr 25;22(8):1500–1501. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.8.1500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill R. E., Hanson I. M. Molecular genetics of the Pax gene family. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;4(6):967–972. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90126-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houston C. S., Opitz J. M., Spranger J. W., Macpherson R. I., Reed M. H., Gilbert E. F., Herrmann J., Schinzel A. The campomelic syndrome: review, report of 17 cases, and follow-up on the currently 17-year-old boy first reported by Maroteaux et al in 1971. Am J Med Genet. 1983 May;15(1):3–28. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320150103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan T., Hanson I., Zaletayev D., Hodgson S., Prosser J., Seawright A., Hastie N., van Heyningen V. The human PAX6 gene is mutated in two patients with aniridia. Nat Genet. 1992 Aug;1(5):328–332. doi: 10.1038/ng0892-328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamachi Y., Sockanathan S., Liu Q., Breitman M., Lovell-Badge R., Kondoh H. Involvement of SOX proteins in lens-specific activation of crystallin genes. EMBO J. 1995 Jul 17;14(14):3510–3519. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07357.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koopman P., Gubbay J., Vivian N., Goodfellow P., Lovell-Badge R. Male development of chromosomally female mice transgenic for Sry. Nature. 1991 May 9;351(6322):117–121. doi: 10.1038/351117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krumlauf R. Hox genes in vertebrate development. Cell. 1994 Jul 29;78(2):191–201. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90290-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laudet V., Stehelin D., Clevers H. Ancestry and diversity of the HMG box superfamily. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 May 25;21(10):2493–2501. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.10.2493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer J., Wirth J., Held M., Schempp W., Scherer G. SOX20, a new member of the SOX gene family, is located on chromosome 17p13. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1996;72(2-3):246–249. doi: 10.1159/000134200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirzayans F., Pearce W. G., MacDonald I. M., Walter M. A. Mutation of the PAX6 gene in patients with autosomal dominant keratitis. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Sep;57(3):539–548. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanyanusin P., Schimmenti L. A., McNoe L. A., Ward T. A., Pierpont M. E., Sullivan M. J., Dobyns W. B., Eccles M. R. Mutation of the PAX2 gene in a family with optic nerve colobomas, renal anomalies and vesicoureteral reflux. Nat Genet. 1995 Apr;9(4):358–364. doi: 10.1038/ng0495-358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schilham M. W., van Eijk M., van de Wetering M., Clevers H. C. The murine Sox-4 protein is encoded on a single exon. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Apr 25;21(8):2009–2009. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.8.2009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair A. H., Berta P., Palmer M. S., Hawkins J. R., Griffiths B. L., Smith M. J., Foster J. W., Frischauf A. M., Lovell-Badge R., Goodfellow P. N. A gene from the human sex-determining region encodes a protein with homology to a conserved DNA-binding motif. Nature. 1990 Jul 19;346(6281):240–244. doi: 10.1038/346240a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevanovic M., Zuffardi O., Collignon J., Lovell-Badge R., Goodfellow P. The cDNA sequence and chromosomal location of the human SOX2 gene. Mamm Genome. 1994 Oct;5(10):640–642. doi: 10.1007/BF00411460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevanović M., Lovell-Badge R., Collignon J., Goodfellow P. N. SOX3 is an X-linked gene related to SRY. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Dec;2(12):2013–2018. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.12.2013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Helix-turn-helix, zinc-finger, and leucine-zipper motifs for eukaryotic transcriptional regulatory proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Apr;14(4):137–140. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90145-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tassabehji M., Read A. P., Newton V. E., Harris R., Balling R., Gruss P., Strachan T. Waardenburg's syndrome patients have mutations in the human homologue of the Pax-3 paired box gene. Nature. 1992 Feb 13;355(6361):635–636. doi: 10.1038/355635a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tommerup N., Schempp W., Meinecke P., Pedersen S., Bolund L., Brandt C., Goodpasture C., Guldberg P., Held K. R., Reinwein H. Assignment of an autosomal sex reversal locus (SRA1) and campomelic dysplasia (CMPD1) to 17q24.3-q25.1. Nat Genet. 1993 Jun;4(2):170–174. doi: 10.1038/ng0693-170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travis A., Amsterdam A., Belanger C., Grosschedl R. LEF-1, a gene encoding a lymphoid-specific protein with an HMG domain, regulates T-cell receptor alpha enhancer function [corrected]. Genes Dev. 1991 May;5(5):880–894. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.5.880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uwanogho D., Rex M., Cartwright E. J., Pearl G., Healy C., Scotting P. J., Sharpe P. T. Embryonic expression of the chicken Sox2, Sox3 and Sox11 genes suggests an interactive role in neuronal development. Mech Dev. 1995 Jan;49(1-2):23–36. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(94)00299-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vriz S., Lovell-Badge R. The zebrafish Zf-Sox 19 protein: a novel member of the Sox family which reveals highly conserved motifs outside of the DNA-binding domain. Gene. 1995 Feb 14;153(2):275–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)00815-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner T., Wirth J., Meyer J., Zabel B., Held M., Zimmer J., Pasantes J., Bricarelli F. D., Keutel J., Hustert E. Autosomal sex reversal and campomelic dysplasia are caused by mutations in and around the SRY-related gene SOX9. Cell. 1994 Dec 16;79(6):1111–1120. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90041-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterman M. L., Jones K. A. Purification of TCF-1 alpha, a T-cell-specific transcription factor that activates the T-cell receptor C alpha gene enhancer in a context-dependent manner. New Biol. 1990 Jul;2(7):621–636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright E. M., Snopek B., Koopman P. Seven new members of the Sox gene family expressed during mouse development. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Feb 11;21(3):744–744. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.3.744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright E., Hargrave M. R., Christiansen J., Cooper L., Kun J., Evans T., Gangadharan U., Greenfield A., Koopman P. The Sry-related gene Sox9 is expressed during chondrogenesis in mouse embryos. Nat Genet. 1995 Jan;9(1):15–20. doi: 10.1038/ng0195-15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan H., Corbi N., Basilico C., Dailey L. Developmental-specific activity of the FGF-4 enhancer requires the synergistic action of Sox2 and Oct-3. Genes Dev. 1995 Nov 1;9(21):2635–2645. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.21.2635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Wetering M., Clevers H. Sequence-specific interaction of the HMG box proteins TCF-1 and SRY occurs within the minor groove of a Watson-Crick double helix. EMBO J. 1992 Aug;11(8):3039–3044. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05374.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Wetering M., Oosterwegel M., van Norren K., Clevers H. Sox-4, an Sry-like HMG box protein, is a transcriptional activator in lymphocytes. EMBO J. 1993 Oct;12(10):3847–3854. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06063.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]