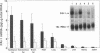Abstract
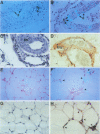
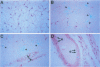
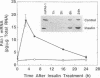
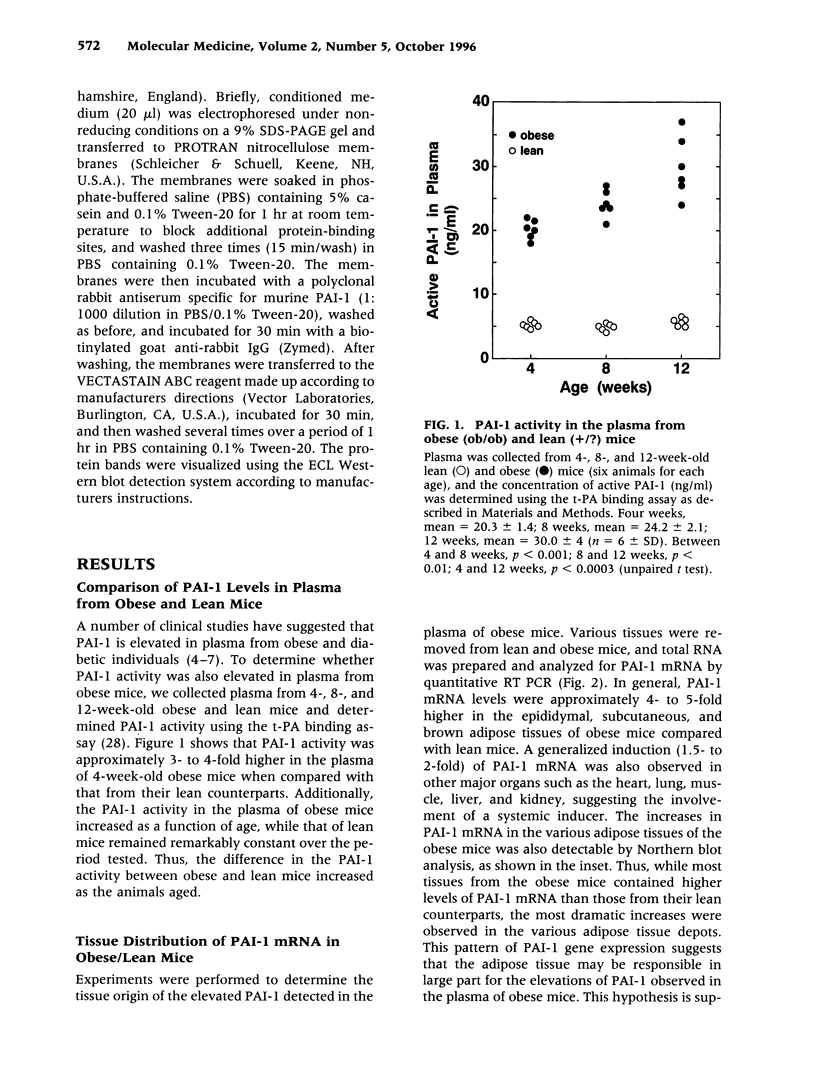
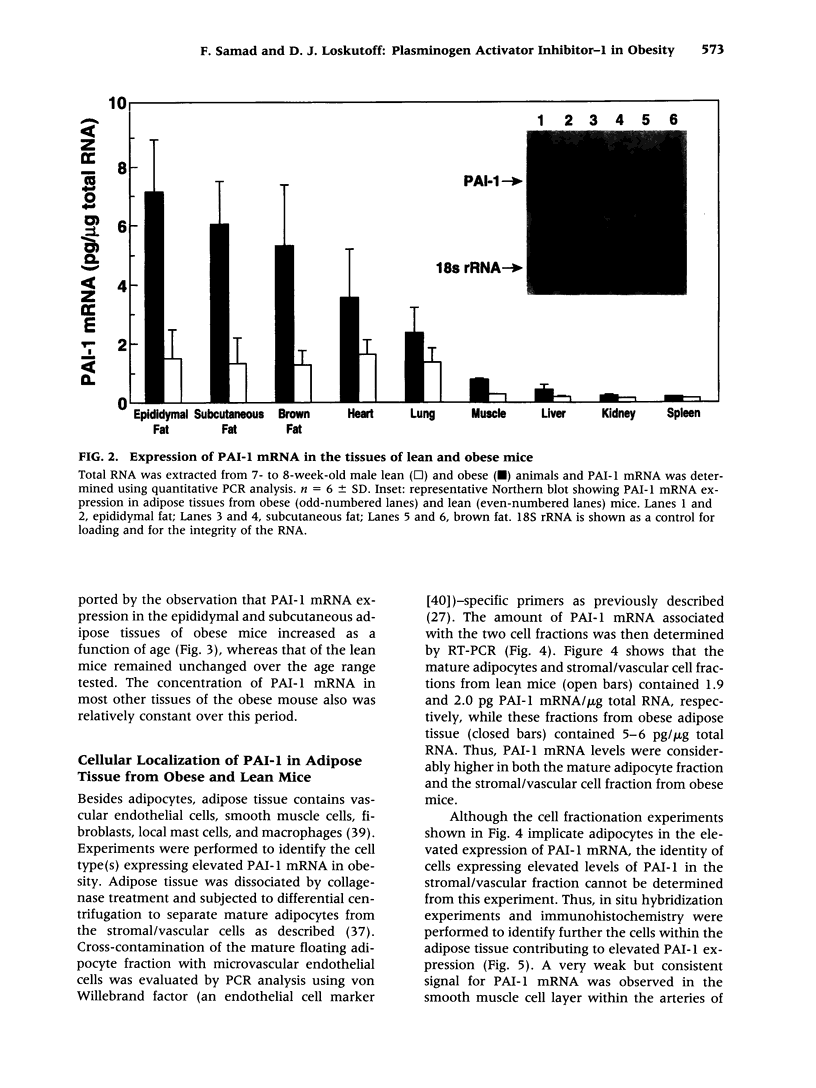
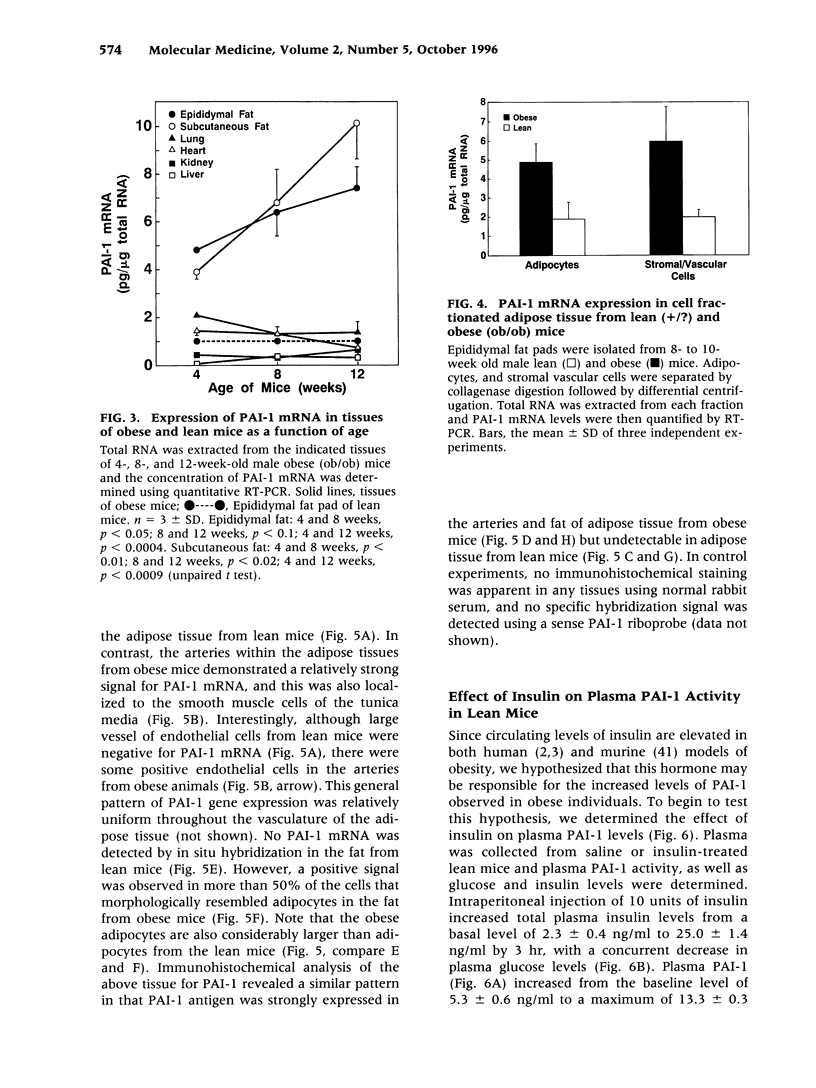
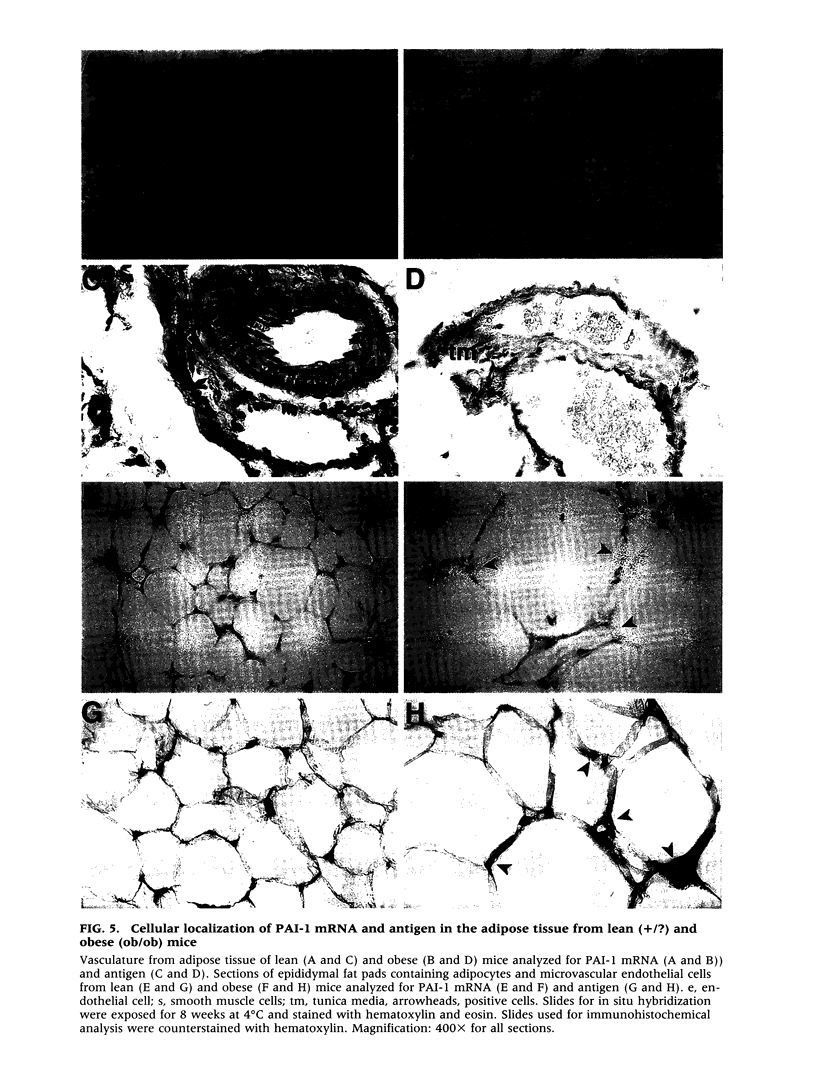
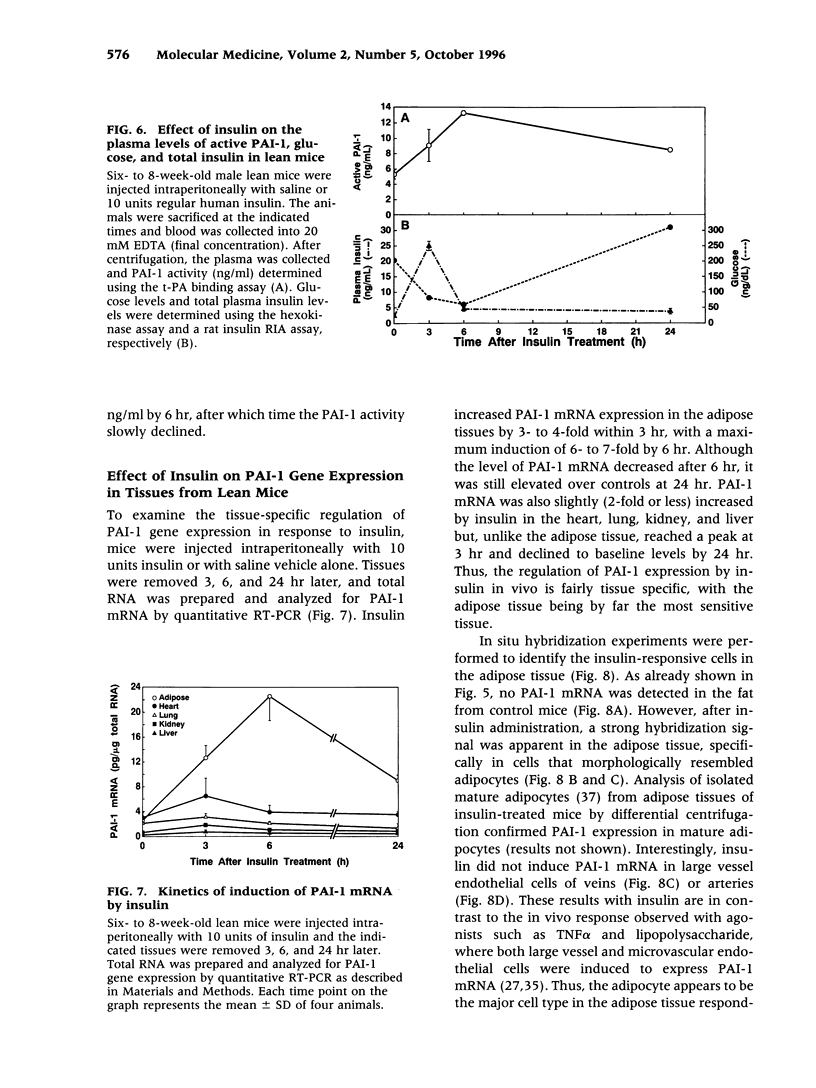
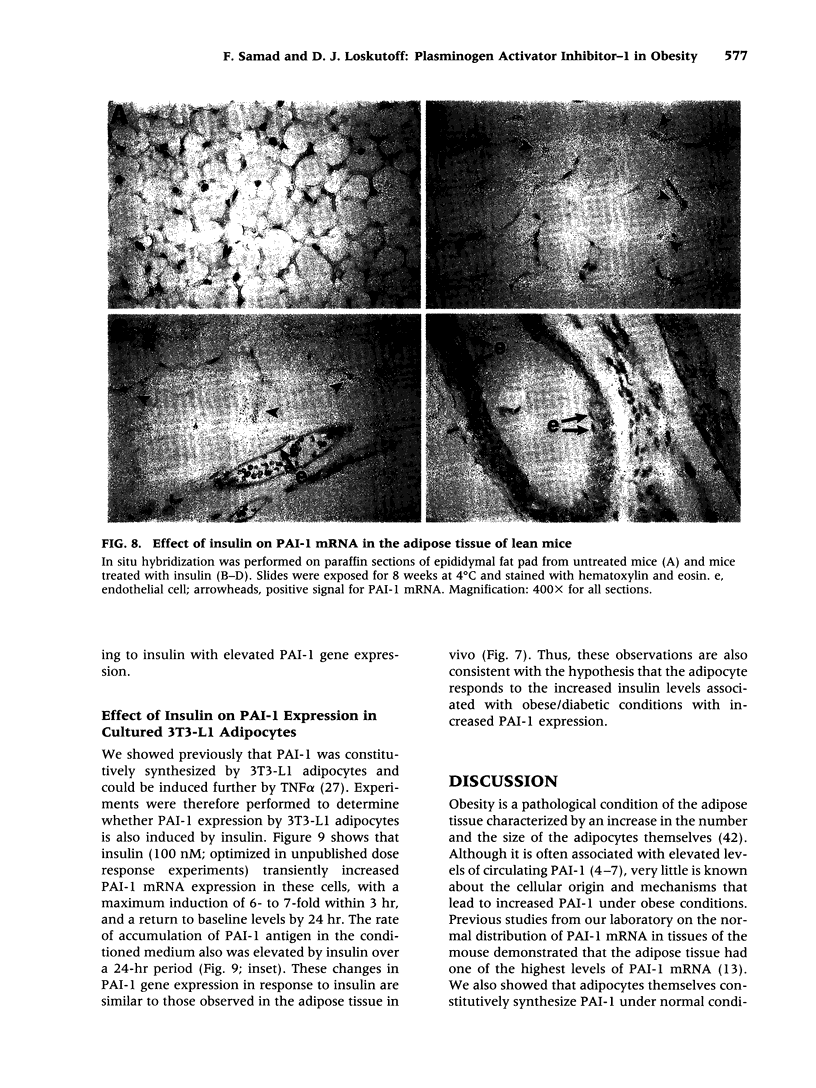
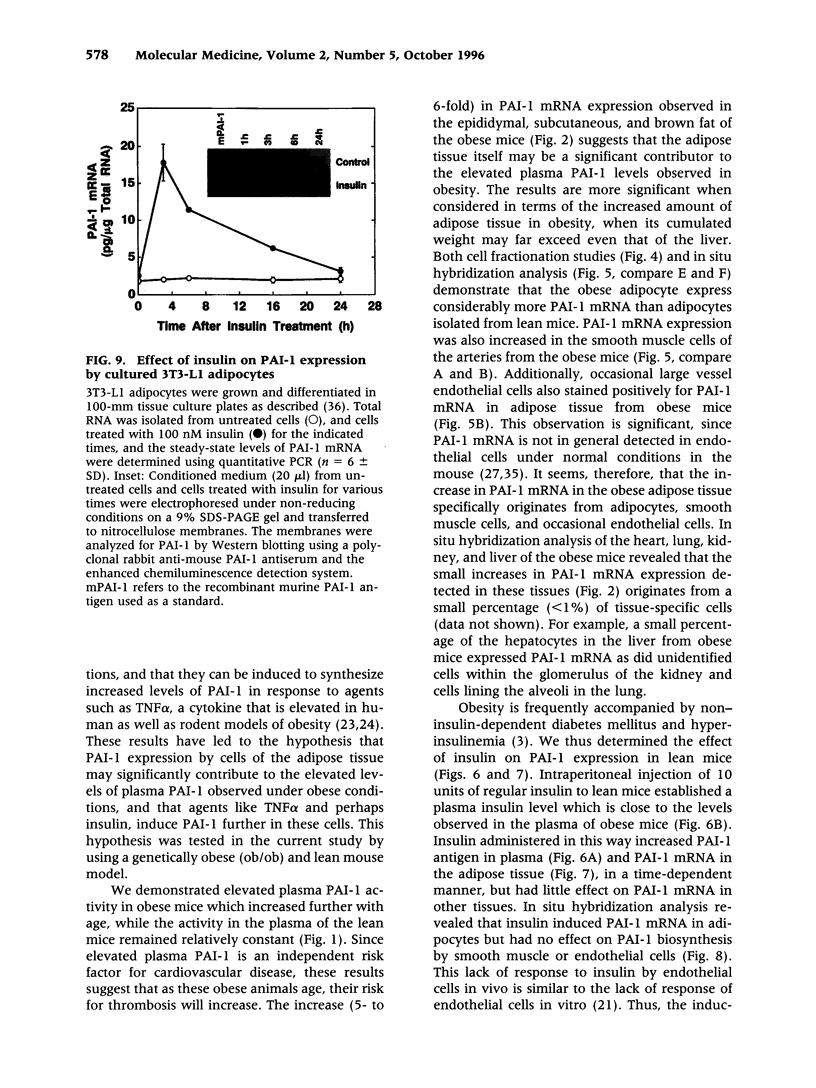
BACKGROUND: Although elevated plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) is associated with obesity and may be a risk factor for cardiovascular disease, the mechanism(s) that lead to this elevation, and the tissue/cellular origins of this increase, remain to be defined. In this report, we have addressed these questions using genetically obese mice (ob/ob) and their lean counterparts (+/?). MATERIALS AND METHODS: PAI-1 activity and antigen levels were determined using a tissue-type plasminogen activator (t-PA) binding assay and Western blotting. The concentration of PAI-1 mRNA in tissues was determined by quantitative reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), and the cellular localization of PAI-1 was evaluated using in situ hybridization, immunohistochemistry, and cell fractionation. RESULTS: PAI-1 activity was approximately 4-fold higher in plasma from ob/ob mice than in that obtained from their lean counterparts, and this difference increased further with age (i.e., 6-fold at 3 months). PAI-1 mRNA levels were elevated 4- to 5-fold in the adipose tissues of obese mice, and these differences in mRNA also increased with age. The elevated PAI-1 mRNA in the adipose tissues of obese mice was localized to mature adipocytes as well as to vascular smooth muscle cells and occasional endothelial cells. Obesity is often associated with hyperinsulinemia, and acute injection of insulin into lean mice increased PAI-1 mRNA 6- to 8-fold in the epididymal fat in cells that morphologically resembled adipocytes. Insulin did not increase PAI-1 in large vessel endothelial or smooth muscle cells. The adipocyte response to insulin was confirmed in cell culture studies where PAI-1 synthesis by mature 3T3-L1 adipocytes was increased 5- to 6-fold by insulin. CONCLUSIONS: Our results suggest that elevated PAI-1 associated with obesity may result in part from insulin-induced induction of PAI-1 specifically by adipocytes within the fat itself.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alessi M. C., Juhan-Vague I., Kooistra T., Declerck P. J., Collen D. Insulin stimulates the synthesis of plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 by the human hepatocellular cell line Hep G2. Thromb Haemost. 1988 Dec 22;60(3):491–494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asplund-Carlson A., Hamsten A., Wiman B., Carlson L. A. Relationship between plasma plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 activity and VLDL triglyceride concentration, insulin levels and insulin sensitivity: studies in randomly selected normo- and hypertriglyceridaemic men. Diabetologia. 1993 Sep;36(9):817–825. doi: 10.1007/BF00400356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björntorp P. Abdominal fat distribution and disease: an overview of epidemiological data. Ann Med. 1992 Feb;24(1):15–18. doi: 10.3109/07853899209164140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Ferrannini E. Insulin resistance. A multifaceted syndrome responsible for NIDDM, obesity, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Diabetes Care. 1991 Mar;14(3):173–194. doi: 10.2337/diacare.14.3.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant P. J., Kruithof E. K., Felley C. P., Felber J. P., Bachmann F. Short-term infusions of insulin, triacylglycerol and glucose do not cause acute increases in plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 concentrations in man. Clin Sci (Lond) 1990 Nov;79(5):513–516. doi: 10.1042/cs0790513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green H., Kehinde O. An established preadipose cell line and its differentiation in culture. II. Factors affecting the adipose conversion. Cell. 1975 May;5(1):19–27. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90087-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herberg L., Coleman D. L. Laboratory animals exhibiting obesity and diabetes syndromes. Metabolism. 1977 Jan;26(1):59–99. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(77)90128-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hotamisligil G. S., Arner P., Caro J. F., Atkinson R. L., Spiegelman B. M. Increased adipose tissue expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in human obesity and insulin resistance. J Clin Invest. 1995 May;95(5):2409–2415. doi: 10.1172/JCI117936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hotamisligil G. S., Shargill N. S., Spiegelman B. M. Adipose expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha: direct role in obesity-linked insulin resistance. Science. 1993 Jan 1;259(5091):87–91. doi: 10.1126/science.7678183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Nachman R. L., Becker C. G., Minick C. R. Culture of human endothelial cells derived from umbilical veins. Identification by morphologic and immunologic criteria. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2745–2756. doi: 10.1172/JCI107470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain S. K., Nagi D. K., Slavin B. M., Lumb P. J., Yudkin J. S. Insulin therapy in type 2 diabetic subjects suppresses plasminogen activator inhibitor (PAI-1) activity and proinsulin-like molecules independently of glycaemic control. Diabet Med. 1993 Jan-Feb;10(1):27–32. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.1993.tb01992.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juhan-Vague I., Moerman B., De Cock F., Aillaud M. F., Collen D. Plasma levels of a specific inhibitor of tissue-type plasminogen activator (and urokinase) in normal and pathological conditions. Thromb Res. 1984 Mar 1;33(5):523–530. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(84)90018-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juhan-Vague I., Roul C., Alessi M. C., Ardissone J. P., Heim M., Vague P. Increased plasminogen activator inhibitor activity in non insulin dependent diabetic patients--relationship with plasma insulin. Thromb Haemost. 1989 Jun 30;61(3):370–373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juhan-Vague I., Vague P. Hypofibrinolysis and insulin-resistance. Diabete Metab. 1991 May;17(1 Pt 2):96–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keeton M., Eguchi Y., Sawdey M., Ahn C., Loskutoff D. J. Cellular localization of type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor messenger RNA and protein in murine renal tissue. Am J Pathol. 1993 Jan;142(1):59–70. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kooistra T., Bosma P. J., Töns H. A., van den Berg A. P., Meyer P., Princen H. M. Plasminogen activator inhibitor 1: biosynthesis and mRNA level are increased by insulin in cultured human hepatocytes. Thromb Haemost. 1989 Sep 29;62(2):723–728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landin K., Tengborn L., Chmielewska J., von Schenck H., Smith U. The acute effect of insulin on tissue plasminogen activator and plasminogen activator inhibitor in man. Thromb Haemost. 1991 Feb 12;65(2):130–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson B. Obesity, fat distribution and cardiovascular disease. Int J Obes. 1991 Sep;15 (Suppl 2):53–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markman B. Anatomy and physiology of adipose tissue. Clin Plast Surg. 1989 Apr;16(2):235–244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGill J. B., Schneider D. J., Arfken C. L., Lucore C. L., Sobel B. E. Factors responsible for impaired fibrinolysis in obese subjects and NIDDM patients. Diabetes. 1994 Jan;43(1):104–109. doi: 10.2337/diab.43.1.104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mykkänen L., Rönnemaa T., Marniemi J., Haffner S. M., Bergman R., Laakso M. Insulin sensitivity is not an independent determinant of plasma plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 activity. Arterioscler Thromb. 1994 Aug;14(8):1264–1271. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.14.8.1264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordt T. K., Sawa H., Fujii S., Sobel B. E. Induction of plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 (PAI-1) by proinsulin and insulin in vivo. Circulation. 1995 Feb 1;91(3):764–770. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.91.3.764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter van Loon B. J., Kluft C., Radder J. K., Blankenstein M. A., Meinders A. E. The cardiovascular risk factor plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 is related to insulin resistance. Metabolism. 1993 Aug;42(8):945–949. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(93)90005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Primrose J. N., Davies J. A., Prentice C. R., Hughes R., Johnston D. Reduction in factor VII, fibrinogen and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 activity after surgical treatment of morbid obesity. Thromb Haemost. 1992 Oct 5;68(4):396–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODBELL M. METABOLISM OF ISOLATED FAT CELLS. I. EFFECTS OF HORMONES ON GLUCOSE METABOLISM AND LIPOLYSIS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Feb;239:375–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaven G. M. Pathophysiology of insulin resistance in human disease. Physiol Rev. 1995 Jul;75(3):473–486. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1995.75.3.473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reik L. M., Maines S. L., Ryan D. E., Levin W., Bandiera S., Thomas P. E. A simple, non-chromatographic purification procedure for monoclonal antibodies. Isolation of monoclonal antibodies against cytochrome P450 isozymes. J Immunol Methods. 1987 Jun 26;100(1-2):123–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90180-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remacle C., Grégoire F. Cellular and molecular biology in the study of the physiopathology of obesity. Acta Clin Belg Suppl. 1992;14:3–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samad F., Yamamoto K., Loskutoff D. J. Distribution and regulation of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in murine adipose tissue in vivo. Induction by tumor necrosis factor-alpha and lipopolysaccharide. J Clin Invest. 1996 Jan 1;97(1):37–46. doi: 10.1172/JCI118404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawdey M. S., Loskutoff D. J. Regulation of murine type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor gene expression in vivo. Tissue specificity and induction by lipopolysaccharide, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and transforming growth factor-beta. J Clin Invest. 1991 Oct;88(4):1346–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI115440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawdey M., Podor T. J., Loskutoff D. J. Regulation of type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor gene expression in cultured bovine aortic endothelial cells. Induction by transforming growth factor-beta, lipopolysaccharide, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10396–10401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleef R. R., Sinha M., Loskutoff D. J. Immunoradiometric assay to measure the binding of a specific inhibitor to tissue-type plasminogen activator. J Lab Clin Med. 1985 Oct;106(4):408–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider D. J., Sobel B. E. Augmentation of synthesis of plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 by insulin and insulin-like growth factor type I: implications for vascular disease in hyperinsulinemic states. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):9959–9963. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.9959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundell I. B., Nilsson T. K., Hallmans G., Hellsten G., Dahlén G. H. Interrelationships between plasma levels of plasminogen activator inhibitor, tissue plasminogen activator, lipoprotein (a), and established cardiovascular risk factors in a north Swedish population. Atherosclerosis. 1989 Nov;80(1):9–16. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(89)90062-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takada Y., Urano T., Watanabe I., Taminato A., Yoshimi T., Takada A. Changes in fibrinolytic parameters in male patients with type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. Thromb Res. 1993 Sep 1;71(5):405–415. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(93)90165-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teufelsbauer H., Proidl S., Havel M., Vukovich T. Early activation of hemostasis during cardiopulmonary bypass: evidence for thrombin mediated hyperfibrinolysis. Thromb Haemost. 1992 Sep 7;68(3):250–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vague P., Juhan-Vague I., Aillaud M. F., Badier C., Viard R., Alessi M. C., Collen D. Correlation between blood fibrinolytic activity, plasminogen activator inhibitor level, plasma insulin level, and relative body weight in normal and obese subjects. Metabolism. 1986 Mar;35(3):250–253. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(86)90209-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vague P., Juhan-Vague I., Chabert V., Alessi M. C., Atlan C. Fat distribution and plasminogen activator inhibitor activity in nondiabetic obese women. Metabolism. 1989 Sep;38(9):913–915. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(89)90241-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanden Heuvel J. P., Tyson F. L., Bell D. A. Construction of recombinant RNA templates for use as internal standards in quantitative RT-PCR. Biotechniques. 1993 Mar;14(3):395–398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada H., Mori Y., Kaneko T., Wakita Y., Nakase T., Minamikawa K., Ohiwa M., Tamaki S., Tanigawa M., Kageyama S. Elevated plasma levels of vascular endothelial cell markers in patients with hypercholesterolemia. Am J Hematol. 1993 Oct;44(2):112–116. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830440208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. M., Doyle M. V., Mark D. F. Quantitation of mRNA by the polymerase chain reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9717–9721. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K., Loskutoff D. J. Fibrin deposition in tissues from endotoxin-treated mice correlates with decreases in the expression of urokinase-type but not tissue-type plasminogen activator. J Clin Invest. 1996 Jun 1;97(11):2440–2451. doi: 10.1172/JCI118691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Hinsbergh V. W., Kooistra T., van den Berg E. A., Princen H. M., Fiers W., Emeis J. J. Tumor necrosis factor increases the production of plasminogen activator inhibitor in human endothelial cells in vitro and in rats in vivo. Blood. 1988 Nov;72(5):1467–1473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]