Abstract
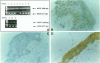
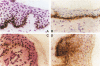
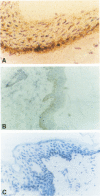
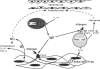
BACKGROUND: IgE/allergen-dependent activation of skin mast cells is involved in acute urticaria and leads to their IL-4 release. Previously we have demonstrated in vitro the induction of the low-affinity receptor for IgE (CD23/Fc epsilon RII) in human keratinocytes (HK) upon stimulation with IL-4. In addition, we have observed that ligation of CD23 on keratinocytes induced type II nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), leading to the release of nitric oxide (NO) and proinflammatory cytokines (TNF-alpha, IL-6). According to these in vitro data, we explored whether keratinocytes could also express iNOS, TNF-alpha, IL-6, and CD23 in acute urticaria, an in vivo model in which activation of mast cells by IgE/allergen immune complexes is involved. MATERIALS AND METHODS: INOS, TNF-alpha, IL-6, and CD23 expression by keratinocytes was studied in acute urticaria (n = 11) in biopsies from lesional and autologous normal skin by immunohistochemistry, in situ hybridization, or RT-PCR. Nitrites and TNF-alpha synthesis were assayed in supernatants of cultured lesional keratinocytes. RESULTS: INOS mRNA expression was demonstrated with RT-PCR in 10 biopsies out of 11 sections of acute urticaria lesional skin. Immunohistochemistry showed that this iNOS positivity originated from keratinocytes located close to the dermoepidermal junction; TNF-alpha and IL-6 mRNA transcription was observed in all but one iNOS+ biopsy. Immunostaining and in situ hybridization with CD23-specific probes were strong in all but one iNOS+ skin biopsy. Noninflamed autologous skin was negative for iNOS (except for a weak positivity in one case), cytokines, and CD23. CONCLUSION: The colocalization of iNOS, proinflammatory cytokines, and CD23 within keratinocytes in acute urticaria demonstrates that these cells play an important role in the initiation and maintenance of the inflammatory reaction during this disease in humans through activation of the iNOS pathway by CD23 ligation with IgE/allergen immune complexes.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arock M., Merle-Béral H., Dugas B., Ouaaz F., Le Goff L., Vouldoukis I., Mencia-Huerta J. M., Schmitt C., Leblond-Missenard V., Debre P. IL-4 release by human leukemic and activated normal basophils. J Immunol. 1993 Aug 1;151(3):1441–1447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosseloir A., Hooghe-Peters E. L., Heinen E., Cormann N., Kinet-Denoël C., Vanhaelst L., Simar L. Localization of interleukin 6 mRNA in human tonsils by in situ hybridization. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Dec;19(12):2379–2381. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830191230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boughton-Smith N. K., Evans S. M., Hawkey C. J., Cole A. T., Balsitis M., Whittle B. J., Moncada S. Nitric oxide synthase activity in ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. Lancet. 1993 Aug 7;342(8867):338–340. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)91476-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bécherel P. A., Le Goff L., Ktorza S., Chosidow O., Francès C., Issaly F., Mencia-Huerta J. M., Debré P., Mossalayi M. D., Arock M. CD23-mediated nitric oxide synthase pathway induction in human keratinocytes is inhibited by retinoic acid derivatives. J Invest Dermatol. 1996 Jun;106(6):1182–1186. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12347939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bécherel P. A., Le Goff L., Ktorza S., Ouaaz F., Mencia-Huerta J. M., Dugas B., Debré P., Mossalayi M. D., Arock M. Interleukin-10 inhibits IgE-mediated nitric oxide synthase induction and cytokine synthesis in normal human keratinocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1995 Oct;25(10):2992–2995. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830251042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bécherel P. A., Mossalayi M. D., LeGoff L., Francès C., Chosidow O., Debré P., Arock M. Mechanism of anti-inflammatory action of retinoids on keratinocytes. Lancet. 1994 Dec 3;344(8936):1570–1571. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)90377-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bécherel P. A., Mossalayi M. D., Ouaaz F., Le Goff L., Dugas B., Paul-Eugène N., Frances C., Chosidow O., Kilchherr E., Guillosson J. J. Involvement of cyclic AMP and nitric oxide in immunoglobulin E-dependent activation of Fc epsilon RII/CD23+ normal human keratinocytes. J Clin Invest. 1994 May;93(5):2275–2279. doi: 10.1172/JCI117227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell A. J., Blake D. R., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. Increased concentrations of nitrite in synovial fluid and serum samples suggest increased nitric oxide synthesis in rheumatic diseases. Ann Rheum Dis. 1992 Nov;51(11):1219–1222. doi: 10.1136/ard.51.11.1219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiebiger E., Maurer D., Holub H., Reininger B., Hartmann G., Woisetschläger M., Kinet J. P., Stingl G. Serum IgG autoantibodies directed against the alpha chain of Fc epsilon RI: a selective marker and pathogenetic factor for a distinct subset of chronic urticaria patients? J Clin Invest. 1995 Dec;96(6):2606–2612. doi: 10.1172/JCI118325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geller D. A., Di Silvio M., Nussler A. K., Wang S. C., Shapiro R. A., Simmons R. L., Billiar T. R. Nitric oxide synthase expression is induced in hepatocytes in vivo during hepatic inflammation. J Surg Res. 1993 Oct;55(4):427–432. doi: 10.1006/jsre.1993.1164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith P. C., Leslie T. A., Hayes N. A., Levell N. J., Dowd P. M., Foreman J. C. Inhibitors of nitric oxide synthase in human skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1996 Jan;106(1):113–118. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12328204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves M. W. Chronic urticaria. N Engl J Med. 1995 Jun 29;332(26):1767–1772. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199506293322608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green L. C., Wagner D. A., Glogowski J., Skipper P. L., Wishnok J. S., Tannenbaum S. R. Analysis of nitrate, nitrite, and [15N]nitrate in biological fluids. Anal Biochem. 1982 Oct;126(1):131–138. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90118-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habib F. M., Springall D. R., Davies G. J., Oakley C. M., Yacoub M. H., Polak J. M. Tumour necrosis factor and inducible nitric oxide synthase in dilated cardiomyopathy. Lancet. 1996 Apr 27;347(9009):1151–1155. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(96)90610-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hide M., Francis D. M., Grattan C. E., Hakimi J., Kochan J. P., Greaves M. W. Autoantibodies against the high-affinity IgE receptor as a cause of histamine release in chronic urticaria. N Engl J Med. 1993 Jun 3;328(22):1599–1604. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199306033282204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan A. P., Horáková Z., Katz S. I. Assessment of tissue fluid histamine levels in patients with urticaria. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1978 Jun;61(6):350–354. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(78)90113-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb-Bachofen V., Fehsel K., Michel G., Ruzicka T. Epidermal keratinocyte expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase in skin lesions of psoriasis vulgaris. Lancet. 1994 Jul 9;344(8915):139–139. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)91328-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüdin C., Hofstetter H., Sarfati M., Levy C. A., Suter U., Alaimo D., Kilchherr E., Frost H., Delespesse G. Cloning and expression of the cDNA coding for a human lymphocyte IgE receptor. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):109–114. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04726.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Higgs A. The L-arginine-nitric oxide pathway. N Engl J Med. 1993 Dec 30;329(27):2002–2012. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199312303292706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Higgs E. A. Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic strategies related to nitric oxide. FASEB J. 1995 Oct;9(13):1319–1330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Palmer R. M., Higgs E. A. Nitric oxide: physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol Rev. 1991 Jun;43(2):109–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natbony S. F., Phillips M. E., Elias J. M., Godfrey H. P., Kaplan A. P. Histologic studies of chronic idiopathic urticaria. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1983 Feb;71(2):177–183. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(83)90096-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niimi N., Francis D. M., Kermani F., O'Donnell B. F., Hide M., Kobza-Black A., Winkelmann R. K., Greaves M. W., Barr R. M. Dermal mast cell activation by autoantibodies against the high affinity IgE receptor in chronic urticaria. J Invest Dermatol. 1996 May;106(5):1001–1006. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12338544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul W. E. Interleukin-4: a prototypic immunoregulatory lymphokine. Blood. 1991 May 1;77(9):1859–1870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson M. G., Zetterström O., Agrenius V., Ihre E., Gustafsson L. E. Single-breath nitric oxide measurements in asthmatic patients and smokers. Lancet. 1994 Jan 15;343(8890):146–147. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)90935-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe A., Farrell A., Kazmi S. H., Bunker C. B. Expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase in dermal microvasculature in psoriasis. Lancet. 1994 Nov 12;344(8933):1371–1371. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)90734-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamler J. S., Singel D. J., Loscalzo J. Biochemistry of nitric oxide and its redox-activated forms. Science. 1992 Dec 18;258(5090):1898–1902. doi: 10.1126/science.1281928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuehr D. J., Griffith O. W. Mammalian nitric oxide synthases. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1992;65:287–346. doi: 10.1002/9780470123119.ch8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]