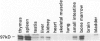Abstract
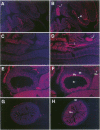
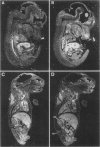
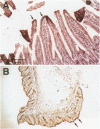
Members of the Ets family of winged helix-loop-helix transcription factors play important roles in the development and function of multiple mammalian cell lineages. Elf-1 is an Ets-related transcription factor that is expressed at high levels in T cells and is known to regulate the expression of several T cell genes, including the granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF) gene, the interleukin-2 receptor alpha subunit (IL-2Ralpha) gene, and the CD4 gene. In the studies described in this report, we have characterized the pattern of expression of Elf-1 in the developing mouse embryo and in adult mouse tissues as well as in multiple immortalized human and murine cell lines. Elf-1 is expressed at high levels throughout thymocyte development, with equivalent levels of Elf-1 expression seen in all subsets of maturing thymocytes and T cells. Somewhat surprisingly, however, Elf-1 is also expressed at high levels in epithelial cells lining the oral cavity, the lung, the CNS, and the gastrointestinal and urinary tracts as well as in the skin of the developing mouse embryo and at lower levels in the adult mouse testis and liver. Western blot analyses of a large number of immortalized cell lines demonstrated high-level Elf-1 expression in T and B lymphocyte and macrophage cell lines as well as in two prostate carcinoma cell lines. Low-level expression was observed in fibroblasts, embryonic stem cells, and myoblasts. Taken together, our data suggest that in addition to its role in regulating T cell development and function, Elf-1 may regulate gene expression in the B cell and myelomonocytic lineages, as well as in multiple epithelial cell types during murine embryonic development.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andreoli J. M., Jang S. I., Chung E., Coticchia C. M., Steinert P. M., Markova N. G. The expression of a novel, epithelium-specific ets transcription factor is restricted to the most differentiated layers in the epidermis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997 Nov 1;25(21):4287–4295. doi: 10.1093/nar/25.21.4287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassuk A. G., Anandappa R. T., Leiden J. M. Physical interactions between Ets and NF-kappaB/NFAT proteins play an important role in their cooperative activation of the human immunodeficiency virus enhancer in T cells. J Virol. 1997 May;71(5):3563–3573. doi: 10.1128/jvi.71.5.3563-3573.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassuk A. G., Leiden J. M. A direct physical association between ETS and AP-1 transcription factors in normal human T cells. Immunity. 1995 Aug;3(2):223–237. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(95)90092-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassuk A. G., Leiden J. M. The role of Ets transcription factors in the development and function of the mammalian immune system. Adv Immunol. 1997;64:65–104. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60887-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beitel G. J., Tuck S., Greenwald I., Horvitz H. R. The Caenorhabditis elegans gene lin-1 encodes an ETS-domain protein and defines a branch of the vulval induction pathway. Genes Dev. 1995 Dec 15;9(24):3149–3162. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.24.3149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bories J. C., Willerford D. M., Grévin D., Davidson L., Camus A., Martin P., Stéhelin D., Alt F. W. Increased T-cell apoptosis and terminal B-cell differentiation induced by inactivation of the Ets-1 proto-oncogene. Nature. 1995 Oct 19;377(6550):635–638. doi: 10.1038/377635a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burtis K. C., Thummel C. S., Jones C. W., Karim F. D., Hogness D. S. The Drosophila 74EF early puff contains E74, a complex ecdysone-inducible gene that encodes two ets-related proteins. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):85–99. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90217-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. H., Scott G. K., Kuo W. L., Xiong X., Suzdaltseva Y., Park J. W., Sayre P., Erny K., Collins C., Gray J. W. ESX: a structurally unique Ets overexpressed early during human breast tumorigenesis. Oncogene. 1997 Apr 3;14(13):1617–1622. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1200978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. N., Roussel M. F. Cloning and expression of the murine Elf-1 cDNA. Gene. 1996 Jun 1;171(2):265–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(96)00013-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernst P., Hahm K., Smale S. T. Both LyF-1 and an Ets protein interact with a critical promoter element in the murine terminal transferase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 May;13(5):2982–2992. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.5.2982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher J. C., Thummel C. S. The Drosophila E74 gene is required for the proper stage- and tissue-specific transcription of ecdysone-regulated genes at the onset of metamorphosis. Development. 1995 May;121(5):1411–1421. doi: 10.1242/dev.121.5.1411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs E. Epidermal differentiation and keratin gene expression. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1993;17:197–208. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1993.supplement_17.28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. I., Schmidt G. H., Roth K. A. Studies of intestinal stem cells using normal, chimeric, and transgenic mice. FASEB J. 1992 Sep;6(12):3039–3050. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.12.1521737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottschalk L. R., Giannola D. M., Emerson S. G. Molecular regulation of the human IL-3 gene: inducible T cell-restricted expression requires intact AP-1 and Elf-1 nuclear protein binding sites. J Exp Med. 1993 Nov 1;178(5):1681–1692. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.5.1681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heydemann A., Juang G., Hennessy K., Parmacek M. S., Simon M. C. The myeloid-cell-specific c-fes promoter is regulated by Sp1, PU.1, and a novel transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1996 Apr;16(4):1676–1686. doi: 10.1128/mcb.16.4.1676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilfinger J. M., Clark N., Smith M., Robinson K., Markovitz D. M. Differential regulation of the human immunodeficiency virus type 2 enhancer in monocytes at various stages of differentiation. J Virol. 1993 Jul;67(7):4448–4453. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.7.4448-4453.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John S., Reeves R. B., Lin J. X., Child R., Leiden J. M., Thompson C. B., Leonard W. J. Regulation of cell-type-specific interleukin-2 receptor alpha-chain gene expression: potential role of physical interactions between Elf-1, HMG-I(Y), and NF-kappa B family proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Mar;15(3):1786–1796. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.3.1786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karim F. D., Urness L. D., Thummel C. S., Klemsz M. J., McKercher S. R., Celada A., Van Beveren C., Maki R. A., Gunther C. V., Nye J. A. The ETS-domain: a new DNA-binding motif that recognizes a purine-rich core DNA sequence. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1451–1453. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kodandapani R., Pio F., Ni C. Z., Piccialli G., Klemsz M., McKercher S., Maki R. A., Ely K. R. A new pattern for helix-turn-helix recognition revealed by the PU.1 ETS-domain-DNA complex. Nature. 1996 Apr 4;380(6573):456–460. doi: 10.1038/380456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuratani S., Martin J. F., Wawersik S., Lilly B., Eichele G., Olson E. N. The expression pattern of the chick homeobox gene gMHox suggests a role in patterning of the limbs and face and in compartmentalization of somites. Dev Biol. 1994 Feb;161(2):357–369. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1994.1037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai Z. C., Rubin G. M. Negative control of photoreceptor development in Drosophila by the product of the yan gene, an ETS domain protein. Cell. 1992 Aug 21;70(4):609–620. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90430-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leiden J. M., Wang C. Y., Petryniak B., Markovitz D. M., Nabel G. J., Thompson C. B. A novel Ets-related transcription factor, Elf-1, binds to human immunodeficiency virus type 2 regulatory elements that are required for inducible trans activation in T cells. J Virol. 1992 Oct;66(10):5890–5897. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.10.5890-5897.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang H., Mao X., Olejniczak E. T., Nettesheim D. G., Yu L., Meadows R. P., Thompson C. B., Fesik S. W. Solution structure of the ets domain of Fli-1 when bound to DNA. Nat Struct Biol. 1994 Dec;1(12):871–875. doi: 10.1038/nsb1294-871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang H., Olejniczak E. T., Mao X., Nettesheim D. G., Yu L., Thompson C. B., Fesik S. W. The secondary structure of the ets domain of human Fli-1 resembles that of the helix-turn-helix DNA-binding motif of the Escherichia coli catabolite gene activator protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Nov 22;91(24):11655–11659. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.24.11655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markovitz D. M., Smith M. J., Hilfinger J., Hannibal M. C., Petryniak B., Nabel G. J. Activation of the human immunodeficiency virus type 2 enhancer is dependent on purine box and kappa B regulatory elements. J Virol. 1992 Sep;66(9):5479–5484. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.9.5479-5484.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki Y., Sun X., Uchida H., Zhang J., Nimer S. MEF, a novel transcription factor with an Elf-1 like DNA binding domain but distinct transcriptional activating properties. Oncogene. 1996 Oct 17;13(8):1721–1729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrisey E. E., Ip H. S., Lu M. M., Parmacek M. S. GATA-6: a zinc finger transcription factor that is expressed in multiple cell lineages derived from lateral mesoderm. Dev Biol. 1996 Jul 10;177(1):309–322. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1996.0165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muthusamy N., Barton K., Leiden J. M. Defective activation and survival of T cells lacking the Ets-1 transcription factor. Nature. 1995 Oct 19;377(6550):639–642. doi: 10.1038/377639a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nye J. A., Petersen J. M., Gunther C. V., Jonsen M. D., Graves B. J. Interaction of murine ets-1 with GGA-binding sites establishes the ETS domain as a new DNA-binding motif. Genes Dev. 1992 Jun;6(6):975–990. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.6.975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill E. M., Rebay I., Tjian R., Rubin G. M. The activities of two Ets-related transcription factors required for Drosophila eye development are modulated by the Ras/MAPK pathway. Cell. 1994 Jul 15;78(1):137–147. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90580-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oettgen P., Akbarali Y., Boltax J., Best J., Kunsch C., Libermann T. A. Characterization of NERF, a novel transcription factor related to the Ets factor ELF-1. Mol Cell Biol. 1996 Sep;16(9):5091–5106. doi: 10.1128/mcb.16.9.5091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oettgen P., Alani R. M., Barcinski M. A., Brown L., Akbarali Y., Boltax J., Kunsch C., Munger K., Libermann T. A. Isolation and characterization of a novel epithelium-specific transcription factor, ESE-1, a member of the ets family. Mol Cell Biol. 1997 Aug;17(8):4419–4433. doi: 10.1128/mcb.17.8.4419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pribyl L. J., Watson D. K., Schulz R. A., Papas T. S. D-elg, a member of the Drosophila ets gene family: sequence, expression and evolutionary comparison. Oncogene. 1991 Jul;6(7):1175–1183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz R. A., The S. M., Hogue D. A., Galewsky S., Guo Q. Ets oncogene-related gene Elg functions in Drosophila oogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 1;90(21):10076–10080. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.21.10076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott E. W., Simon M. C., Anastasi J., Singh H. Requirement of transcription factor PU.1 in the development of multiple hematopoietic lineages. Science. 1994 Sep 9;265(5178):1573–1577. doi: 10.1126/science.8079170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. B., Wang C. Y., Ho I. C., Bohjanen P. R., Petryniak B., June C. H., Miesfeldt S., Zhang L., Nabel G. J., Karpinski B. cis-acting sequences required for inducible interleukin-2 enhancer function bind a novel Ets-related protein, Elf-1. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):1043–1053. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.1043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. C., Brown T. A., McKnight S. L. Convergence of Ets- and notch-related structural motifs in a heteromeric DNA binding complex. Science. 1991 Aug 16;253(5021):762–768. doi: 10.1126/science.1876833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tymms M. J., Ng A. Y., Thomas R. S., Schutte B. C., Zhou J., Eyre H. J., Sutherland G. R., Seth A., Rosenberg M., Papas T. A novel epithelial-expressed ETS gene, ELF3: human and murine cDNA sequences, murine genomic organization, human mapping to 1q32.2 and expression in tissues and cancer. Oncogene. 1997 Nov 13;15(20):2449–2462. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1201427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urness L. D., Thummel C. S. Molecular interactions within the ecdysone regulatory hierarchy: DNA binding properties of the Drosophila ecdysone-inducible E74A protein. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):47–61. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90287-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C. Y., Bassuk A. G., Boise L. H., Thompson C. B., Bravo R., Leiden J. M. Activation of the granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor promoter in T cells requires cooperative binding of Elf-1 and AP-1 transcription factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;14(2):1153–1159. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.2.1153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C. Y., Petryniak B., Thompson C. B., Kaelin W. G., Leiden J. M. Regulation of the Ets-related transcription factor Elf-1 by binding to the retinoblastoma protein. Science. 1993 May 28;260(5112):1330–1335. doi: 10.1126/science.8493578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Hahn S. L., Giovane A. The Ets family of transcription factors. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Jan 15;211(1-2):7–18. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-78757-7_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner M. H., Clore M., Fisher C. L., Fisher R. J., Trinh L., Shiloach J., Gronenborn A. M. The solution structure of the human ETS1-DNA complex reveals a novel mode of binding and true side chain intercalation. Cell. 1995 Dec 1;83(5):761–771. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90189-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson D. A., Neale G. A., Mao S., Naeve C. W., Goorha R. M. Elf-2, a rhombotin-2 binding ets transcription factor: discovery and potential role in T cell leukemia. Leukemia. 1997 Jan;11(1):86–96. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2400516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wotton D., Ghysdael J., Wang S., Speck N. A., Owen M. J. Cooperative binding of Ets-1 and core binding factor to DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;14(1):840–850. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.1.840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wurster A. L., Siu G., Leiden J. M., Hedrick S. M. Elf-1 binds to a critical element in a second CD4 enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;14(10):6452–6463. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.10.6452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang M., Maass N., Magit D., Sager R. Transactivation through Ets and Ap1 transcription sites determines the expression of the tumor-suppressing gene maspin. Cell Growth Differ. 1997 Feb;8(2):179–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]