Abstract
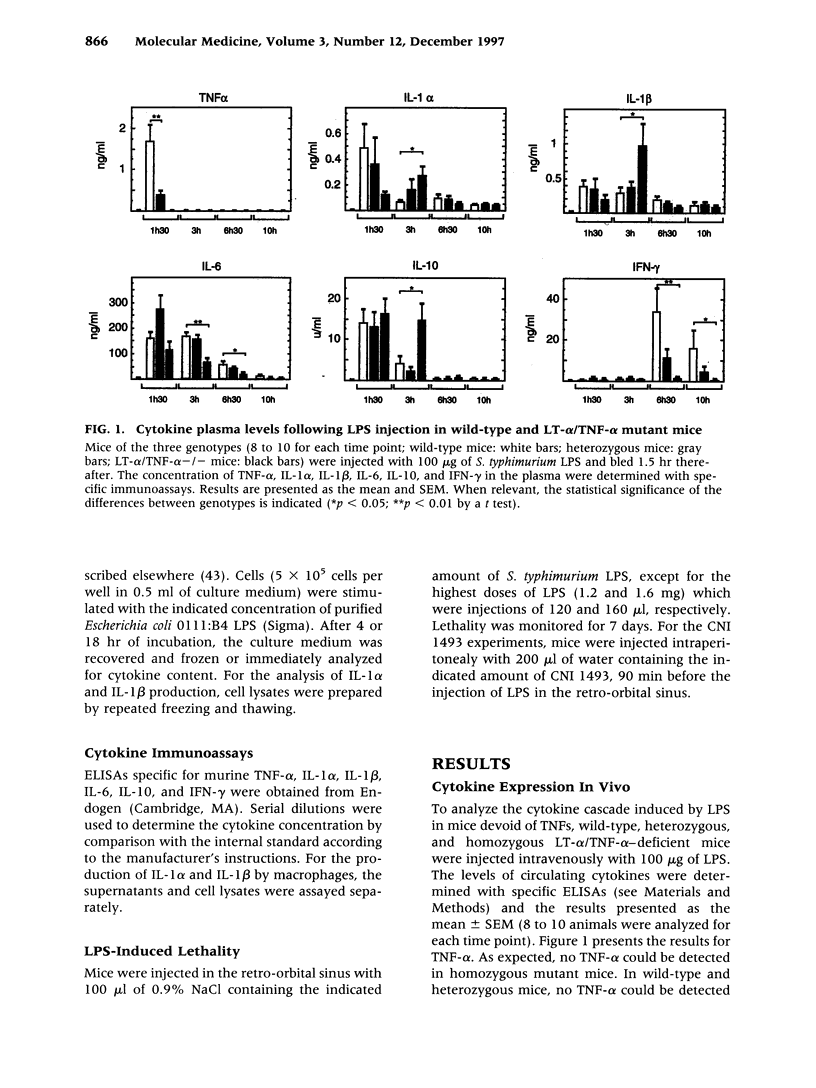
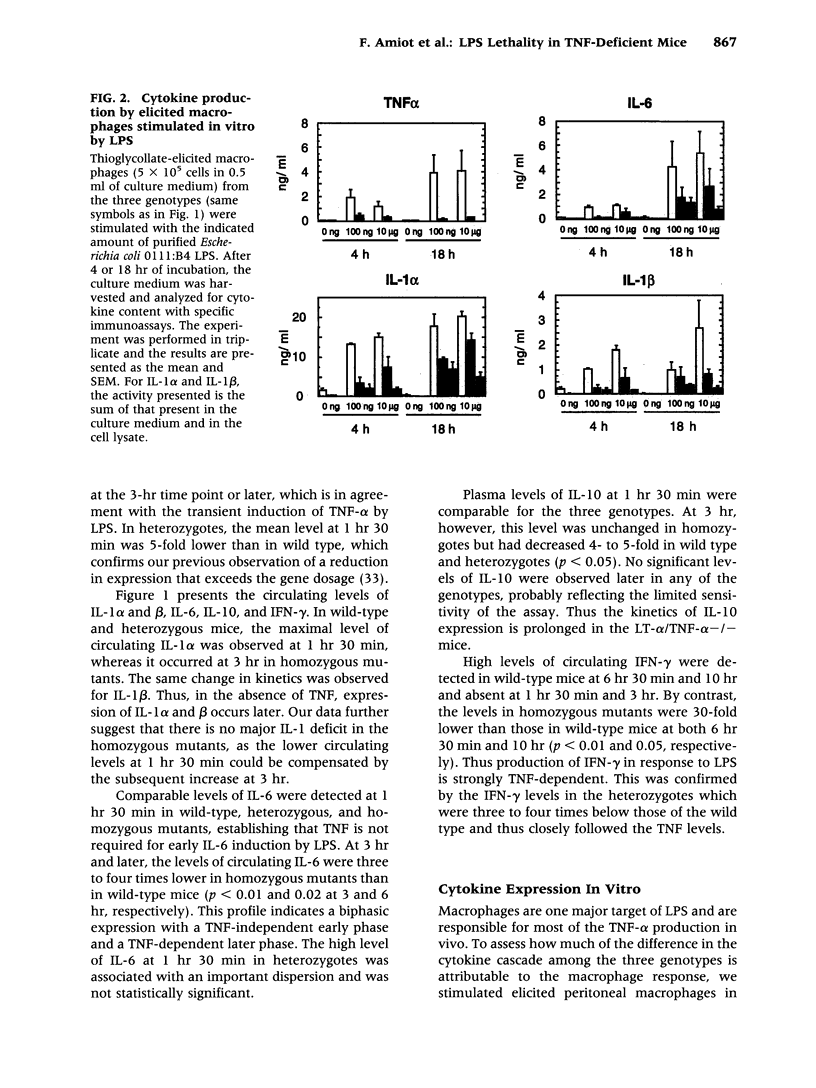
BACKGROUND: Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) is often considered the main proinflammatory cytokine induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and consequently the critical mediator of the lethality associated with septic shock. MATERIALS AND METHODS: We used mice carrying a deletion of both the lymphotoxin alpha (LT-alpha) and TNF-alpha genes to assess the role of TNF in the cytokine cascade and lethality induced by LPS. RESULTS: Initial production of IL-1 alpha, IL-1 beta, IL-6, and IL-10 is comparable in wild-type and mutant mice. However, at later times, expression of IL-1 alpha, IL-1 beta, and IL-10 is prolonged, whereas that of IL-6 decreases in mutant mice. Expression of IFN-gamma is almost completely abrogated in mutants, which is in agreement with a more significant alteration of the late phase of the cytokine cascade. We measured similar LD50 (600 micrograms) for the intravenous injection of LPS in mice of the three genotypes (+/+, +/-, -/-), demonstrating that the absence of TNF does not confer long-term protection from lethality. However, death occurred much more slowly in mutant mice, who were protected more efficiently from death by CNI 1493, an inhibitor of proinflammatory cytokine production, than were wild-type mice. DISCUSSION: Thus, while TNF-alpha is not required for the induction of these cytokines by LPS, it modulates the kinetics of their expression. The lethality studies simultaneously confirm a role for TNF as a mediator of early lethality and establish that, in the absence of these cytokines, other mediators take over, resulting in the absence of long-term protection from LPS toxicity.
Full text
PDF

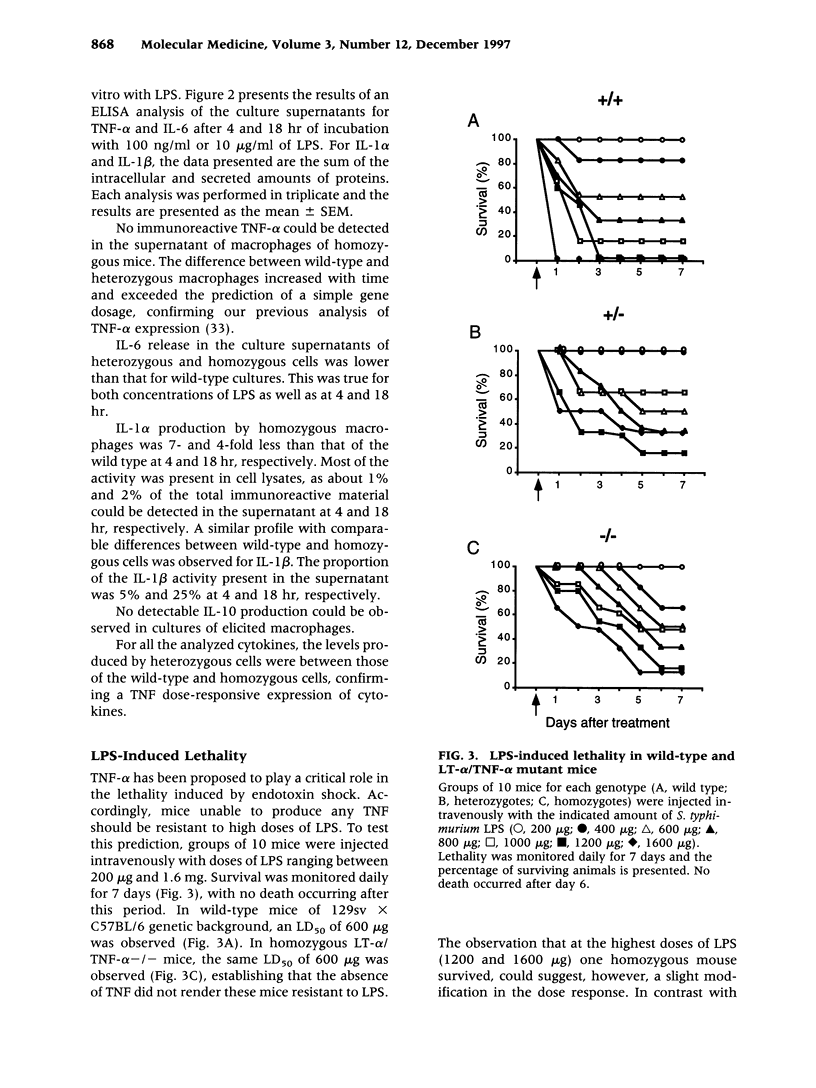
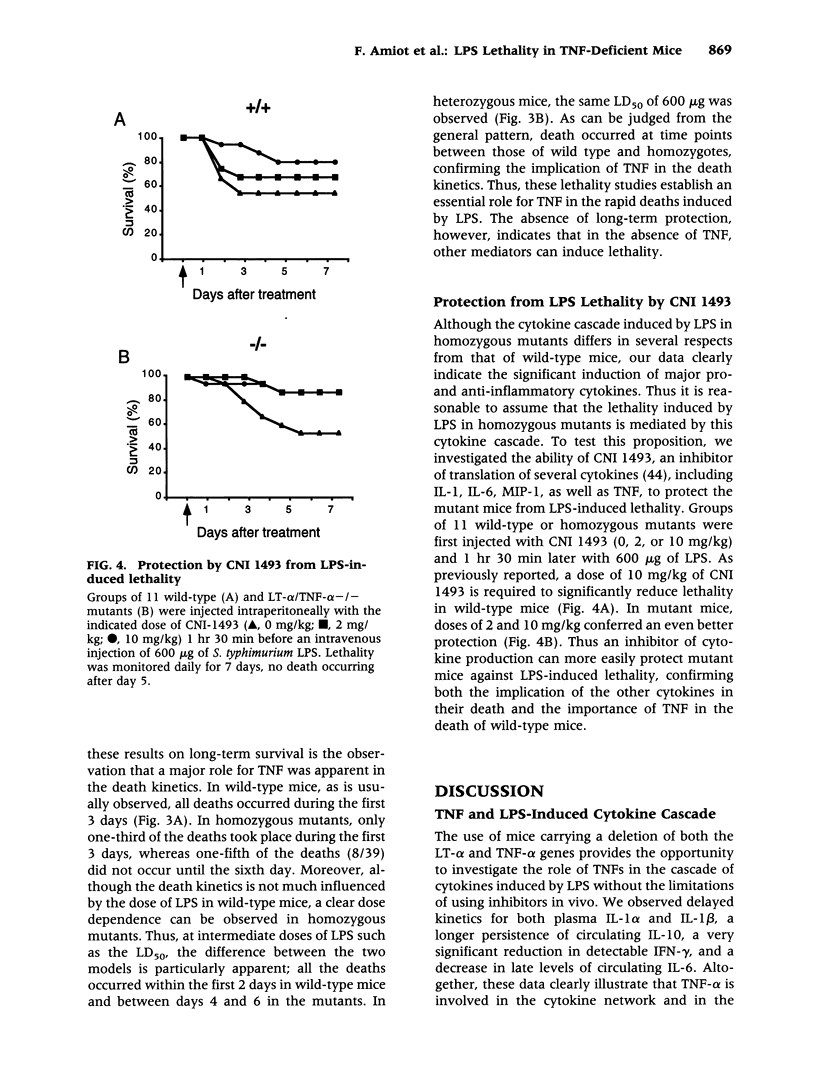






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham E., Wunderink R., Silverman H., Perl T. M., Nasraway S., Levy H., Bone R., Wenzel R. P., Balk R., Allred R. Efficacy and safety of monoclonal antibody to human tumor necrosis factor alpha in patients with sepsis syndrome. A randomized, controlled, double-blind, multicenter clinical trial. TNF-alpha MAb Sepsis Study Group. JAMA. 1995 Mar 22;273(12):934–941. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amiot F., Bellkaid Y., Lebastard M., Ave P., Dautry F., Milon G. Abnormal organisation of the splenic marginal zone and the correlated leukocytosis in lymphotoxin-alpha and tumor necrosis factor alpha double deficient mice. Eur Cytokine Netw. 1996 Dec;7(4):733–739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amiot F., Boussadia O., Cases S., Fitting C., Lebastard M., Cavaillon J. M., Milon G., Dautry F. Mice heterozygous for a deletion of the tumor necrosis factor-alpha and lymphotoxin-alpha genes: biological importance of a nonlinear response of tumor necrosis factor-alpha to gene dosage. Eur J Immunol. 1997 Apr;27(4):1035–1042. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830270434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashkenazi A., Marsters S. A., Capon D. J., Chamow S. M., Figari I. S., Pennica D., Goeddel D. V., Palladino M. A., Smith D. H. Protection against endotoxic shock by a tumor necrosis factor receptor immunoadhesin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10535–10539. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barsig J., Küsters S., Vogt K., Volk H. D., Tiegs G., Wendel A. Lipopolysaccharide-induced interleukin-10 in mice: role of endogenous tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Eur J Immunol. 1995 Oct;25(10):2888–2893. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830251027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernhagen J., Calandra T., Mitchell R. A., Martin S. B., Tracey K. J., Voelter W., Manogue K. R., Cerami A., Bucala R. MIF is a pituitary-derived cytokine that potentiates lethal endotoxaemia. Nature. 1993 Oct 21;365(6448):756–759. doi: 10.1038/365756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Milsark I. W., Cerami A. C. Passive immunization against cachectin/tumor necrosis factor protects mice from lethal effect of endotoxin. Science. 1985 Aug 30;229(4716):869–871. doi: 10.1126/science.3895437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi M., Bloom O., Raabe T., Cohen P. S., Chesney J., Sherry B., Schmidtmayerova H., Calandra T., Zhang X., Bukrinsky M. Suppression of proinflammatory cytokines in monocytes by a tetravalent guanylhydrazone. J Exp Med. 1996 Mar 1;183(3):927–936. doi: 10.1084/jem.183.3.927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi M., Ulrich P., Bloom O., Meistrell M., 3rd, Zimmerman G. A., Schmidtmayerova H., Bukrinsky M., Donnelley T., Bucala R., Sherry B. An inhibitor of macrophage arginine transport and nitric oxide production (CNI-1493) prevents acute inflammation and endotoxin lethality. Mol Med. 1995 Mar;1(3):254–266. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block M. I., Berg M., McNamara M. J., Norton J. A., Fraker D. L., Alexander H. R. Passive immunization of mice against D factor blocks lethality and cytokine release during endotoxemia. J Exp Med. 1993 Sep 1;178(3):1085–1090. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.3.1085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brach M. A., de Vos S., Arnold C., Gruss H. J., Mertelsmann R., Herrmann F. Leukotriene B4 transcriptionally activates interleukin-6 expression involving NK-chi B and NF-IL6. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Oct;22(10):2705–2711. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830221034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brouckaert P., Spriggs D. R., Demetri G., Kufe D. W., Fiers W. Circulating interleukin 6 during a continuous infusion of tumor necrosis factor and interferon gamma. J Exp Med. 1989 Jun 1;169(6):2257–2262. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.6.2257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon J. G., Tompkins R. G., Gelfand J. A., Michie H. R., Stanford G. G., van der Meer J. W., Endres S., Lonnemann G., Corsetti J., Chernow B. Circulating interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor in septic shock and experimental endotoxin fever. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jan;161(1):79–84. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.1.79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassatella M. A., Guasparri I., Ceska M., Bazzoni F., Rossi F. Interferon-gamma inhibits interleukin-8 production by human polymorphonuclear leucocytes. Immunology. 1993 Feb;78(2):177–184. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavaillon J. M., Marie C., Pitton C., Fitting C. The production of TNF alpha and IL-8 in whole blood assays are differently regulated upon activation by LPS. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1995;392:433–439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. S., Nakshatri H., Dennis J., Caragine T., Bianchi M., Cerami A., Tracey K. J. CNI-1493 inhibits monocyte/macrophage tumor necrosis factor by suppression of translation efficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Apr 30;93(9):3967–3971. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.9.3967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeForge L. E., Kenney J. S., Jones M. L., Warren J. S., Remick D. G. Biphasic production of IL-8 in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated human whole blood. Separation of LPS- and cytokine-stimulated components using anti-tumor necrosis factor and anti-IL-1 antibodies. J Immunol. 1992 Apr 1;148(7):2133–2141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debs R. J., Fuchs H. J., Philip R., Montgomery A. B., Brunette E. N., Liggitt D., Patton J. S., Shellito J. E. Lung-specific delivery of cytokines induces sustained pulmonary and systemic immunomodulation in rats. J Immunol. 1988 May 15;140(10):3482–3488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty G. M., Lange J. R., Langstein H. N., Alexander H. R., Buresh C. M., Norton J. A. Evidence for IFN-gamma as a mediator of the lethality of endotoxin and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J Immunol. 1992 Sep 1;149(5):1666–1670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson T. E., Jr, Lindsey D. C., Jesmok G. J., Duerr M. L., Fournel M. A. Efficacy of monoclonal antibody against tumor necrosis factor alpha in an endotoxemic baboon model. Circ Shock. 1992 Oct;38(2):75–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson S. L., de Sauvage F. J., Kikly K., Carver-Moore K., Pitts-Meek S., Gillett N., Sheehan K. C., Schreiber R. D., Goeddel D. V., Moore M. W. Decreased sensitivity to tumour-necrosis factor but normal T-cell development in TNF receptor-2-deficient mice. Nature. 1994 Dec 8;372(6506):560–563. doi: 10.1038/372560a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espat N. J., Cendan J. C., Beierle E. A., Auffenberg T. A., Rosenberg J., Russell D., Kenney J. S., Fischer E., Montegut W., Lowry S. F. PEG-BP-30 monotherapy attenuates the cytokine-mediated inflammatory cascade in baboon Escherichia coli septic shock. J Surg Res. 1995 Jul;59(1):153–158. doi: 10.1006/jsre.1995.1147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferran C., Dautry F., Mérite S., Sheehan K., Schreiber R., Grau G., Bach J. F., Chatenoud L. Anti-tumor necrosis factor modulates anti-CD3-triggered T cell cytokine gene expression in vivo. J Clin Invest. 1994 May;93(5):2189–2196. doi: 10.1172/JCI117215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiedler V. B., Loof I., Sander E., Voehringer V., Galanos C., Fournel M. A. Monoclonal antibody to tumor necrosis factor--alpha prevents lethal endotoxin sepsis in adult rhesus monkeys. J Lab Clin Med. 1992 Oct;120(4):574–588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firestein G. S., Boyle D., Bullough D. A., Gruber H. E., Sajjadi F. G., Montag A., Sambol B., Mullane K. M. Protective effect of an adenosine kinase inhibitor in septic shock. J Immunol. 1994 Jun 15;152(12):5853–5859. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher C. J., Jr, Agosti J. M., Opal S. M., Lowry S. F., Balk R. A., Sadoff J. C., Abraham E., Schein R. M., Benjamin E. Treatment of septic shock with the tumor necrosis factor receptor:Fc fusion protein. The Soluble TNF Receptor Sepsis Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1996 Jun 27;334(26):1697–1702. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199606273342603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong Y., Tracey K. J., Moldawer L. L., Hesse D. G., Manogue K. B., Kenney J. S., Lee A. T., Kuo G. C., Allison A. C., Lowry S. F. Antibodies to cachectin/tumor necrosis factor reduce interleukin 1 beta and interleukin 6 appearance during lethal bacteremia. J Exp Med. 1989 Nov 1;170(5):1627–1633. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.5.1627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franks A. K., Kujawa K. I., Yaffe L. J. Experimental elimination of tumor necrosis factor in low-dose endotoxin models has variable effects on survival. Infect Immun. 1991 Aug;59(8):2609–2614. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.8.2609-2614.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freudenberg M. A., Galanos C. Tumor necrosis factor alpha mediates lethal activity of killed gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria in D-galactosamine-treated mice. Infect Immun. 1991 Jun;59(6):2110–2115. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.6.2110-2115.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fushimi T., Okayama H., Seki T., Shimura S., Shirato K. Dexamethasone suppressed gene expression and production of interleukin-10 by human peripheral blood mononuclear cells and monocytes. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1997 Jan;112(1):13–18. doi: 10.1159/000237425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia I., Miyazaki Y., Araki K., Araki M., Lucas R., Grau G. E., Milon G., Belkaid Y., Montixi C., Lesslauer W. Transgenic mice expressing high levels of soluble TNF-R1 fusion protein are protected from lethal septic shock and cerebral malaria, and are highly sensitive to Listeria monocytogenes and Leishmania major infections. Eur J Immunol. 1995 Aug;25(8):2401–2407. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830250841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinshaw L. B., Emerson T. E., Jr, Taylor F. B., Jr, Chang A. C., Duerr M., Peer G. T., Flournoy D. J., White G. L., Kosanke S. D., Murray C. K. Lethal Staphylococcus aureus-induced shock in primates: prevention of death with anti-TNF antibody. J Trauma. 1992 Oct;33(4):568–573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinson R. M., Williams J. A., Shacter E. Elevated interleukin 6 is induced by prostaglandin E2 in a murine model of inflammation: possible role of cyclooxygenase-2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 May 14;93(10):4885–4890. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.10.4885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jesmok G., Lindsey C., Duerr M., Fournel M., Emerson T., Jr Efficacy of monoclonal antibody against human recombinant tumor necrosis factor in E. coli-challenged swine. Am J Pathol. 1992 Nov;141(5):1197–1207. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Junger W. G., Hoyt D. B., Redl H., Liu F. C., Loomis W. H., Davies J., Schlag G. Tumor necrosis factor antibody treatment of septic baboons reduces the production of sustained T-cell suppressive factors. Shock. 1995 Mar;3(3):173–178. doi: 10.1097/00024382-199503000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesslauer W., Tabuchi H., Gentz R., Brockhaus M., Schlaeger E. J., Grau G., Piguet P. F., Pointaire P., Vassalli P., Loetscher H. Recombinant soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor proteins protect mice from lipopolysaccharide-induced lethality. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Nov;21(11):2883–2886. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830211134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marino M. W., Dunn A., Grail D., Inglese M., Noguchi Y., Richards E., Jungbluth A., Wada H., Moore M., Williamson B. Characterization of tumor necrosis factor-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Jul 22;94(15):8093–8098. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.15.8093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martich G. D., Danner R. L., Ceska M., Suffredini A. F. Detection of interleukin 8 and tumor necrosis factor in normal humans after intravenous endotoxin: the effect of antiinflammatory agents. J Exp Med. 1991 Apr 1;173(4):1021–1024. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.4.1021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. A., Silva A. T., Cohen J. Effect of anti-TNF-alpha treatment in an antibiotic treated murine model of shock due to Streptococcus pyogenes. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1993 Jun 15;110(2):175–178. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1993.tb06316.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeehan G. M., Becherer J. D., Bast R. C., Jr, Boyer C. M., Champion B., Connolly K. M., Conway J. G., Furdon P., Karp S., Kidao S. Regulation of tumour necrosis factor-alpha processing by a metalloproteinase inhibitor. Nature. 1994 Aug 18;370(6490):558–561. doi: 10.1038/370558a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michie H. R., Manogue K. R., Spriggs D. R., Revhaug A., O'Dwyer S., Dinarello C. A., Cerami A., Wolff S. M., Wilmore D. W. Detection of circulating tumor necrosis factor after endotoxin administration. N Engl J Med. 1988 Jun 9;318(23):1481–1486. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198806093182301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohler K. M., Torrance D. S., Smith C. A., Goodwin R. G., Stremler K. E., Fung V. P., Madani H., Widmer M. B. Soluble tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptors are effective therapeutic agents in lethal endotoxemia and function simultaneously as both TNF carriers and TNF antagonists. J Immunol. 1993 Aug 1;151(3):1548–1561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musso T., Espinoza-Delgado I., Pulkki K., Gusella G. L., Longo D. L., Varesio L. IL-2 induces IL-6 production in human monocytes. J Immunol. 1992 Feb 1;148(3):795–800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mándi Y., Farkas G., Ocsovszky I., Nagy Z. Inhibition of tumor necrosis factor production and ICAM-1 expression by pentoxifylline: beneficial effects in sepsis syndrome. Res Exp Med (Berl) 1995;195(5):297–307. doi: 10.1007/BF02576800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Netea M. G., Blok W. L., Kullberg B. J., Bemelmans M., Vogels M. T., Buurman W. A., van der Meer J. W. Pharmacologic inhibitors of tumor necrosis factor production exert differential effects in lethal endotoxemia and in infection with live microorganisms in mice. J Infect Dis. 1995 Feb;171(2):393–399. doi: 10.1093/infdis/171.2.393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsson K., Björk P., Bergenfeldt M., Hageman R., Thompson R. C. Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist reduces mortality from endotoxin shock. Nature. 1990 Dec 6;348(6301):550–552. doi: 10.1038/348550a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer K., Matsuyama T., Kündig T. M., Wakeham A., Kishihara K., Shahinian A., Wiegmann K., Ohashi P. S., Krönke M., Mak T. W. Mice deficient for the 55 kd tumor necrosis factor receptor are resistant to endotoxic shock, yet succumb to L. monocytogenes infection. Cell. 1993 May 7;73(3):457–467. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90134-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redl H., Schlag G., Bahrami S., Schade U., Ceska M., Stütz P. Plasma neutrophil-activating peptide-1/interleukin-8 and neutrophil elastase in a primate bacteremia model. J Infect Dis. 1991 Aug;164(2):383–388. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.2.383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothe J., Lesslauer W., Lötscher H., Lang Y., Koebel P., Köntgen F., Althage A., Zinkernagel R., Steinmetz M., Bluethmann H. Mice lacking the tumour necrosis factor receptor 1 are resistant to TNF-mediated toxicity but highly susceptible to infection by Listeria monocytogenes. Nature. 1993 Aug 26;364(6440):798–802. doi: 10.1038/364798a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J., Arondel J., Cavaillon J. M., Huerre M. Role of interleukin-1 in the pathogenesis of experimental shigellosis. J Clin Invest. 1995 Aug;96(2):884–892. doi: 10.1172/JCI118135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schandené L., Vandenbussche P., Crusiaux A., Alègre M. L., Abramowicz D., Dupont E., Content J., Goldman M. Differential effects of pentoxifylline on the production of tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) by monocytes and T cells. Immunology. 1992 May;76(1):30–34. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J. A., Abdulla E. Down-regulation of IL-1 beta biosynthesis by inducers of the heat-shock response. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 15;141(6):2027–2034. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheron N., Williams R. IL-8 as a circulating cytokine: induction by recombinant tumour necrosis factor-alpha. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Jul;89(1):100–103. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb06885.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. M., Lackides G. A., Epstein L. B. Coordinated induction of autocrine tumor necrosis factor and interleukin 1 in normal human monocytes and the implications for monocyte-mediated cytotoxicity. Cancer Res. 1990 Jun 1;50(11):3146–3153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder D. S., Unanue E. R. Corticosteroids inhibit murine macrophage Ia expression and interleukin 1 production. J Immunol. 1982 Nov;129(5):1803–1805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sower L. E., Froelich C. J., Carney D. H., Fenton J. W., 2nd, Klimpel G. R. Thrombin induces IL-6 production in fibroblasts and epithelial cells. Evidence for the involvement of the seven-transmembrane domain (STD) receptor for alpha-thrombin. J Immunol. 1995 Jul 15;155(2):895–901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suffredini A. F., Reda D., Banks S. M., Tropea M., Agosti J. M., Miller R. Effects of recombinant dimeric TNF receptor on human inflammatory responses following intravenous endotoxin administration. J Immunol. 1995 Nov 15;155(10):5038–5045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teti G., Mancuso G., Tomasello F., Chiofalo M. S. Production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-6 in mice infected with group B streptococci. Circ Shock. 1992 Oct;38(2):138–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teti G., Mancuso G., Tomasello F. Cytokine appearance and effects of anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha antibodies in a neonatal rat model of group B streptococcal infection. Infect Immun. 1993 Jan;61(1):227–235. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.1.227-235.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thivierge M., Rola-Pleszczynski M. Platelet-activating factor enhances interleukin-6 production by alveolar macrophages. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1992 Nov;90(5):796–802. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(92)90104-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Fong Y., Hesse D. G., Manogue K. R., Lee A. T., Kuo G. C., Lowry S. F., Cerami A. Anti-cachectin/TNF monoclonal antibodies prevent septic shock during lethal bacteraemia. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):662–664. doi: 10.1038/330662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Damme J., Opdenakker G., Simpson R. J., Rubira M. R., Cayphas S., Vink A., Billiau A., Van Snick J. Identification of the human 26-kD protein, interferon beta 2 (IFN-beta 2), as a B cell hybridoma/plasmacytoma growth factor induced by interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor. J Exp Med. 1987 Mar 1;165(3):914–919. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.3.914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Zee K. J., Kohno T., Fischer E., Rock C. S., Moldawer L. L., Lowry S. F. Tumor necrosis factor soluble receptors circulate during experimental and clinical inflammation and can protect against excessive tumor necrosis factor alpha in vitro and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 1;89(11):4845–4849. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.4845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasilescu C., Berger D., Buttenschön K., Seidelmann M., Beger H. G. Endotoxin-induced release of interleukin 6 and interleukin 1 beta in human blood is independent of tumor necrosis factor alpha. Eur Surg Res. 1996;28(1):55–62. doi: 10.1159/000129440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanidworanun C., Strober W. Predominant role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in human monocyte IL-10 synthesis. J Immunol. 1993 Dec 15;151(12):6853–6861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollenberg G. K., DeForge L. E., Bolgos G., Remick D. G. Differential expression of tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-6 by peritoneal macrophages in vivo and in culture. Am J Pathol. 1993 Oct;143(4):1121–1130. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada H., Iwase S., Mohri M., Kufe D. Involvement of a nuclear factor-kappa B-like protein in induction of the macrophage colony-stimulating factor gene by tumor necrosis factor. Blood. 1991 Oct 15;78(8):1988–1995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Poll T., Jansen J., Levi M., ten Cate H., ten Cate J. W., van Deventer S. J. Regulation of interleukin 10 release by tumor necrosis factor in humans and chimpanzees. J Exp Med. 1994 Nov 1;180(5):1985–1988. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.5.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Poll T., Levi M., van Deventer S. J., ten Cate H., Haagmans B. L., Biemond B. J., Büller H. R., Hack C. E., ten Cate J. W. Differential effects of anti-tumor necrosis factor monoclonal antibodies on systemic inflammatory responses in experimental endotoxemia in chimpanzees. Blood. 1994 Jan 15;83(2):446–451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]