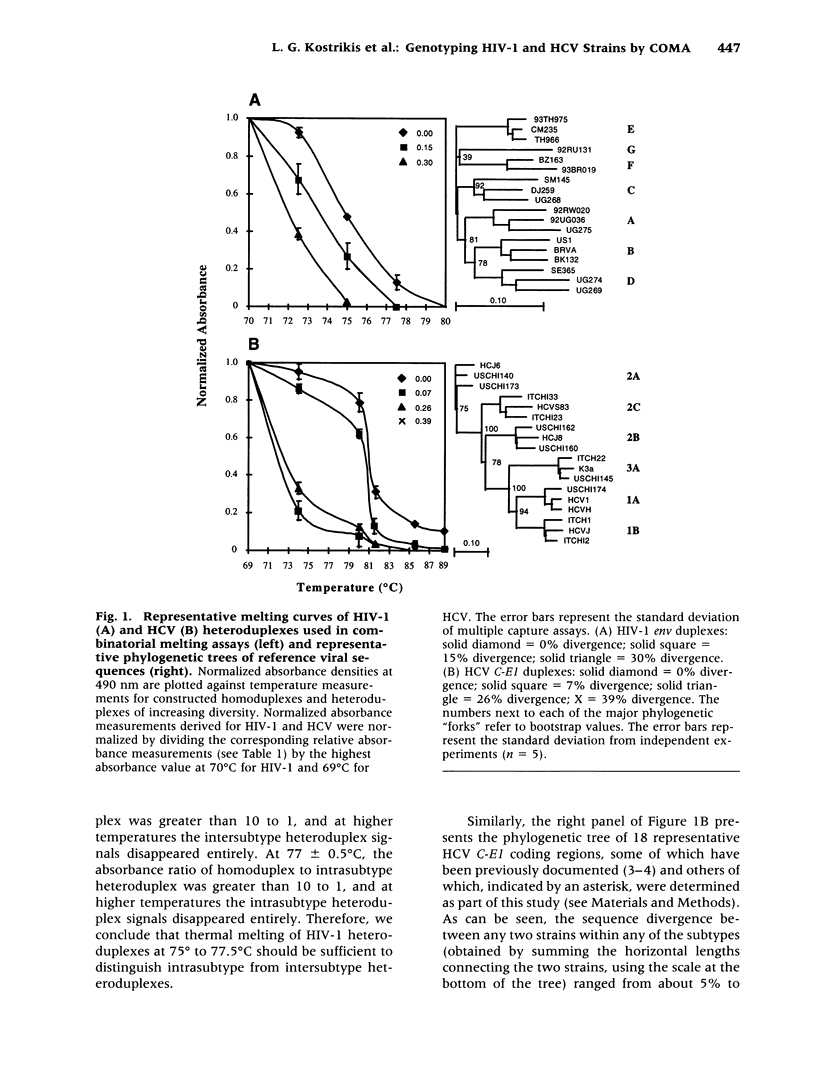
Abstract
BACKGROUND: Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) strains can be genetically classified into genetic lineages known as genetic types or subtypes according to phylogenetic analyses of complete or partial nucleotide sequences of their genomes. The genetic classification of HIV-1 and HCV strains has important implications for the development of globally effective vaccines and for the management of patients. MATERIALS AND METHODS: A new method, termed combinatorial DNA melting assay (COMA), allows rapid accessing of comparative genetic information between related DNA sequences, making it possible to rapidly and accurately genotype unknown HIV-1 and HCV strains. COMA is mainly based on the differential melting properties of long DNA heteroduplexes. Combinatorial arrays of DNA heteroduplexes are formed when captured PCR-amplified reference DNA with known nucleotide sequences are combined with solution-phase complementary and antigenically labeled DNA with unknown sequences. Genetic divergence between the known and the unknown sequences is inferred as the experimentally derived melting curves of the two strands of the DNA heteroduplexes increasingly diverge. RESULTS: COMA was successfully applied to the genetic classification of HIV-1 and HCV strains into phylogenetic lineages or subtypes. CONCLUSIONS: Use of this assay should accelerate current efforts to understand the global molecular epidemiology of HIV-1 and HCV and may extend to the genetic characterization of other genetically diverse infectious pathogens associated with numerous diseases.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson B., Ying J. H., Lewis D. E., Gibbs R. A. Rapid characterization of HIV-1 sequence diversity using denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis and direct automated DNA sequencing of PCR products. PCR Methods Appl. 1993 May;2(4):293–300. doi: 10.1101/gr.2.4.293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner T. I., Brenner D. J., Neufeld B. R., Britten R. J. Reduction in the rate of DNA reassociation by sequence divergence. J Mol Biol. 1973 Dec 5;81(2):123–135. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90184-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukh J., Miller R. H., Purcell R. H. Genetic heterogeneity of hepatitis C virus: quasispecies and genotypes. Semin Liver Dis. 1995 Feb;15(1):41–63. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1007262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukh J., Purcell R. H., Miller R. H. At least 12 genotypes of hepatitis C virus predicted by sequence analysis of the putative E1 gene of isolates collected worldwide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 1;90(17):8234–8238. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.17.8234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukh J., Purcell R. H., Miller R. H. Sequence analysis of the 5' noncoding region of hepatitis C virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 1;89(11):4942–4946. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.4942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukh J., Purcell R. H., Miller R. H. Sequence analysis of the core gene of 14 hepatitis C virus genotypes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Aug 16;91(17):8239–8243. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.17.8239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delwart E. L., Shpaer E. G., Louwagie J., McCutchan F. E., Grez M., Rübsamen-Waigmann H., Mullins J. I. Genetic relationships determined by a DNA heteroduplex mobility assay: analysis of HIV-1 env genes. Science. 1993 Nov 19;262(5137):1257–1261. doi: 10.1126/science.8235655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao F., Morrison S. G., Robertson D. L., Thornton C. L., Craig S., Karlsson G., Sodroski J., Morgado M., Galvao-Castro B., von Briesen H. Molecular cloning and analysis of functional envelope genes from human immunodeficiency virus type 1 sequence subtypes A through G. The WHO and NIAID Networks for HIV Isolation and Characterization. J Virol. 1996 Mar;70(3):1651–1667. doi: 10.1128/jvi.70.3.1651-1667.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostrikis L. G., Bagdades E., Cao Y., Zhang L., Dimitriou D., Ho D. D. Genetic analysis of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 strains from patients in Cyprus: identification of a new subtype designated subtype I. J Virol. 1995 Oct;69(10):6122–6130. doi: 10.1128/jvi.69.10.6122-6130.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Fischer S. G., Lerman L. S., Maniatis T. Nearly all single base substitutions in DNA fragments joined to a GC-clamp can be detected by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 May 10;13(9):3131–3145. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.9.3131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Fischer S. G., Maniatis T., Lerman L. S. Modification of the melting properties of duplex DNA by attachment of a GC-rich DNA sequence as determined by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 May 10;13(9):3111–3129. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.9.3111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Lumelsky N., Lerman L. S., Maniatis T. Detection of single base substitutions in total genomic DNA. Nature. 1985 Feb 7;313(6002):495–498. doi: 10.1038/313495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Maniatis T., Lerman L. S. Detection and localization of single base changes by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:501–527. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55033-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson D. L., Hahn B. H., Sharp P. M. Recombination in AIDS viruses. J Mol Evol. 1995 Mar;40(3):249–259. doi: 10.1007/BF00163230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson D. L., Sharp P. M., McCutchan F. E., Hahn B. H. Recombination in HIV-1. Nature. 1995 Mar 9;374(6518):124–126. doi: 10.1038/374124b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharara A. I., Hunt C. M., Hamilton J. D. Hepatitis C. Ann Intern Med. 1996 Oct 15;125(8):658–668. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-125-8-199610150-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmonds P., Holmes E. C., Cha T. A., Chan S. W., McOmish F., Irvine B., Beall E., Yap P. L., Kolberg J., Urdea M. S. Classification of hepatitis C virus into six major genotypes and a series of subtypes by phylogenetic analysis of the NS-5 region. J Gen Virol. 1993 Nov;74(Pt 11):2391–2399. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-74-11-2391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Pathirana S., Davidson F., Lawlor E., Power J., Yap P. L., Simmonds P. The origin of hepatitis C virus genotypes. J Gen Virol. 1997 Feb;78(Pt 2):321–328. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-78-2-321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetmur J. G., Davidson N. Kinetics of renaturation of DNA. J Mol Biol. 1968 Feb 14;31(3):349–370. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90414-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zein N. N., Rakela J., Krawitt E. L., Reddy K. R., Tominaga T., Persing D. H. Hepatitis C virus genotypes in the United States: epidemiology, pathogenicity, and response to interferon therapy. Collaborative Study Group. Ann Intern Med. 1996 Oct 15;125(8):634–639. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-125-8-199610150-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]