Abstract
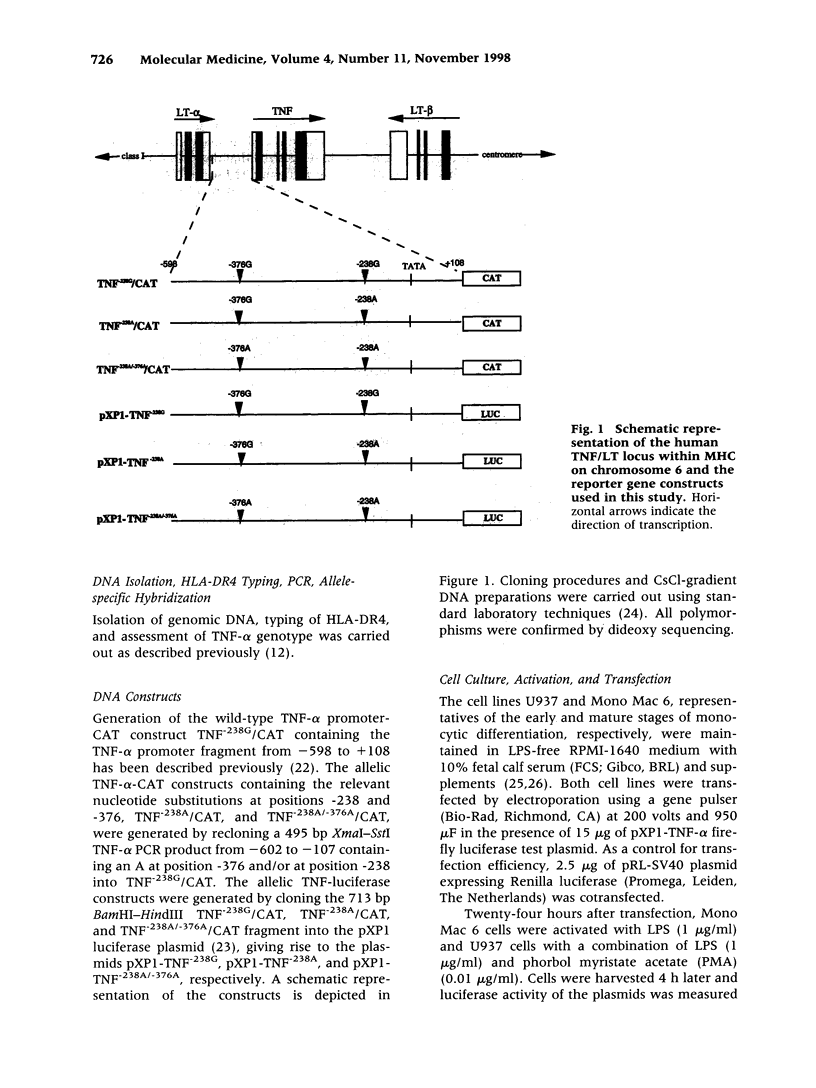
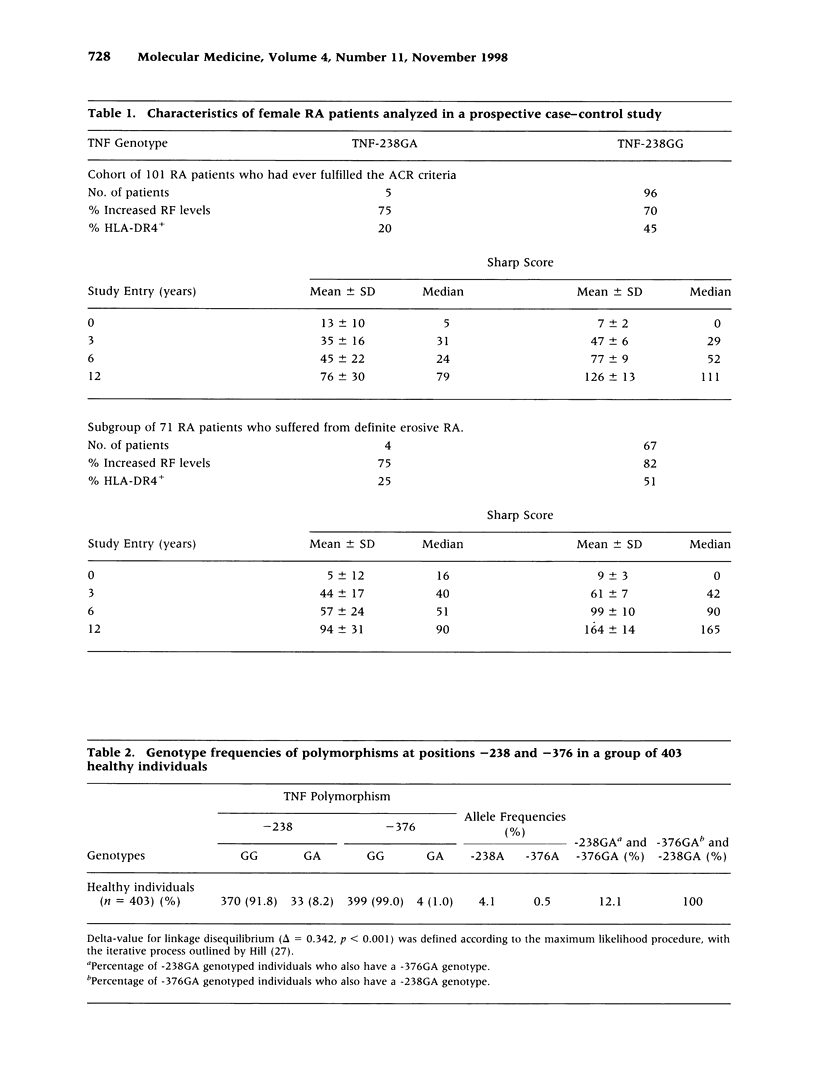
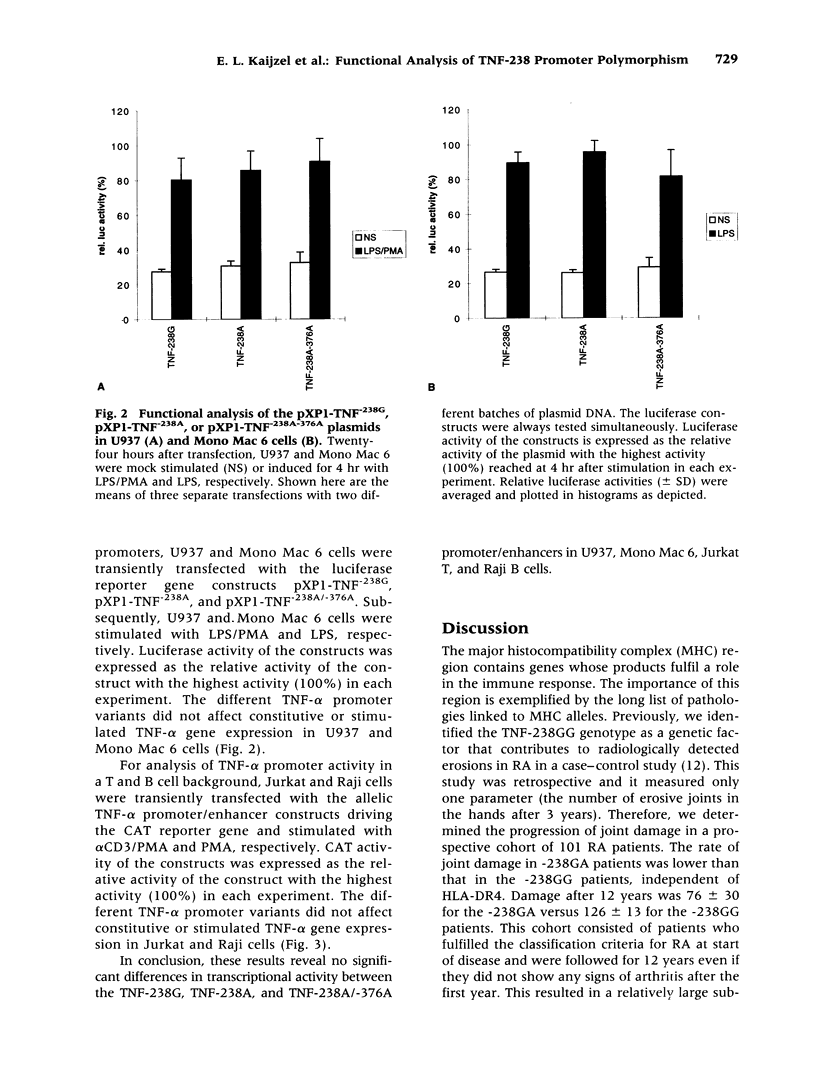
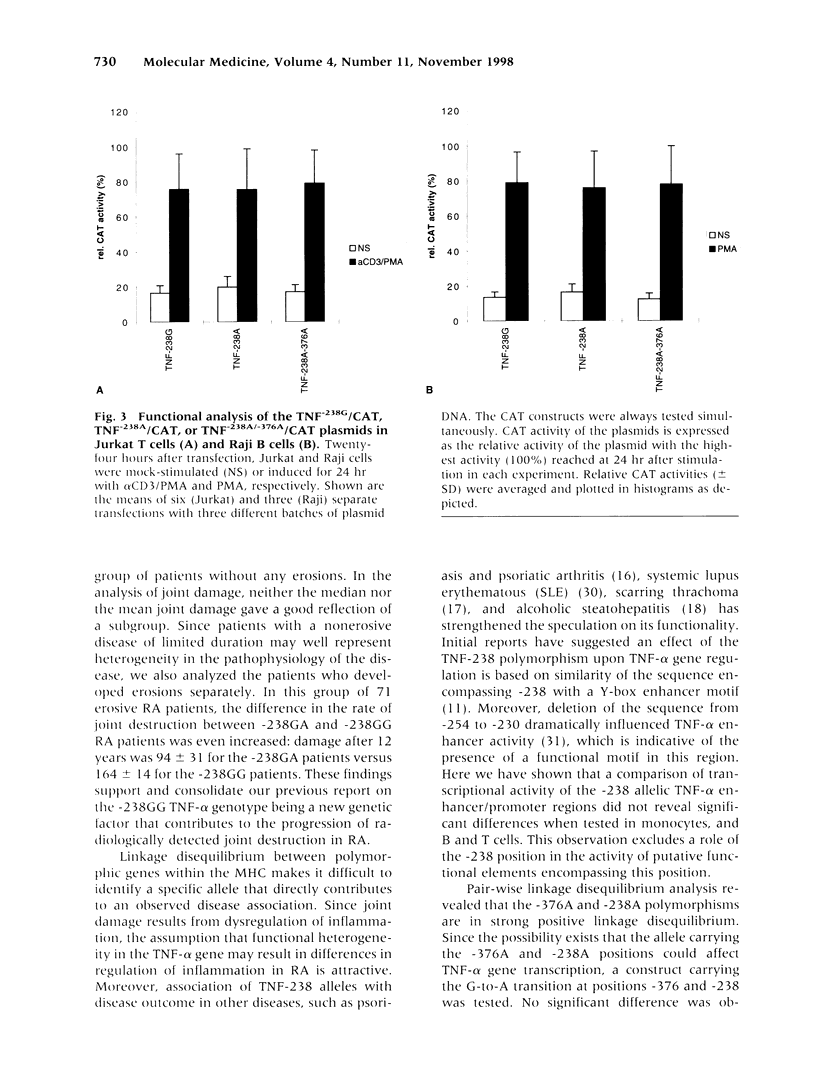
BACKGROUND: Functional heterogeneity in the tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) gene may be responsible for the TNF-alpha response in infectious and autoimmune diseases. Recently, the TNF-238 promoter polymorphism was observed as being associated with a more destructive disease in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). To determine the relation between TNF-238 and disease progression, the extent of joint destruction in a cohort of 101 RA patients followed for 12 years was analyzed. Furthermore, we have attempted to link this polymorphism to TNF-alpha gene transcription in monocytes and lymphocytes in vitro. PATIENTS, MATERIALS, AND METHODS: The extent of joint destruction determined on X-rays of hands and feet assessed after 0, 3, 6, and 12 years was compared with TNF-238 genotypes. Functional consequences of TNF-alpha gene polymorphisms using reporter gene constructs were analyzed in cells of the monocyte and lymphocyte lineage by means of transient transfection systems. RESULTS: The rate of joint damage in -238GA patients was lower than that in the -238GG patients, independent of HLA-DR4. Damage after 12 years was 76 +/- 30 for the -238GA versus 126 +/- 13 for the -238GG patients as determined by the van der Heijde's modification of Sharp's method. Furthermore, TNF-238A was found to be in linkage disequilibrium with an additional polymorphism at position -376. Functional assays revealed no significant differences in the level of inducible reporter gene expression between the TNF-238/-376 promoter constructs in the cell types tested. CONCLUSION: In a prospective study, we show that the TNF-238GG genotype contributes to progression of joint destruction in RA, independent of the presence of HLA-DR4. However, in vitro transfection assays indicate that TNF-238A by itself or in combination with TNF-376A is not likely to be of direct functional relevance for transcriptional activation. Therefore, these polymorphisms may serve as markers for additional polymorphisms in the TNF/LT locus or neighboring genes that may influence disease severity.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albertella M. R., Campbell R. D. Characterization of a novel gene in the human major histocompatibility complex that encodes a potential new member of the I kappa B family of proteins. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 May;3(5):793–799. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.5.793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amiot F., Boussadia O., Cases S., Fitting C., Lebastard M., Cavaillon J. M., Milon G., Dautry F. Mice heterozygous for a deletion of the tumor necrosis factor-alpha and lymphotoxin-alpha genes: biological importance of a nonlinear response of tumor necrosis factor-alpha to gene dosage. Eur J Immunol. 1997 Apr;27(4):1035–1042. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830270434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendtzen K., Morling N., Fomsgaard A., Svenson M., Jakobsen B., Odum N., Svejgaard A. Association between HLA-DR2 and production of tumour necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 1 by mononuclear cells activated by lipopolysaccharide. Scand J Immunol. 1988 Nov;28(5):599–606. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1988.tb01492.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B. Application of transcriptional and posttranscriptional reporter constructs to the analysis of tumor necrosis factor gene regulation. Am J Med Sci. 1992 Feb;303(2):129–133. doi: 10.1097/00000441-199202000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkman B. M., Huizinga T. W., Kurban S. S., van der Velde E. A., Schreuder G. M., Hazes J. M., Breedveld F. C., Verweij C. L. Tumour necrosis factor alpha gene polymorphisms in rheumatoid arthritis: association with susceptibility to, or severity of, disease? Br J Rheumatol. 1997 May;36(5):516–521. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/36.5.516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkman B. M., Zuijdeest D., Kaijzel E. L., Breedveld F. C., Verweij C. L. Relevance of the tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF alpha) -308 promoter polymorphism in TNF alpha gene regulation. J Inflamm. 1995;46(1):32–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabrera M., Shaw M. A., Sharples C., Williams H., Castes M., Convit J., Blackwell J. M. Polymorphism in tumor necrosis factor genes associated with mucocutaneous leishmaniasis. J Exp Med. 1995 Nov 1;182(5):1259–1264. doi: 10.1084/jem.182.5.1259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conway D. J., Holland M. J., Bailey R. L., Campbell A. E., Mahdi O. S., Jennings R., Mbena E., Mabey D. C. Scarring trachoma is associated with polymorphism in the tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) gene promoter and with elevated TNF-alpha levels in tear fluid. Infect Immun. 1997 Mar;65(3):1003–1006. doi: 10.1128/iai.65.3.1003-1006.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Alfonso S., Richiardi P. M. A polymorphic variation in a putative regulation box of the TNFA promoter region. Immunogenetics. 1994;39(2):150–154. doi: 10.1007/BF00188619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Alfonso S., Richiardi P. M. An intragenic polymorphism in the human tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFA) chain-encoding gene. Immunogenetics. 1996;44(4):321–322. doi: 10.1007/BF02602566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Economou J. S., Rhoades K., Essner R., McBride W. H., Gasson J. C., Morton D. L. Genetic analysis of the human tumor necrosis factor alpha/cachectin promoter region in a macrophage cell line. J Exp Med. 1989 Jul 1;170(1):321–326. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.1.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott M. J., Maini R. N., Feldmann M., Kalden J. R., Antoni C., Smolen J. S., Leeb B., Breedveld F. C., Macfarlane J. D., Bijl H. Randomised double-blind comparison of chimeric monoclonal antibody to tumour necrosis factor alpha (cA2) versus placebo in rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 1994 Oct 22;344(8930):1105–1110. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)90628-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott M. J., Maini R. N., Feldmann M., Long-Fox A., Charles P., Bijl H., Woody J. N. Repeated therapy with monoclonal antibody to tumour necrosis factor alpha (cA2) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 1994 Oct 22;344(8930):1125–1127. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)90632-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong C. L., Siddiqui A. H., Mark D. F. Identification and characterization of a novel repressor site in the human tumor necrosis factor alpha gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Mar 25;22(6):1108–1114. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.6.1108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfeld A. E., Doyle C., Maniatis T. Human tumor necrosis factor alpha gene regulation by virus and lipopolysaccharide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9769–9773. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grove J., Daly A. K., Bassendine M. F., Day C. P. Association of a tumor necrosis factor promoter polymorphism with susceptibility to alcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology. 1997 Jul;26(1):143–146. doi: 10.1002/hep.510260119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamann A., Mantzoros C., Vidal-Puig A., Flier J. S. Genetic variability in the TNF-alpha promoter is not associated with type II diabetes mellitus (NIDDM). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995 Jun 26;211(3):833–839. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1995.1887. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill W. G. Estimation of linkage disequilibrium in randomly mating populations. Heredity (Edinb) 1974 Oct;33(2):229–239. doi: 10.1038/hdy.1974.89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huizinga T. W., Westendorp R. G., Bollen E. L., Keijsers V., Brinkman B. M., Langermans J. A., Breedveld F. C., Verweij C. L., van de Gaer L., Dams L. TNF-alpha promoter polymorphisms, production and susceptibility to multiple sclerosis in different groups of patients. J Neuroimmunol. 1997 Feb;72(2):149–153. doi: 10.1016/s0165-5728(96)00182-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höhler T., Kruger A., Schneider P. M., Schopf R. E., Knop J., Rittner C., Meyer zum Büschenfelde K. H., Märker-Hermann E. A TNF-alpha promoter polymorphism is associated with juvenile onset psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. J Invest Dermatol. 1997 Oct;109(4):562–565. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12337469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob C. O., Fronek Z., Lewis G. D., Koo M., Hansen J. A., McDevitt H. O. Heritable major histocompatibility complex class II-associated differences in production of tumor necrosis factor alpha: relevance to genetic predisposition to systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1233–1237. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jongeneel C. V. Regulation of the TNF alpha gene. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1994;388:367–381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keffer J., Probert L., Cazlaris H., Georgopoulos S., Kaslaris E., Kioussis D., Kollias G. Transgenic mice expressing human tumour necrosis factor: a predictive genetic model of arthritis. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4025–4031. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04978.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroeger K. M., Carville K. S., Abraham L. J. The -308 tumor necrosis factor-alpha promoter polymorphism effects transcription. Mol Immunol. 1997 Apr;34(5):391–399. doi: 10.1016/s0161-5890(97)00052-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marino M. W., Dunn A., Grail D., Inglese M., Noguchi Y., Richards E., Jungbluth A., Wada H., Moore M., Williamson B. Characterization of tumor necrosis factor-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Jul 22;94(15):8093–8098. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.15.8093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonnell P. C., DiLella A. G., Lee J. C., Young P. R. Localization of the human stress responsive MAP kinase-like CSAIDs binding protein (CSBP) gene to chromosome 6q21.3/21.2. Genomics. 1995 Sep 1;29(1):301–302. doi: 10.1006/geno.1995.1252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire W., Hill A. V., Allsopp C. E., Greenwood B. M., Kwiatkowski D. Variation in the TNF-alpha promoter region associated with susceptibility to cerebral malaria. Nature. 1994 Oct 6;371(6497):508–510. doi: 10.1038/371508a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meulenbelt I., Williams C. J., Te Koppele J. M., Van de Giessen G. C., Slagboom P. E. Population haplotype analysis and evolutionary relations of the COL2A1 gene. Ann Hum Genet. 1996 May;60(Pt 3):189–199. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1996.tb00422.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner C. M., Campbell R. D. The G9a gene in the human major histocompatibility complex encodes a novel protein containing ankyrin-like repeats. Biochem J. 1993 Mar 15;290(Pt 3):811–818. doi: 10.1042/bj2900811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordeen S. K. Luciferase reporter gene vectors for analysis of promoters and enhancers. Biotechniques. 1988 May;6(5):454–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philip R., Epstein L. B. Tumour necrosis factor as immunomodulator and mediator of monocyte cytotoxicity induced by itself, gamma-interferon and interleukin-1. Nature. 1986 Sep 4;323(6083):86–89. doi: 10.1038/323086a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pociot F., D'Alfonso S., Compasso S., Scorza R., Richiardi P. M. Functional analysis of a new polymorphism in the human TNF alpha gene promoter. Scand J Immunol. 1995 Oct;42(4):501–504. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1995.tb03686.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuber F., Udalova I. A., Book M., Drutskaya L. N., Kuprash D. V., Turetskaya R. L., Schade F. U., Nedospasov S. A. -308 tumor necrosis factor (TNF) polymorphism is not associated with survival in severe sepsis and is unrelated to lipopolysaccharide inducibility of the human TNF promoter. J Inflamm. 1995;46(1):42–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundström C., Nilsson K. Establishment and characterization of a human histiocytic lymphoma cell line (U-937). Int J Cancer. 1976 May 15;17(5):565–577. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910170504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udalova I. A., Knight J. C., Vidal V., Nedospasov S. A., Kwiatkowski D. Complex NF-kappaB interactions at the distal tumor necrosis factor promoter region in human monocytes. J Biol Chem. 1998 Aug 14;273(33):21178–21186. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.33.21178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinasco J., Beraún Y., Nieto A., Fraile A., Mataran L., Pareja E., Martín J. Polymorphism at the TNF loci in rheumatoid arthritis. Tissue Antigens. 1997 Jan;49(1):74–78. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1997.tb02715.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson A. G., Symons J. A., McDowell T. L., McDevitt H. O., Duff G. W. Effects of a polymorphism in the human tumor necrosis factor alpha promoter on transcriptional activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Apr 1;94(7):3195–3199. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.7.3195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson A. G., de Vries N., Pociot F., di Giovine F. S., van der Putte L. B., Duff G. W. An allelic polymorphism within the human tumor necrosis factor alpha promoter region is strongly associated with HLA A1, B8, and DR3 alleles. J Exp Med. 1993 Feb 1;177(2):557–560. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.2.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler-Heitbrock H. W., Thiel E., Fütterer A., Herzog V., Wirtz A., Riethmüller G. Establishment of a human cell line (Mono Mac 6) with characteristics of mature monocytes. Int J Cancer. 1988 Mar 15;41(3):456–461. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910410324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Zeben D., Hazes J. M., Zwinderman A. H., Cats A., Schreuder G. M., D'Amaro J., Breedveld F. C. Association of HLA-DR4 with a more progressive disease course in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Results of a followup study. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Jul;34(7):822–830. doi: 10.1002/art.1780340707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Zeben D., Hazes J. M., Zwinderman A. H., Vandenbroucke J. P., Breedveld F. C. The severity of rheumatoid arthritis: a 6-year followup study of younger women with symptoms of recent onset. J Rheumatol. 1994 Sep;21(9):1620–1625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Heijde D. M., van Leeuwen M. A., van Riel P. L., van de Putte L. B. Radiographic progression on radiographs of hands and feet during the first 3 years of rheumatoid arthritis measured according to Sharp's method (van der Heijde modification). J Rheumatol. 1995 Sep;22(9):1792–1796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]