Abstract
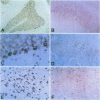
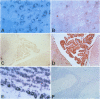
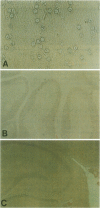
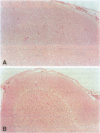
BACKGROUND: The mediator known historically as macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) has been identified recently as being released into the circulation by the anterior pituitary gland as a consequence of stress or during a systemic inflammatory response. Macrophages and T cells also secrete MIF, both in response to proinflammatory factors or upon stimulation with glucocorticoids. Once released, MIF "overrides" or counterregulates the immunosuppressive effects of steroids on cytokine production and immune cellular activation. To further investigate the biology of MIF and its role in the neuroendocrine system, we have studied the regional and cellular expression of MIF in brain tissue obtained from normal rats and rats administered LPS intracisternally. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Rat brain sections were analyzed by immunohistochemistry utilizing an affinity-purified, anti-MIF antibody raised to recombinant MIF, and by in situ hybridization using a digoxigenin-labeled, antisense MIF cRNA probe. The kinetics of MIF mRNA expression in brain were compared with that of IL-1, IL-6, and TNF-alpha by RT-PCR of total brain RNA. The cerebrospinal fluid content of MIF and TNF-alpha proteins was analyzed by Western blotting and ELISA. RESULTS: A strong baseline expression pattern for MIF was observed in neurons of the cortex, hypothalamus, hippocampus, cerebellum, and pons. By in situ hybridization, MIF mRNA was found predominantly in cell bodies whereas MIF protein was detected mostly within the terminal fields associated with neurons. There was a marked pattern of MIF immunoreactivity within the mossy fibers of the dentate gyrus and dendrites of the hippocampal CA3 field. These structures have been shown previously to be involved in glucocorticoid-induced tissue damage within the hippocampus, suggesting an association between MIF and targets of glucocorticoid action. The intracisternal injection of LPS increased MIF mRNA and protein expression in brain and MIF immunoreactivity was due in part to infiltrating monocytes/macrophages. MIF protein also was found to be rapidly released into the cerebrospinal fluid. This response corresponded with that of LPS-induced cytokine release and MIF mRNA expression increased in a distribution that colocalized in large part with that of TNF-alpha, IL-1 beta, and IL-6. CONCLUSION: The significant levels of baseline and inducible MIF expression in the brain and its regional association with glucocorticoid action underscore the importance of this mediator as a physiological regulator of the inflammatory stress response and further define its role within the neuroendocrine system.
Full text
PDF













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bacher M., Meinhardt A., Lan H. Y., Mu W., Metz C. N., Chesney J. A., Calandra T., Gemsa D., Donnelly T., Atkins R. C. Migration inhibitory factor expression in experimentally induced endotoxemia. Am J Pathol. 1997 Jan;150(1):235–246. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacher M., Metz C. N., Calandra T., Mayer K., Chesney J., Lohoff M., Gemsa D., Donnelly T., Bucala R. An essential regulatory role for macrophage migration inhibitory factor in T-cell activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Jul 23;93(15):7849–7854. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.15.7849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandtlow C. E., Meyer M., Lindholm D., Spranger M., Heumann R., Thoenen H. Regional and cellular codistribution of interleukin 1 beta and nerve growth factor mRNA in the adult rat brain: possible relationship to the regulation of nerve growth factor synthesis. J Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;111(4):1701–1711. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.4.1701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernhagen J., Bacher M., Calandra T., Metz C. N., Doty S. B., Donnelly T., Bucala R. An essential role for macrophage migration inhibitory factor in the tuberculin delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction. J Exp Med. 1996 Jan 1;183(1):277–282. doi: 10.1084/jem.183.1.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernhagen J., Calandra T., Mitchell R. A., Martin S. B., Tracey K. J., Voelter W., Manogue K. R., Cerami A., Bucala R. MIF is a pituitary-derived cytokine that potentiates lethal endotoxaemia. Nature. 1993 Oct 21;365(6448):756–759. doi: 10.1038/365756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernhagen J., Mitchell R. A., Calandra T., Voelter W., Cerami A., Bucala R. Purification, bioactivity, and secondary structure analysis of mouse and human macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF). Biochemistry. 1994 Nov 29;33(47):14144–14155. doi: 10.1021/bi00251a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom B. R., Bennett B. Mechanism of a reaction in vitro associated with delayed-type hypersensitivity. Science. 1966 Jul 1;153(3731):80–82. doi: 10.1126/science.153.3731.80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calandra T., Bernhagen J., Metz C. N., Spiegel L. A., Bacher M., Donnelly T., Cerami A., Bucala R. MIF as a glucocorticoid-induced modulator of cytokine production. Nature. 1995 Sep 7;377(6544):68–71. doi: 10.1038/377068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calandra T., Bernhagen J., Mitchell R. A., Bucala R. The macrophage is an important and previously unrecognized source of macrophage migration inhibitory factor. J Exp Med. 1994 Jun 1;179(6):1895–1902. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.6.1895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claiborne B. J., Amaral D. G., Cowan W. M. A light and electron microscopic analysis of the mossy fibers of the rat dentate gyrus. J Comp Neurol. 1986 Apr 22;246(4):435–458. doi: 10.1002/cne.902460403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David J. R. Delayed hypersensitivity in vitro: its mediation by cell-free substances formed by lymphoid cell-antigen interaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jul;56(1):72–77. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.1.72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GEORGE M., VAUGHAN J. H. In vitro cell migration as a model for delayed hypersensitivity. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1962 Nov;111:514–521. doi: 10.3181/00379727-111-27841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadient R. A., Otten U. Identification of interleukin-6 (IL-6)-expressing neurons in the cerebellum and hippocampus of normal adult rats. Neurosci Lett. 1994 Dec 5;182(2):243–246. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(94)90807-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galat A., Rivière S., Bouet F. Purification of macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) from bovine brain cytosol. FEBS Lett. 1993 Mar 22;319(3):233–236. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80553-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins G. A., Olschowka J. A. Induction of interleukin-1 beta mRNA in adult rat brain. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1991 Jan;9(1-2):143–148. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(91)90139-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter C. A., Roberts C. W., Alexander J. Kinetics of cytokine mRNA production in the brains of mice with progressive toxoplasmic encephalitis. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Sep;22(9):2317–2322. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krugers H. J., Koolhaas J. M., Bohus B., Korf J. A single social stress-experience alters glutamate receptor-binding in rat hippocampal CA3 area. Neurosci Lett. 1993 May 14;154(1-2):73–77. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(93)90174-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lan H. Y., Mu W., NG Y. Y., Nikolic-Paterson D. J., Atkins R. C. A simple, reliable, and sensitive method for nonradioactive in situ hybridization: use of microwave heating to improve hybridization efficiency and preserve tissue morphology. J Histochem Cytochem. 1996 Mar;44(3):281–287. doi: 10.1177/44.3.8648089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lan H. Y., Mu W., Yang N., Meinhardt A., Nikolic-Paterson D. J., Ng Y. Y., Bacher M., Atkins R. C., Bucala R. De Novo renal expression of macrophage migration inhibitory factor during the development of rat crescentic glomerulonephritis. Am J Pathol. 1996 Oct;149(4):1119–1127. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lechan R. M., Toni R., Clark B. D., Cannon J. G., Shaw A. R., Dinarello C. A., Reichlin S. Immunoreactive interleukin-1 beta localization in the rat forebrain. Brain Res. 1990 Apr 23;514(1):135–140. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)90445-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magariños A. M., McEwen B. S., Flügge G., Fuchs E. Chronic psychosocial stress causes apical dendritic atrophy of hippocampal CA3 pyramidal neurons in subordinate tree shrews. J Neurosci. 1996 May 15;16(10):3534–3540. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-10-03534.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinhardt A., Bacher M., McFarlane J. R., Metz C. N., Seitz J., Hedger M. P., de Kretser D. M., Bucala R. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor production by Leydig cells: evidence for a role in the regulation of testicular function. Endocrinology. 1996 Nov;137(11):5090–5095. doi: 10.1210/endo.137.11.8895383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell R., Bacher M., Bernhagen J., Pushkarskaya T., Seldin M. F., Bucala R. Cloning and characterization of the gene for mouse macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF). J Immunol. 1995 Apr 15;154(8):3863–3870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishibori M., Nakaya N., Tahara A., Kawabata M., Mori S., Saeki K. Presence of macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) in ependyma, astrocytes and neurons in the bovine brain. Neurosci Lett. 1996 Aug 9;213(3):193–196. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(96)12864-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishino T., Bernhagen J., Shiiki H., Calandra T., Dohi K., Bucala R. Localization of macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) to secretory granules within the corticotrophic and thyrotrophic cells of the pituitary gland. Mol Med. 1995 Nov;1(7):781–788. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northemann W., Braciak T. A., Hattori M., Lee F., Fey G. H. Structure of the rat interleukin 6 gene and its expression in macrophage-derived cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 25;264(27):16072–16082. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nudel U., Zakut R., Shani M., Neuman S., Levy Z., Yaffe D. The nucleotide sequence of the rat cytoplasmic beta-actin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1759–1771. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai M., Nishihira J., Hibiya Y., Koyama Y., Nishi S. Glutathione binding rat liver 13k protein is the homologue of the macrophage migration inhibitory factor. Biochem Mol Biol Int. 1994 Jun;33(3):439–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sapolsky R. M., Uno H., Rebert C. S., Finch C. E. Hippocampal damage associated with prolonged glucocorticoid exposure in primates. J Neurosci. 1990 Sep;10(9):2897–2902. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-09-02897.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöbitz B., Voorhuis D. A., De Kloet E. R. Localization of interleukin 6 mRNA and interleukin 6 receptor mRNA in rat brain. Neurosci Lett. 1992 Mar 2;136(2):189–192. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(92)90046-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uno H., Tarara R., Else J. G., Suleman M. A., Sapolsky R. M. Hippocampal damage associated with prolonged and fatal stress in primates. J Neurosci. 1989 May;9(5):1705–1711. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-05-01705.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waeber G., Calandra T., Roduit R., Haefliger J. A., Bonny C., Thompson N., Thorens B., Temler E., Meinhardt A., Bacher M. Insulin secretion is regulated by the glucose-dependent production of islet beta cell macrophage migration inhibitory factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Apr 29;94(9):4782–4787. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.9.4782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolley C. S., Gould E., McEwen B. S. Exposure to excess glucocorticoids alters dendritic morphology of adult hippocampal pyramidal neurons. Brain Res. 1990 Oct 29;531(1-2):225–231. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)90778-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan H. Q., Banos M. A., Herregodts P., Hooghe R., Hooghe-Peters E. L. Expression of interleukin (IL)-1 beta, IL-6 and their respective receptors in the normal rat brain and after injury. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Nov;22(11):2963–2971. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830221131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]