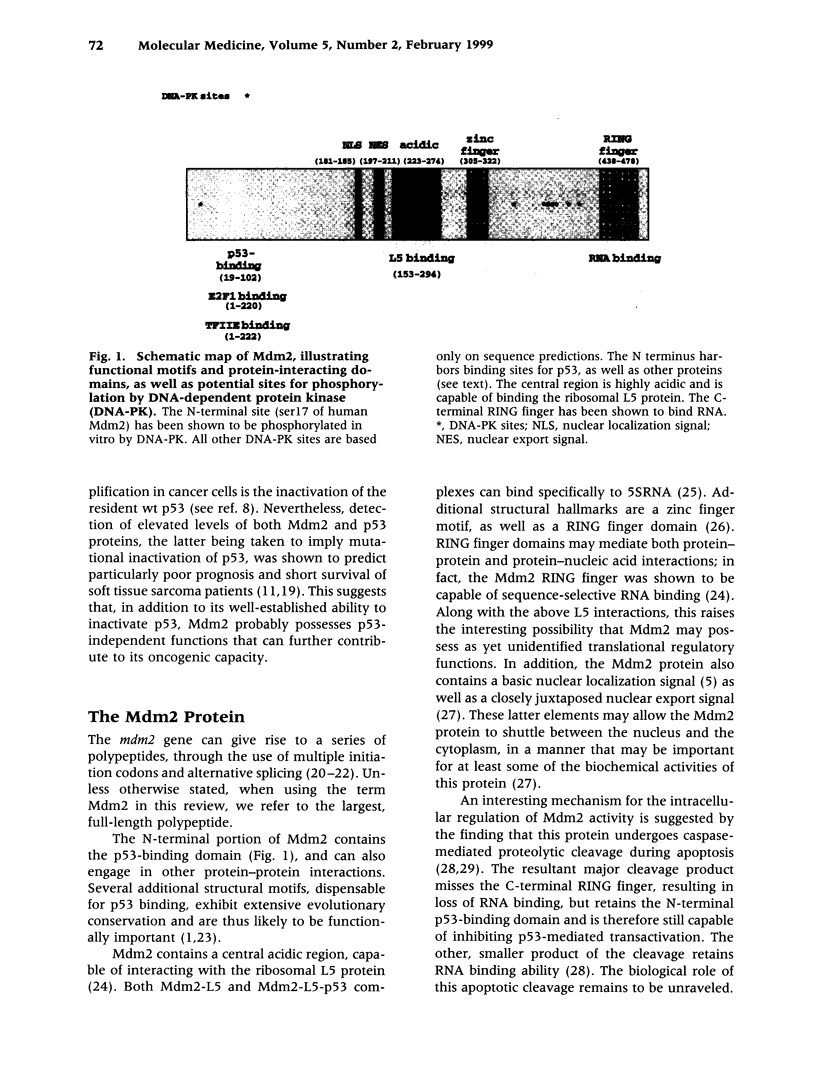
Full text
PDF




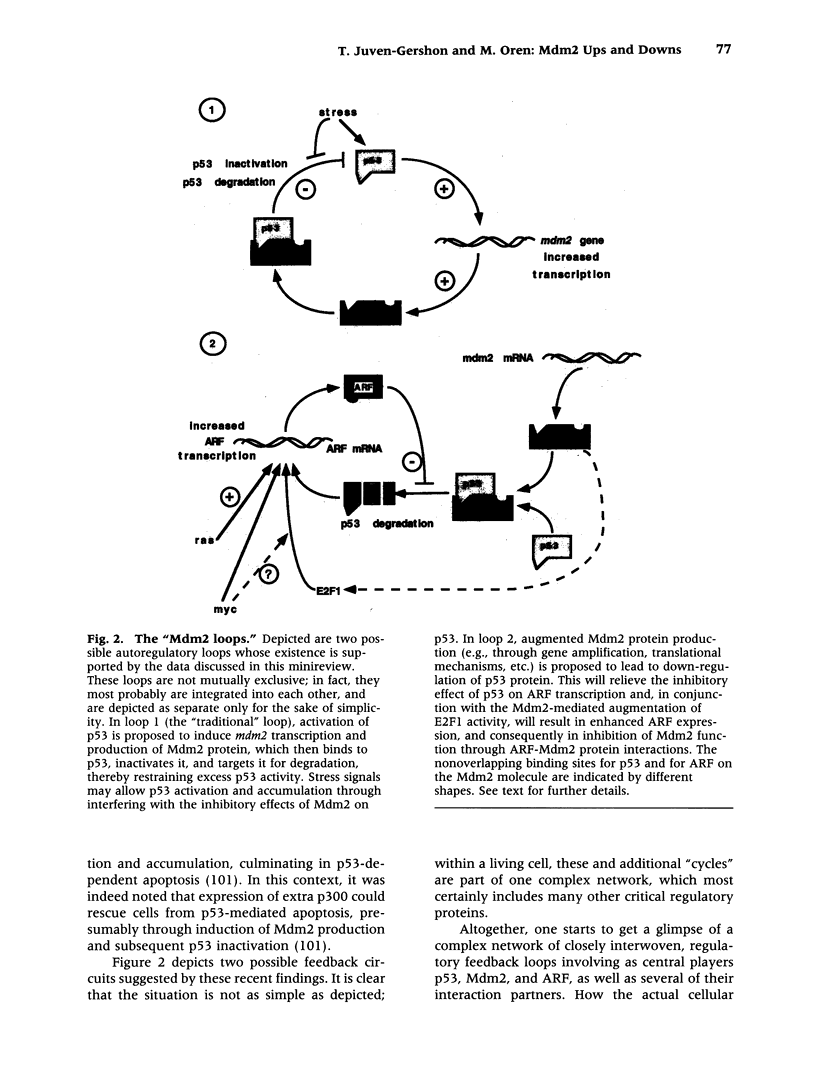

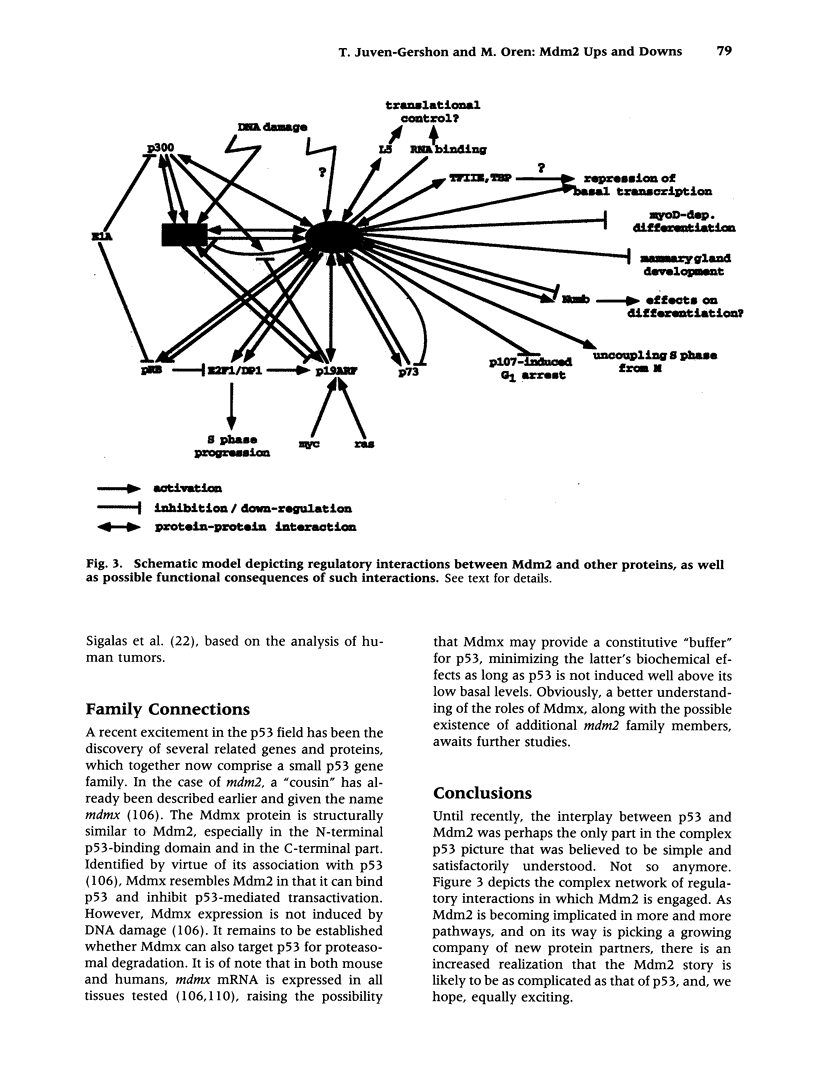




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avantaggiati M. L., Ogryzko V., Gardner K., Giordano A., Levine A. S., Kelly K. Recruitment of p300/CBP in p53-dependent signal pathways. Cell. 1997 Jun 27;89(7):1175–1184. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80304-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banin S., Moyal L., Shieh S., Taya Y., Anderson C. W., Chessa L., Smorodinsky N. I., Prives C., Reiss Y., Shiloh Y. Enhanced phosphorylation of p53 by ATM in response to DNA damage. Science. 1998 Sep 11;281(5383):1674–1677. doi: 10.1126/science.281.5383.1674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barak Y., Gottlieb E., Juven-Gershon T., Oren M. Regulation of mdm2 expression by p53: alternative promoters produce transcripts with nonidentical translation potential. Genes Dev. 1994 Aug 1;8(15):1739–1749. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.15.1739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barak Y., Juven T., Haffner R., Oren M. mdm2 expression is induced by wild type p53 activity. EMBO J. 1993 Feb;12(2):461–468. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05678.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barak Y., Oren M. Enhanced binding of a 95 kDa protein to p53 in cells undergoing p53-mediated growth arrest. EMBO J. 1992 Jun;11(6):2115–2121. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05270.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bates S., Phillips A. C., Clark P. A., Stott F., Peters G., Ludwig R. L., Vousden K. H. p14ARF links the tumour suppressors RB and p53. Nature. 1998 Sep 10;395(6698):124–125. doi: 10.1038/25867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaydes J. P., Wynford-Thomas D. The proliferation of normal human fibroblasts is dependent upon negative regulation of p53 function by mdm2. Oncogene. 1998 Jun 25;16(25):3317–3322. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1201880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. R., Thomas C. A., Deb S. P. The human oncoprotein MDM2 arrests the cell cycle: elimination of its cell-cycle-inhibitory function induces tumorigenesis. EMBO J. 1998 May 1;17(9):2513–2525. doi: 10.1093/emboj/17.9.2513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böttger A., Böttger V., Garcia-Echeverria C., Chène P., Hochkeppel H. K., Sampson W., Ang K., Howard S. F., Picksley S. M., Lane D. P. Molecular characterization of the hdm2-p53 interaction. J Mol Biol. 1997 Jun 27;269(5):744–756. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1997.1078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böttger A., Böttger V., Sparks A., Liu W. L., Howard S. F., Lane D. P. Design of a synthetic Mdm2-binding mini protein that activates the p53 response in vivo. Curr Biol. 1997 Nov 1;7(11):860–869. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(06)00374-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böttger V., Böttger A., Howard S. F., Picksley S. M., Chène P., Garcia-Echeverria C., Hochkeppel H. K., Lane D. P. Identification of novel mdm2 binding peptides by phage display. Oncogene. 1996 Nov 21;13(10):2141–2147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahilly-Snyder L., Yang-Feng T., Francke U., George D. L. Molecular analysis and chromosomal mapping of amplified genes isolated from a transformed mouse 3T3 cell line. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1987 May;13(3):235–244. doi: 10.1007/BF01535205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canman C. E., Lim D. S., Cimprich K. A., Taya Y., Tamai K., Sakaguchi K., Appella E., Kastan M. B., Siliciano J. D. Activation of the ATM kinase by ionizing radiation and phosphorylation of p53. Science. 1998 Sep 11;281(5383):1677–1679. doi: 10.1126/science.281.5383.1677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang Y. C., Lee Y. S., Tejima T., Tanaka K., Omura S., Heintz N. H., Mitsui Y., Magae J. mdm2 and bax, downstream mediators of the p53 response, are degraded by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Cell Growth Differ. 1998 Jan;9(1):79–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. Y., Oliner J. D., Zhan Q., Fornace A. J., Jr, Vogelstein B., Kastan M. B. Interactions between p53 and MDM2 in a mammalian cell cycle checkpoint pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 29;91(7):2684–2688. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.7.2684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J., Lin J., Levine A. J. Regulation of transcription functions of the p53 tumor suppressor by the mdm-2 oncogene. Mol Med. 1995 Jan;1(2):142–152. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J., Marechal V., Levine A. J. Mapping of the p53 and mdm-2 interaction domains. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;13(7):4107–4114. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.4107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J., Wu X., Lin J., Levine A. J. mdm-2 inhibits the G1 arrest and apoptosis functions of the p53 tumor suppressor protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1996 May;16(5):2445–2452. doi: 10.1128/mcb.16.5.2445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L., Agrawal S., Zhou W., Zhang R., Chen J. Synergistic activation of p53 by inhibition of MDM2 expression and DNA damage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Jan 6;95(1):195–200. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.1.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L., Marechal V., Moreau J., Levine A. J., Chen J. Proteolytic cleavage of the mdm2 oncoprotein during apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 1997 Sep 5;272(36):22966–22973. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.36.22966. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordon-Cardo C., Latres E., Drobnjak M., Oliva M. R., Pollack D., Woodruff J. M., Marechal V., Chen J., Brennan M. F., Levine A. J. Molecular abnormalities of mdm2 and p53 genes in adult soft tissue sarcomas. Cancer Res. 1994 Feb 1;54(3):794–799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corvi R., Savelyeva L., Breit S., Wenzel A., Handgretinger R., Barak J., Oren M., Amler L., Schwab M. Non-syntenic amplification of MDM2 and MYCN in human neuroblastoma. Oncogene. 1995 Mar 16;10(6):1081–1086. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl A. M., Beverley P. C., Stauss H. J. A synthetic peptide derived from the tumor-associated protein mdm2 can stimulate autoreactive, high avidity cytotoxic T lymphocytes that recognize naturally processed protein. J Immunol. 1996 Jul 1;157(1):239–246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubs-Poterszman M. C., Tocque B., Wasylyk B. MDM2 transformation in the absence of p53 and abrogation of the p107 G1 cell-cycle arrest. Oncogene. 1995 Dec 7;11(11):2445–2449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elenbaas B., Dobbelstein M., Roth J., Shenk T., Levine A. J. The MDM2 oncoprotein binds specifically to RNA through its RING finger domain. Mol Med. 1996 Jul;2(4):439–451. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erhardt P., Tomaselli K. J., Cooper G. M. Identification of the MDM2 oncoprotein as a substrate for CPP32-like apoptotic proteases. J Biol Chem. 1997 Jun 13;272(24):15049–15052. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.24.15049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fakharzadeh S. S., Trusko S. P., George D. L. Tumorigenic potential associated with enhanced expression of a gene that is amplified in a mouse tumor cell line. EMBO J. 1991 Jun;10(6):1565–1569. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07676.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiddler T. A., Smith L., Tapscott S. J., Thayer M. J. Amplification of MDM2 inhibits MyoD-mediated myogenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1996 Sep;16(9):5048–5057. doi: 10.1128/mcb.16.9.5048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay C. A. The mdm-2 oncogene can overcome wild-type p53 suppression of transformed cell growth. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):301–306. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman D. A., Levine A. J. Nuclear export is required for degradation of endogenous p53 by MDM2 and human papillomavirus E6. Mol Cell Biol. 1998 Dec;18(12):7288–7293. doi: 10.1128/mcb.18.12.7288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman S. R., Perez M., Kung A. L., Joseph M., Mansur C., Xiao Z. X., Kumar S., Howley P. M., Livingston D. M. p300/MDM2 complexes participate in MDM2-mediated p53 degradation. Mol Cell. 1998 Oct;2(4):405–415. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80140-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu W., Shi X. L., Roeder R. G. Synergistic activation of transcription by CBP and p53. Nature. 1997 Jun 19;387(6635):819–823. doi: 10.1038/42972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerra B., Götz C., Wagner P., Montenarh M., Issinger O. G. The carboxy terminus of p53 mimics the polylysine effect of protein kinase CK2-catalyzed MDM2 phosphorylation. Oncogene. 1997 Jun 5;14(22):2683–2688. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1201112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haines D. S., Landers J. E., Engle L. J., George D. L. Physical and functional interaction between wild-type p53 and mdm2 proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;14(2):1171–1178. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.2.1171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haupt Y., Barak Y., Oren M. Cell type-specific inhibition of p53-mediated apoptosis by mdm2. EMBO J. 1996 Apr 1;15(7):1596–1606. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haupt Y., Maya R., Kazaz A., Oren M. Mdm2 promotes the rapid degradation of p53. Nature. 1997 May 15;387(6630):296–299. doi: 10.1038/387296a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henning W., Rohaly G., Kolzau T., Knippschild U., Maacke H., Deppert W. MDM2 is a target of simian virus 40 in cellular transformation and during lytic infection. J Virol. 1997 Oct;71(10):7609–7618. doi: 10.1128/jvi.71.10.7609-7618.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda R., Tanaka H., Yasuda H. Oncoprotein MDM2 is a ubiquitin ligase E3 for tumor suppressor p53. FEBS Lett. 1997 Dec 22;420(1):25–27. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(97)01480-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh J. K., Fredersdorf S., Kouzarides T., Martin K., Lu X. E2F1-induced apoptosis requires DNA binding but not transactivation and is inhibited by the retinoblastoma protein through direct interaction. Genes Dev. 1997 Jul 15;11(14):1840–1852. doi: 10.1101/gad.11.14.1840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. N., Roe A. E., Donehower L. A., Bradley A. Rescue of embryonic lethality in Mdm2-deficient mice by absence of p53. Nature. 1995 Nov 9;378(6553):206–208. doi: 10.1038/378206a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. N., Sands A. T., Hancock A. R., Vogel H., Donehower L. A., Linke S. P., Wahl G. M., Bradley A. The tumorigenic potential and cell growth characteristics of p53-deficient cells are equivalent in the presence or absence of Mdm2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Nov 26;93(24):14106–14111. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.24.14106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juven-Gershon T., Shifman O., Unger T., Elkeles A., Haupt Y., Oren M. The Mdm2 oncoprotein interacts with the cell fate regulator Numb. Mol Cell Biol. 1998 Jul;18(7):3974–3982. doi: 10.1128/mcb.18.7.3974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juven T., Barak Y., Zauberman A., George D. L., Oren M. Wild type p53 can mediate sequence-specific transactivation of an internal promoter within the mdm2 gene. Oncogene. 1993 Dec;8(12):3411–3416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamijo T., Weber J. D., Zambetti G., Zindy F., Roussel M. F., Sherr C. J. Functional and physical interactions of the ARF tumor suppressor with p53 and Mdm2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Jul 7;95(14):8292–8297. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.14.8292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowalik T. F., DeGregori J., Leone G., Jakoi L., Nevins J. R. E2F1-specific induction of apoptosis and p53 accumulation, which is blocked by Mdm2. Cell Growth Differ. 1998 Feb;9(2):113–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubbutat M. H., Jones S. N., Vousden K. H. Regulation of p53 stability by Mdm2. Nature. 1997 May 15;387(6630):299–303. doi: 10.1038/387299a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubbutat M. H., Ludwig R. L., Ashcroft M., Vousden K. H. Regulation of Mdm2-directed degradation by the C terminus of p53. Mol Cell Biol. 1998 Oct;18(10):5690–5698. doi: 10.1128/mcb.18.10.5690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kussie P. H., Gorina S., Marechal V., Elenbaas B., Moreau J., Levine A. J., Pavletich N. P. Structure of the MDM2 oncoprotein bound to the p53 tumor suppressor transactivation domain. Science. 1996 Nov 8;274(5289):948–953. doi: 10.1126/science.274.5289.948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladanyi M., Cha C., Lewis R., Jhanwar S. C., Huvos A. G., Healey J. H. MDM2 gene amplification in metastatic osteosarcoma. Cancer Res. 1993 Jan 1;53(1):16–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landers J. E., Cassel S. L., George D. L. Translational enhancement of mdm2 oncogene expression in human tumor cells containing a stabilized wild-type p53 protein. Cancer Res. 1997 Aug 15;57(16):3562–3568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landers J. E., Haines D. S., Strauss J. F., 3rd, George D. L. Enhanced translation: a novel mechanism of mdm2 oncogene overexpression identified in human tumor cells. Oncogene. 1994 Sep;9(9):2745–2750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leach F. S., Tokino T., Meltzer P., Burrell M., Oliner J. D., Smith S., Hill D. E., Sidransky D., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. p53 Mutation and MDM2 amplification in human soft tissue sarcomas. Cancer Res. 1993 May 15;53(10 Suppl):2231–2234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lill N. L., Grossman S. R., Ginsberg D., DeCaprio J., Livingston D. M. Binding and modulation of p53 by p300/CBP coactivators. Nature. 1997 Jun 19;387(6635):823–827. doi: 10.1038/42981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J., Chen J., Elenbaas B., Levine A. J. Several hydrophobic amino acids in the p53 amino-terminal domain are required for transcriptional activation, binding to mdm-2 and the adenovirus 5 E1B 55-kD protein. Genes Dev. 1994 May 15;8(10):1235–1246. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.10.1235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundgren K., Montes de Oca Luna R., McNeill Y. B., Emerick E. P., Spencer B., Barfield C. R., Lozano G., Rosenberg M. P., Finlay C. A. Targeted expression of MDM2 uncouples S phase from mitosis and inhibits mammary gland development independent of p53. Genes Dev. 1997 Mar 15;11(6):714–725. doi: 10.1101/gad.11.6.714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Léveillard T., Gorry P., Niederreither K., Wasylyk B. MDM2 expression during mouse embryogenesis and the requirement of p53. Mech Dev. 1998 Jun;74(1-2):189–193. doi: 10.1016/s0925-4773(98)00074-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marechal V., Elenbaas B., Piette J., Nicolas J. C., Levine A. J. The ribosomal L5 protein is associated with mdm-2 and mdm-2-p53 complexes. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Nov;14(11):7414–7420. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.11.7414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marechal V., Elenbaas B., Taneyhill L., Piette J., Mechali M., Nicolas J. C., Levine A. J., Moreau J. Conservation of structural domains and biochemical activities of the MDM2 protein from Xenopus laevis. Oncogene. 1997 Mar 27;14(12):1427–1433. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1200967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marston N. J., Jenkins J. R., Vousden K. H. Oligomerisation of full length p53 contributes to the interaction with mdm2 but not HPV E6. Oncogene. 1995 May 4;10(9):1709–1715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin K., Trouche D., Hagemeier C., Sørensen T. S., La Thangue N. B., Kouzarides T. Stimulation of E2F1/DP1 transcriptional activity by MDM2 oncoprotein. Nature. 1995 Jun 22;375(6533):691–694. doi: 10.1038/375691a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayo L. D., Turchi J. J., Berberich S. J. Mdm-2 phosphorylation by DNA-dependent protein kinase prevents interaction with p53. Cancer Res. 1997 Nov 15;57(22):5013–5016. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMasters K. M., Montes de Oca Luna R., Peña J. R., Lozano G. mdm2 deletion does not alter growth characteristics of p53-deficient embryo fibroblasts. Oncogene. 1996 Oct 17;13(8):1731–1736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midgley C. A., Lane D. P. p53 protein stability in tumour cells is not determined by mutation but is dependent on Mdm2 binding. Oncogene. 1997 Sep 4;15(10):1179–1189. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1201459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Momand J., Jung D., Wilczynski S., Niland J. The MDM2 gene amplification database. Nucleic Acids Res. 1998 Aug 1;26(15):3453–3459. doi: 10.1093/nar/26.15.3453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Momand J., Zambetti G. P. Analysis of the proportion of p53 bound to mdm-2 in cells with defined growth characteristics. Oncogene. 1996 Jun 6;12(11):2279–2289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Momand J., Zambetti G. P. Mdm-2: "big brother" of p53. J Cell Biochem. 1997 Mar 1;64(3):343–352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Momand J., Zambetti G. P., Olson D. C., George D., Levine A. J. The mdm-2 oncogene product forms a complex with the p53 protein and inhibits p53-mediated transactivation. Cell. 1992 Jun 26;69(7):1237–1245. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90644-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montes de Oca Luna R., Wagner D. S., Lozano G. Rescue of early embryonic lethality in mdm2-deficient mice by deletion of p53. Nature. 1995 Nov 9;378(6553):203–206. doi: 10.1038/378203a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor D. J., Lam E. W., Griffin S., Zhong S., Leighton L. C., Burbidge S. A., Lu X. Physical and functional interactions between p53 and cell cycle co-operating transcription factors, E2F1 and DP1. EMBO J. 1995 Dec 15;14(24):6184–6192. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00309.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliner J. D., Kinzler K. W., Meltzer P. S., George D. L., Vogelstein B. Amplification of a gene encoding a p53-associated protein in human sarcomas. Nature. 1992 Jul 2;358(6381):80–83. doi: 10.1038/358080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliner J. D., Pietenpol J. A., Thiagalingam S., Gyuris J., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. Oncoprotein MDM2 conceals the activation domain of tumour suppressor p53. Nature. 1993 Apr 29;362(6423):857–860. doi: 10.1038/362857a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson D. C., Marechal V., Momand J., Chen J., Romocki C., Levine A. J. Identification and characterization of multiple mdm-2 proteins and mdm-2-p53 protein complexes. Oncogene. 1993 Sep;8(9):2353–2360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmero I., Pantoja C., Serrano M. p19ARF links the tumour suppressor p53 to Ras. Nature. 1998 Sep 10;395(6698):125–126. doi: 10.1038/25870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry M. E., Piette J., Zawadzki J. A., Harvey D., Levine A. J. The mdm-2 gene is induced in response to UV light in a p53-dependent manner. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 15;90(24):11623–11627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.24.11623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picksley S. M., Lane D. P. The p53-mdm2 autoregulatory feedback loop: a paradigm for the regulation of growth control by p53? Bioessays. 1993 Oct;15(10):689–690. doi: 10.1002/bies.950151008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picksley S. M., Vojtesek B., Sparks A., Lane D. P. Immunochemical analysis of the interaction of p53 with MDM2;--fine mapping of the MDM2 binding site on p53 using synthetic peptides. Oncogene. 1994 Sep;9(9):2523–2529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piette J., Neel H., Maréchal V. Mdm2: keeping p53 under control. Oncogene. 1997 Aug 28;15(9):1001–1010. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1201432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pomerantz J., Schreiber-Agus N., Liégeois N. J., Silverman A., Alland L., Chin L., Potes J., Chen K., Orlow I., Lee H. W. The Ink4a tumor suppressor gene product, p19Arf, interacts with MDM2 and neutralizes MDM2's inhibition of p53. Cell. 1998 Mar 20;92(6):713–723. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81400-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price B. D., Park S. J. DNA damage increases the levels of MDM2 messenger RNA in wtp53 human cells. Cancer Res. 1994 Feb 15;54(4):896–899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reifenberger G., Liu L., Ichimura K., Schmidt E. E., Collins V. P. Amplification and overexpression of the MDM2 gene in a subset of human malignant gliomas without p53 mutations. Cancer Res. 1993 Jun 15;53(12):2736–2739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reifenberger G., Reifenberger J., Ichimura K., Meltzer P. S., Collins V. P. Amplification of multiple genes from chromosomal region 12q13-14 in human malignant gliomas: preliminary mapping of the amplicons shows preferential involvement of CDK4, SAS, and MDM2. Cancer Res. 1994 Aug 15;54(16):4299–4303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J., Dobbelstein M., Freedman D. A., Shenk T., Levine A. J. Nucleo-cytoplasmic shuttling of the hdm2 oncoprotein regulates the levels of the p53 protein via a pathway used by the human immunodeficiency virus rev protein. EMBO J. 1998 Jan 15;17(2):554–564. doi: 10.1093/emboj/17.2.554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saucedo L. J., Carstens B. P., Seavey S. E., Albee L. D., 2nd, Perry M. E. Regulation of transcriptional activation of mdm2 gene by p53 in response to UV radiation. Cell Growth Differ. 1998 Feb;9(2):119–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scolnick D. M., Chehab N. H., Stavridi E. S., Lien M. C., Caruso L., Moran E., Berger S. L., Halazonetis T. D. CREB-binding protein and p300/CBP-associated factor are transcriptional coactivators of the p53 tumor suppressor protein. Cancer Res. 1997 Sep 1;57(17):3693–3696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibagaki I., Tanaka H., Shimada Y., Wagata T., Ikenaga M., Imamura M., Ishizaki K. p53 mutation, murine double minute 2 amplification, and human papillomavirus infection are frequently involved but not associated with each other in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 1995 Jul;1(7):769–773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shieh S. Y., Ikeda M., Taya Y., Prives C. DNA damage-induced phosphorylation of p53 alleviates inhibition by MDM2. Cell. 1997 Oct 31;91(3):325–334. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80416-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shvarts A., Bazuine M., Dekker P., Ramos Y. F., Steegenga W. T., Merckx G., van Ham R. C., van der Houven van Oordt W., van der Eb A. J., Jochemsen A. G. Isolation and identification of the human homolog of a new p53-binding protein, Mdmx. Genomics. 1997 Jul 1;43(1):34–42. doi: 10.1006/geno.1997.4775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shvarts A., Steegenga W. T., Riteco N., van Laar T., Dekker P., Bazuine M., van Ham R. C., van der Houven van Oordt W., Hateboer G., van der Eb A. J. MDMX: a novel p53-binding protein with some functional properties of MDM2. EMBO J. 1996 Oct 1;15(19):5349–5357. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigalas I., Calvert A. H., Anderson J. J., Neal D. E., Lunec J. Alternatively spliced mdm2 transcripts with loss of p53 binding domain sequences: transforming ability and frequent detection in human cancer. Nat Med. 1996 Aug;2(8):912–917. doi: 10.1038/nm0896-912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siliciano J. D., Canman C. E., Taya Y., Sakaguchi K., Appella E., Kastan M. B. DNA damage induces phosphorylation of the amino terminus of p53. Genes Dev. 1997 Dec 15;11(24):3471–3481. doi: 10.1101/gad.11.24.3471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stott F. J., Bates S., James M. C., McConnell B. B., Starborg M., Brookes S., Palmero I., Ryan K., Hara E., Vousden K. H. The alternative product from the human CDKN2A locus, p14(ARF), participates in a regulatory feedback loop with p53 and MDM2. EMBO J. 1998 Sep 1;17(17):5001–5014. doi: 10.1093/emboj/17.17.5001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun P., Dong P., Dai K., Hannon G. J., Beach D. p53-independent role of MDM2 in TGF-beta1 resistance. Science. 1998 Dec 18;282(5397):2270–2272. doi: 10.1126/science.282.5397.2270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sørensen T. S., Girling R., Lee C. W., Gannon J., Bandara L. R., La Thangue N. B. Functional interaction between DP-1 and p53. Mol Cell Biol. 1996 Oct;16(10):5888–5895. doi: 10.1128/mcb.16.10.5888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas A., White E. Suppression of the p300-dependent mdm2 negative-feedback loop induces the p53 apoptotic function. Genes Dev. 1998 Jul 1;12(13):1975–1985. doi: 10.1101/gad.12.13.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thut C. J., Goodrich J. A., Tjian R. Repression of p53-mediated transcription by MDM2: a dual mechanism. Genes Dev. 1997 Aug 1;11(15):1974–1986. doi: 10.1101/gad.11.15.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woo R. A., McLure K. G., Lees-Miller S. P., Rancourt D. E., Lee P. W. DNA-dependent protein kinase acts upstream of p53 in response to DNA damage. Nature. 1998 Aug 13;394(6694):700–704. doi: 10.1038/29343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu L., Levine A. J. Differential regulation of the p21/WAF-1 and mdm2 genes after high-dose UV irradiation: p53-dependent and p53-independent regulation of the mdm2 gene. Mol Med. 1997 Jul;3(7):441–451. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu X., Bayle J. H., Olson D., Levine A. J. The p53-mdm-2 autoregulatory feedback loop. Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7A):1126–1132. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7a.1126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Würl P., Meye A., Schmidt H., Lautenschläger C., Kalthoff H., Rath F. W., Taubert H. High prognostic significance of Mdm2/p53 co-overexpression in soft tissue sarcomas of the extremities. Oncogene. 1998 Mar 5;16(9):1183–1185. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1201646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao Z. X., Chen J., Levine A. J., Modjtahedi N., Xing J., Sellers W. R., Livingston D. M. Interaction between the retinoblastoma protein and the oncoprotein MDM2. Nature. 1995 Jun 22;375(6533):694–698. doi: 10.1038/375694a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zauberman A., Flusberg D., Haupt Y., Barak Y., Oren M. A functional p53-responsive intronic promoter is contained within the human mdm2 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1995 Jul 25;23(14):2584–2592. doi: 10.1093/nar/23.14.2584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y., Xiong Y., Yarbrough W. G. ARF promotes MDM2 degradation and stabilizes p53: ARF-INK4a locus deletion impairs both the Rb and p53 tumor suppression pathways. Cell. 1998 Mar 20;92(6):725–734. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81401-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zindy F., Eischen C. M., Randle D. H., Kamijo T., Cleveland J. L., Sherr C. J., Roussel M. F. Myc signaling via the ARF tumor suppressor regulates p53-dependent apoptosis and immortalization. Genes Dev. 1998 Aug 1;12(15):2424–2433. doi: 10.1101/gad.12.15.2424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Stanchina E., McCurrach M. E., Zindy F., Shieh S. Y., Ferbeyre G., Samuelson A. V., Prives C., Roussel M. F., Sherr C. J., Lowe S. W. E1A signaling to p53 involves the p19(ARF) tumor suppressor. Genes Dev. 1998 Aug 1;12(15):2434–2442. doi: 10.1101/gad.12.15.2434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]