Abstract
Among metabolic diseases, diabetes is considered one of the most prevalent throughout the world. Currently, statistics show that over 10% of the world's aged population (60 years and older) suffers from diabetes. As a consequence, it consumes a considerable proportion of world health expenditure. This review considers both past and current research into the molecular basis of insulin resistance found in type II diabetes and focuses on the role of inositol-containing phospholipid metabolism. It has been firmly established that the activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3-K) is important for the propagation of the metabolic actions of insulin. In addition to the 3-phosphorylated phosphatidylinositols formed via the action of PI3-K, the glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol/inositol phosphoglycan (GPI/IPG) signaling component is also strongly implicated in mediating numerous metabolic actions of insulin. Although all the elements within the type II diabetes phenotype have not been fully defined, it has been proposed that defects in insulin transmembrane signaling through malfunction of inositol-containing phospholipid metabolism and absenteeism of the generation of phospholipid-derived second messengers may be associated with the appearance of the type II diabetic phenotype. Pharmaceutical approaches using synthetically produced IPG analogues, which themselves mimic insulin's actions, alone or in combination with other drugs, may lead the way toward introducing alternative therapies for type II diabetes in the coming years.
Full text
PDF

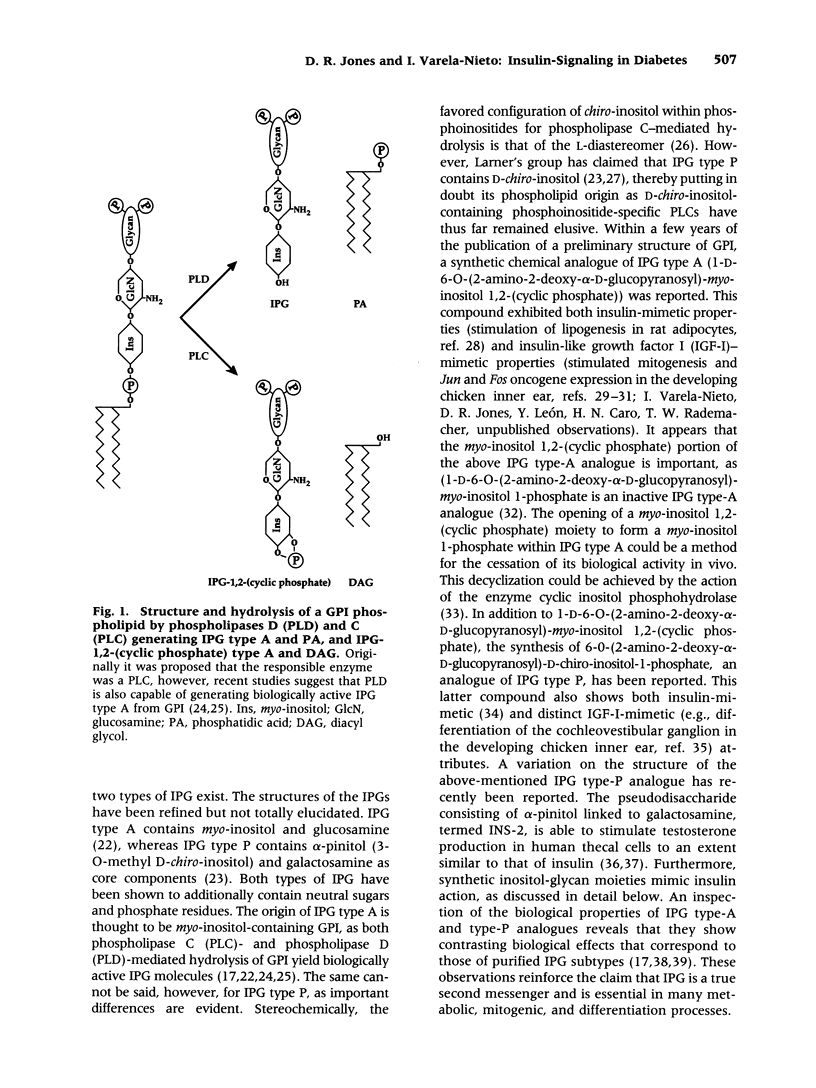


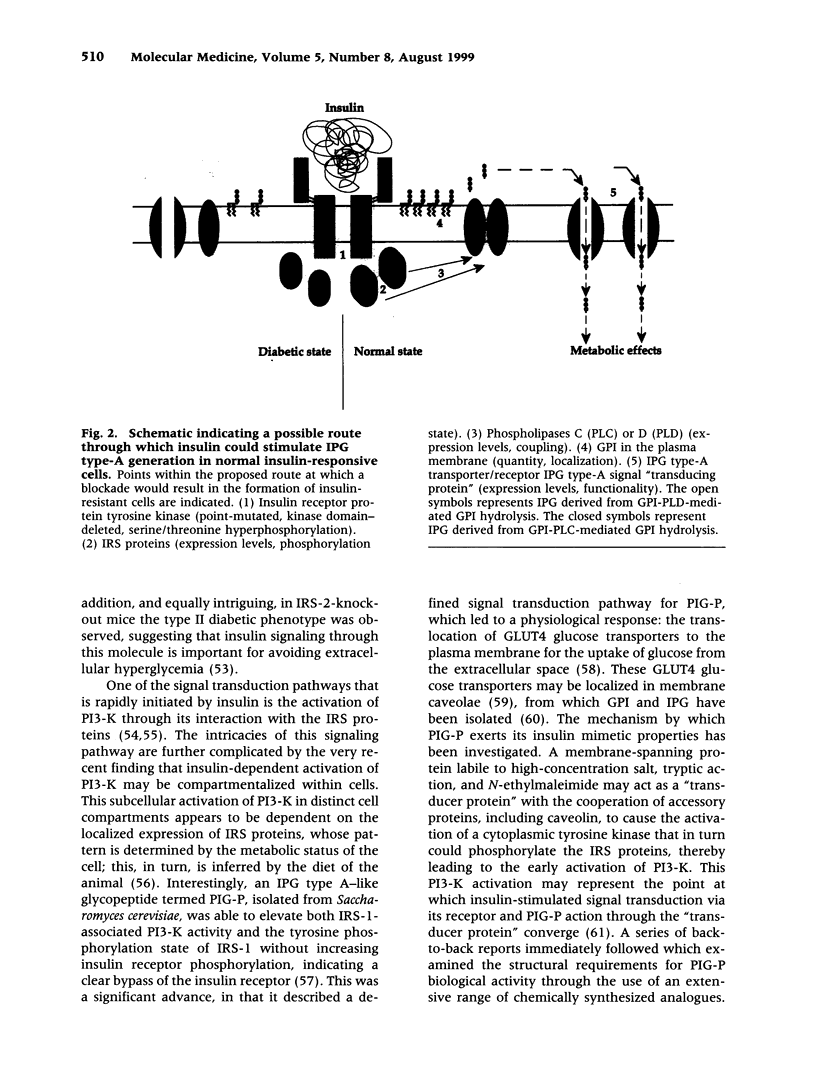




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alessi D. R., Downes C. P. The role of PI 3-kinase in insulin action. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1998 Dec 8;1436(1-2):151–164. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2760(98)00133-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anai M., Ono H., Funaki M., Fukushima Y., Inukai K., Ogihara T., Sakoda H., Onishi Y., Yazaki Y., Kikuchi M. Different subcellular distribution and regulation of expression of insulin receptor substrate (IRS)-3 from those of IRS-1 and IRS-2. J Biol Chem. 1998 Nov 6;273(45):29686–29692. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.45.29686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asplin I., Galasko G., Larner J. chiro-inositol deficiency and insulin resistance: a comparison of the chiro-inositol- and the myo-inositol-containing insulin mediators isolated from urine, hemodialysate, and muscle of control and type II diabetic subjects. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):5924–5928. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.5924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnett A. H., Eff C., Leslie R. D., Pyke D. A. Diabetes in identical twins. A study of 200 pairs. Diabetologia. 1981 Feb;20(2):87–93. doi: 10.1007/BF00262007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett P. H., Rushforth N. B., Miller M., LeCompte P. M. Epidemiologic studies of diabetes in the Pima Indians. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1976;32:333–376. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571132-6.50021-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björnholm M., Kawano Y., Lehtihet M., Zierath J. R. Insulin receptor substrate-1 phosphorylation and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity in skeletal muscle from NIDDM subjects after in vivo insulin stimulation. Diabetes. 1997 Mar;46(3):524–527. doi: 10.2337/diab.46.3.524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruzik K. S., Hakeem A. A., Tsai M. D. Are D- and L-chiro-phosphoinositides substrates of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C? Biochemistry. 1994 Jul 12;33(27):8367–8374. doi: 10.1021/bi00193a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemente R., Jones D. R., Ochoa P., Romero G., Mato J. M., Varela-Nieto I. Role of glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol hydrolysis as a mitogenic signal for epidermal growth factor. Cell Signal. 1995 May;7(4):411–421. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(95)00002-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crisá L., Mordes J. P., Rossini A. A. Autoimmune diabetes mellitus in the BB rat. Diabetes Metab Rev. 1992 Apr;8(1):4–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Bonadonna R. C., Ferrannini E. Pathogenesis of NIDDM. A balanced overview. Diabetes Care. 1992 Mar;15(3):318–368. doi: 10.2337/diacare.15.3.318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenbarth G. S., Connelly J., Soeldner J. S. The "natural" history of type I diabetes. Diabetes Metab Rev. 1987 Oct;3(4):873–891. doi: 10.1002/dmr.5610030404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farese R. V., Standaert M. L., Yamada K., Huang L. C., Zhang C., Cooper D. R., Wang Z., Yang Y., Suzuki S., Toyota T. Insulin-induced activation of glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase by a chiro-inositol-containing insulin mediator is defective in adipocytes of insulin-resistant, type II diabetic, Goto-Kakizaki rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Nov 8;91(23):11040–11044. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.23.11040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fonteles M. C., Huang L. C., Larner J. Infusion of pH 2.0 D-chiro-inositol glycan insulin putative mediator normalizes plasma glucose in streptozotocin diabetic rats at a dose equivalent to insulin without inducing hypoglycaemia. Diabetologia. 1996 Jun;39(6):731–734. doi: 10.1007/BF00418546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frick W., Bauer A., Bauer J., Wied S., Müller G. Insulin-mimetic signalling of synthetic phosphoinositolglycans in isolated rat adipocytes. Biochem J. 1998 Nov 15;336(Pt 1):163–181. doi: 10.1042/bj3360163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frick W., Bauer A., Bauer J., Wied S., Müller G. Structure-activity relationship of synthetic phosphoinositolglycans mimicking metabolic insulin action. Biochemistry. 1998 Sep 22;37(38):13421–13436. doi: 10.1021/bi9806201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galasko G. T., Abe S., Lilley K., Zhang C., Larner J. Circulating factors and insulin resistance. II. The action of the novel myo-inositol cyclic 1,2-inositol phosphate phosphoglycan insulin antagonist from human plasma in regulating pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphatase. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1996 Mar;81(3):1051–1057. doi: 10.1210/jcem.81.3.8772575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galasko G. T., Bao Y., Broomfield S. J., Hooper N. M., Turner A. J., Larner J. Circulating factors and insulin resistance. I. A novel myoinositol 1,2-cyclic phosphate phosphoglycan insulin antagonist from human plasma is elevated in noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1995 Aug;80(8):2419–2429. doi: 10.1210/jcem.80.8.7629237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodyear L. J., Giorgino F., Sherman L. A., Carey J., Smith R. J., Dohm G. L. Insulin receptor phosphorylation, insulin receptor substrate-1 phosphorylation, and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity are decreased in intact skeletal muscle strips from obese subjects. J Clin Invest. 1995 May;95(5):2195–2204. doi: 10.1172/JCI117909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustavsson J., Parpal S., Strålfors P. Insulin-stimulated glucose uptake involves the transition of glucose transporters to a caveolae-rich fraction within the plasma membrane: implications for type II diabetes. Mol Med. 1996 May;2(3):367–372. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang L. C., Fonteles M. C., Houston D. B., Zhang C., Larner J. Chiroinositol deficiency and insulin resistance. III. Acute glycogenic and hypoglycemic effects of two inositol phosphoglycan insulin mediators in normal and streptozotocin-diabetic rats in vivo. Endocrinology. 1993 Feb;132(2):652–657. doi: 10.1210/endo.132.2.8425485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang L. C., Heimark D., Linko J., Nolan R., Larner J. A model phosphatase 2C --> phosphatase 1 activation cascade via dual control of inhibitor-1 (INH-1) and DARPP-32 dephosphorylation by two inositol glycan putative insulin mediators from beef liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999 Feb 5;255(1):150–156. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1999.0111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarrett R. J., Keen H. Hyperglycaemia and diabetes mellitus. Lancet. 1976 Nov 6;2(7993):1009–1012. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)90844-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. R., Avila M. A., Sanz C., Varela-Nieto I. Glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol-phospholipase type D: a possible candidate for the generation of second messengers. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1997 Apr 17;233(2):432–437. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1997.6475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. R., Varela-Nieto I. The role of glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol in signal transduction. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 1998 Mar;30(3):313–326. doi: 10.1016/s1357-2725(97)00144-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennington A. S., Hill C. R., Craig J., Bogardus C., Raz I., Ortmeyer H. K., Hansen B. C., Romero G., Larner J. Low urinary chiro-inositol excretion in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1990 Aug 9;323(6):373–378. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199008093230603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerouz N. J., Hörsch D., Pons S., Kahn C. R. Differential regulation of insulin receptor substrates-1 and -2 (IRS-1 and IRS-2) and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase isoforms in liver and muscle of the obese diabetic (ob/ob) mouse. J Clin Invest. 1997 Dec 15;100(12):3164–3172. doi: 10.1172/JCI119872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler A., Müller G., Wied S., Crecelius A., Eckel J. Signalling pathways of an insulin-mimetic phosphoinositolglycan-peptide in muscle and adipose tissue. Biochem J. 1998 Feb 15;330(Pt 1):277–286. doi: 10.1042/bj3300277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larner J., Allan G., Kessler C., Reamer P., Gunn R., Huang L. C. Phosphoinositol glycan derived mediators and insulin resistance. Prospects for diagnosis and therapy. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 1998;9(2-4):127–137. doi: 10.1515/jbcpp.1998.9.2-4.127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larner J., Craig J. W. Urinary myo-inositol-to-chiro-inositol ratios and insulin resistance. Diabetes Care. 1996 Jan;19(1):76–78. doi: 10.2337/diacare.19.1.76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larner J., Huang L. C., Schwartz C. F., Oswald A. S., Shen T. Y., Kinter M., Tang G. Z., Zeller K. Rat liver insulin mediator which stimulates pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphate contains galactosamine and D-chiroinositol. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Mar 30;151(3):1416–1426. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80520-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavan B. E., Lane W. S., Lienhard G. E. The 60-kDa phosphotyrosine protein in insulin-treated adipocytes is a new member of the insulin receptor substrate family. J Biol Chem. 1997 Apr 25;272(17):11439–11443. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.17.11439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazar D. F., Knez J. J., Medof M. E., Cuatrecasas P., Saltiel A. R. Stimulation of glycogen synthesis by insulin in human erythroleukemia cells requires the synthesis of glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Oct 11;91(21):9665–9669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.21.9665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lernmark A., Bärmeier H., Dube S., Hagopian W., Karlsen A., Wassmuth R. Autoimmunity of diabetes. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 1991 Sep;20(3):589–617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- León Y., Sanz C., Giráldez F., Varela-Nieto I. Induction of cell growth by insulin and insulin-like growth factor-I is associated with Jun expression in the otic vesicle. J Comp Neurol. 1998 Aug 31;398(3):323–332. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1096-9861(19980831)398:3<323::aid-cne2>3.0.co;2-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macaulay S. L., Larkins R. G. Isolation of insulin-sensitive phosphatidylinositol-glycan from rat adipocytes. Its impaired breakdown in the streptozotocin-diabetic rat. Biochem J. 1990 Oct 15;271(2):427–435. doi: 10.1042/bj2710427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misek D. E., Saltiel A. R. An inositol phosphate glycan derived from a Trypanosoma brucei glycosyl phosphatidylinositol promotes protein dephosphorylation in rat epididymal adipocytes. Endocrinology. 1994 Nov;135(5):1869–1876. doi: 10.1210/endo.135.5.7956908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misek D. E., Saltiel A. R. An inositol phosphate glycan derived from a Trypanosoma brucei glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol mimics some of the metabolic actions of insulin. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 15;267(23):16266–16273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller G., Wied S., Crecelius A., Kessler A., Eckel J. Phosphoinositolglycan-peptides from yeast potently induce metabolic insulin actions in isolated rat adipocytes, cardiomyocytes, and diaphragms. Endocrinology. 1997 Aug;138(8):3459–3475. doi: 10.1210/endo.138.8.5308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller G., Wied S., Piossek C., Bauer A., Bauer J., Frick W. Convergence and divergence of the signaling pathways for insulin and phosphoinositolglycans. Mol Med. 1998 May;4(5):299–323. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nestler J. E. Inositolphosphoglycans (IPGs) as mediators of insulin's steroidogenic actions. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 1998;9(2-4):197–204. doi: 10.1515/jbcpp.1998.9.2-4.197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nestler J. E., Jakubowicz D. J., de Vargas A. F., Brik C., Quintero N., Medina F. Insulin stimulates testosterone biosynthesis by human thecal cells from women with polycystic ovary syndrome by activating its own receptor and using inositolglycan mediators as the signal transduction system. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1998 Jun;83(6):2001–2005. doi: 10.1210/jcem.83.6.4886. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortmeyer H. K. Insulin increases liver protein phosphatase-1 and protein phosphatase-2C activities in lean, young adult rhesus monkeys. Horm Metab Res. 1998 Dec;30(12):705–710. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-978963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pak Y., Hong Y., Kim S., Piccariello T., Farese R. V., Larner J. In vivo chiro-inositol metabolism in the rat: a defect in chiro-inositol synthesis from myo-inositol and an increased incorporation of chiro-[3H]inositol into phospholipid in the Goto-Kakizaki (G.K) rat. Mol Cells. 1998 Jun 30;8(3):301–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parpal S., Gustavsson J., Strålfors P. Isolation of phosphooligosaccharide/phosphoinositol glycan from caveolae and cytosol of insulin-stimulated cells. J Cell Biol. 1995 Oct;131(1):125–135. doi: 10.1083/jcb.131.1.125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proud C. G., Denton R. M. Molecular mechanisms for the control of translation by insulin. Biochem J. 1997 Dec 1;328(Pt 2):329–341. doi: 10.1042/bj3280329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rondinone C. M., Wang L. M., Lonnroth P., Wesslau C., Pierce J. H., Smith U. Insulin receptor substrate (IRS) 1 is reduced and IRS-2 is the main docking protein for phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in adipocytes from subjects with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Apr 15;94(8):4171–4175. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.8.4171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltiel A. R., Cuatrecasas P. Insulin stimulates the generation from hepatic plasma membranes of modulators derived from an inositol glycolipid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5793–5797. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Arias J. A., Sanchez-Gutierrez J. C., Guadaño A., Alvarez J. F., Samper B., Mato J. M., Feliu J. E. Impairment of glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol-dependent insulin signaling system in isolated rat hepatocytes by streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Endocrinology. 1992 Oct;131(4):1727–1733. doi: 10.1210/endo.131.4.1396318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sciacchitano S., Taylor S. I. Cloning, tissue expression, and chromosomal localization of the mouse IRS-3 gene. Endocrinology. 1997 Nov;138(11):4931–4940. doi: 10.1210/endo.138.11.5518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shashkin P. N., Shashkina E. F., Fernqvist-Forbes E., Zhou Y. P., Grill V., Katz A. Insulin mediators in man: effects of glucose ingestion and insulin resistance. Diabetologia. 1997 May;40(5):557–563. doi: 10.1007/s001250050715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd P. R., Withers D. J., Siddle K. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase: the key switch mechanism in insulin signalling. Biochem J. 1998 Aug 1;333(Pt 3):471–490. doi: 10.1042/bj3330471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strålfors P. Insulin second messengers. Bioessays. 1997 Apr;19(4):327–335. doi: 10.1002/bies.950190410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki S., Taneda Y., Hirai S., Yamamoto-Honda R., Toyota T. Mutated insulin receptor Val996 reduces insulin-dependent generation of inositol glycan and diacylglycerol. Diabetes. 1992 Nov;41(11):1373–1379. doi: 10.2337/diab.41.11.1373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varela-Nieto I., León Y., Caro H. N. Cell signalling by inositol phosphoglycans from different species. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 1996 Oct;115(2):223–241. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(96)00087-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villalba M., Alvarez J. F., Russell D. S., Mato J. M., Rosen O. M. Hydrolysis of glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol in response to insulin is reduced in cells bearing kinase-deficient insulin receptors. Growth Factors. 1990;2(2-3):91–97. doi: 10.3109/08977199009071496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villar A. V., Goñi F. M., Alonso A., Jones D. R., León Y., Varela-Nieto I. Phospholipase cleavage of glycosylphosphatidylinositol reconstituted in liposomal membranes. FEBS Lett. 1998 Aug 7;432(3):150–154. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(98)00853-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. F., Yenush L. The IRS-signaling system: a network of docking proteins that mediate insulin and cytokine action. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1998;228:179–208. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-80481-6_8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Withers D. J., Gutierrez J. S., Towery H., Burks D. J., Ren J. M., Previs S., Zhang Y., Bernal D., Pons S., Shulman G. I. Disruption of IRS-2 causes type 2 diabetes in mice. Nature. 1998 Feb 26;391(6670):900–904. doi: 10.1038/36116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapata A., León Y., Mato J. M., Varela-Nieto I., Penadés S., Martín-Lomas M. Synthesis and investigation of the possible insulin-like activity of 1D-4-O- and 1D-6-O-(2-amino-2-deoxy-alpha-D-glucopyranosyl)-myo-inositol 1-phosphate and 1D-6-O-(2-amino-2-deoxy-alpha-D-glucopyranosyl)-myo-inositol 1,2-(cyclic phosphate). Carbohydr Res. 1994 Nov 1;264(1):21–31. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(94)00178-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



