Abstract
Transcription of SV40 DNA was measured during lytic infection and in five SV40 transformed mouse cell lines. During productive infection, 50 per cent of viral DNA reacted with saturating amounts of lytic RNA. Varying portions of the SV40 genome were transcribed in transformed mouse cells, ranging from 15 per cent in a line which failed to yield virus, to 50 per cent in one line from which high titers of virus were obtained following cell fusion. The RNA from the SV40 transformed cell line, which saturated 50 per cent of the viral DNA, could not be distinguished from SV40 lytic RNA in reciprocal competition-hybridization experiments. These results suggest that some block or defect, subsequent to the transcription of SV40 DNA, prevents the appearance of progeny virus in this transformed 3T3 cell.
Full text
PDF


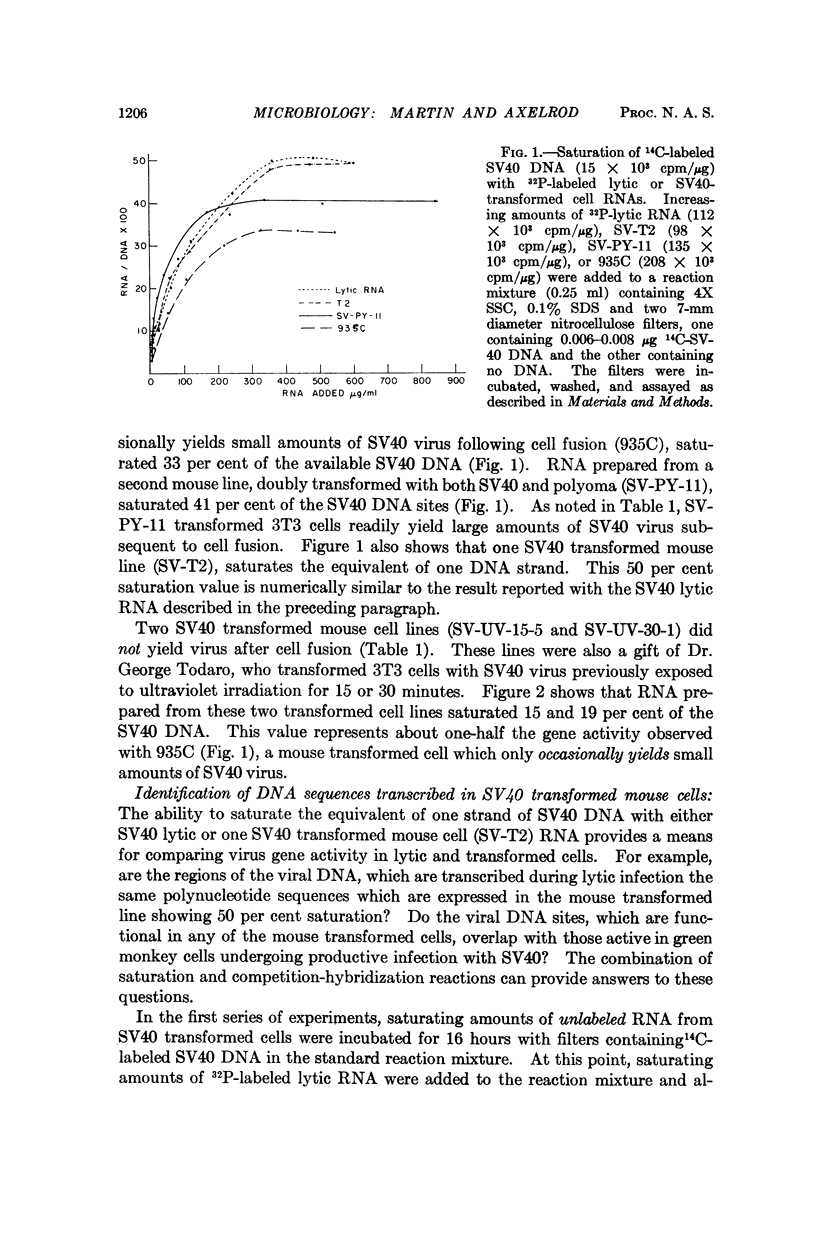
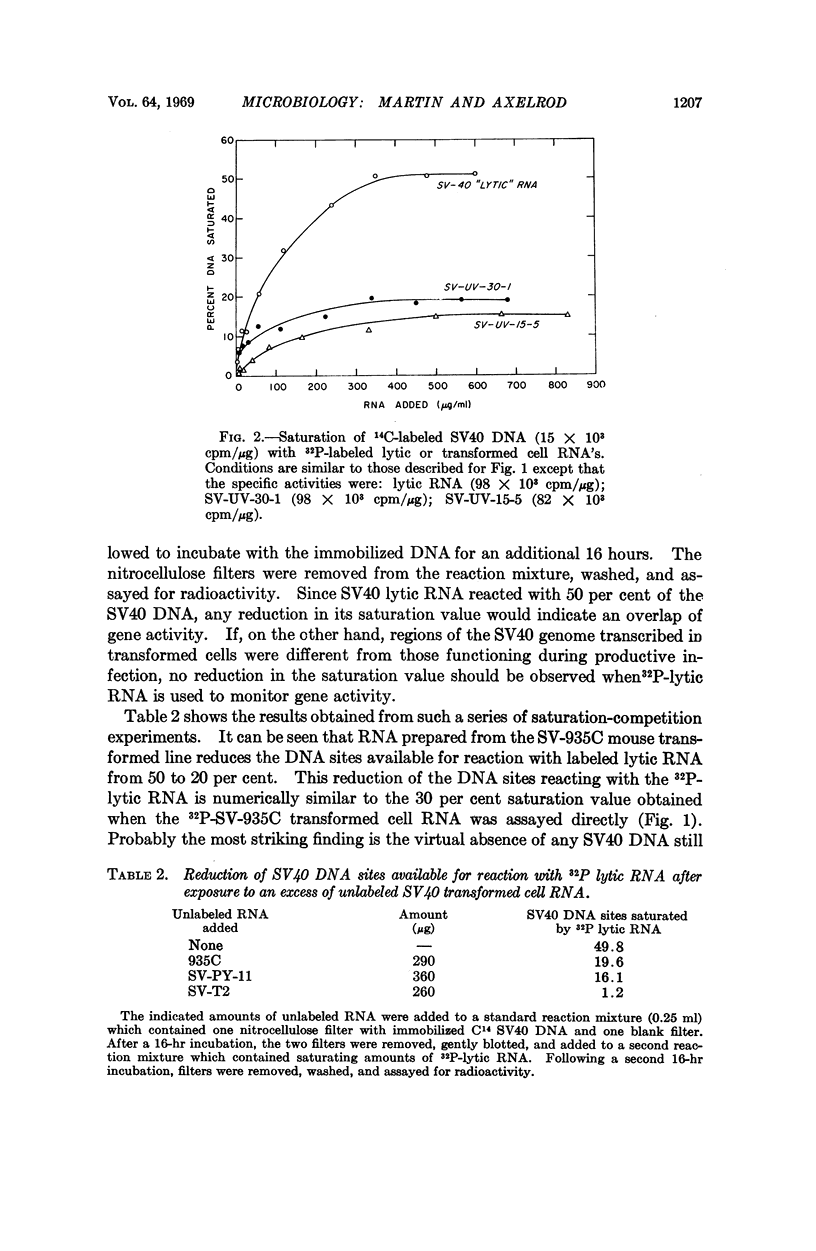



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aloni Y., Winocour E., Sachs L. Characterization of the simian virus 40-specific RNA in virus-yielding and transformed cells. J Mol Biol. 1968 Feb 14;31(3):415–429. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90418-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earley E., Peralta P. H., Johnson K. M. A plaque neutralization method for arboviruses. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Jul;125(3):741–747. doi: 10.3181/00379727-125-32194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber P. Studies on the transfer of subviral infectivity from SV40-induced hamster tumor cells to indicator cells. Virology. 1966 Apr;28(4):501–509. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90234-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie D., Spiegelman S. A quantitative assay for DNA-RNA hybrids with DNA immobilized on a membrane. J Mol Biol. 1965 Jul;12(3):829–842. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80331-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin M. A., Axelrod D. Polyoma virus gene activity during lytic infection and in transformed animal cells. Science. 1969 Apr 4;164(3875):68–70. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3875.68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oda K., Dulbecco R. Regulation of transcription of the SV40 DNA in productively infected and in transformed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jun;60(2):525–532. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.2.525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagano J. S., McCutchan J. H., Vaheri A. Factors influencing the enhancement of the infectivity of poliovirus ribonucleic acid by diethylaminoethyl-dextran. J Virol. 1967 Oct;1(5):891–897. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.5.891-897.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radloff R., Bauer W., Vinograd J. A dye-buoyant-density method for the detection and isolation of closed circular duplex DNA: the closed circular DNA in HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 May;57(5):1514–1521. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.5.1514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauer G., Kidwai J. R. The transcription of the SV40 genome in productively infected and transformed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Dec;61(4):1256–1263. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.4.1256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins J. F., Dulbecco R. Production of SV40 virus in heterokaryons of transformed and susceptible cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Oct;58(4):1396–1403. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.4.1396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



