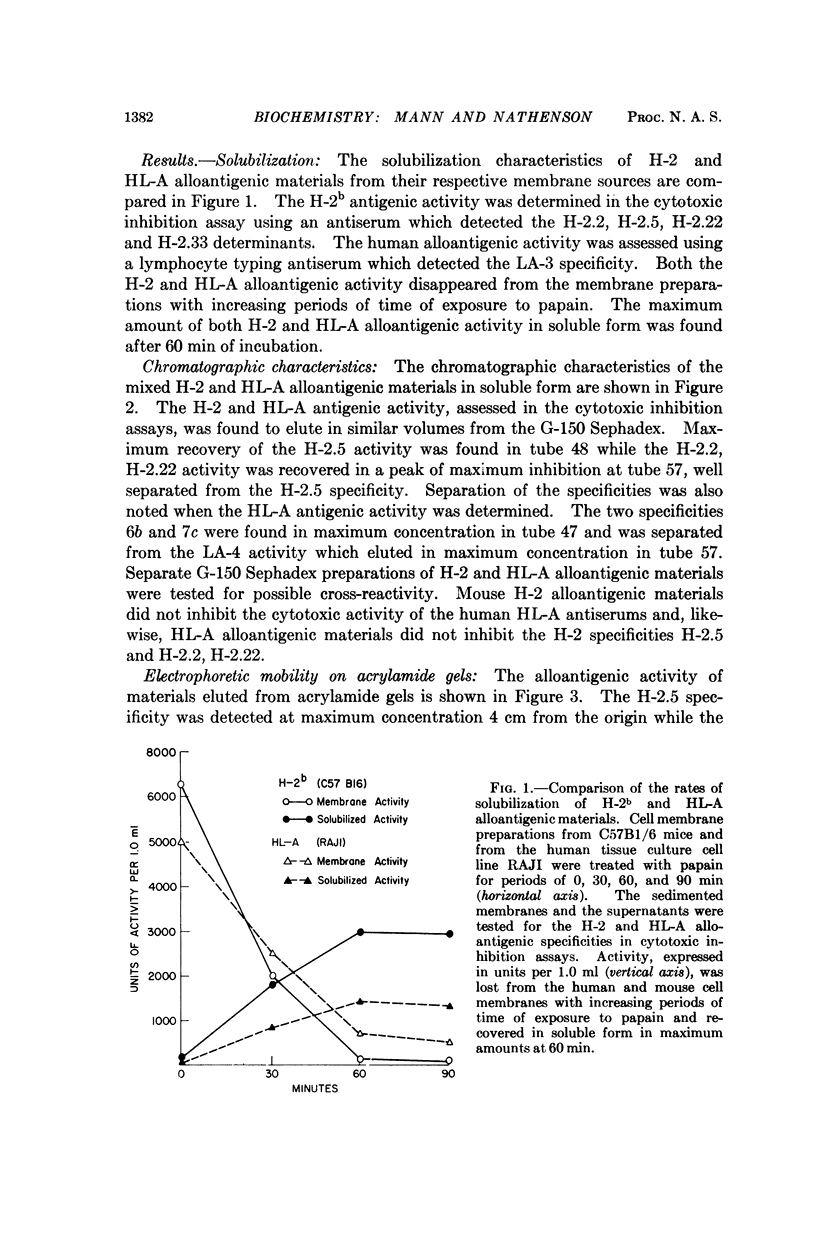
Abstract
The molecular and chemical characteristics of membrane components bearing the major transplantation antigen systems in mouse (H-2) and man (HL-A) were compared and found to be strikingly similar.
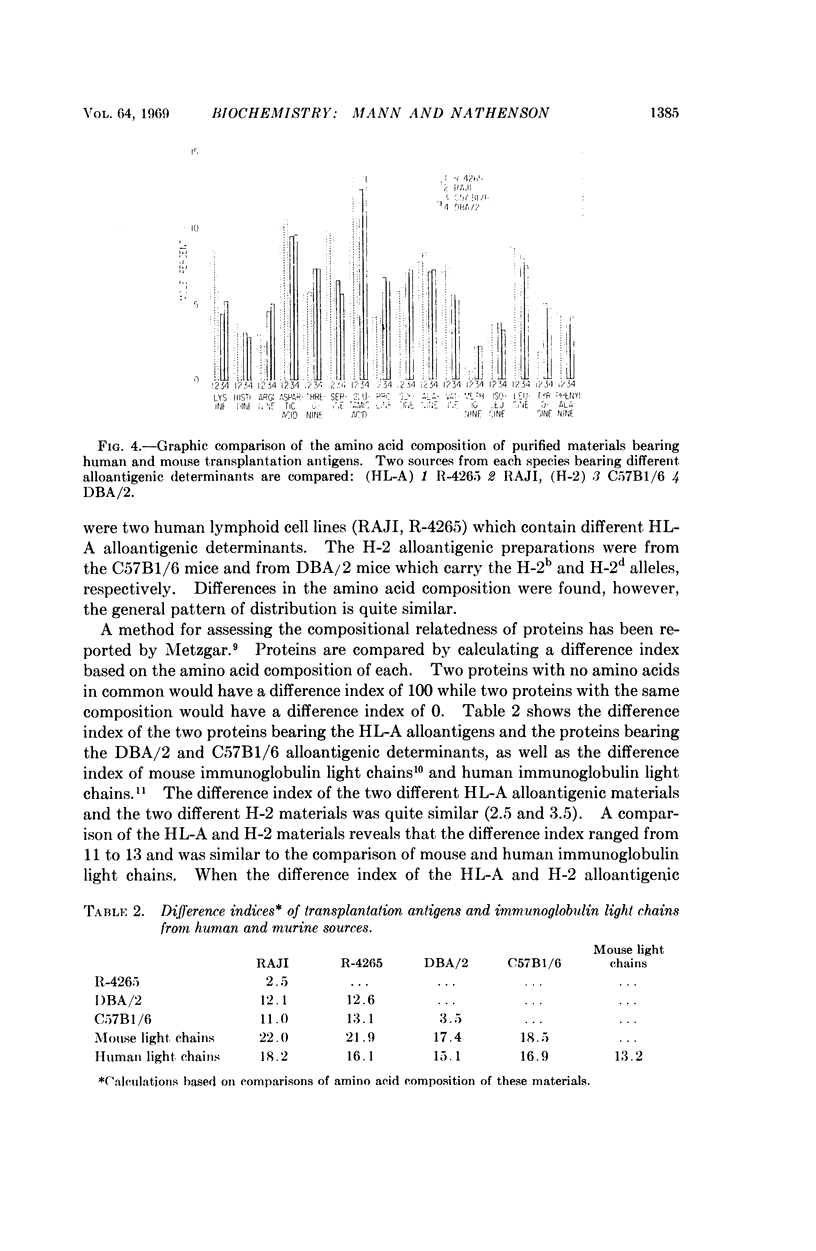
Kinetics of papain solubilization from cell membranes, gel filtration, and electrophoretic patterns of the alloantigenic components were found to be nearly identical. Comparable size heterogeneity of the solubilized materials was also demonstrated. Some differences in amino acid and carbohydrate content of the purified H-2 and HL-A alloantigenic materials were found. The general pattern of distribution of the amino acid residues, however, appears to be quite similar and indicate compositional relatedness in these materials.
These physical and chemical similarities in the characteristics of molecules bearing the transplantation antigens are in accord with biologic studies indicating a comparable functional immunologic role for the mouse H-2 and human HL-A antigen systems. These studies support the view that the genes determining these major transplantation antigen systems may have evolved from a common precursor.
Full text
PDF

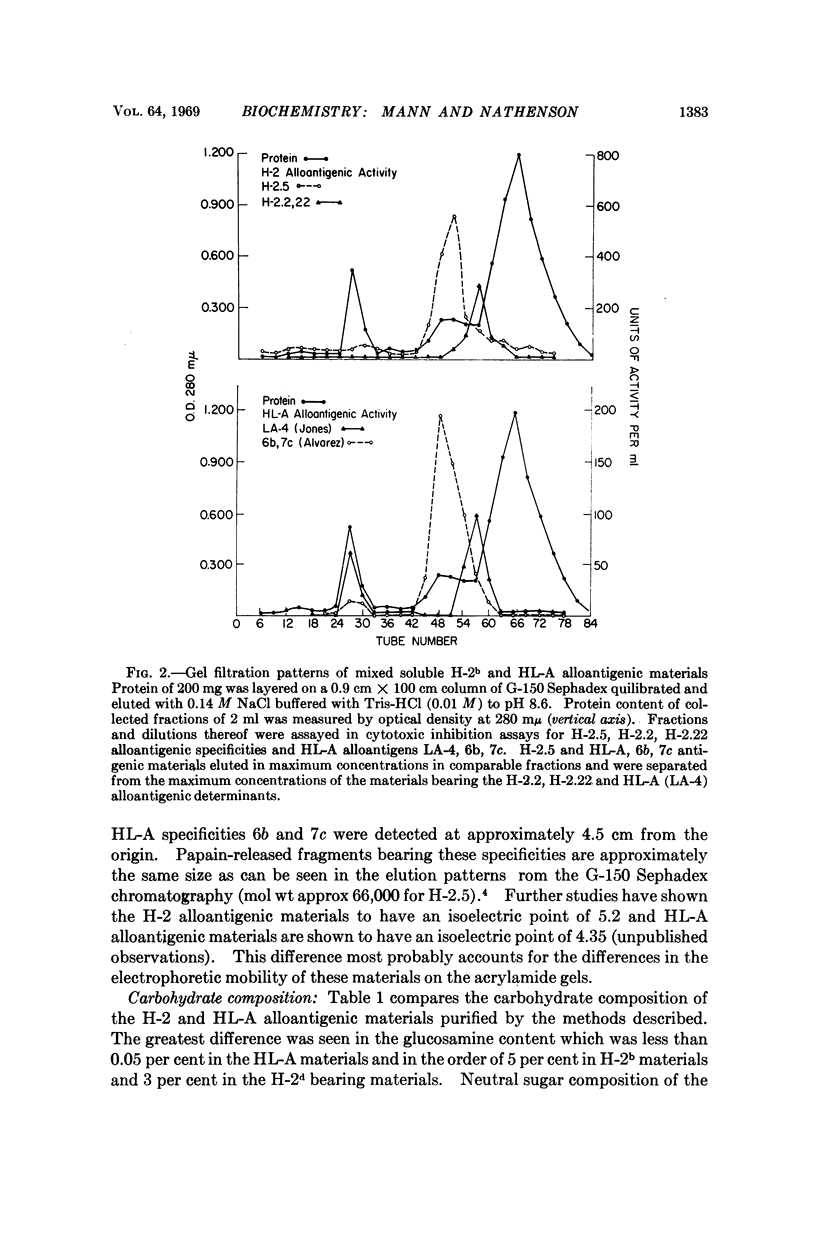
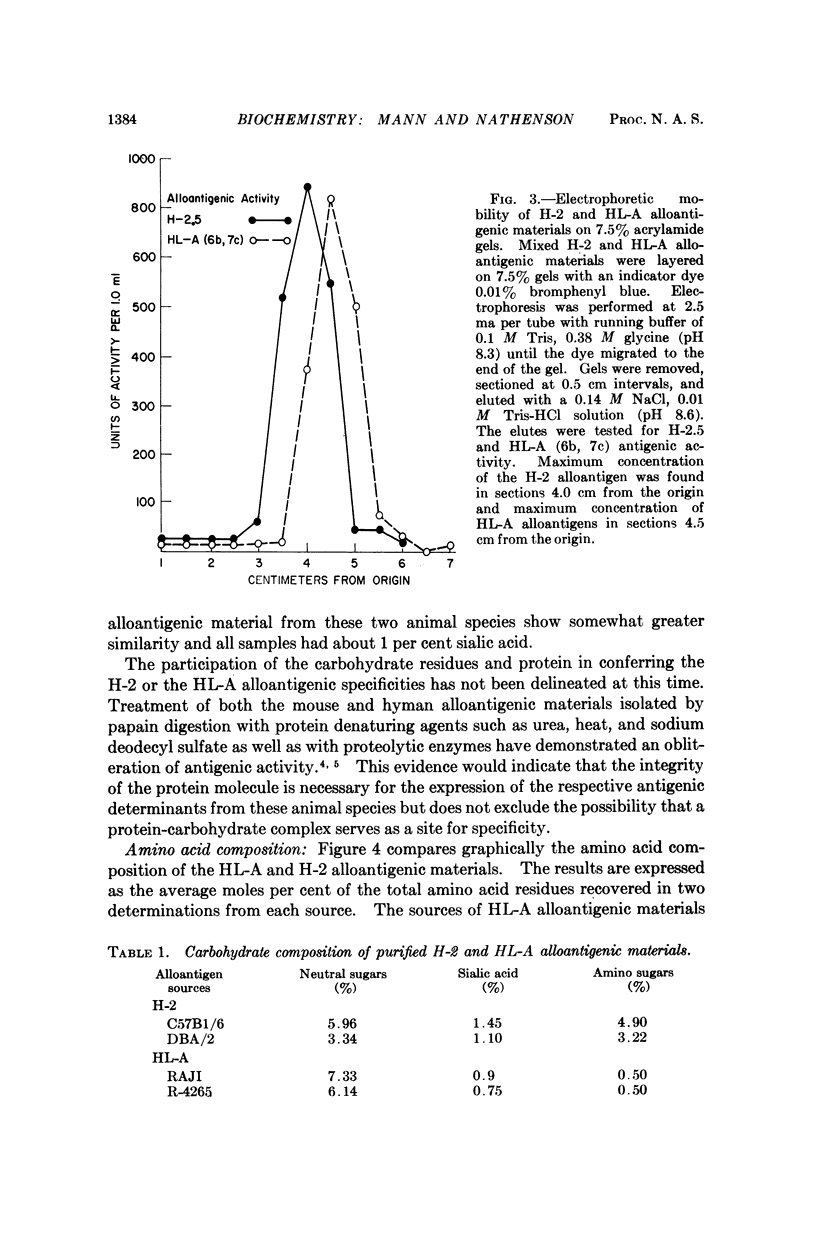


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amos B. Immunologic factors in organ transplantation. Am J Med. 1968 May;44(5):767–775. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(68)90257-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENNETT J. C., HOOD L. E., DREYER W. J., POTTER M. EVIDENCE FOR AMINO ACID SEQUENCE DIFFERENCES AMONG PROTEINS RESEMBLING THE L-CHAIN SUBUNITS OF IMMUNOGLOBULINS. J Mol Biol. 1965 May;12:81–87. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80284-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahan B. D., Reisfeld R. A. Differences in the amino acid compositions of allogeneic guinea pig transplantation antigens. J Immunol. 1968 Aug;101(2):237–241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann D. L., Rogentine G. N., Jr, Fahey J. L., Nathenson S. G. Molecular heterogeneity of human lymphoid (HL-A) alloantigens. Science. 1969 Mar 28;163(3874):1460–1462. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3874.1460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann D. L., Rogentine G. N., Jr, Fahey J. L., Nathenson S. G. Solubilization of human leucocyte membrane isoantigens. Nature. 1968 Mar 23;217(5134):1180–1181. doi: 10.1038/2171180a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger H., Shapiro M. B., Mosimann J. E., Vinton J. E. Assessment of compositional relatedness between proteins. Nature. 1968 Sep 14;219(5159):1166–1168. doi: 10.1038/2191166a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathenson S. G., Davies D. A. Solubilization and partial purification of mouse histocompatibility antigens from a membranous lipoprotein fraction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Aug;56(2):476–483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.2.476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PUTNAM F. W., EASLEY C. W. STRUCTURAL STUDIES OF THE IMMUNOGLOBULINS. I. THE TRYPTIC PEPTIDES OF BENCE-JONES PROTEINS. J Biol Chem. 1965 Apr;240:1626–1638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin A. D. Possible control of lymphocyte growth at the level of ribosome assembly. Nature. 1968 Oct 12;220(5163):196–197. doi: 10.1038/220196a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada A., Nathenson S. G. Solubilization of membrane H-2 isoantigens: chromatographic separation of specificities determined by a single H-2 genotype. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Dec 29;29(6):828–833. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90294-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L. The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1971–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L. The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1971–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]