Abstract
We studied the effect of monovalent thallium ion (Tl+) on the gating of single Kir2.1 channels, which open and close spontaneously at a constant membrane potential. In cell-attached recordings of single-channel inward current, changing the external permeant ion from K+ to Tl+ decreases the mean open-time by ∼20-fold. Furthermore, the channel resides predominantly at a subconductance level, which results from a slow decay (τ = 2.7 ms at −100 mV) from the fully open level immediately following channel opening. Mutation of a pore-lining cysteine (C169) to valine abolishes the slow decay and subconductance level, and single-channel recordings from channels formed by tandem tetramers containing one to three C169V mutant subunits indicate that Tl+ must interact with at least three C169 residues to induce these effects. However, the C169V mutation does not alter the single-channel closing kinetics of Tl+ current. These results suggest that Tl+ ions change the conformation of the ion conduction pathway during permeation and alter gating by two distinct mechanisms. First, they interact with the thiolate groups of C169 lining the cavity to induce conformational changes of the ion passageway, and thereby produce a slow decay of single-channel current and a dominant subconductance state. Second, they interact more strongly than K+ with the main chain carbonyl oxygens lining the selectivity filter to destabilize the open state of the channel and, thus, alter the open/close kinetics of gating. In addition to altering gating, Tl+ greatly diminishes Ba2+ block. The unblocking rate of Ba2+ is increased by >22-fold when the external permeant ion is switched from K+ to Tl+ regardless of the direction of Ba2+ exit. This effect cannot be explained solely by ion–ion interactions, but is consistent with the notion that Tl+ induces conformational changes in the selectivity filter.
Keywords: permeation, Tl+, conformational change, selectivity filter, backbone mutation
INTRODUCTION
In many ion channels, gating is tightly coupled to ion permeation and is strongly influenced by the nature of the permeant ion. For example, gating of the Cl− channel of Torpedo electroplax is coupled to the transmembrane electrochemical gradient of Cl− ions (Richard and Miller 1990). Moreover, elevation of extracellular Cl− concentration increases the open probability and opening rate of ClC chloride channels, and Cl−-movement within the pore appears to constitute the actual gating charge (Pusch et al. 1995; Chen and Miller 1996). Likewise, permeant ions affect the open probability and gating of cardiac Na+ channels by binding to a site deep in the pore (Townsend et al. 1997; Townsend and Horn 1999). In K+ channels, where the effect of permeant ions on gating has been studied most extensively, elevation of extracellular K+ concentration tends to increase channel open probability and the rate of activation, reduce the rate of closing (deactivation) and C-type inactivation, and accelerate the rate of recovery from C-type inactivation (Swenson and Armstrong 1981; Clay 1986; Matteson and Swenson 1986; Neyton and Pelleschi 1991; Demo and Yellen 1992; Pardo et al. 1992; Lopez-Barneo et al. 1993; Gomez-Lagunas and Armstrong 1994; Baukrowitz and Yellen 1995, Baukrowitz and Yellen 1996; Levy and Deutsch 1996a,Levy and Deutsch 1996b; Kiss and Korn 1998; Wood and Korn 2000). Addition of certain permeant ion species such as Rb+ and Cs+ that bind the pore tightly also impedes the closing of the channel (Swenson and Armstrong 1981; Matteson and Swenson 1986; Demo and Yellen 1992). These effects have been generally explained by the “foot-in-the-door” model of gating, which proposes that the channel pore cannot close or undergo C-type inactivation with an ion in it.
The crystal structure of the prokaryotic KcsA channel shows that three permeant ions are bound in the pore (Doyle et al. 1998). Two ions reside in the selectivity filter and are coordinated by main chain carbonyl oxygens from the signature sequence, TXGYG (with X mainly being either V or I). The third ion is located in the water-filled central cavity, where it is stabilized in part by a negative electrostatic potential generated by the tilted pore helices (Doyle et al. 1998; Roux and MacKinnon 1999). There is evidence that occupancy of the selectivity filter by permeant ions hinders C-type inactivation (Kiss and Korn 1998; Kiss et al. 1999).
Inward rectifier K+ (Kir) channels are gated by a variety of mechanisms, including intracellular Mg2+ ions and polyamines, G proteins, and ATP (Nichols and Lopatin 1997). In addition, activated single Kir channels open and close spontaneously and exhibit a wide range of gating kinetics. In cloned G protein-coupled or ATP-sensitive Kir channels, single-channel gating is characterized by bursts of rapid openings (millisecond time scale) separated by long closed intervals (Trapp et al. 1998; Enkvetchakul et al. 2000; Yakubovich et al. 2000). On the other hand, single Kir2.1 channels typically open for long periods of time (tens to hundreds of milliseconds) and exhibit three closed states (Choe et al. 1999; Lu et al. 2001). We recently have shown that the single-channel gating behavior of Kir2.1 is dramatically altered when the amide carbonyl oxygens of the two conserved glycines in the TXGYG signature sequence are changed to ester carbonyls, suggesting that conformational changes of the selectivity filter contribute directly to channel gating (Lu et al. 2001). To further test this hypothesis, we have examined in this study the effect of changing the permeant ion species from K+ to Tl+ on gating of single Kir2.1 channels. Tl+ has nearly the same radius as K+ (1.40 vs. 1.33 Å) and is highly permeable through K+ channels (Hille 1992). Thus, it serves well as a substitute for K+. On the other hand, Tl+ has a higher polarizability and electron affinity than K+ (Lee 1971; Marcus 1997), therefore, it is expected to interact more strongly than K+ with polarizable ligand groups in the pore.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Molecular Biology and Oocyte Expression
C169V mutation was made by oligonucleotide insertion method and was confirmed by sequencing. Tandem tetramers containing varying numbers of C169V mutant subunits were constructed using a method described previously (Yang et al. 1995; Lu et al. 1999). Oocytes were obtained from adult Xenopus laevis and were injected with 0.2–1 ng of cRNA transcribed in vitro as described previously (Lu et al. 1999). Injected oocytes were maintained in an 18°C incubator.
Electrophysiological Recordings
Recordings were performed 1–7 d after RNA injection. Whole-cell current was measured by two-electrode voltage clamp (TEVC) with the oocyte clamp amplifier (model OC-725C; Warner Instruments). Recording glass electrodes were filled with 3 M KCl and had a resistance of 0.4-0.8 MΩ. The external solution contained either 100 mM KNO3 or 100 mM TlNO3, with 2 mM MgCl2 and 1 mM HEPES (pH adjusted to 7.4 with NMDG). In some experiments, 2.3 mM EDTA was added to the solution. In anomalous mole fraction experiments, external solutions contained mixtures of different concentrations of KNO3 or TlNO3, with the total concentration of both salts being kept at 100 mM. Current was evoked from a holding potential of 0 or +10 mV either by a −100-mV voltage pulse or a voltage ramp from −100 to +80 mV with an increment of 0.5 mV/ms. In Ba2+ blocking experiments, the duration of the pulse or the interpulse interval was adjusted to achieve steady-state Ba2+ blockage and complete recovery from the blockage.
Single-channel recordings were obtained in cell-attached membrane patches. Electrodes were fabricated from Corning Pyrex glass tubes, coated with sylgard, and heat polished to a resistance of 5–8 MΩ when filled with a solution containing 110 mM KCl, 10 mM HEPES, 9 mM EGTA, and 1 mM EDTA (pH adjusted to 7.4 with KOH). In some experiments, we also filled the pipette with a solution containing 120 mM KNO3, 1 mM KCl, 10 mM HEPES, 9 mM EGTA, and 1 mM EDTA (pH adjusted to 7.4 with NMDG). No significant difference in single-channel properties was observed with either K+ solutions, and, therefore, the data were pooled together. When Tl+ was used as the permeant ion, the solution contained 120 mM TlNO3, 1 mM TlCl, 10 mM HEPES, 9 mM EGTA, and 1 mM EDTA (pH adjusted to 7.4 with NMDG). In Ba2+ blockage experiments, the pipette solution contained either 130 mM KCl or 130 mM TlNO3 and 1 mM TlCl, with 10 mM HEPES and a known concentration of BaCl2 (pH adjusted to 7.4 with NMDG). All reagents were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich.
For TEVC recordings, data acquisition and analysis were performed with a customized program written in Axobasic (Axon Instruments Inc.). Single-channel current was recorded with the pClamp 6 program (Axon Instruments, Inc.) at a constant negative potential ranging from −40 to −200 mV. Unless indicated otherwise, currents were filtered at 1 KHz with an 8-pole Bessel filter, digitized at 2–10 KHz with a 12-bit A/D interface (Axon Instruments Inc.) and stored on a computer. All recordings were conducted at temperatures 21–23°C.
Data Analysis
The permeability ratios, P Tl/P K, was calculated from changes of the reversal potential upon switching from K+ to Tl+ solution according to the equation: ΔE rev = E rev, Tl − E rev, K = 2.30RT/F log (P Tl/P K), where R, T, and F have their usual thermodynamic meanings. The voltage dependence of Ba2+ blockage was determined using the Woodhull 1973 model according to the equation: K d (V) = K d (0)exp(zδFV/RT), where K d (0) is the apparent dissociation constant at 0-mV membrane potential, z is the valence of the blocking ion, and δ is the fractional electrical distance of the blocking ion binding site from the outside.
Single-channel current was analyzed with the pClamp6 program. Only patches that contained one channel were included in the analysis. Dwell-time distributions were constructed from records of varying length (from 2 to 30 min depending on the frequency of open/closed or blocked transitions) using logarithmic binning and square-root transformation and were fit with one or more exponential functions. No corrections were made for filter dead-time and missed events. The Ba2+ unblocking rate was computed as the inverse of the blocked time. Data are presented as mean ± SD (number of observations). Statistical analysis was done with t test.
RESULTS
Tl+ Is Highly Permeant in Kir2.1 Channels
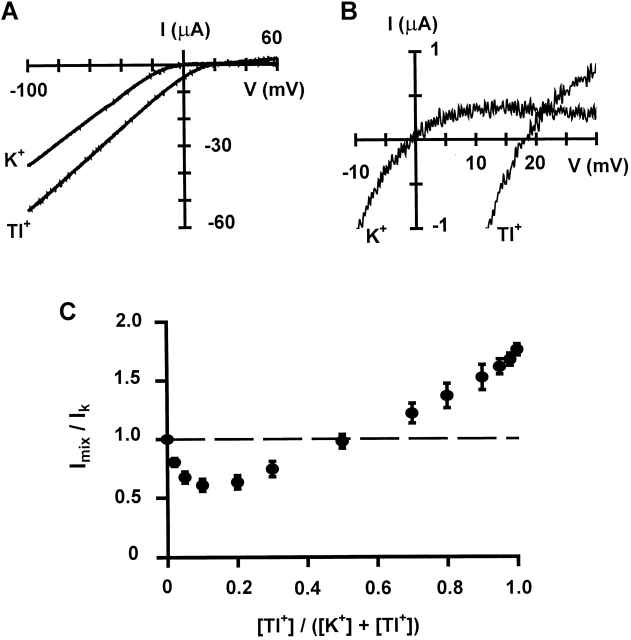
We first examined Tl+ permeation properties in Kir2.1 channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Fig. 1 A shows whole-cell currents evoked by voltage ramps from −100 to +60 mV, with either K+ or Tl+ as the external permeant ion. The currents displayed strong inward rectification with either species of ions. Upon switching the external solution from K+ to Tl+, the reversal potential was shifted to the positive direction (see close-up in Fig. 1 B) and the inward current increased significantly. The average shift of reversal potential is 12.6 ± 3.6 mV, corresponding to a permeability ratio PTl/PK of 1.65, which is similar to the value of 1.5 reported for a native inward rectifier K+ channel (Hagiwara and Takahashi 1974). This result indicates that Tl+ is more permeant than K+ in Kir2.1 channels, as it is in other types of K+ channels (Hille 1992). At a membrane potential of −100 mV, the Tl+ current was 1.75-fold larger than the K+ current (Fig. 1 C). This increase appears to be mainly due to a reduced blockage of Tl+ current by external divalent cations—2 mM Mg2+ (which was added to reduce the leak current and maintain long-lasting stable recordings) as well as contaminating Ba2+—since the Tl+ current was only 1.06 (±0.02, n = 5)-fold larger than the K+ current when external divalent cations were chelated by EDTA.
Figure 1.
Permeation properties of Tl+ ions. (A) Whole-cell current-voltage relations of Kir2.1 channels recorded by TEVC with either K+ or Tl+ as the external permeant ion. (B) Close-up of A to show the outward current and reversal potential. (C) Relative whole-cell current recorded at −100 mV by TEVC in external solutions containing different concentrations of K+ and Tl+. The total concentration of both ions is 100 mM. Each data point is the average of four to eight measurements. Error bars are SD.
Kir2.1 channels also displayed a strong anomalous mole fraction effect: when Tl+ and K+ ions were mixed together (while total concentration of both ions was kept at a constant level of 100 mM), the whole-cell current became smaller than with either ion alone outside (Fig. 1 C). This behavior is very similar to that observed in a native inward rectifier channel (Hagiwara et al. 1977), and is indicative of multiple ion binding sites and strong ion–ion interactions in the pore.
Tl+ Alters Single-channel Gating Kinetics
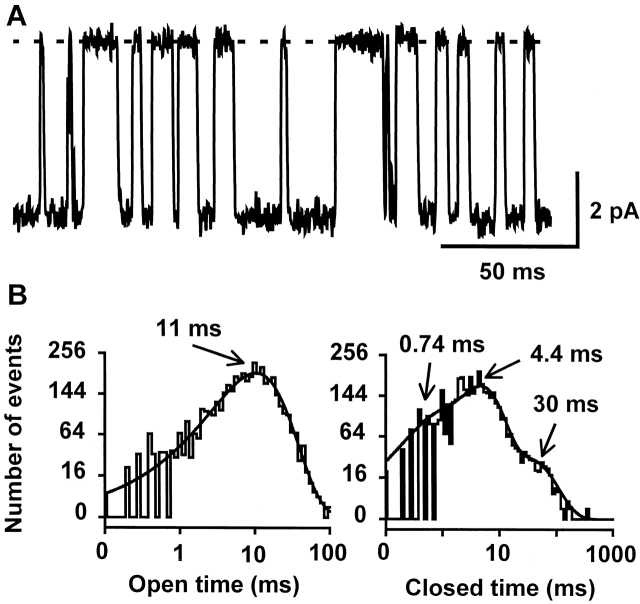
As we reported previously (Lu et al. 2001), Kir2.1 channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes undergo spontaneous open and close transitions when recorded in cell-attached patches at constant membrane potentials more negative than the potassium equilibrium potential. Fig. 2 A shows representative inward single-channel currents recorded at −100 mV with K+ as the external permeant ion. The open- and closed-time distributions show that there are one open and three closed states (Fig. 2 C). The open-time was voltage-dependent, decreasing e-fold with 67-mV hyperpolarization, from 293 ms at −80 mV to 45 ms at −200 mV (Fig. 2 E). The two longer closed-times were also voltage-dependent, decreasing e-fold with 71- and 62-mV hyperpolarization, respectively (Fig. 2 F). The shortest closed-time was relatively independent of membrane voltage. Previous studies have shown that these closed states are not produced by open-pore blockage by external or internal blocking ions (Choe et al. 1999; Lu et al. 2001).
Figure 2.

Alteration of single-channel gating by Tl+ ions. (A and B) Consecutive records of single-channel K+ (A) or Tl+ (B) currents recorded at −100 mV in a cell-attached membrane patch. The dashed lines indicate the closed level in this and all subsequent figures. Arrows in B indicate the dominant subconductance level and arrowheads mark a relatively rare subconductance level. (C and D) Open- and closed-time distributions of channels recorded with K+ (C) or Tl+ (D) as the external permeant ion. The open-time distributions were best fit by a single exponential and the closed-time distributions by three exponentials. The time constants of the fits are indicated. (E) Voltage dependence of the open-time with either K+ or Tl+ as the permeant ion (n = 4–6). (F and G) Voltage dependence of the closed times with either K+ (F) or Tl+ (G) as the permeant ion (n = 4–12). Error bars are SD and are smaller than the symbols in some cases.
Single-channel behavior was greatly altered when Tl+ was used as the external permeant ion. Representative single-channel Tl+ currents recorded at −100 mV from a cell-attached patch are shown in Fig. 2 B. Compared with K+ currents, two major changes in the gating kinetics are readily seen. First, the channel closed more frequently and the open-time was decreased by ∼20-fold across the voltage range studied (Fig. 2B and Fig. E), indicating a dramatic destabilization of the open state by Tl+. Second, although there were still three closed states (Fig. 2 D), the dwell-time of the two longer closed states were altered, and they remained relatively constant in the voltage range of −140 to −200 mV and increased rather than decreasing with hyperpolarization in the voltage range of −80 to −140 mV (Fig. 2 G). Both dwell times were shorter than those obtained with K+ as the permeant ion at −100 mV. On the other hand, as the membrane potential was hyperpolarized to −200 mV, both dwell times became longer than those obtained with K+ as the permeant ion. Due to these two effects, the overall open probability at −100 mV decreased from ∼0.9 for K+ to ∼0.6 for Tl+. These results indicate that the single-channel gating kinetics is strongly influenced by the species of the permeant ion.
Tl+ Induces Decay of Single-channel Current and a Subconductance Level
In addition to its dramatic effect on open/close gating kinetics, Tl+ also induced marked changes in sublevel behavior (Fig. 2 B). Notably, the channel resided primarily at a subconductance level (Fig. 2 B, arrows) rather than the closed or fully open level. When the channel opened from the closed level, it often jumped to a large conductance level, from which it relaxed to the predominant sublevel within several milliseconds. Fig. 3 A shows 12 superimposed single-channel current events with a slow decay, aligned by their opening to the full level. The ensemble average trace shows a decay phase that can be fitted by a single exponential function with a time constant of 2.7 ms (Fig. 3 B). The unitary current at −100 mV is 4.2 ± 0.2 pA for the fully open level and 3.1 ± 0.2 pA (n = 10) for the subconductance level. Transitions to other subconductance levels were also observed (Fig. 2 B, arrowheads) but were not investigated further due to their rare occurrence. We also recorded Tl+ single-channel current with filtering at 3 kHz and found no difference in single-channel properties.
Figure 3.
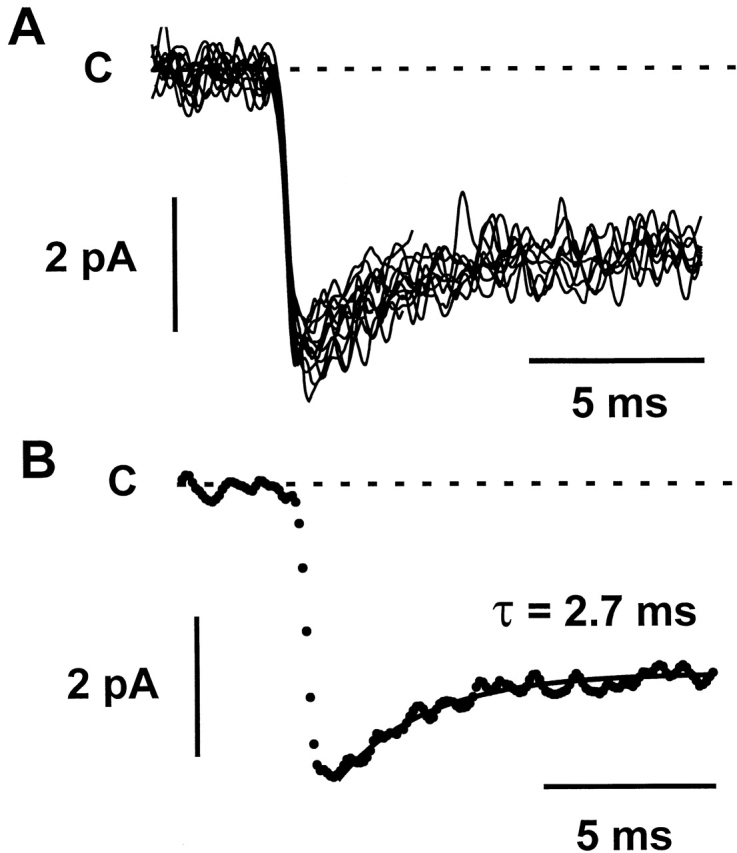
Slow decay of single-channel Tl+ current. (A) 12 selected single-channel current events that exhibit a slow decay are aligned by their initial opening and are superimposed. The currents were recorded at −100 mV in a cell-attached membrane patch with Tl+ as the external permeant ion. (B) The dotted line shows the ensemble average of the traces in A. The decay phase is fitted by a single exponential function with a time constant of 2.7 ms (solid line).
The Single-channel Current Decay and Subconductance Level Are Produced by Interactions between Tl+ and Residue C169
Interestingly, gating of Kir2.1 channels in the presence of external Tl+ exhibits a remarkable time asymmetry (Fig. 2 B). The decay and subconductance state occur faithfully after nearly every opening to the fully open level. However, from the subconductance state, the channel predominantly enters a closed state and only occasionally transition back to the fully open level. This type of nonequilibrium gating is phenomenologically reminiscent of that seen in a Cl− channel, which is coupled to Cl− permeation (Richard and Miller 1990). The observation that the decay of single-channel Tl+ current always occurs immediately after channel opening to the full level suggests that it is tightly coupled to Tl+ permeation. Since Tl+ interacts strongly with soft ligands, we hypothesized that the decay might be caused by interactions between Tl+ and the thiolate group of a pore-lining cysteine residue. C169 in the second transmembrane segment (TM2) appeared to be a perfect target. We previously have shown that the side chain of C169 reacts covalently with methanethiosulfonate reagents applied internally and presumably faces the pore (Lu et al. 1999). The crystal structure of KcsA shows that the side chain of the analogous residue in that channel is at the same level as the cavity ion and points to the central cavity (Doyle et al. 1998). The single-channel current decay and the associated subconductance level were abolished when C169 was mutated to valine, its counterpart in Kir1.1 channels (Fig. 4 A), indicating that they were indeed produced by interactions between C169 and Tl+ ions permeating the pore. The mutant channel underwent transitions only between the closed and fully open levels, with an unitary current of 4.8 ± 0.1 pA (n = 4) at −100 mV.
Figure 4.
C169V mutation abolishes the slow decay of single-channel current and subconductance level. (A) Representative single-channel Tl+ currents recorded at −100 mV from a C169V mutant channel in a cell-attached membrane patch. Notice the lack of decay of single-channel current and subconductance level. (B) Open- and closed-time distributions of channels recorded with Tl+ as the external permeant ion. The open-time distribution was best fit by a single exponential and the closed-time distributions by three exponentials. The time constants of the fits are similar to those for the wild-type channel (Fig. 2 D).
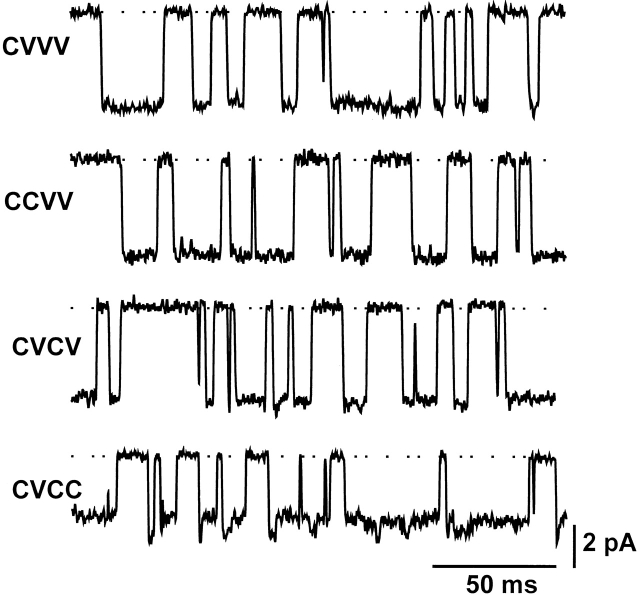
Kir2.1 channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes are homotetramers and, thus, have four identical C169 thiol groups. Does Tl+ need to interact with multiple thiolate groups or with only one thiolate group to induce the decay and subconductance level? If the latter were the case, one would expect that a channel containing one C169 still exhibits the decay but with one-fourth of the frequency observed in the wild-type channel. To address this question, we constructed tandem tetramers containing one to three C169V mutant subunits by using a strategy described previously (Yang et al. 1995; Lu et al. 1999). Although single channels formed by tandem tetramers containing three C169V mutant subunits still showed the decay and subconductance level, those formed by tandem tetramers bearing one or two C169V mutant subunits (either adjacent or opposite to each other) did not (Fig. 5). These results indicate that Tl+ must interact with at least three C169 thiolate groups to induce the single-channel current decay and subconductance level.
Figure 5.
Tl+ must interact with three or four C169 thiolate groups to induce the slow decay of single-channel current and subconductance level. The traces show representative cell-attached single-channel Tl+ currents recorded at −100 mV from four different types of channels. The channels are formed by tandem tetramers containing one to three C169V mutant subunits: WT-C169V-C169V-C169V (CVVV), WT-WT-C169V-C169V (CCVV), WT-C169V-WT-C169V (CVCV), and WT-C169V-WT-WT (CVCC).
Kinetics of Single-channel Tl+ Current Was not Altered by C169V Mutation
Although Tl+ did not induce decay of single-channel current and subconductance level in C169V mutant channels, it still greatly destabilized the open state (Fig. 4). The mean open time at −100 mV was decreased from 87 ± 3 ms (n = 4) with K+ as the permeant ion to 10.8 ± 0.4 ms (n = 4) with Tl+ as the permeant ion, which is similar to that for the wild-type channel. With Tl+, the dwell time of the three closed states at −100 mV was 0.63 ± 0.25, 5.1 ± 0.7, and 35 ± 6 ms (n = 4), respectively, which are also similar to those for the wild-type channel (0.7 ± 0.25, 4.5 ± 1.7, and 21 ± 11 ms, n = 10). These results suggest that the effect of Tl+ on single-channel gating kinetics is caused by interactions between Tl+ and other parts of the pore. The most likely region is the selectivity filter, where the more electron “hungry” Tl+ is expected to interact more strongly than K+ with the main chain carbonyl oxygens.
Tl+ Diminishes Ba2+ Blockage
To test the hypothesis that the effect of Tl+ on single-channel kinetics is exerted through its interactions with the selectivity filter, we investigated whether Tl+ induces conformational changes in the filter region. Such conformational changes, if there were any, would most likely be very subtle. To detect such conformational changes, we used Ba2+ as a probe and compared inhibition of K+ or Tl+ current by external Ba2+. Since Ba2+ binds to a high affinity site in the selectivity filter (Neyton and Miller 1988a,Neyton and Miller 1988b; Jiang and MacKinnon 2000), its binding kinetics is expected to be sensitive to even very subtle conformational changes in the region.
In whole-cell two-electrode voltage clamp recordings, 30 μM Ba2+ had little effect on the peak K+ current evoked by a test pulse to −100 mV from a holding potential of 0 mV, but it produced a time-dependent blockage of the current during the voltage pulse (Fig. 6 A). As Ba2+ blocks K+ channels by one-to-one binding (Jiang and MacKinnon 2000), the apparent K d at a given membrane voltage can be calculated according to the Hill equation: Fractional I = 1/(1 + ([Ba2+]/K d)), where fractional I is the ratio of steady-state current in the presence and absence of a given concentration of Ba2+. At −100 mV and with 30 μM Ba2+, the steady-state K+ current was reduced by 91 ± 5% (n = 22), yielding an apparent K d of 2.97 ± 1.65 μM for Ba2+. By contrast, 3 mM Ba2+ blocked only 79 ± 5% (n = 10) of the Tl+ current (Fig. 6 B), giving rise to a 277-fold higher apparent K d of 824 ± 229 μM. Thus, Ba2+ is much less effective in blocking Tl+ current than K+ current. This reduced blockage was also observed at other membrane voltages (Fig. 6 C). With either K+ or Tl+ as the permeant ion, the apparent K d of Ba2+ decreased significantly with increasing negative membrane voltage between −40 and −120 mV, reaching a minimum at −140 mV, and then increased slightly at −160 mV (Fig. 6 C). At even more negative membrane voltages, steady-state Ba2+ blockage became markedly reduced, which is indicative of permeation of Ba2+ to the inside. The equivalent valence (zδ) derived from data points from −40 to −100 mV was identical (0.8) in the presence of K+ or Tl+, suggesting that in both cases Ba2+ blocks the channel by binding to a site similarly located in the membrane electrical field. This zδ value is similar to the value of 1.08 reported previously for Kir2.1 channels (Shieh et al. 1998).
Figure 6.
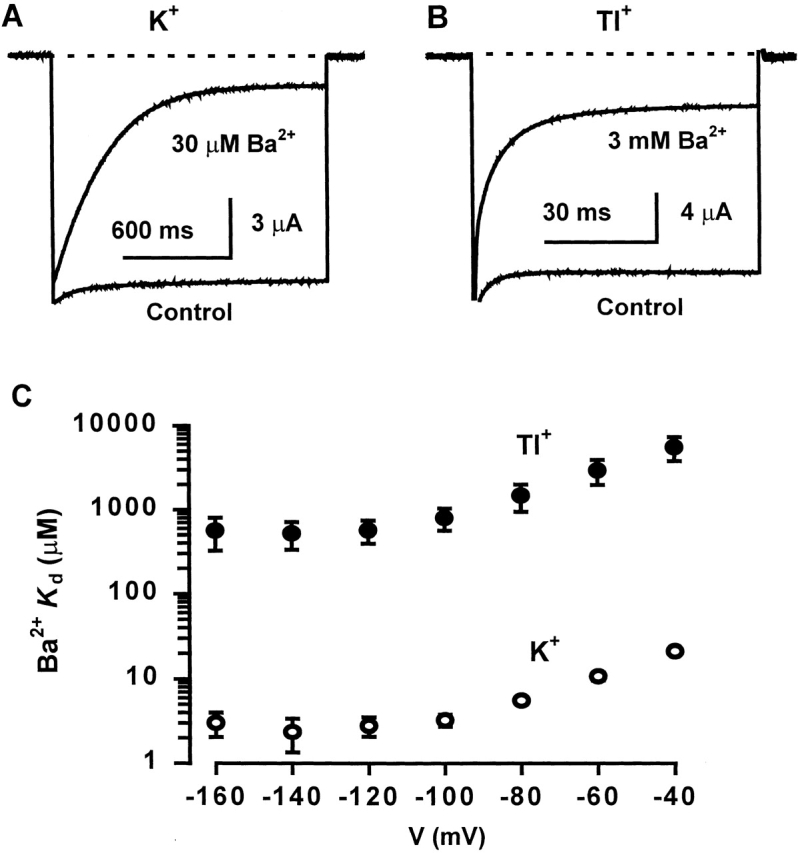
Comparison of Ba2+ blockage of K+ and Tl+ currents. (A and B) Blockage by external Ba2+ of whole-cell K+ (A) or Tl+ (B) current recorded by TEVC. Currents were recorded from the same oocyte and were evoked by a test pulse to −100 mV from a holding potential of 0 mV. The dashed lines indicate the zero current level. Notice the difference in time scale in the two figures. (C) Voltage dependence of the apparent K d of Ba2+ with either K+ or Tl+ as the external permeant ion (n = 5–6).
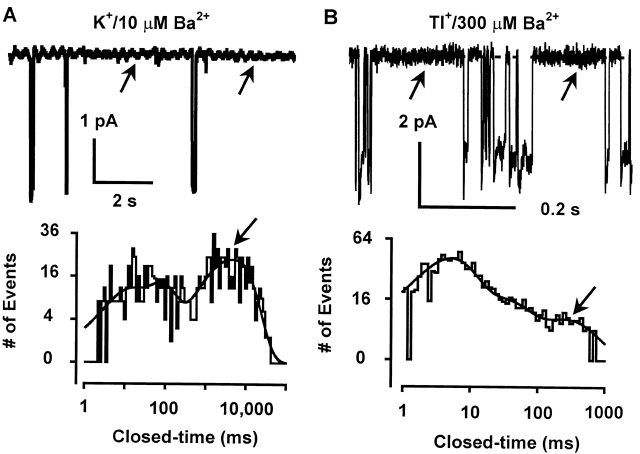
A much reduced Ba2+ blockage of Tl+ current was also evident at the single-channel level. With K+ as the external permeant ion, 10 μM external Ba2+ induced frequent long-lived blocking events lasting 5.27 ± 1.03 s (n = 5) at −100 mV (Fig. 7 A). When Tl+ was used as the external permeant ion, however, a much higher concentration of Ba2+ (300 μM) was required to induce significant numbers of blocking events (Fig. 7 B). The blocked state had a much shorter mean lifetime of 112 ± 19 ms (n = 8) at −100 mV, corresponding to a 47-fold increase in the Ba2+ unblocking rate (k off). The voltage dependence of Ba2+ k off was mild with either K+ or Tl+ as the permeant ion (Fig. 8). Nevertheless, in both cases, the k off decreased significantly with increasing negative membrane potential in the range between −60 and −120 mV (or −140 mV for Tl+). With Tl+ as the permeant ion, the Ba2+ k off at −60 and −140 mV was 11.4 ± 2.3 s−1 and 7.8 ± 1.8 s−1 (n = 7), respectively, and was significantly different from each other (P < 0.01). This is indicative that the bound Ba2+ exits mainly to the external side in this voltage range. When the membrane potential was increased beyond −120 mV (or −140 mV for Tl+), the Ba2+ k off started to increase again, indicating that the bound Ba2+ now leaves mainly to the internal side. However, regardless of the direction of Ba2+ exit, its dissociation rate was increased by >22-fold when the permeant ion was switched from K+ to Tl+.
Figure 7.
Blockage of single-channel K+ or Tl+ current by external Ba2+. (A and B) Single-channel K+ or Tl+ current were recorded at −100 mV from two separate cell-attached membrane patches with 10 μM (A) or 300 μM (B) Ba2+ in the pipette solution. The arrows in the single-channel traces and in the closed-time distributions indicate Ba2+ blocked states. The dashed lines indicate the zero current level. The current record in A was filtered at 100 Hz and digitized at 2 KHz.
Figure 8.
Tl+ speeds up dissociation of Ba2+ from the channel. The Ba2+ unblocking rate determined from single-channel recordings is plotted against the membrane potential with either K+ or Tl+ as the external permeant ion (n = 3–9).
Due to the long duration of the blocking events, we were unable to determine the Ba2+ blocking rate at the single-channel level. However, the apparent Ba2+ blocking rate can be obtained by using the equation k on = k off/K d, where k off is obtained from single-channel recordings and K d from whole-cell recordings. According to this method, the Ba2+ blocking rate at −100 mV is reduced by nearly sixfold when the external permeant ion is switched from K+ to Tl+.
Since C169 interacts with Tl+ and since the C169V mutation abolished Tl+-induced decay of single-channel current and subconductance level, we asked whether it also eliminated Tl+-induced changes in Ba2+ blockage. Ba2+ blocked whole-cell K+ or Tl+ current at −100 mV in C169V mutant channels with an apparent K d of 2.2 ± 0.2 μM (n = 5) and 863 ± 405 μM (n = 8), respectively, similar to that obtained in the wild-type channel. Furthermore, in single-channel recordings, the Ba2+ dwell time at −100 mV was decreased from 5.4 ± 0.6 s (n = 4) in the presence of external K+ to 145 ± 16 ms (n = 4) in the presence of external Tl+, again similar to that observed in the wild-type channel. These results indicate that the Tl+-induced changes in Ba2+ blockage do not result from interactions between Tl+ and C169.
DISCUSSION
Permeation and gating are two fundamental biophysical properties of ion channels. Although these two processes were originally thought to be independent, there is increasing evidence that they are tightly coupled and that permeant ions strongly affect gating (see introduction). In this study, we demonstrate that substitution of K+ with another permeant ion (Tl+) dramatically alters gating of Kir2.1 channels in two ways. First, Tl+ induces a slow decay of the single-channel current, resulting in a dominant subconductance level. Second, Tl+ greatly destabilizes the open state of the channel and changes the open/close kinetics of gating.
Slow Decay of Single-channel Current
The slow decay of single-channel current immediately after channel opening (Fig. 2 and Fig. 3) is unusual and, to our knowledge, is unprecedented. Such decay was observed in every channel recorded with Tl+ (>30 patches with various recording conditions), but was never observed with K+ as the permeant ion (>100 patches including results from our previous studies), indicating that it is conferred by the unique chemical properties of Tl+. The observation that the C169V mutation eliminates the slow decay and the associated subconductance level indicates that they result from interactions between Tl+ and the thiolate group of C169. In KcsA, the residue (I100) occupying the same position as C169 points directly at the cavity ion (Doyle et al. 1998), and our previous study indicates that the thiol group of C169 is exposed to the cavity as it can be covalently modified by thiol reactive reagents applied to the internal side (Lu et al. 1999). Thus, the thiolate group of C169 is ideally situated to interact with the cavity ion. Since Tl+ has a higher electron affinity than K+ and tends to seek out, wherever possible, polarizable ligand groups (Lee 1971; Taylor and Brothers 1993), the interaction between Tl+ and the thiolate group is much stronger than that with K+. Indeed, covalent thiol derivatives of Tl+ (RSTl) have been synthesized (Lee 1971). However, the reversibility of both the slow decay and subconductance level indicates that the interaction between Tl+ and the thiolate group of C169 is predominantly ionic.
How does such ionic interactions result in the slow decay of single-channel current and the subconductance level? One possibility is that each of the four thiolate groups binds one Tl+ independently, partially occluding the ion conduction pathway, and thereby reducing the single-channel current. Previous work has shown that covalent modification of one of the four subunits at a nearby position, 172, by a thiol reactive reagent does indeed produce partial inhibition of the single-channel current (Lu et al. 1999). Although such a partial blocking mechanism can provide an explanation for the Tl+-induced subconductance level, it does not explain the slow decay. More important, our results indicate that Tl+ must interact with at least three thiolate groups simultaneously to induce the slow decay and subconductance level as mutant channels containing only one or two C169 thiol groups did not exhibit either behavior (Fig. 5).
An alternative possibility is that when Tl+ permeates the cavity, it initiates an interaction with at least three thiolate groups of C169. This process involves reorientation of and optimal coordination by the thiolate groups. Since side chain rotation is generally extremely rapid (on the time scale of 10−11–10−8 s; Creighton 1993), it is unlikely to be a major cause of the slow rate of the decay, which is of millisecond time scale. Instead, the interaction between Tl+ and C169 most likely induces a slow conformational change of the ion conduction pathway (the exact location is unclear) that leads to a slow decrease of Tl+ flux. This conformational change occurs rarely in K+ but frequently in Tl+. However, it should be noted that in the open channel Tl+ ions are streaming through the pore at a rate of >2 × 107 ions/s at a membrane potential of −100 mV. Hence, the residence time of each permeating ion in the cavity is <50 ns. This raises an intriguing question of how Tl+ is coordinated in the cavity by the thiolate groups of C169. Fig. 9 A presents two possible scenarios. In one case, one can imagine that as Tl+ ions flow through the cavity in single file, the thiolate groups constantly change their orientation and coordination to track the permeating Tl+ ions, triggering the slow conformational change. Although the interaction between the thiolate groups and each permeating Tl+ is very brief, the altered conformation is maintained as long as Tl+ permeation continues. In another scenario, a Tl+ may be tightly coordinated by three of the four thiolate groups, which induces and maintains the slow conformational change, but the cavity is sufficiently wide to permit Tl+ ions to flow by the bound Tl+. Previous work suggests that it indeed may be structurally and electrostatically possible to support non–single file conduction through the cavity of Kir2.1 channels (Lu et al. 1999). In that study, one or two monovalently charged moieties were covalently linked to the D172 position and the partially modified channels were still able to conduct K+ current, albeit at a reduced rate.
Figure 9.
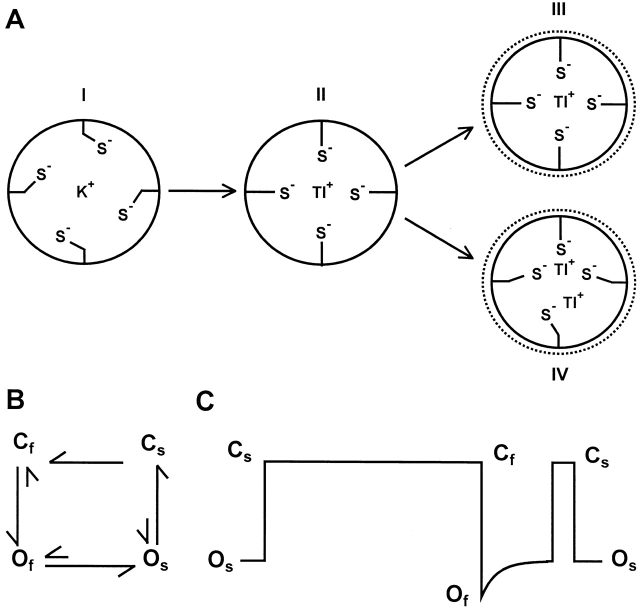
Models of Tl+ interaction with the thiolate groups of C169 and open↔ close transitions of channels in the presence external Tl+. (A) The schematics represent cross sections of the pore at the position of C169. Under our recording conditions, the external and internal permeant ion species are Tl+ and K+, respectively. When the channel is closed, due to conformational changes in the selectivity filter, the cavity is equilibrated with the internal solution and is presumably occupied by K+, which interacts weakly with the thiolate groups (I). As Tl+ permeates the cavity immediately following channel opening, it induces a reorientation of the thiolate groups and seeks to form an optimal coordination (II). This process triggers a slow conformational change of the pore, such as a constriction (but the exact nature of the conformational change is unclear). Two models are proposed for the subsequent interaction between Tl+ and the thiolate groups. In one case (III), the permeating Tl+ is optimally coordinated by all four thiolate groups, but its residence time is <50 ns. In another case (IV), a Tl+ is optimally and tightly coordinated by three thiolate groups, and the cavity is sufficiently wide to permit Tl+ ions to flow by the bound Tl+. (B) A qualitative model of transitions among the proposed closed and open states in the presence of external Tl+ (discussion). (C) An idealized single-channel Tl+ current trace. The two predominant types of channel openings, Cf to Of and Cs to Os, are preceded by two and one closed states, respectively.
Fig. 9 B depicts a model to qualitatively describe the slow decay of single-channel current and the subconductance level induced by Tl+. In this model, we postulate that, with Tl+ as the permeant ion, the channel can adopt a fully open state (Of), a subconductance state (Os), and two closed states, Cf and Cs. We also assume that in Cf the thiol group of C169 does not interact with Tl+, either because the side chain orientation or ionization is not optimal or because the cavity is devoid of Tl+. With this assumption, Cf→Cs and Cf→Os transitions are not permitted. The closed channel can open to Of only from Cf (Fig. 9 C). This transition generates full amplitude Tl+ inward current. Permeating Tl+ then binds to at least three thiolate groups of C169 and this binding triggers a slow conformational change of the ion conduction pathway, resulting in a slow decay of Tl+ current and a subconductance state Os. From Os, the channel can occasionally transition to Of, but most of the time it enters Cs (Fig. 9 C), which still retains the conformational change induced by Tl+. Cs can subsequently open to Os or enter Cf (Fig. 9 C). The latter transition (Cs→Cf) involves a conformation change opposite that of the Of→Os transition and enables the channel to conduct full amplitude Tl+ current when it undergoes the Cf→Of transition again.
According to this model, channel openings to the full level (Cf→Of transitions) should be, in most cases, preceded by two closed states (i.e., Cs and Cf) and those to the subconductance level (Cs→Os transitions) by only one closed state (i.e., Cs; Fig. 9 C). We segregated these two types of openings and analyzed the closed-time distribution (at −100 mV) of their preceding closed states, and found that indeed full openings are preceded by two closed states with a dwell time of 6.7 ± 1.1 ms and 26 ± 6 ms (n = 3) and subconductance openings by a single closed state with a dwell time of 1.6 ± 0.2 ms (n = 3). These closed times are similar to those obtained with both types of openings mingled together (see results). The kinetics of the open↔closed transitions are likely governed by interactions between permeant ions and the selectivity filter, as will be discussed below.
Permeant Ion-induced Conformational Changes in the Selectivity Filter
Our previous results with amide-to-ester mutations suggest that permeant ion-dependent conformational changes of the selectivity filter contribute directly to the spontaneous gating of single Kir2.1 channels (Lu et al. 2001). In this study we found that Tl+ dramatically destabilizes the open state, resulting in much more frequent closures of the channel. This effect was not dependent on interactions between Tl+ and C169 since it persisted in the C169V mutant channel. Instead, it most likely results from strong interactions between permeating Tl+ ions and the main chain carbonyl oxygen atoms lining the selectivity filter.
The mechanism by which permeant ions produce channel closure has been studied by Choe et al. 1998 on Kir1.1b channels, which display only a brief closed state. These investigators found that the rate of entering the closed state varied with the extracellular K+ concentration and was proportional to current amplitude, suggesting a linkage between channel closure and K+ permeation (Choe et al. 1998). They proposed that K+ ions occasionally trigger a conformational change of the pore during permeation, thus altering the permeation energy profile and turning themselves into blocking ions. It is possible that the three closed states in Kir2.1 channels also represent permeant ion-blocked states. Consistent with this hypothesis, the rate of entering the closed states is much higher with Tl+ than with K+ as the permeant ion (Fig. 2 E), probably owing to stronger interactions between Tl+ and the selectivity filter. Furthermore, the dwell times of the closed states and their voltage dependence depend on the species of the permeant ion (Fig. 2F and Fig. G), indicating that the closed channels can register which ions are trapped in the pore. The multiple closed states may represent occupation by different numbers of permeant-turned-blocking ions at different locations in the selectivity filter. The voltage dependence of the dwell time of the closed states (Fig. 2F and Fig. G) further suggests that K+ ions trapped in the closed channel can escape internally, whereas trapped Tl+ ions cannot not permeate the channel.
In addition to the dramatic effects on gating, Tl+ also greatly diminishes Ba2+ blockage of the channel. In particular, the Ba2+ unblocking rate is increased by >22-fold within a wide range of membrane potential when the permeant ion is switched from K+ to Tl+ (Fig. 8). What is the biophysical mechanism underlying this dramatic destabilization of Ba2+ binding? X-ray crystallography shows that in KcsA Ba2+ binds to a single site at the end of the selectivity filter close to the central cavity (Jiang and MacKinnon 2000). Single-channel analysis of Ba2+ blockage of Ca2+-activated K+ channels indicates that there are at least three ion binding sites in addition to the Ba2+ binding site (Neyton and Miller 1988a,Neyton and Miller 1988b). Two sites are located external to the Ba2+ site and are refereed to as the external lock-in site and the enhancement site. One site is located internal to the Ba2+ site and is termed the internal lock-in site. These sites have different affinities for different species of ions and their occupancy greatly affects the kinetics of Ba2+ binding (Neyton and Miller 1988a,Neyton and Miller 1988b).
Assuming that the same set of ion binding sites is present in Kir2.1 channels, can the large difference in Ba2+ unblocking rate with either K+ or Tl+ as the permeant ion be explained by the difference in the occupancy of these sites? In a Ba2+-blocked channel, the internal lock-in site is in true equilibrium with the oocyte cytoplasm in the cell-attached recording configuration and, thus, is visited only by K+ regardless of the species of the external permeant ion. On the other hand, since the external lock-in site has a micromolar affinity for Tl+ and K+ (Neyton and Miller 1988a), it is always occupied by either species of ions. Therefore, the difference comes down to the occupancy of the enhancement site by Tl+ or K+. If Tl+ has a higher occupancy of the enhancement site (or, indeed, of any site external to the Ba2+ binding site) than K+, one would expect that in the voltage range of −40 to −120 mV, when the bound Ba2+ exits mainly to the external side, the Ba2+ unblocking rate would be decreased due to obstruction by Tl+. This is contrary to our experimental results that shows a >22-fold increase when switching from K+ to Tl+ (Fig. 8). Thus, the effect of Tl+ on Ba2+ unblocking rate is difficult to explain based solely on electrostatic interactions between the ions. However, the effect is consistent with the idea that Tl+ ions change the conformation of the selectivity filter as they permeate and interact with that pore region, and that such conformational changes diminish Ba2+ binding. We propose that the same conformational changes also underlie the dramatic effect of Tl+ on the kinetics of single-channel gating.
Permeant ion-dependent conformational changes have been reported for other types of K+ channels. The C-type inactivation of voltage-gated K+ (Kv) channels involves a conformational change of the outer mouth of the pore, including the selectivity filter (Yellen et al. 1994; Liu et al. 1996; Starkus et al. 1997; Yellen 1998; Kiss et al. 1999). Elevation of extracellular [K+], which increases the occupancy of the outer mouth of the pore by K+, slows the rate of entry into the C-type inactivated state (Lopez-Barneo et al. 1993; Baukrowitz and Yellen 1996; Kiss and Korn 1998). On the other hand, manipulations that decrease the occupancy of the outer mouth of the pore speed up entry into the C-type inactivated state (Lopez-Barneo et al. 1993; Baukrowitz and Yellen 1995, Baukrowitz and Yellen 1996). Another example of permeant ion-dependent conformational changes comes from studies on the modulation by K+ of TEA blockage of Kv2.1 channels (Immke et al. 1999; Immke and Korn 2000; Wood and Korn 2000). In this case, binding of K+ to a high-affinity site in the selectivity filter changes the structure of the outer mouth of the pore, resulting in an enhanced blockage of the channel by TEA.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grant HL58552 (to J. Yang) and fellowship NS11097 (to T. Lu) from the National Institutes of Health. J. Yang was a recipient of the McKnight Scholar Award.
Footnotes
Abbreviations used in this paper: Kir channels, inward rectifier K+ channels; Kv channels, voltage-gated K+ channels; TEVC, two-electrode voltage clamp.
References
- Baukrowitz T., Yellen G. Modulation of K+ current by frequency and external [K+]a tale of two inactivation mechanisms. Neuron. 1995;15:951–960. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90185-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baukrowitz T., Yellen G. Use-dependent blockers and exit rate of the last ion from the multi-ion pore of a K+ channel. Science. 1996;271:653–656. doi: 10.1126/science.271.5249.653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen T.-Y., Miller C. Nonequilibrium gating and voltage dependence of the CLC-0 Cl− channel. J. Gen. Physiol. 1996;108:237–250. doi: 10.1085/jgp.108.4.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choe H., Sackin H., Palmer L.G. Permeation and gating of an inwardly rectifying potassium channelEvidence for a variable energy well. J. Gen. Physiol. 1998;112:433–446. doi: 10.1085/jgp.112.4.433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choe H., Palmer L.G., Sackin H. Structural determinants of gating in inward-rectifier K+ channels. Biophys. J. 1999;76:1988–2003. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(99)77357-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clay J.R. Potassium ion accumulation slows the closing rate of potassium channels in squid axons. Biophys. J. 1986;50:197–200. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83452-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creighton T.E. ProteinsStructures and Molecular Properties 2nd ed 1993. W.H. Freeman and Company; New York: pp. 507 pp [Google Scholar]
- Demo S.D., Yellen G. Ion effects on gating of the Ca2+-activated K+ channels correlate with occupancy of the pore. Biophys. J. 1992;61:639–648. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81869-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle D.A., Cabral J.M., Pfuetzner R.A., Kuo A., Gulbis J.M., Cohen S.L., Chait B.T., MacKinnon R. The structure of the potassium channelMolecular basis of K+ conduction and selectivity. Science. 1998;280:69–77. doi: 10.1126/science.280.5360.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enkvetchakul D., Loussouarn G., Makhina E., Shyng S.-L., Nichols C.G. The kinetic and physical basis of KATP channel gatingtoward a unified molecular understanding. Biophys. J. 2000;78:2334–2348. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(00)76779-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Lagunas F., Armstrong C.M. The relation between ion permeation and recovery from inactivation of Shaker B K+ channels. Biophys. J. 1994;67:1806–1815. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80662-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Takahashi K. The anomalous rectification and cation selectivity of the membrane of a starfish egg cell. J. Membr. Biol. 1974;18:61–80. doi: 10.1007/BF01870103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Miyazaki S., Krasne S., Ciani S. Anomalous permeabilities of the egg cell membrane of a starfish in K+-Tl+ mixtures. J. Gen. Physiol. 1977;70:269–281. doi: 10.1085/jgp.70.3.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. Ionic Channels of Excitable Membranes 2nd ed 1992. Sinauer Associates, Inc; Sunderland, MA: pp. 607 pp [Google Scholar]
- Immke D., Korn S.J. Ion–ion interactions at the selectivity filterevidence from K+-dependent modulation of tetraethylammonium efficacy in Kv2.1 potassium channels. J. Gen. Physiol. 2000;115:509–518. doi: 10.1085/jgp.115.4.509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Immke D., Wood M., Kiss L., Korn S.J. Potassium-dependent changes in the conformation of the Kv2.1 potassium channel pore. J. Gen. Physiol. 1999;113:819–836. doi: 10.1085/jgp.113.6.819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang Y., MacKinnon R. The barium site in a potassium channel by X-ray crystallography. J. Gen. Physiol. 2000;115:269–272. doi: 10.1085/jgp.115.3.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiss L., Korn S.J. Modulation of C-type inactivation by K+ at the potassium channel selectivity filter. Biophys. J. 1998;74:1840–1849. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(98)77894-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiss L., LoTurco J., Korn S.J. Contribution of the selectivity filter to inactivation in potassium channels. Biophys. J. 1999;76:253–263. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(99)77194-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee A.G. The Chemistry of Thallium 1971. Elsevier Publishing Company; London: pp. 336 pp [Google Scholar]
- Levy D.I., Deutsch C. Recovery from C-type inactivation is modulated by extracellular potassium Biophys. J. 70 1996. 798 805a [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy D.I., Deutsch C. A voltage-dependent role for K+ in recovery from C-type inactivation Biophys. J. 71 1996. 3157 3166b [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y., Jurman M.E., Yellen G. Dynamic rearrangement of the outer mouth of a K+ channel during gating. Neuron. 1996;16:859–867. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80106-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Barneo J., Hoshi T., Heinemann S.H., Aldrich R.W. Effects of external cations and mutations in the pore region on C-type inactivation of Shaker potassium channels. Recept. Channels. 1993;1:61–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu T., Nguyen B., Zhang X.-M., Yang J. Architecture of a K+ channel inner pore revealed by stoichiometric covalent modification. Neuron. 1999;22:571–580. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80711-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu T., Ting A.Y., Mainland J., Jan L.Y., Schultz P.G., Yang J. Probing ion permeation and gating in a K+ channel with backbone mutations in the selectivity filter. Nat. Neurosci. 2001;4:239–246. doi: 10.1038/85080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus Y. Ion Properties 1997. Marcel Dekker, Inc; New York: pp. 261 pp [Google Scholar]
- Matteson D.R., Swenson R.P. External monovalent cations that impede the closing of K channels. J. Gen. Physiol. 1986;87:795–816. doi: 10.1085/jgp.87.5.795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neyton J., Miller C. Discrete Ba2+ block as a probe of ion occupancy and pore structure in the high-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel J. Gen. Physiol 92 1988. 569 586a [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neyton J., Miller C. Potassium block barium permeation through a calcium-activated potassium channel J. Gen. Physiol 92 1988. 549 567b [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neyton J., Pelleschi M. Multi-ion occupancy alters gating in high-conductance, Ca2+-activated K+ channels. J. Gen. Physiol. 1991;97:641–665. doi: 10.1085/jgp.97.4.641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols C.G., Lopatin A.N. Inward rectifier potassium channels. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 1997;59:171–191. doi: 10.1146/annurev.physiol.59.1.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardo L.A., Heinemann S.H., Terlau H., Ludewig U., Lorra C., Pongs O., Stuhmer W. Extracellular K+ specifically modulates a rat brain K+ channel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1992;89:2466–2470. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pusch M., Ludewig U., Rehfeldt A., Jentsch T.J. Gating of the voltage-dependent chloride channel CIC-0 by the permeant anion. Nature. 1995;373:527–531. doi: 10.1038/373527a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richard E.A., Miller C. Steady-state coupling of ion-channel conformations to a transmembrane ion gradient. Science. 1990;247:1208–1210. doi: 10.1126/science.2156338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roux B., MacKinnon R. The cavity and pore helices in the KcsA K+ channelelectrostatic stabilization of monovalent cations. Science. 1999;285:100–102. doi: 10.1126/science.285.5424.100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shieh R.-C., Chang J.-C., Arreola J. Interaction of Ba2+ with the pores of the cloned inward rectifier K+ channels Kir2.1 expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Biophys. J. 1998;75:2313–2322. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(98)77675-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starkus J.G., Kuschel L., Rayner M., Heinemann S.H. Ion conduction through C-type inactivated Shaker channels. J. Gen. Physiol. 1997;110:539–550. doi: 10.1085/jgp.110.5.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenson R.P., Armstrong C.M. K+ channels close more slowly in the presence of external K+ and Rb+ . Nature. 1981;291:427–429. doi: 10.1038/291427a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor M.J., Brothers P.J. Inorganic derivatives of the elements. In: Downs A.J., editor. Chemistry of Aluminum. Gallium, Indium and Thallium. Blackie Academic & Professional; Glasgow, NZ: 1993. pp. 111–247. [Google Scholar]
- Townsend C., Horn R. Interaction between the pore and a fast gate of the cardiac sodium channel. J. Gen. Physiol. 1999;113:321–331. doi: 10.1085/jgp.113.2.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townsend C., Hartmann H.A., Horn R. Anomalous effect of permeant ion concentration on peak open probability of cardiac Na+ channels. J. Gen. Physiol. 1997;110:11–21. doi: 10.1085/jgp.110.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trapp S., Proks P., Tucker S.J., Ashcroft F.M. Molecular analysis of KATP channel gating and implications for channel inhibition by ATP. J. Gen. Physiol. 1998;112:333–350. doi: 10.1085/jgp.112.3.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood M.J., Korn S.J. Two mechanisms of K+-dependent potentiation in Kv2.1 potassium channels. Biophys. J. 2000;79:2535–2546. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(00)76494-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodhull A.M. Ionic blockage of sodium channels in nerve. J. Gen. Physiol. 1973;61:687–708. doi: 10.1085/jgp.61.6.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J., Jan Y.N., Jan L.Y. Determination of the subunit stoichiometry of an inwardly rectifying potassium channel. Neuron. 1995;15:1441–1447. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yakubovich D., Pastushenko V., Bitler A., Dessauer C.W., Dascal N. Slow modal gating of single G protein-activated K+ channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes. J. Physiol. 2000;524:737–755. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2000.00737.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yellen G. The moving parts of voltage-gated ion channels. Q. Rev. Biophys. 1998;31:239–295. doi: 10.1017/s0033583598003448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yellen G., Sodickson D., Chen T.-Y., Jurman M.E. An engineered cysteine in the external mouth of a K+ channel allows inactivation to be modulated by metal binding. Biophys. J. 1994;66:1068–1075. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80888-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]