Abstract
Methyl chloride transferase, a novel enzyme found in several fungi, marine algae, and halophytic plants, is a biological catalyst responsible for the production of atmospheric methyl chloride. A previous paper reports the purification of this methylase from Batis maritima and the isolation of a cDNA clone of the gene for this enzyme. In this paper, we describe the isolation of a genomic clone of the methylase gene and the expression of recombinant methyl chloride transferase in Escherichia coli and compare the kinetic behavior of the wild-type and recombinant enzyme. The recombinant enzyme is active and promotes the production of methyl chloride by E. coli under in vivo conditions. The kinetic data indicate that the recombinant and wild-type enzymes have similar halide (Cl−, Br−, and I−)-binding capacities. Both the recombinant and wild-type enzymes were found to function well in high NaCl concentrations. This high salt tolerance resembles the activity of halobacterial enzymes rather than halophytic plant enzymes. These findings support the hypothesis that this enzyme functions in the control and regulation of the internal concentration of chloride ions in halophytic plant cells.
It is estimated that methyl chloride, the most abundant halohydrocarbon species in the upper atmosphere, is produced at a level of 5 × 106 tons per year (1). The biological production of CH3Cl and other volatile halogenated organic compounds in ocean waters has been commonly viewed as one of the major source of chlorinated halohydrocarbons in the upper atmosphere (2). In 1990, Wuosmaa and Hager (3) discovered the presence of methyl chloride transferase (MCT) in fungi, marine algae, and a halophytic plant. MCT catalyzes the conversion of chloride to methyl chloride by using S-adenosyl-l-methionine (AdoMet) as the methyl donor. Wuosmaa and Hager showed that cell-free extracts of Phellinus pomaceus (a white rot fungus), Endocladia muricata (a marine red algae), and Mesembryanthemum crystallium (ice plant, a halophytic plant) contain MCT activity. Wuosmaa (4) also found that 20 of 31 marine algae collected along the Pacific coastal water near Monterey, CA produced methyl chloride. The production of methyl choride by halophytic plants suggests that halophytic plants may be an additional major source of atmospheric methyl chloride (3, 4). Methyl chloride and other halogenated methanes pollute the atmosphere (5) and affect the integrity of the stratospheric ozone layer (6).
Previous work led to the isolation of a homogenous MCT preparation and allowed the cDNA cloning of the MCT gene (7). The isolated native enzyme has a Mr of 22,434 as determined by matrix-assisted laser-desorption ionization (MALDI) MS, whereas the ORF in the cDNA clone has 230 codons coding for an enzyme having a calculated Mr of 25,761. Thus, there is a ≈3.3-kDa difference in the molecular masses of the isolated enzyme and the deduced amino acid sequence. It is unclear whether this difference is due to proteolytic cleavage during isolation of the native enzyme or to a posttranslational maturation event that generates the active form of MCT from a proenzyme. To test whether the full-length (230 residues) recombinant enzyme is active, it has been expressed in Escherichia coli, and both the wild-type and the recombinant enzyme have been compared in kinetic studies.
Transformed E. coli cells containing the recombinant methylase are able to synthesize methyl chloride in vivo when they are grown in high concentrations of NaCl and the synthesized methyl chloride distills into the air above the culture medium. Both the wild-type and recombinant enzymes were found to be salt-tolerant, an unusual feature for a halophytic plant enzyme. Possible implications of the production of methyl chloride by MCT are discussed.
METHODS
Construction of the Expression Vector pETMCT.
A full-length coding cDNA sequence of MCT was generated by PCR using the MCT5 and MCT3b primers as described (7). MCT5 corresponds to amino acid residues 1–9 and MCT3b to residues 222–230 in the enzyme. A NdeI site and a BamHI site were introduced at the 5′ ends of MCT5 and MCT3b, respectively, and one base (T) was deleted from the antisense codon (GTT) for the C-terminal residue Asn in MCT3b. This deletion permitted a reading-frame adjustment that allowed for the insertion of a His-6 tag into the C terminus of the recombinant enzyme. The mRNA and double-stranded cDNA were prepared as described (7). PCR was carried out by using double-stranded cDNA as template under the following conditions: denaturation at 94°C for 30 sec and extension at 72°C for 1 min, followed by annealing for 15 sec at 70°C for 2 cycles, 67°C for 2 cycles, 64°C for 5 cycles, 60°C for 5 cycles, 57°C for 5 cycles, 55°C for 30 cycles, and finally 72°C for 7 min. The ≈700-bp PCR fragment was gel-purified, ligated into NdeI- and BamHI-digested pET 22b (Novagen), and used to transform the E. coli BL21 cells.
Expression of MCT in E. coli.
BL21 (DE3) cells, transformed with pETMCT plasmid, were grown to an OD600 of 0.8–1.0 in LB containing 100 μg/ml ampicillin at 37°C. Isopropyl β-d-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) was then added to a final concentration of 1.0 mM, and the cells were allowed to continue to grow for an additional 4–8 hr. The cells (25 ml) were harvested by centrifugation at 5,000 × g for 5 min, and the pellet was collected and resuspended to 2.5 ml of TE buffer (50 mM Tris⋅HCl/2 mM EDTA, pH 8.0). Lysozyme and Triton X-100 were added to the cell suspension to final concentrations of 100 μg/ml and 0.1%, respectively, and the suspension was incubated at 30°C for 15 min, sonicated twice for 20 sec, and centrifuged at 12,000 × g for 15 min. The supernatant fraction was removed, and the pellet was washed with 1.25 ml of TE buffer. After washing, the pellet was recovered by centrifugation at 12,000 × g for 15 min. The pellet was dissolved in 5 ml of 8 M urea in Tris buffer (50 mM Tris⋅HCl/50 mM sodium phosphate, pH 8.0) and centrifuged at 12,000 × g for 15 min. The supernatant fraction was transferred to a dialysis membrane tube (Spectrum Medical Industries, 10,000-molecular weight cutoff) and the active enzyme was recovered by dialysis against 2 M urea in TS buffer (20 mM Tris⋅HCl/20 mM Na2S2O5, pH 6.8) for 1 hr, against 0.5 M urea in TS buffer for 1 hr, and against TS buffer overnight. Proteins were analyzed by using SDS/PAGE under denaturing conditions using 20% acrylamide gels in the Phast system (Amersham Pharmacia). Protein concentrations were estimated by the method of Bradford (8) using the Coomassie Plus protein assay reagents (Pierce) with BSA as the standard.
Assay for Methyl Chloride Transferase Activity.
Methyl chloride transferase activity was usually measured in a methyl iodide assay unless otherwise stated. In this assay, aliquots of the enzyme in a total volume of 400 μl of TS buffer are mixed with 200 μl of AdoMet (1 mg/ml), 200 μl of KI (1.2 M), and 20 μl of DTT (100 mM) in a 5-ml vial that is closed with a rubber stopper and an aluminum seal. Usually, the reaction is carried out at room temperature for 30 min for the recombinant enzyme and 1 hr for the native enzyme. Methyl iodide production is analyzed by using gas chromatography. After incubation, 1 ml of aliquot of headspace gas is collected and injected into a 6-foot Chromosorb 101 column (Varian) installed on a Varian 3700 Aerograph GC. The column temperature was 134°C, and the flow rate of the carrier gas (N2) was 30 ml/min. The instrument was calibrated with standard methyl halides, all obtained from Aldrich.
Synthesis of Methyl Chloride by E. coli.
Separate cultures of pETMCT-transformed E. coli cells (BL21) and pET22b (control) cells were induced with IPTG as described above. One milliliter of each cell culture was transferred to a 5-ml vial that contained 1 ml of LB and 2 M sodium chloride. The vials were closed with a rubber stopper and an aluminum seal, and the cells were allowed to continue to grow at 37°C for 4 hr. A 1-ml aliquot of headspace gas was then removed with a gas-tight Hamilton syringe and subjected to GC analysis for methyl chloride.
Cloning of MCT Genomic DNA.
Genomic DNA was isolated from live Batis maritima plants using the DNeasy plant mini kit (Qiagen). Full-length genomic DNA was generated by PCR using primers MCT5 and MCT3 under the following conditions: denaturation at 94°C for 30 sec, extension at 72°C for 90 sec, and annealing for 15 sec at 64°C for 5 cycles, 60°C for 5 cycles, 57°C for 5 cycles, 55°C for 30 cycles, and finally extension at 72°C for 7 min. The 1.2-kb PCR fragment was gel-purified, ligated into NdeI- and BamHI-digested pET 22b, and used to transform E. coli to ampicillin resistance. Independent clones containing inserts of the proper size were isolated, and the DNA sequences were determined.
RESULTS
Expression of MCT in E. coli.
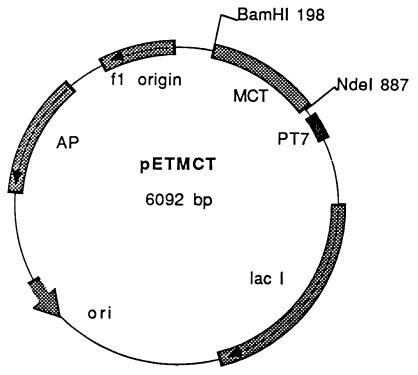
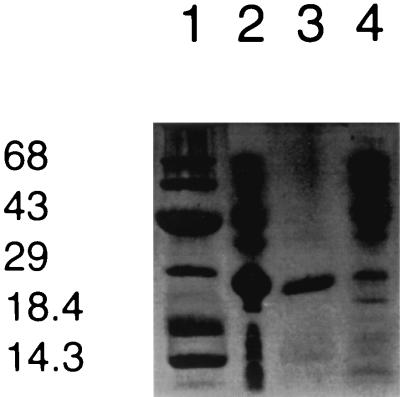
Fig. 1 shows the construct of the expression vector pETMCT. The expressed protein contains amino acid residues 1–229 of MCT, a mutation from Asn to Thr at residue 230, and an extra 21-aa sequence containing a His-6 tag (DPNSSSVDKL-AAALEHHHHHH) at the C terminus. The expressed recombinant methylase constitutes ≈10–15% of the total E. coli cellular proteins, and about 93% of the MCT protein is present in the inclusion body fraction. The remaining 7% of the enzyme is located in the soluble fraction. Denatured recombinant MCT is easily purified by separating the inclusion-body fraction from the soluble fraction. The denatured methylase can be solubilized in urea, and active enzyme can be generated by removing the urea by dialysis. The purity of the isolated recombinant enzyme was estimated to be ≈95%, and the molecular mass is ≈28 kDa as shown in Fig. 2. The calculated Mr of the recombinant MCT is 28,093.
Figure 1.
Construction of plasmid pETMCT. The expression plasmid pETMCT was prepared by inserting the NdeI/BamHI-digested PCR-amplified MCT gene into pET 22b (Novagen) that also had been digested with NdeI/BamHI.
Figure 2.
SDS/20% PAGE analysis of recombinant MCT. (Lane 1) Protein molecular mass markers (Novex) in kDa. (Lane 2) Total cellular proteins. (Lane 3) Recombinant MCT after separation from the soluble fraction and overnight dialysis. (Lane 4) Soluble fraction of cellular proteins.
Synthesis of Methyl Chloride by pETMCT-Transformed E. coli Cells.
Cultures of the pETMCT-transformed BL21and the pET 22b (control) cells were grown separately under identical conditions, and both were induced with IPTG as described in Materials and Methods. Aliquots of the transformed and control cell cultures were transferred to sealed tubes and grown for 4 hr in LB supplemented with 2 M sodium chloride. After incubation, an aliquot of the headspace gas was analyzed for methyl chloride. The rate of methyl chloride production by the transformed cells was 30–40 pmol⋅hr−1⋅ml−1 of cells. In contrast, there was no detectable amount of methyl chloride produced by the control cells.
Effect of Salts on Methyl Chloride Transferase.
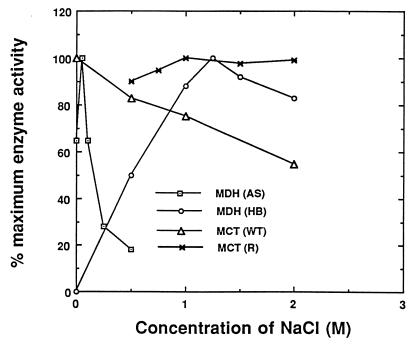
Fig. 3 shows the effect of NaCl on the activity of MCT (both wild-type and recombinant) and malate dehydrogenase from a halophytic plant (Atriplex spongiosa) (9) and a halobacterium (10). To conserve precious amounts of purified wild type MCT, the effect of sodium chloride on the activity of wild type MCTwas measured in the standard methyl iodide assay with varying concentrations of NaCl. The enzyme retains over 55% of its methyl iodide activity in 2 M NaCl. Because chloride is a substrate and thus is a competitive inhibitor of iodide, this 55% retention of activity reflects little or no inhibition by high salt. For recombinant MCT, which is available in plentiful amounts, methyl chloride production was directly measured at varying concentrations of NaCl. Two M sodium chloride had little effect on methyl chloride production by the recombinant methylase. Similarly, the halobacterium malate dehydrogenase is very stable and active in high concentrations of NaCl. In contrast, malate dehydrogenase from the halophyte, A. spongiosa, is very sensitive to NaCl and loses >80% of its activity in the presence of 0.5 M NaCl.
Figure 3.
The effect of salt on the activity of recombinant (R) and wild-type (WT) MCT and malate dehydrogenases from A. spongiosa (AS) and Halobacteriaum spp. (HB). The methyl iodide assay was used for analyzing the activity of native MCT, and the methyl chloride assay was used for recombinant MCT. The data for the MDH activity of A. spongiosa (9) is replotted from the original data by using the maximum activity obtained at 0.05 M NaCl as 100% activity. The data for the Halobacterium MDH (10) is replotted from the original by using the results from 0–2M NaCl.
The recombinant methylase also can tolerate high concentrations of ammonium sulfate (1.4 M) and urea (3.5 M). The activity of the recombinant methylase in 0.5 M and 1.0 M ammonium sulfate is ≈1.25-fold higher than in the absence of ammonium sulfate. Similarly, the MCT activity in 1, 2, and 3 M urea is ≈1.75-, 2-, and 1.5-fold higher than in the absence of urea.
Kinetic Analysis.
Km values for each of the substrates with both wild-type and recombinant enzymes are shown in Table 1. The Km values for Cl−, Br−, I−, and AdoMet with native MCT are 155 mM, 18.5 mM, 8.5 mM, and 29.4 μM, respectively. The Km values for Cl−, Br−, I−, and AdoMet with the recombinant enzyme are 100 mM, 25 mM, 6.5 mM, and 230 μM, respectively. The Km values for AdoMet and iodide with the recombinant methylase also were measured in the presence of 1 M urea. As shown in Table 1, the Km values in the presence of urea were reduced by approximately two-thirds. The Km value for AdoMet with the recombinant methylase is ≈8-fold higher than the Km with wild-type enzyme.
Table 1.
Kinetic parameters and pH optima for MCT
| Substrate |
km, mM
|
pH optima of wild-type MCT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wild-type MCT | Recombinant MCT | ||
| Cl | 155 | 100 | 6.2–6.8 |
| Br | 18.5 | 25 | 6.2 |
| I | 8.5 | 6.5 (2.8)* | 6.8–7.5 |
| AdoMet | 29.4 × 10−3 | 230 × 10−3 (70)* | |
Saturation kinetic measurements for chloride, bromide, and iodide were carried out at a constant AdoMet concentration with variable concentrations of halide anions. Saturation kinetic measurements for AdoMet were caried out at constant iodide concentrations.
The numbers in parentheses are Km values measured in the presence of 1 M urea.
The Km values for Cl−, Br−, I−, and AdoMet with halide/bisufide methyltransferase (11), a methylase enzyme from Brassica oleracea, are 85 mM, 29 mM, 1.3 mM, and 30 μM, indicating that these two enzymes are very similar. However, neither the wild-type nor the recombinant MCT enzyme from Ba. maritima catalyze the methylation of sulfide. Thus, although both the Br. olercea and Ba. maritima enzymes catalyze the methylation of halide anions, only the cabbage enzyme utilizes bisulfide as a methyl acceptor. It has been suggested that the cabbage enzyme functions in sulfur rather than halide metabolism in nonhalophytic plants.
Effect of pH on Methyl Halide Production by MCT.
The production of methyl chloride, methyl bromide, and methyl iodide by MCT was assayed over a broad range of pH values. The pH optimum for methyl chloride, methyl bromide, and methyl iodide production is 6.2–6.8, 6.2, and 6.8–7.5, respectively (see Table 1).
Cloning of Genomic DNA of MCT.
Fig. 4 shows the 1,264-nt sequence of the genomic DNA clone of MCT. By comparison with the cDNA sequence (7), the MCT gene was found to consist of eight exons and seven introns. As shown in Fig. 4, exons I, II, III, IV, V, VI, VII, and VIII consist of 103, 131, 87, 101, 100, 47, 82, and 39 nt, respectively, and introns I, II, III, IV, V, VI, and VII consist of 78, 93, 88, 78, 78, 93, and 66 nt, respectively. Introns I, II, III, IV, and V contain 12–28% more A/U than their adjacent exons, and introns VI and VII contain ≈8% more A/U than their adjacent exons. The average length of introns in the MCT gene is 82 nt, a length that is in the range of the average size of plant introns (12). All exon–intron splicing junction sequences follow the GT–AG rules (13).
Figure 4.
The nucleotide sequence of MCT genomic DNA. Nucleotide position 1 is assigned to the A of the ATG initiation codon. The deduced amino acid sequence for each exon is indicated. The intron sequences are underlinded.
DISCUSSION
A previous report from this laboratory documented the isolation of MCT from Ba. maritima and the preparation of a cDNA clone of the MCT gene (7). The deduced amino acid sequence of MCT contains two motifs that are conserved among small molecule (14) and protein (15) methyltransferases and one motif that is conserved among the DNA N-6- and DNA N-4-methyltransferases (16). These results indicate that MCT is a typical AdoMet-dependent methyltransferase. The molecular mass of the protein encoded by the cDNA clone is ≈3.3 kDa greater than the molecular mass of the isolated native enzyme. One of the objectives of this study was to compare the activity of a full-length recombinant methyl chloride transferase with the shorter purified enzyme. For isolation purposes, a His-6 tag was added to the C terminus of the recombinant MCT. This step actually proved to be unnecessary because most of the expressed enzyme is found an inclusion body fraction, and denatured recombinant MCT can be easily isolated from the transformed cells. After renaturation, the recombinant enzyme was found to be active and able to catalyze the methylation of halides in a manner identical to that of the wild-type enzyme. The Km values for chloride, bromide, and iodide for the recombinant enzyme are very close to those determined for the native enzyme. However, the Km value for AdoMet is ≈8-fold higher for the recombinant MCT. These results indicate that the purified native enzyme binds AdoMet with higher affinity. One possible explanation is that the native enzyme is synthesized as a proenzyme and subsequently processed to a mature species. In this scenario, the conversion of the proenzyme to native enzyme could actually be a step in the regulation of MCT activity in halophytic plants. However, as previously indicated, the possibility remains that the isolated enzyme is subjected to limited proteolysis during isolation and the native in vivo species of the enzyme is actually the full length version.
Salt is an inescapable and persistent problem for halophytic plants. Water stress imparted by high salinity is a major detriment and constitutes the most stringent factor in limiting plant distribution and productivity (17). Thus, improving salt tolerance in crop plants remains an urgent issue in plant molecular biology.
Halophytic plants have evolved a number of strategies that enable them to grow under high-saline conditions. These strategies include changes in photosynthetic activity, alterations in membrane structure, exclusion and/or pumping of salt, the accumulation and partitioning of ions, an increase in intracellular organic solutes, and precocious entry into a reproductive phase and senescence (18). Clearly, some halophytes possess unique adaptations, such as the development of salt glands, to alleviate the deleterious effects of high ion concentrations. However, intrinsic cellular processes also must make major contributions to the capacity of the plants for salt adaptation. It is not clear to what extent halophytes have evolved unique cellular determinants that make them more salt-tolerant than glycophytes.
One approach to understanding the mechanisms of salt adaptation at the molecular level is to identify the responsible genes. Genes that are up-regulated by sodium chloride have been studied (19–22). Zhu et al. (20) have identified nine groups of genes that are possibly involved in plant osmotic stress adaptation. However, the majority of these genes encode proteins that have essential housekeeping functions. Apparently, these gene products are required to a greater extent during salt stress or are induced as part of the general stress response. Thus, this group of salt-regulated genes has little likelihood of actually being involved in an adaptive response to high salt (19–22).
MCT is distinguished from other halophytic plant enzymes by virtue of its high salt tolerance. Both the wild-type and the recombinant enzymes function at high concentrations of sodium chloride. This is a very unusual activity for a halophytic plant enzyme. Unlike halophytic bacteria, which can grow in 4–5 M salt and contain many enzymes that have an absolute high ion concentration requirement (23), halophytic plants apparently have not evolved high-salt-tolerant/requiring enzyme systems. Flowers (24) has shown that glucose 6-phosphate and malate dehydrogeanase from Sudaeda maritima are 60–70% inhibited in the presence of 333 mM NaCl. Greenway and Osmond (9) report that malate dehydrogenase, aspartate transaminase, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, and isocitrate dehydrogenase from A. spongiosa, Salicornia australis, and the glycophyte, Phaseolus vulgaris, show great similarity in terms of their in vitro NaCl sensitivity despite the great differences in the salt tolerance of the plants from which they are derived. In general, enzymes from halophytic plants, like enzymes from glycophytic plants, are very sensitive to salts (see Fig. 3). The salt tolerance of MCT resembles more that of enzymes from halophytic bacteria. However, unlike the bacterial enzymes, MCT does not require high salt, it merely tolerates high salt conditions.
We have previously suggested that MCT may play a significant role in salt metabolism in halophytic plants (7). MCT is able to transform chloride ion into a small, neutral molecule that is able to diffuse through cell membranes. MCT thus provides a mechanism for halophytic plants to regulate their internal chloride ion concentrations. The findings that pETMCT-transformed E. coli cells can synthesize methyl chloride in vivo when they are grown in high-NaCl medium plus the fact that MCT is a salt-tolerant methylase lends support to this hypothesis.
In summary, Ba. maritima methyl chloride transferase is a novel enzyme and possibly is involved in the regulation of intracellular chloride ion concentrations in halophytic plants. The availability of the MCT gene allows this hypothesis to be tested directly via transformation of a suitable nonhalophytic plant.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by a grant from the National Institutes of Health (GM07768).
ABBREVIATIONS
- MCT
methyl chloride transferase
- AdoMet
S-adenosyl-l-methionine
- MALDI
matrix-assisted laser-desorption ionization
Footnotes
Data deposition: The sequence reported in this paper has been deposited in the GenBank database (accession no. AF109128).
References
- 1.Rasmussen R A, Rasmussen L E, Kahlil M A K, Dalluge R W. J Geophys Res. 1980;85:7350–7353. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Harper D B. Nature (London) 1985;315:55–57. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Wuuosmaa A, Hager L P. Science. 1990;249:160–162. doi: 10.1126/science.2371563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Wuuosmaa A. Ph.D. thesis. Urbana, IL: Univ. of Illinois; 1994. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Gschwend P W, MacFarlane J K, Newman K A. Science. 1985;227:1033–1035. doi: 10.1126/science.227.4690.1033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Prather M J, Watson R T. Nature (London) 1990;344:729–734. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ni X, Hager L P. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998;95:12866–12871. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.22.12866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Bradford M M. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Greenway H, Osmond C B. Plant Physiol. 1972;49:256–259. doi: 10.1104/pp.49.2.256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Mevarech M, Newmann E. Biochemistry. 1977;16:3786–3792. doi: 10.1021/bi00636a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Attiech J M, Hanson A D, Saini H S. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:9250–9257. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.16.9250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Simpson G G, Filipowicz W. Plant Mol Biol. 1996;32:1–41. doi: 10.1007/BF00039375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Breathnach R, Chambon P. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–398. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Gomi T, Tanihara K, Data T, Fujioka M. Int J Biochem. 1992;24:1639–1649. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(92)90182-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kagan R M, Clarke S. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1994;310:417–427. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1994.1187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Malone T, Blumenthal R M, Cheng X. J Mol Biol. 1995;253:618–632. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1995.0577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Boyer J S. Science. 1982;218:442–448. doi: 10.1126/science.218.4571.443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Jefferies R L. Bioscience. 1981;31:42–46. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Niu X, Pardo J, Bressan R A, Hasegawa P M. Plant Physiol. 1995;109:735–742. doi: 10.1104/pp.109.3.735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Zhu J-K, Hasegawa P M, Bressan R A. Crit Rev Plant Sci. 1997;16:253–277. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Bohnert H J, Nelson D E, Jensen R J. Plant Cell. 1995;7:1099–1111. doi: 10.1105/tpc.7.7.1099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Serrano R, Gaxiola R. Crit Rev Plant Sci. 1994;13:121–138. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Eisenberg H, Mevarech M, Zaccai G. Adv Protein Chem. 1992;43:1–61. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60553-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Flowers T J. J Exp Bot. 1972;23:310–321. [Google Scholar]