Abstract
We discuss published molecular evidence concerning the relationship of man to African apes and Old World monkeys. Quantitative comparisons of their serum albumins, transferrins, hemoglobins, and DNA show that man is genetically much more similar to the African apes than to the Old World monkeys.
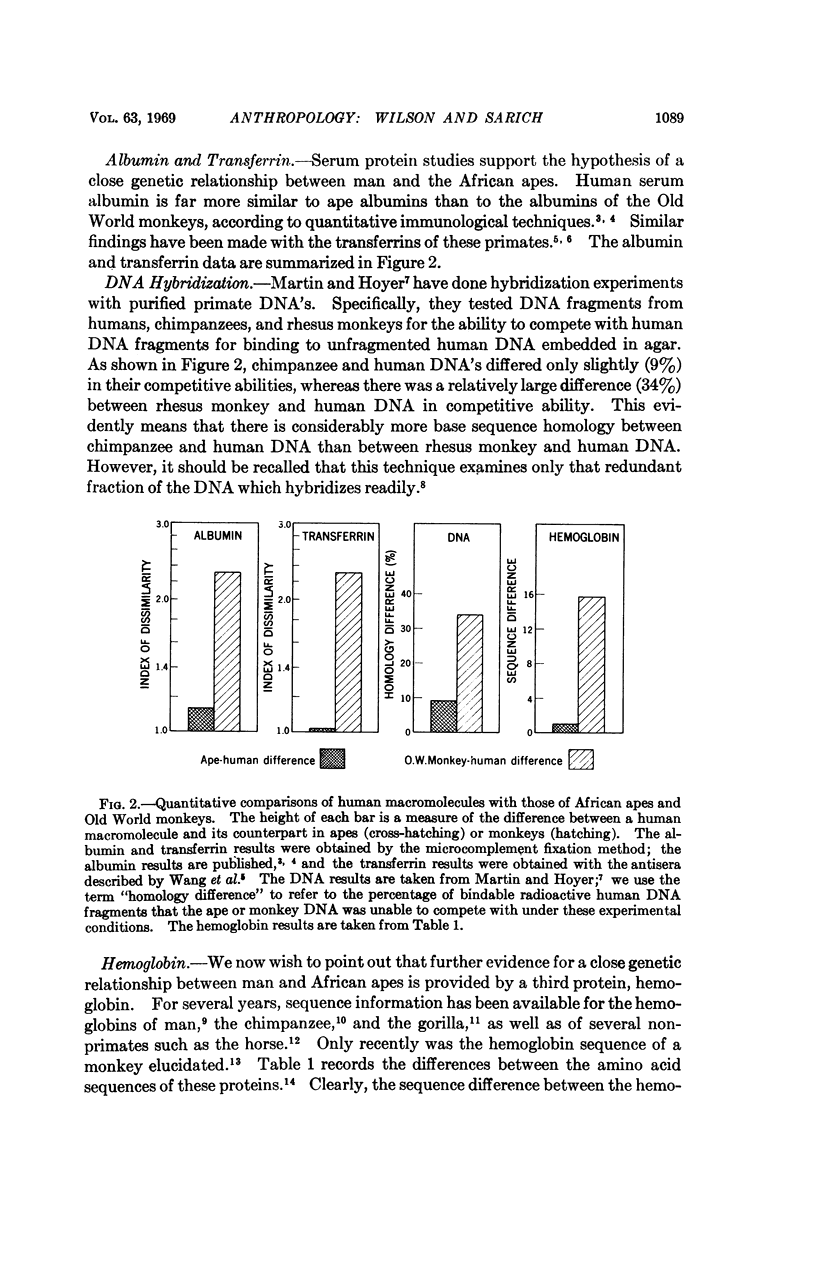
The amino acid sequences of hemoglobins from humans, chimpanzees, gorillas, and rhesus monkeys are consistent with the hypothesis that the probability of an amino acid substitution occurring in a given interval of time is the same for every hemoglobin lineage. This allows the use of these data as a hemoglobin evolutionary clock, just as we have previously done with the albumins. It is shown that concordance exists between the hemoglobin and albumin results and that both support the suggestion that the human lineage diverged from that leading to the African apes far more recently than is generally supposed. Considering both the albumin and hemoglobin data, we would set the most probable date at 4 to 5 million years.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRAUNITZER G., GEHRING-MUELLER R., HILSCHMANN N., HILSE K., HOBOM G., RUDLOFF V., WITTMANN-LIEBOLD B. [The structure of normal adult human hemoglobins]. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1961 Sep 20;325:283–286. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1961.325.1.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRAUNITZER G., MATSUDA G. Primary structure of the alpha-chain from horse hemoglobin. J Biochem. 1963 Mar;53:262–263. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a127691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton W., Cox J. M., Perutz M. F. Structure and function of haemoglobin. IV. A three-dimensional Fourier synthesis of horse deoxyhaemoglobin at 5.5 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1968 Apr 14;33(1):283–297. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90294-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britten R. J., Kohne D. E. Repeated sequences in DNA. Hundreds of thousands of copies of DNA sequences have been incorporated into the genomes of higher organisms. Science. 1968 Aug 9;161(3841):529–540. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3841.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hafleigh A. S., Williams C. A., Jr Antigenic correspondence of serum albumins among the primates. Science. 1966 Mar 25;151(3717):1530–1535. doi: 10.1126/science.151.3717.1530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JUKES T. H. SOME RECENT ADVANCES IN STUDIES OF THE TRANSCRIPTION OF THE GENETIC MESSAGE. Adv Biol Med Phys. 1963;9:1–41. doi: 10.1016/b978-1-4832-3108-2.50005-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura M. Evolutionary rate at the molecular level. Nature. 1968 Feb 17;217(5129):624–626. doi: 10.1038/217624a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin M. A., Hoyer B. H. Adenine plus thymine and guanine plus cytosine enriched fractions of animal DNA's as indicators of polynucleotide homologies. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jul 14;27(1):113–129. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90355-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda G., Maita T., Takei H., Ota H., Yamaguchi M. The primary structure of adult hemoglobin from Macaca mulatta moneky. J Biochem. 1968 Aug;64(2):279–282. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore G. W., Goodman M. A set theoretical approach to immunotaxonomy: analysis of species comparisons in modified Ochterlony plates. Bull Math Biophys. 1968 Jun;30(2):279–289. doi: 10.1007/BF02476695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolan C., Margoliash E. Comparative aspects of primary structures of proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1968;37:727–790. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.37.070168.003455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilbeam D. The earliest hominids. Nature. 1968 Sep 28;219(5161):1335–1338. doi: 10.1038/2191335a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rifkin D., Konigsberg W. The characterization of the tryptic peptides from the hemoglobin of the chimpanzee (Pan troglodytes). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jul 8;104(2):457–461. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(65)90350-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarich V. M., Wilson A. C. Immunological time scale for hominid evolution. Science. 1967 Dec 1;158(3805):1200–1203. doi: 10.1126/science.158.3805.1200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarich V. M., Wilson A. C. Rates of albumin evolution in primates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jul;58(1):142–148. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.1.142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. C., Shuster J., Epstein A., Fudenberg H. H. Evolution of antigenic determimants of transferrin and other serum proteins in primates. Biochem Genet. 1968 Mar;1(4):347–358. doi: 10.1007/BF00491490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



