Abstract
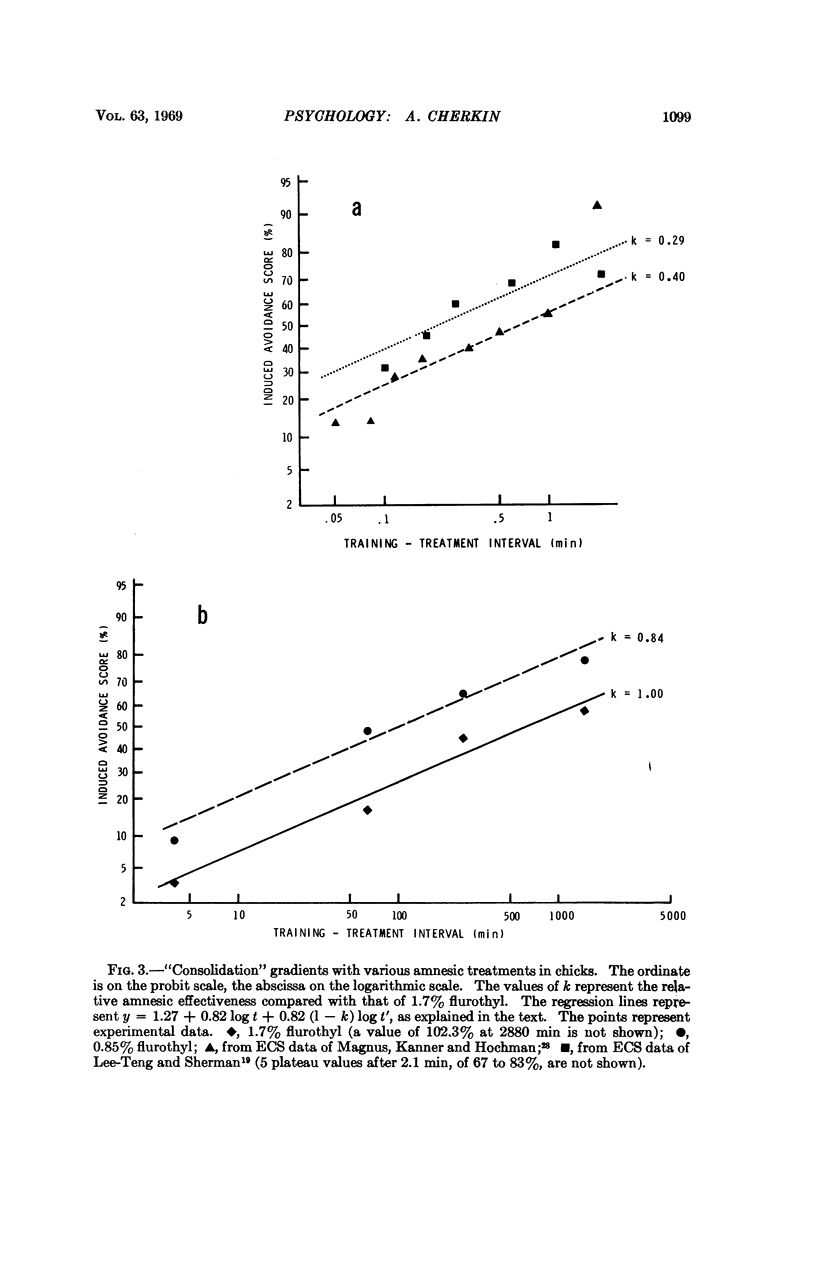
The consolidation theory states that with the passage of time the engram of a recent learning experience grows increasingly resistant to disruption by amnesic treatment. The time required to reach complete resistance (“consolidation time”) is a controversial issue; current estimates range from 101 to 105 seconds. The present study suggests a parsimonious interpretation of the divergence, namely, that weak amnesic treatments fail to block memory consolidation but do slow its rate, so that post-treatment consolidation inflates the retention scores measured 24 hours later and leads to variably shortened “consolidation times.”
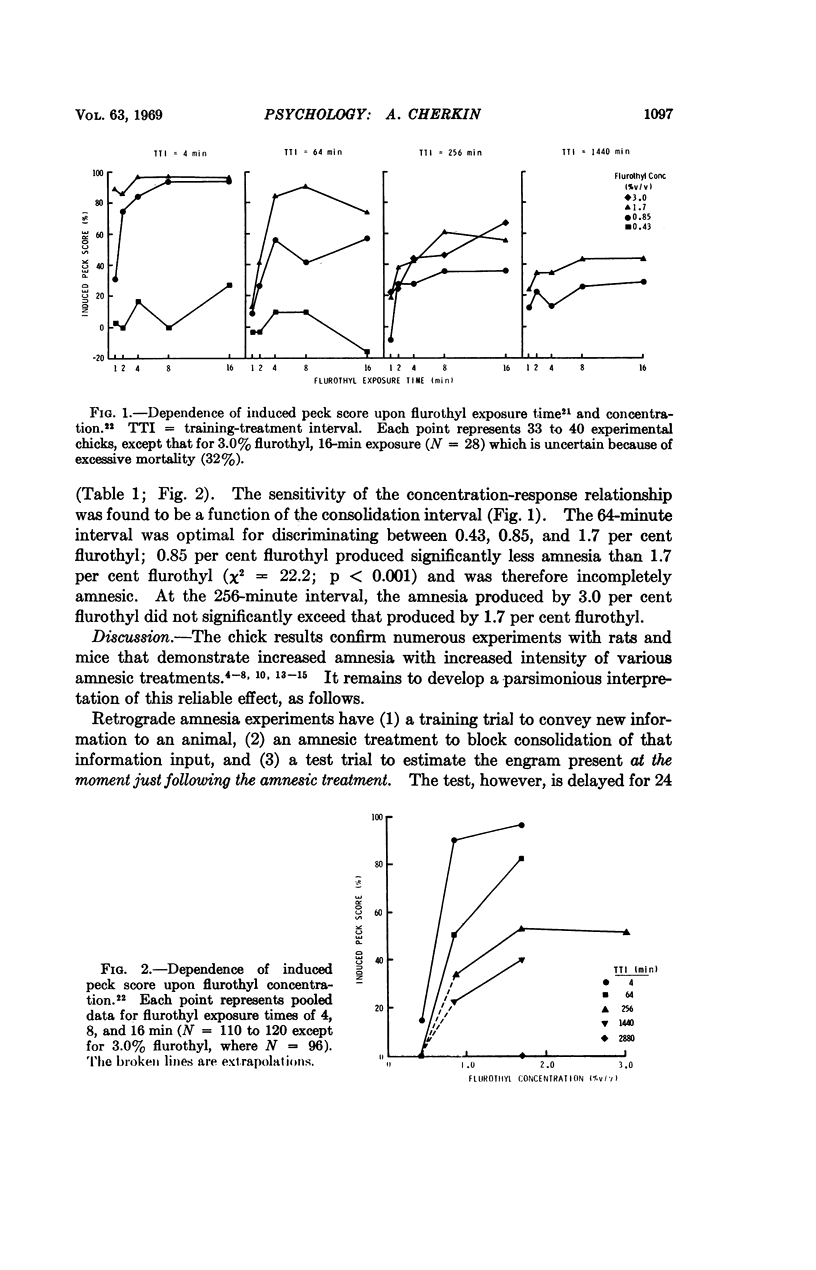
This study utilized 2880 neonate chicks trained in a one-trial avoidance paradigm. Retrograde amnesia was induced by treatment with flurothyl (CF3CH2-OCH2CF3) vapor. Apparent “consolidation times” determined by conventional data analysis varied widely as a function of flurothyl concentration and exposure time, ranging from 4 minutes under weak amnesic conditions (0.85% flurothyl; 1-min exposure) to 24 hours under strong conditions (1.7% flurothyl; 8-min exposure). With 1.7% flurothyl, the consolidation half-time was found to be 9.8 hours.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alpern H. P., Kimble D. P. Retrograde amnesic effects of diethyl ether and bis(trifluoroethyl) ether. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1967 Feb;63(1):168–171. doi: 10.1037/h0020841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alpern H. P., McGaugh J. L. Retrograde amnesia as a function of duration of electroshock stimulation. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1968 Apr;65(2):265–269. doi: 10.1037/h0025536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohdanechky Z., Kopp R., Jarvik M. E. Comparison of ECS and flurothyl-induced retrograde amnesia in mice. Psychopharmacologia. 1968;12(2):91–95. doi: 10.1007/BF00401537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth D. A. Vertebrate brain ribonucleic acids and memory retention. Psychol Bull. 1967 Sep;68(3):149–177. doi: 10.1037/h0024906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHEVALIER J. A. PERMANENCE OF AMNESIA AFTER A SINGLE POSTTRIAL ELECTROCONVULSIVE SEIZURE. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1965 Feb;59:125–127. doi: 10.1037/h0021605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHOROVER S. L., SCHILLER P. H. SHORT-TERM RETROGRADE AMNESIA IN RATS. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1965 Feb;59:73–78. doi: 10.1037/h0021606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherkin A. Toward a quantitative view of the engram. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jan;55(1):88–91. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.1.88. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch J. A. The physiological basis of memory. Annu Rev Psychol. 1969;20:85–104. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ps.20.020169.000505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLICKMAN S. E. Perseverative neural processes and consolidation of the memory trace. Psychol Bull. 1961 May;58:218–233. doi: 10.1037/h0044212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herz M. J., Peeke H. V., Zinkin S., Miller A. J. Permanence of retrograde amnesia produced by electroconvulsive shock. Science. 1967 Jun 9;156(3780):1396–1397. doi: 10.1126/science.156.3780.1396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvik M. E., Kopp R. Transcorneal electroconvulsive shock and retrograde amnesia in mice. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1967 Dec;64(3):431–433. doi: 10.1037/h0025199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kesner R. P., Doty R. W. Amnesia produced in cats by local seizure activity initiated from the amygdala. Exp Neurol. 1968 May;21(1):58–68. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(68)90034-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee-Teng E. Retrograde amnesia in relation to subconvulsive and convulsive currents in chicks. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1969 Feb;67(2):135–139. doi: 10.1037/h0026791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee-Teng E., Sherman S. M. Memory consolidation of one-trial learning in chicks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Sep;56(3):926–931. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.3.926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis D. J., Misanin J. R., Miller R. R. Recovery of memory following amnesia. Nature. 1968 Nov 16;220(5168):704–705. doi: 10.1038/220704a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGaugh J. L., Alpern H. P. Effects of Electroshock on Memory: Amnesia without Convulsions. Science. 1966 Apr 29;152(3722):665–666. doi: 10.1126/science.152.3722.665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. J. Variations in retrograde amnesia with parameters of electroconvulsive shock and time of testing. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1968 Aug;66(1):40–47. doi: 10.1037/h0025965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieschulz O. Experimentelle retrograde Amnesien bei Mäusen. Arzneimittelforschung. 1967 Sep;17(9):1151–1155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paolino R. M., Quatermainquartermain D., Miller N. E. Different temporal gradients of retrograde amnesia produced by carbon dioxide anesthesia and electroconvulsive shock. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1966 Oct;62(2):270–274. doi: 10.1037/h0023676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quartermain D., Paolino R. M., Miller N. E. A brief temporal gradient of retrograde amnesia independent of situational change. Science. 1965 Sep 3;149(3688):1116–1118. doi: 10.1126/science.149.3688.1116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddell W. I. Effect of electroconvulsive shock: permanent or temporary retrograde amnesia. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1969 Feb;67(2):140–144. doi: 10.1037/h0026794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEISSMAN A. EFFECT OF ANTICONVULSANT DRUGS ON ELECTROCONVULSIVE SHOCK-INDUCED RETROGRADE AMNESIA. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1965 Mar;154:122–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEISSMAN A. EFFECT OF ELECTROCONVULSIVE SHOCK INTENSITY AND SEIZURE PATTERN ON RETROGRADE AMNESIA IN RATS. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1963 Oct;56:806–810. doi: 10.1037/h0045742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkin S., Miller A. J. Recovery of memory after amnesia induced by electroconvulsive shock. Science. 1967 Jan 6;155(3758):102–104. doi: 10.1126/science.155.3758.102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



