Abstract
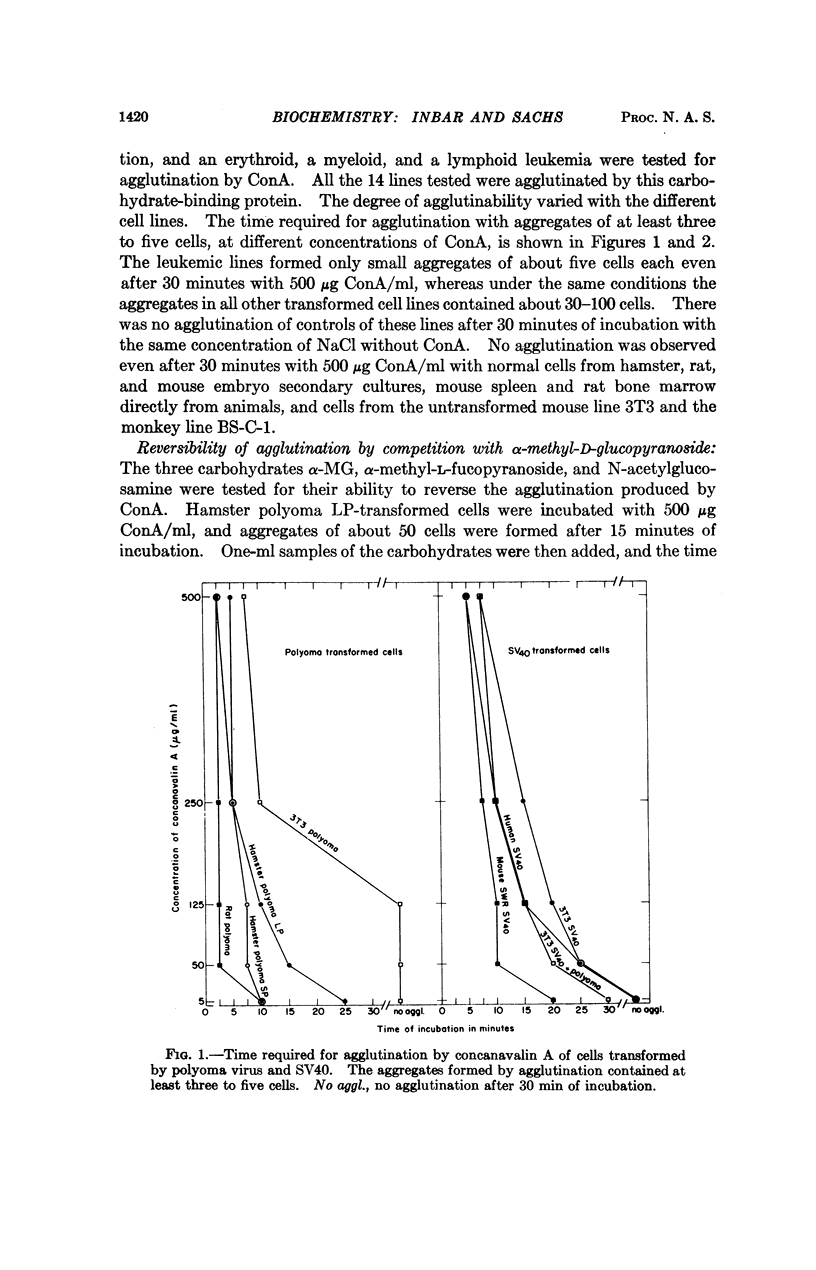
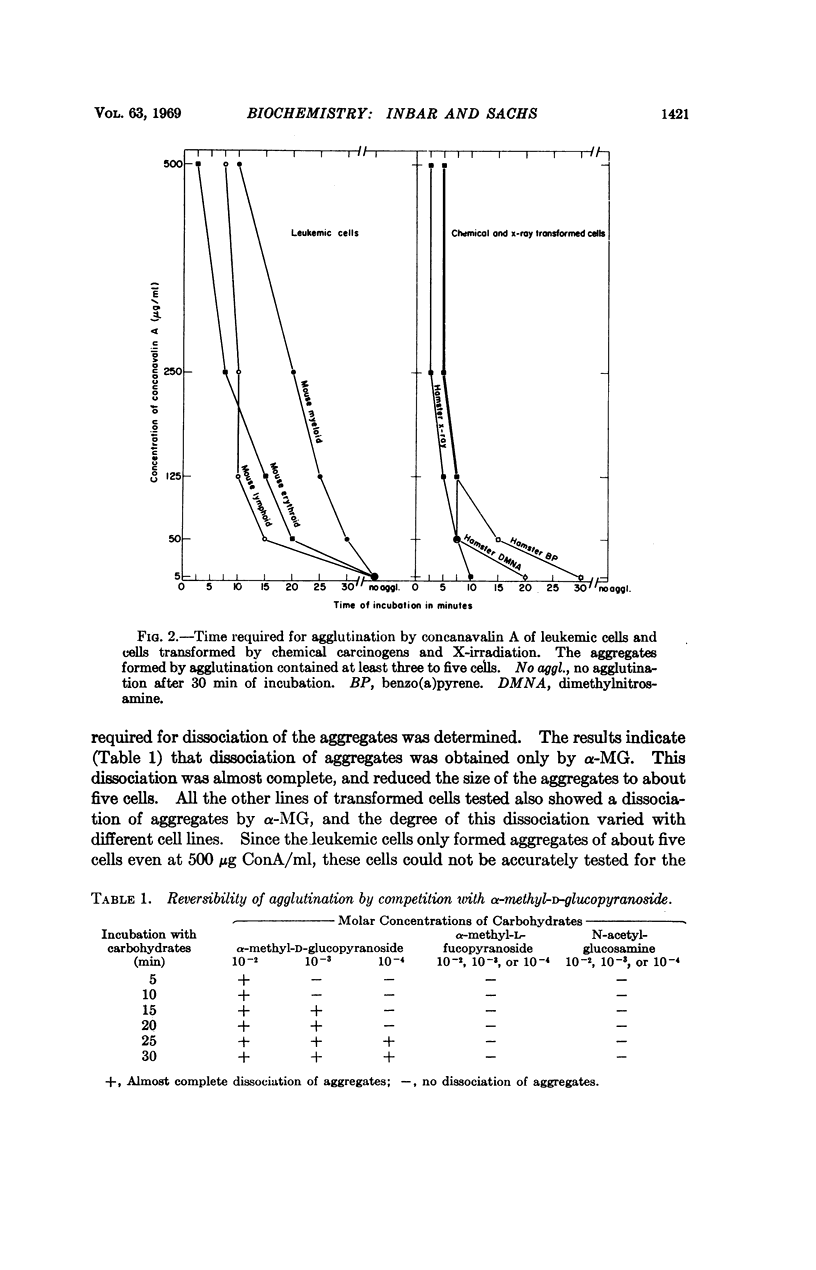
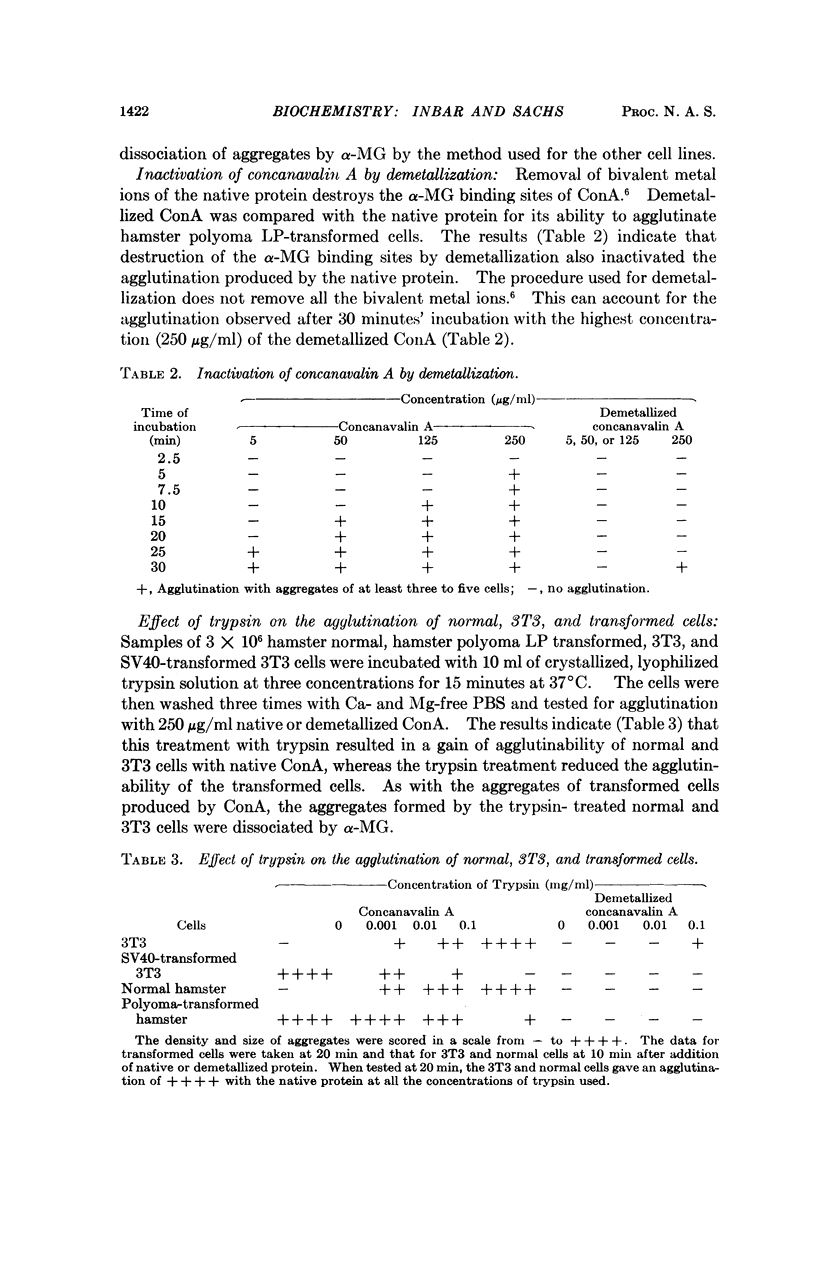
It has been shown that the carbohydrate-binding protein concanavalin A (ConA) can agglutinate leukemic cells and cells transformed by polyoma virus, simian virus 40, chemical carcinogens, and X-irradiation. This protein did not agglutinate normal cells under the same conditions. The agglutination was reversed by competition with α-methyl-D-glucopyranoside (α-MG), a carbohydrate that strongly binds to ConA, but not by the carbohydrates α-methyl-L-fucopyranoside or N-acetylglucosamine, with no binding or weak binding to ConA. Destruction of the α-MG binding sites of the native protein by removal of bivalent metal ions abolished the agglutination produced by the native protein. The treatment of cells with trypsin resulted in the agglutination of normal cells by ConA and a decrease of agglutinability of transformed cells. When nonagglutinating untransformed 3T3 cells were infected with simian virus 40 and normal rat cells were infected with polyoma virus, the infected cells became agglutinable several days after virus infection. The percentage of cells agglutinated, about 50 per cent, was much higher than the percentage of cells hereditarily transformed. The results indicate that the surface membrane of transformed cells contains sites that interact with the α-MG binding sites of ConA, that such sites can be found on the surface membrane of normal cells after treatment with trypsin, and that the change in the surface structure from normal to transformed occurs in cells that are abortively transformed.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AUB J. C., TIESLAU C., LANKESTER A. REACTIONS OF NORMAL AND TUMOR CELL SURFACES TO ENZYMES. I. WHEAT-GERM LIPASE AND ASSOCIATED MUCOPOLYSACCHARIDES. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Oct;50:613–619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.4.613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aub J. C., Sanford B. H., Cote M. N. Studies on reactivity of tumor and normal cells to a wheat germ agglutinin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Aug;54(2):396–399. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.2.396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berwald Y., Sachs L. In vitro transformation of normal cells to tumor cells by carcinogenic hydrocarbons. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1965 Oct;35(4):641–661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borek C., Sachs L. In vitro cell transformation by x-irradiation. Nature. 1966 Apr 16;210(5033):276–278. doi: 10.1038/210276a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger M. M. A difference in the architecture of the surface membrane of normal and virally transformed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Mar;62(3):994–1001. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.3.994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger M. M. Isolation of a receptor complex for a tumor specific agglutinin from the neoplastic cell surface. Nature. 1968 Aug 3;219(5153):499–500. doi: 10.1038/219499a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDSTEIN I. J., HOLLERMAN C. E., SMITH E. E. PROTEIN-CARBOHYDRATE INTERACTION. II. INHIBITION STUDIES ON THE INTERACTION OF CONCANAVALIN A WITH POLYSACCHARIDES. Biochemistry. 1965 May;4:876–883. doi: 10.1021/bi00881a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershon D., Sachs L., Winocour E. The induction of cellular DNA synthesis by simian virus 40 in contact-inhibited and in x-irradiated cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Sep;56(3):918–925. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.3.918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakomori S. I., Teather C., Andrews H. Organizational difference of cell surface "hematoside" in normal and virally transformed cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Nov 25;33(4):563–568. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90332-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huberman E., Salzberg S., Sachs L. The in vitro induction of an increase in cell multiplication and cellular life span by the water-soluble carcinogen dimethylnitrosamine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jan;59(1):77–82. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inbar M., Sachs L. Structural difference in sites on the surface membrane of normal and transformed cells. Nature. 1969 Aug 16;223(5207):710–712. doi: 10.1038/223710a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalb A. J., Levitzki A. Metal-binding sites of concanavalin A and their role in the binding of alpha-methyl d-glucopyranoside. Biochem J. 1968 Oct;109(4):669–672. doi: 10.1042/bj1090669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paran M., Ichikawa Y., Sachs L. Production of the inducer for macrophage and granulocyte colonies by leukemic cells. J Cell Physiol. 1968 Dec;72(3):251–254. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040720313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paran M., Sachs L. The continued requirement for inducer for the development of macrophage and granulocyte colonies. J Cell Physiol. 1968 Dec;72(3):247–250. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040720312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pluznik D. H., Sachs L. The cloning of normal "mast" cells in tissue culture. J Cell Physiol. 1965 Dec;66(3):319–324. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030660309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinowitz Z., Sachs L. Reversion of properties in cells transformed by polyoma virus. Nature. 1968 Dec 21;220(5173):1203–1206. doi: 10.1038/2201203a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs L. A theory on the mechanism of carcinogenesis by small deoxyribonucleic acid tumour viruses. Nature. 1965 Sep 18;207(5003):1272–1274. doi: 10.1038/2071272a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoker M. Abortive transformation by polyoma virus. Nature. 1968 Apr 20;218(5138):234–238. doi: 10.1038/218234a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumner J. B., Howell S. F. Identification of Hemagglutinin of Jack Bean with Concanavalin A. J Bacteriol. 1936 Aug;32(2):227–237. doi: 10.1128/jb.32.2.227-237.1936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINOCOUR E., SACHS L. Tumor induction by genetically homogeneous lines of polyoma virus. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1961 Mar;26:737–753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yariv J., Kalb A. J., Levitzki A. The interaction of concanavalin A with methyl alpha-D-glucopyranoside. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Sep 3;165(2):303–305. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(68)90063-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


