Full text
PDF

















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borman E. K., Stuart C. A., Wheeler K. M. Taxonomy of the Family Enterobacteriaceae. J Bacteriol. 1944 Sep;48(3):351–367. doi: 10.1128/jb.48.3.351-367.1944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EWING W. H., EDWARDS P. R., HUCKS M. C. Thermolabile antigens of Shigella boydii 2 cultures with special reference to an encapsulated culture. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1951 Oct;78(1):100–105. doi: 10.3181/00379727-78-18988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EWING W. H. Shigella grouping antiserums. J Lab Clin Med. 1950 Sep;36(3):471–472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
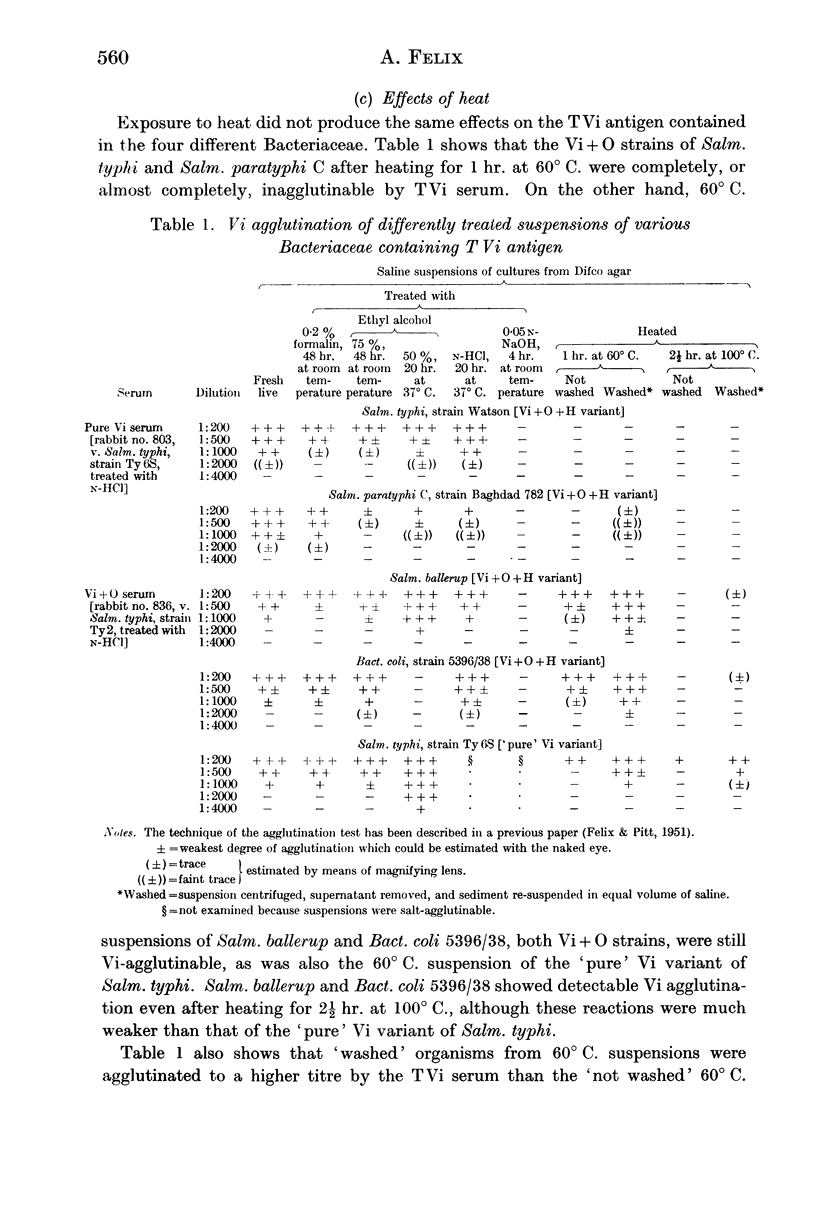
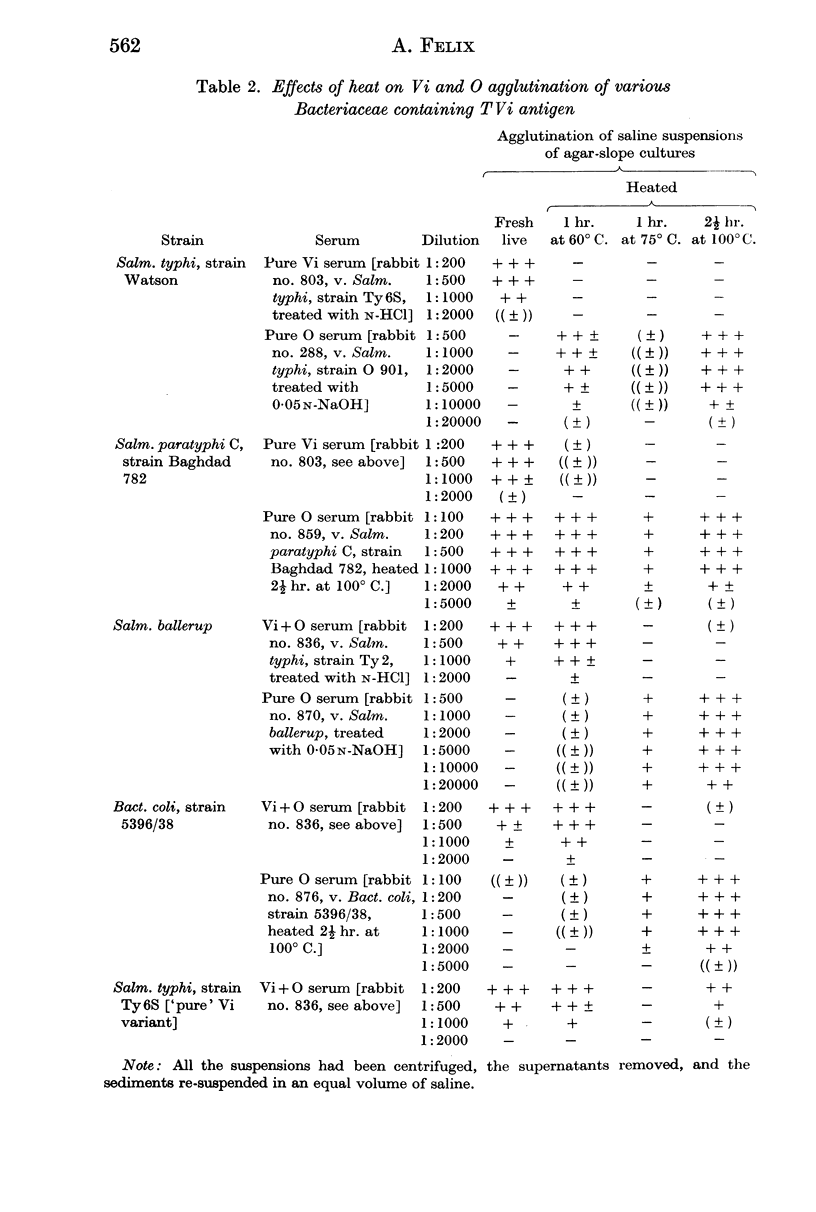
- FELIX A. The Vi antigen of Salmonella paratyphi A. J Hyg (Lond) 1952 Dec;50(4):540–549. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400019793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELIX A. The Vi antigen of Salmonella paratyphi B. J Hyg (Lond) 1952 Dec;50(4):550–557. doi: 10.1017/s002217240001980x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
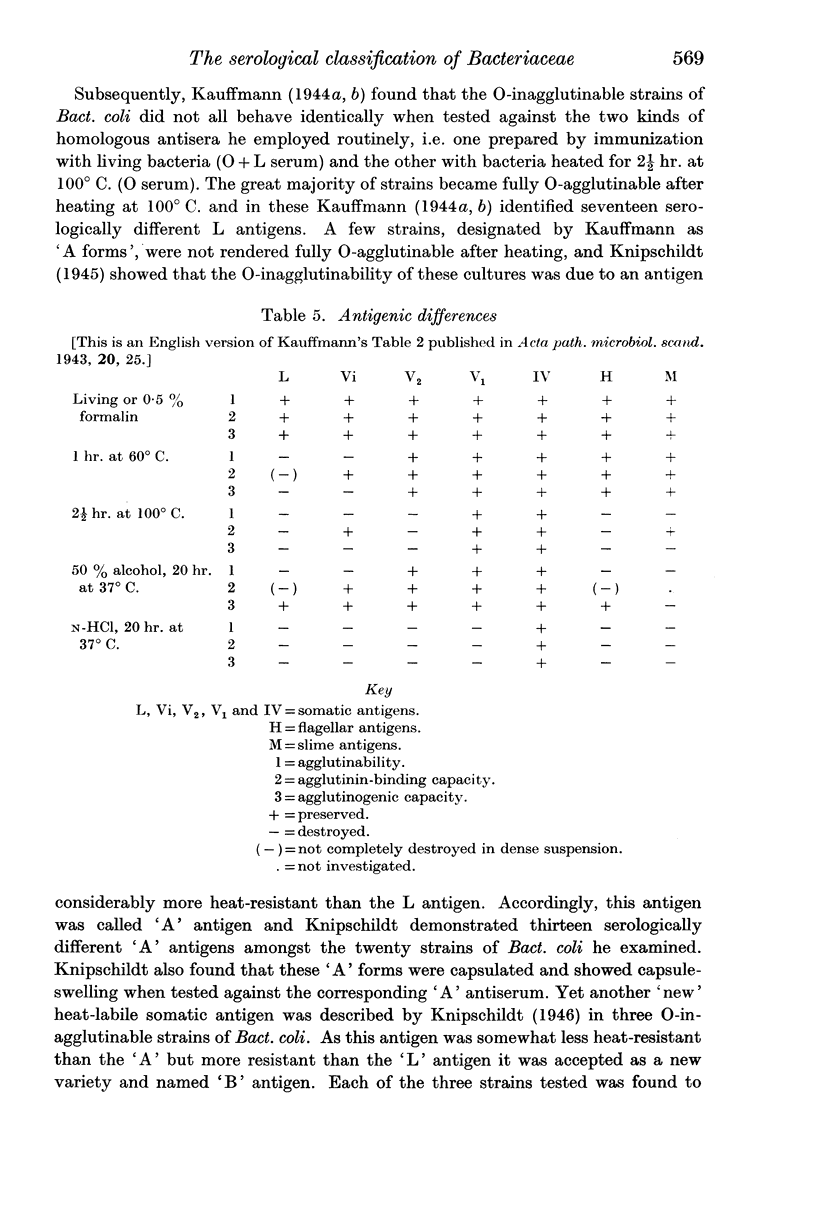
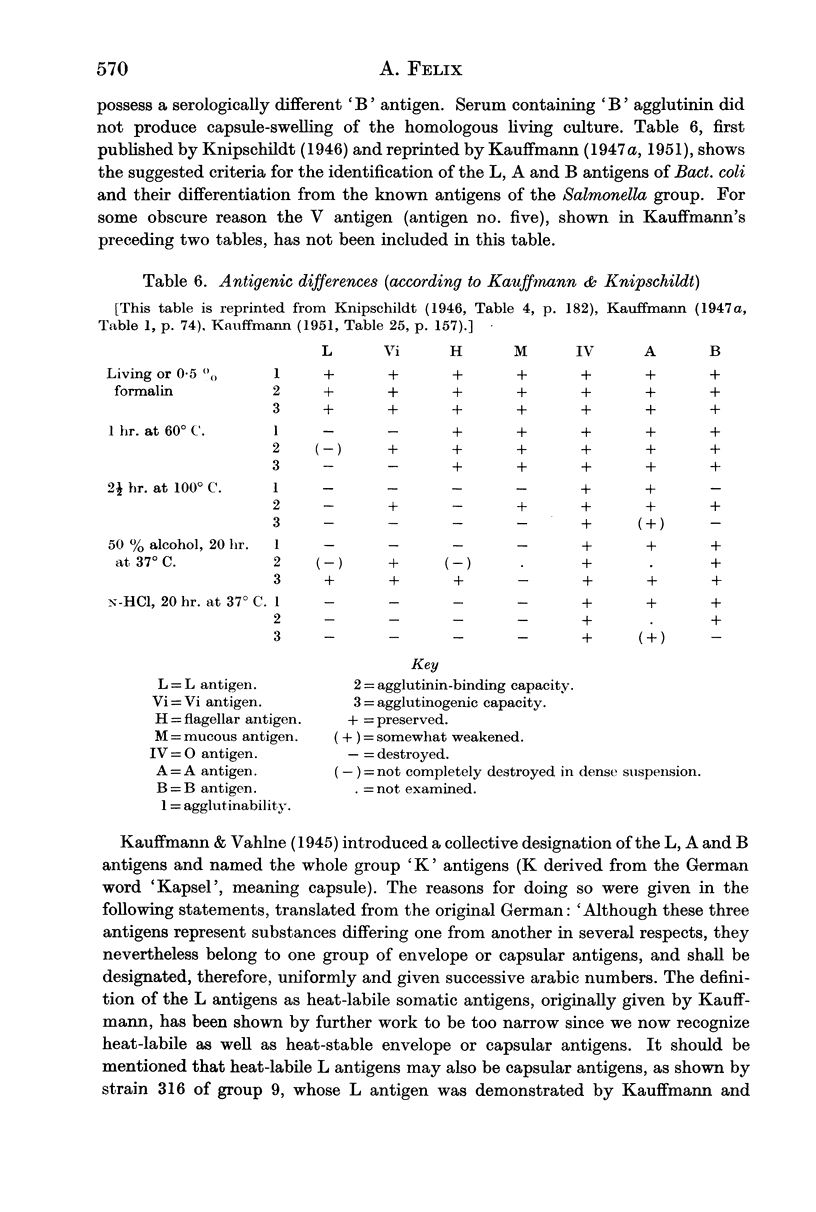
- FELIX A. The properties of different Salmonella Vi antigens. J Hyg (Lond) 1952 Dec;50(4):515–539. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400019781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILES C., SANGSTER G., SMITH J. Epidemic gastro-enteritis of infants in Aberdeen during 1947. Arch Dis Child. 1949 Mar;24(117):45–53. doi: 10.1136/adc.24.117.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENRIKSEN S. D. Cross-reacting M-antigens in Escherichia coli and Salmonella paratyphi B. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1950;27(1):107–109. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1950.tb05199.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENRIKSEN S. D. Serological reactivity of mucoid strains of Escherichia coli. J Immunol. 1949 Jul;62(3):271–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOSEPHSEN J. O., HENRIKSEN S. D. On the cross-reaction between the M-antigens of Salmonella and Escherichia. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1951;28(4):343–351. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1951.tb03700.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JUDE A., NICOLLE P. Conditions thermiques différentes pour la production de l'antigène Vi par quelques entérobactériacées. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1952 May 12;234(20):2028–2030. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANDY M., WEBSTER M. E. Studies on Vi antigen. III. Immunological properties of purified Vi antigen derived from Escherichia coli 5396/38. J Immunol. 1952 Aug;69(2):143–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luippold G. F. ANTITYPHOID ACTIVITY OF Vi ANTIGEN FROM EXTRA-GENERIC SOURCES. Science. 1944 Jun 16;99(2581):497–498. doi: 10.1126/science.99.2581.497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NICOLLE P., JUDE A. Estimation quantitative de l'antigene Vi élabore par quelques entérobacteriacées cultivées a differentes températures. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1952 Jun 4;234(23):2313–2315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERCH B. Capsular swelling of Salmonella M forms and their antigenic relationships to Klebsiella capsules. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1950;27(4):565–571. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1950.tb04928.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH J. The association of certain types (alpha and beta) of Bact. coli with infantile gastro-enteritis. J Hyg (Lond) 1949 Sep;47(3):221–226. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400014522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR J., POWELL B. W., WRIGHT J. Infantile diarrhoea and vomiting; a clinical and bacteriological investigation. Br Med J. 1949 Jul 16;2(4619):117–125. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.4619.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEBSTER M. E., LANDY M., FREEMAN M. E. Studies on Vi antigen. II. Purification of Vi antigen from Escherichia coli 5395/38. J Immunol. 1952 Aug;69(2):135–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


