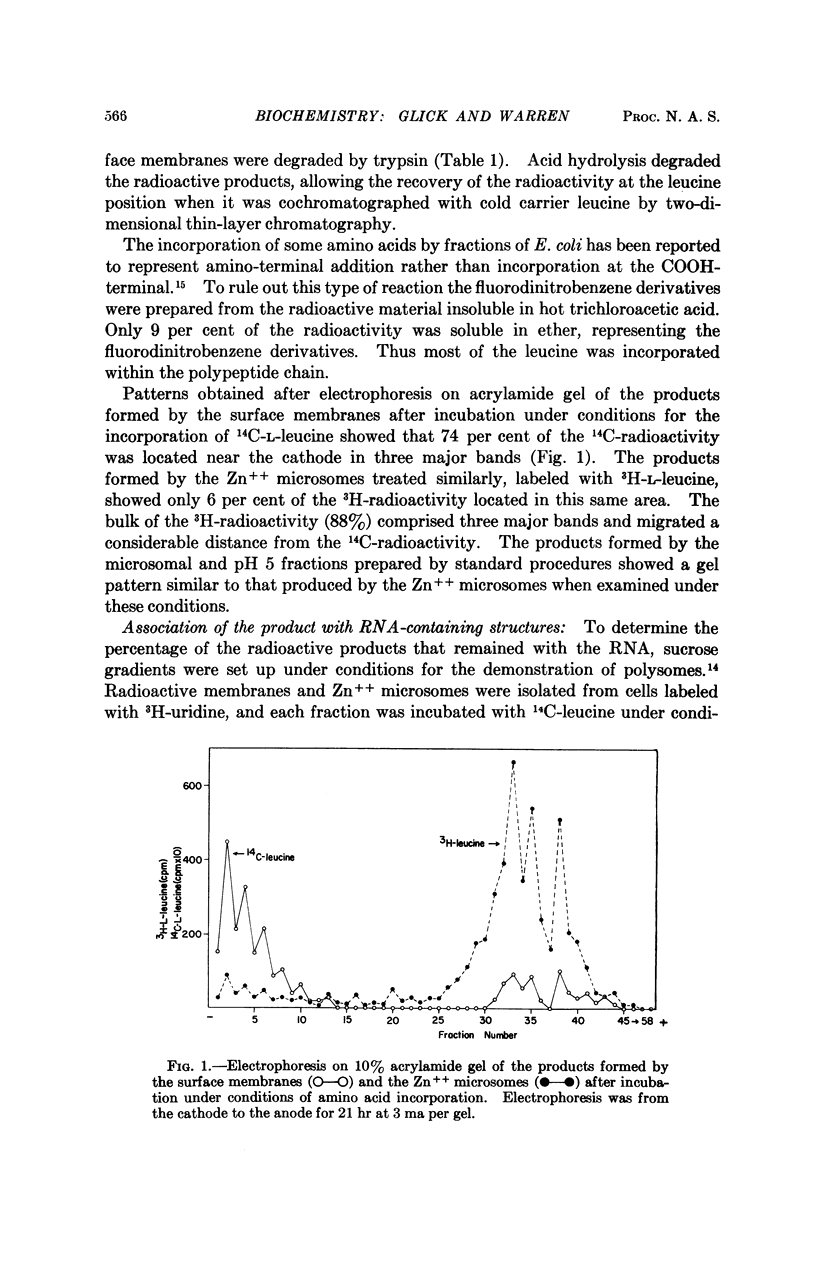
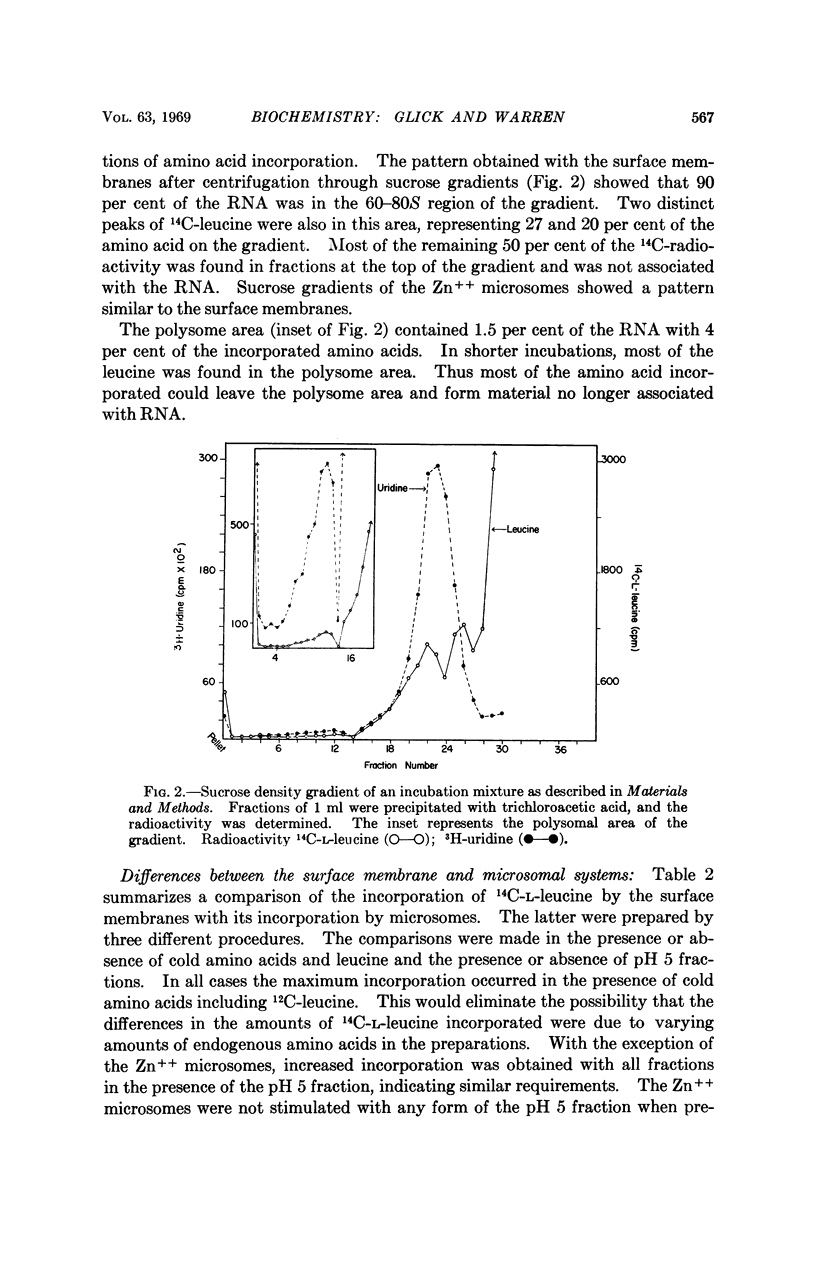
Abstract
Surface membranes isolated from mouse fibroblasts contain RNA organized in ribosome-like particles. These surface membranes can incorporate radioactive amino acids into material insoluble in hot trichloroacetic acid. Characterization of the radioactive products indicated that they are large polypeptides. Most requirements and inhibitors of the system were similar to those of the microsomal system of the endoplasmic reticulum. Further comparisons were made with microsomal and pH 5 fractions prepared from L-cells by standard procedures and by two methods attempting to simulate the conditions necessary for isolating surface membranes. The amount of L-leucine incorporated by the surface membranes per mg of RNA was comparable to the values obtained by the microsomal and pH 5 fractions prepared by standard procedures. In contrast, the activity of the two other microsomal fractions was less than 10 per cent of this amount. The most striking difference noted was in the products formed by the surface membranes and by the microsomal systems. These products were demonstrated to be quite different by electrophoresis on acrylamide gels. It is suggested that the surface membranes participate actively in protein synthesis in vivo, and that, because of this location, the protein-synthesizing mechanism may be able to perform special functions more efficiently.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRAENKEL-CONRAT H., HARRIS J. I., LEVY A. L. Recent developments in techniques for terminal and sequence studies in peptides and proteins. Methods Biochem Anal. 1955;2:359–425. doi: 10.1002/9780470110188.ch12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUTCHISON W. C., MUNRO H. N. The determination of nucleic acids in biological materials. A review. Analyst. 1961 Dec;86:768–813. doi: 10.1039/an9618600768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton D., Tanimura A., Wolfrom M. L. Two-dimensional thin-layer chromatography of amino acids on microcrystalline cellulose. J Chromatogr. 1966 Jul;23(2):309–312. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)98690-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight E., Jr, Darnell J. E. Distribution of 5 s RNA in HeLa cells. J Mol Biol. 1967 Sep 28;28(3):491–502. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(67)80099-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koehler J. K. Freeze-etching observations on nucleated erythrocytes with special reference to the nuclear and plasma membranes. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1968;85(1):1–17. doi: 10.1007/BF00330582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Momose K., Kaji A. Soluble amino acid-incorporating system. 3. Further studies on the product and its relation to the ribosomal system for incorporation. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jul 25;241(14):3294–3307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbell M. Metabolism of isolated fat cells. VI. The effects of insulin, lipolytic hormones, and theophylline on glucose transport and metabolism in "ghosts". J Biol Chem. 1967 Dec 25;242(24):5751–5756. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama T., Nakada D. Translational control of bacteriophage MS2 RNA cistrons by MS2 coat protein: polyacrylamide gel electrophoretic analysis of proteins synthesized in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1968 Feb 14;31(3):431–440. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90419-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein R. S., Bullivant S. The application of freeze-cleaving technics to studies on red blood cell fine structure. Blood. 1967 May;29(5):780–789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



