Abstract
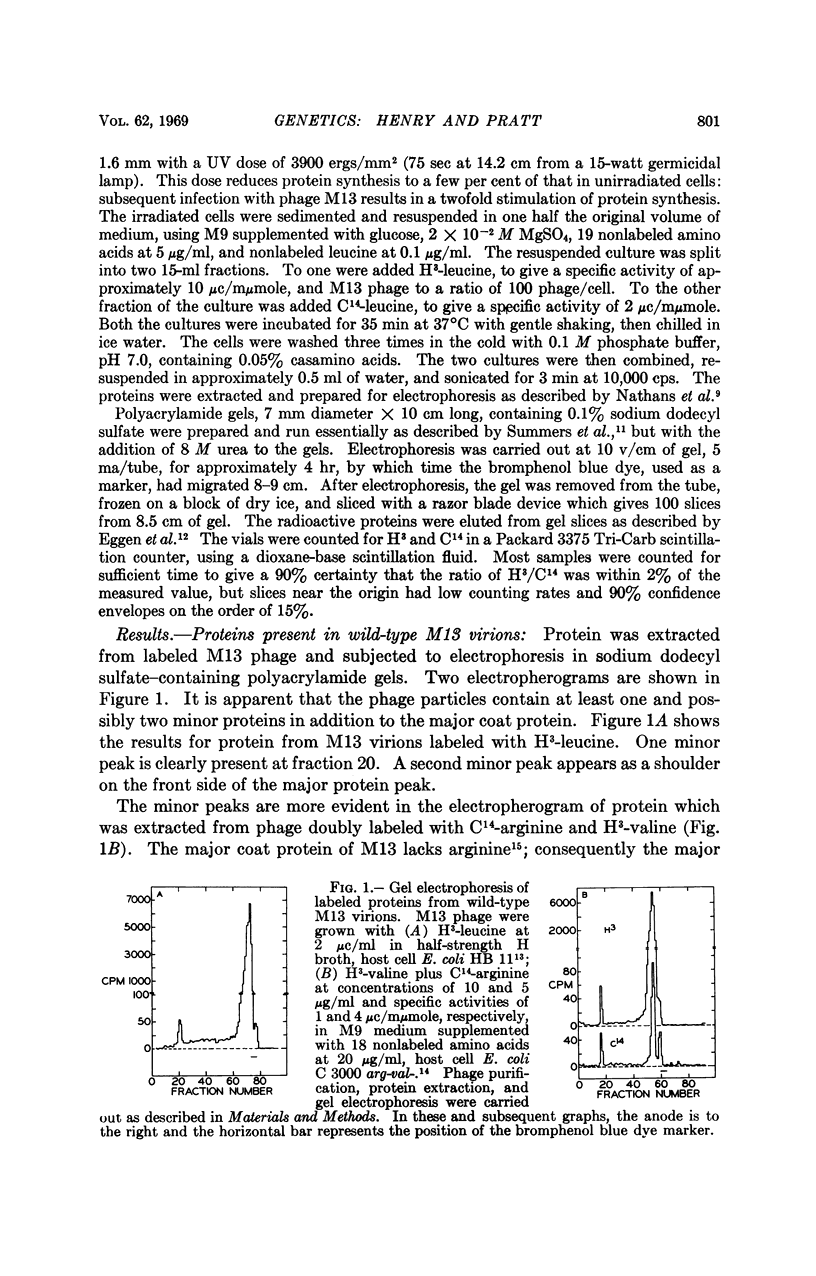
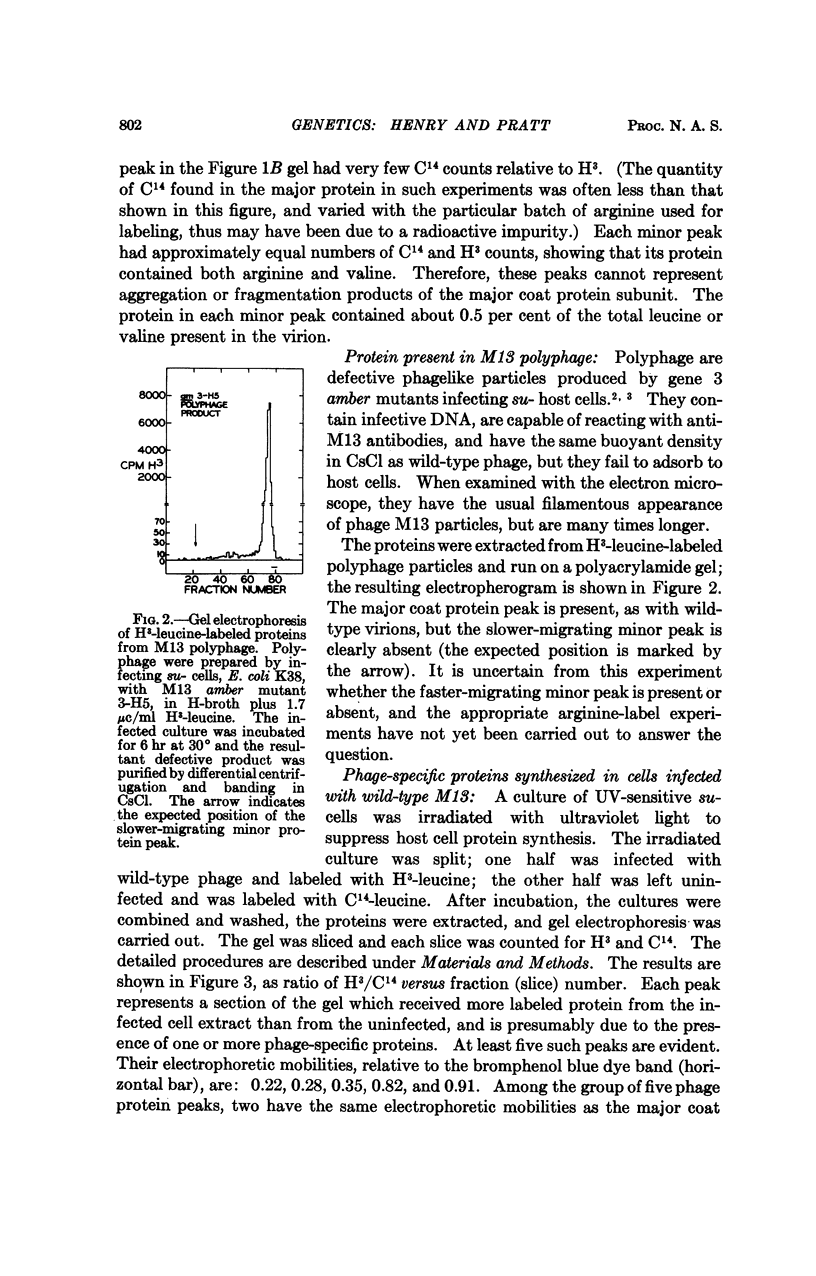
Particles of the small filamentous coliphage M13 contain not only the major coat protein, which is the product of phage gene 8, but also a minor coat protein, the A protein, which is the product of gene 3. The A protein has a molecular weight of approximately 70,000 daltons, is present in one copy per virion, and is responsible for phage attachment to host cells. Also associated with purified M13 particles is a minor quantity of very small proteinaceous material, but its origin as a phage-coded product has not been demonstrated.
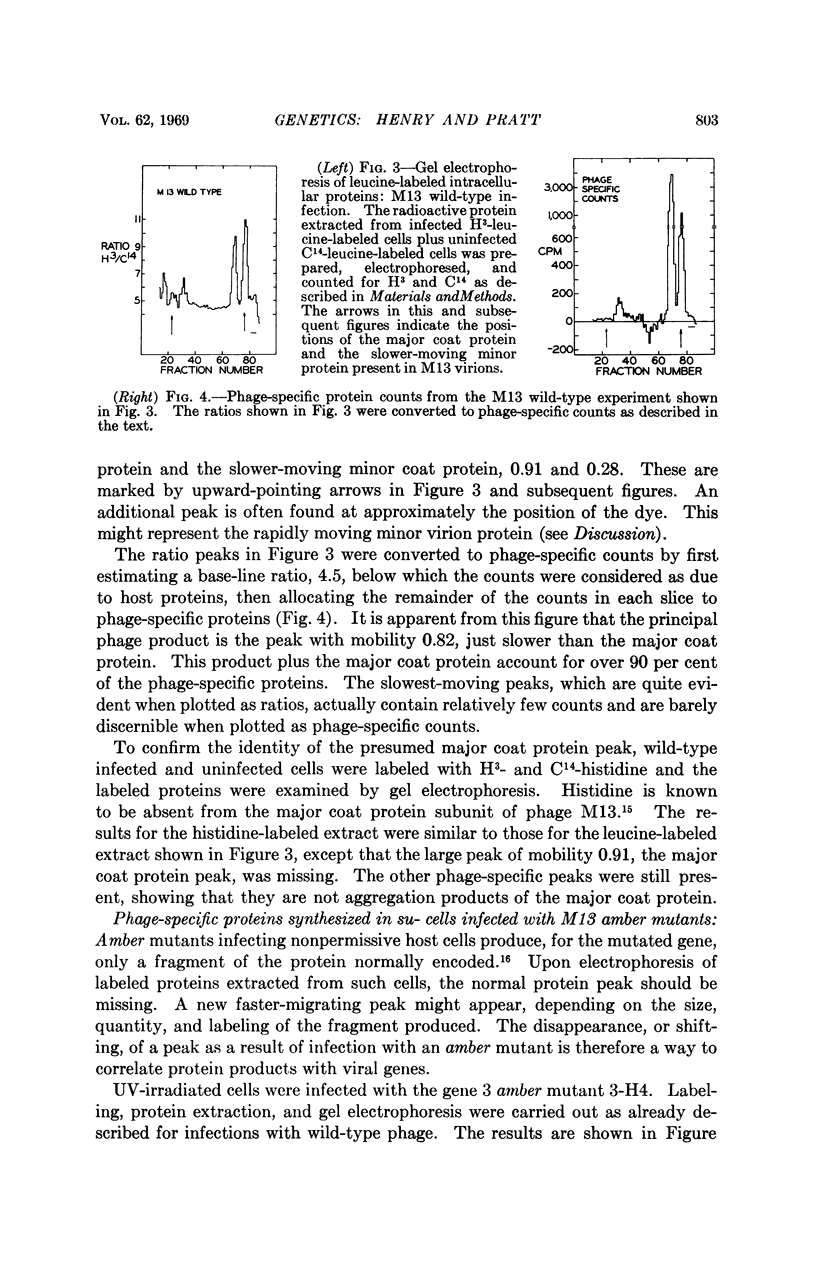
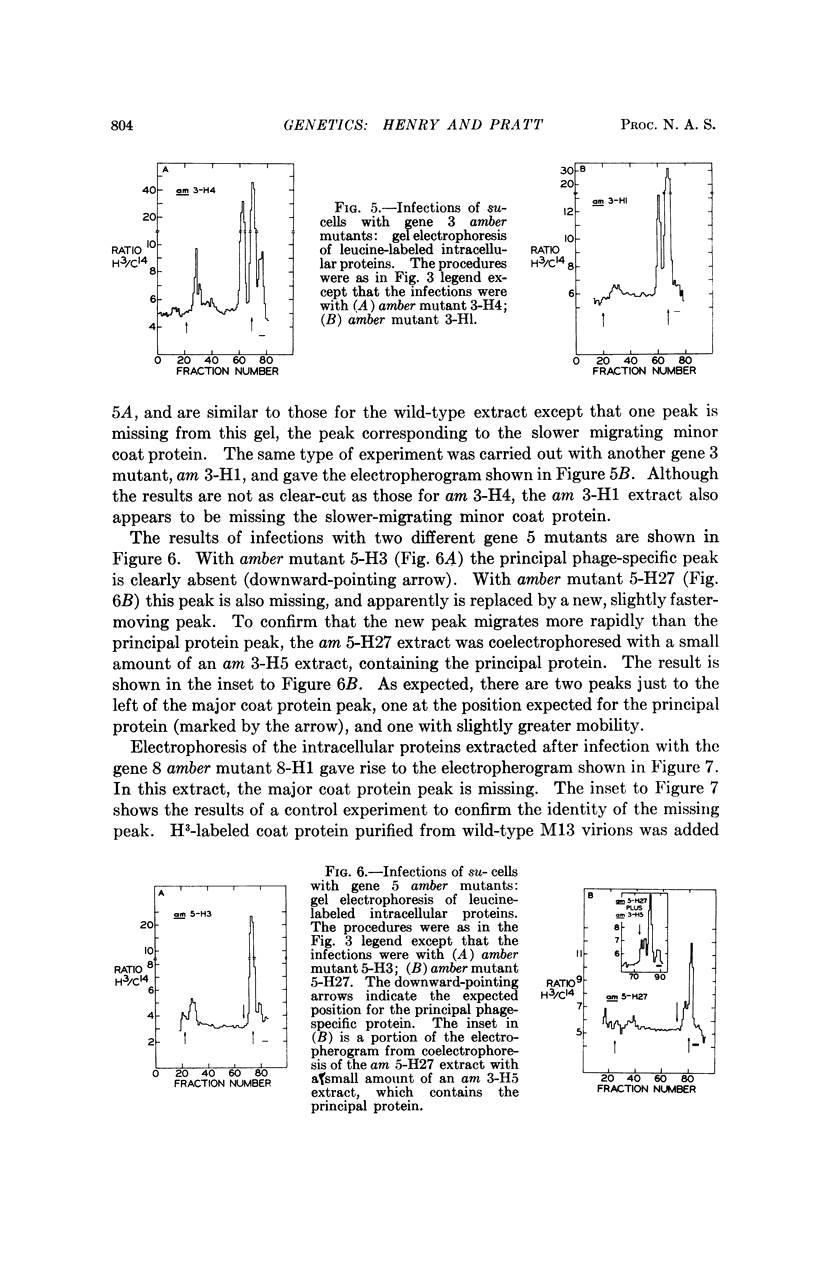
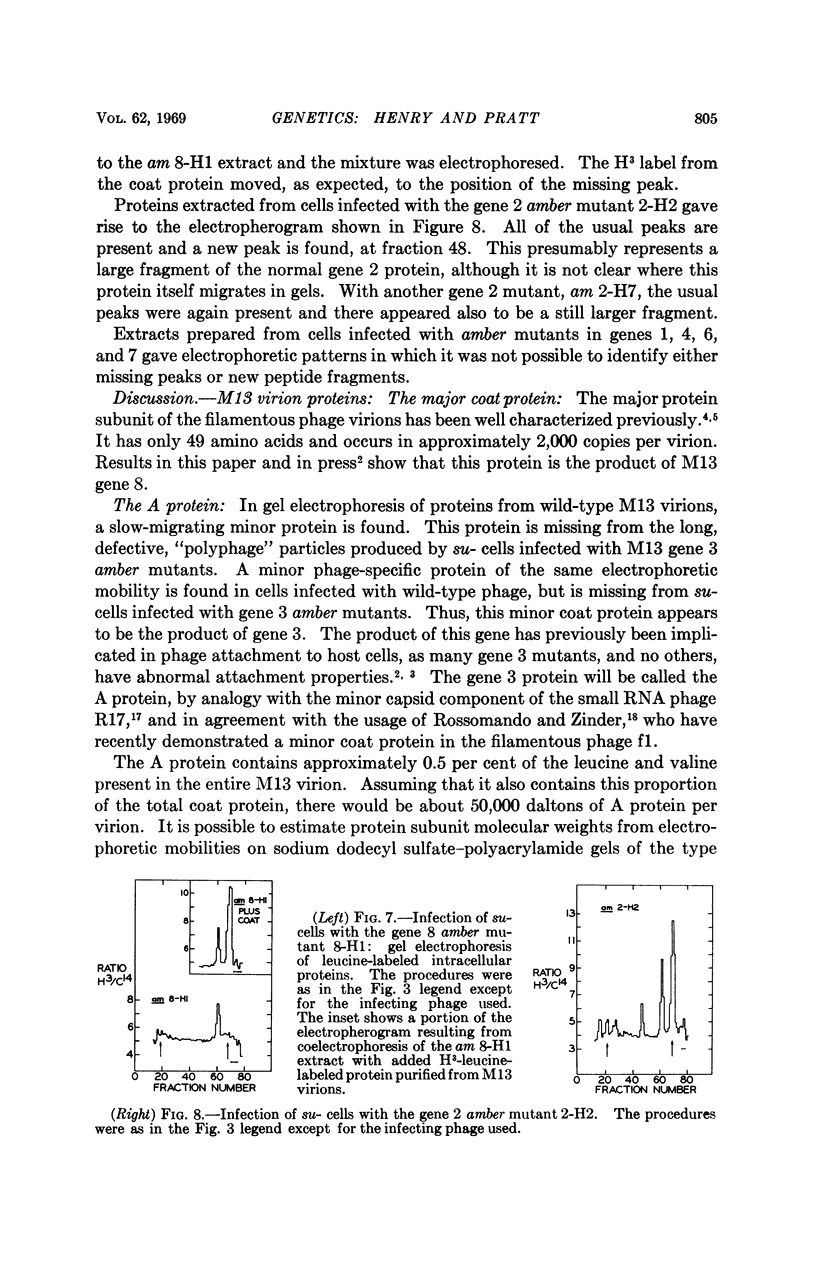
At least five phage-specific proteins, including the two coat proteins, are present in appreciable quantities in M13-infected cells. The principal phage protein synthesized is the product of gene 5, which is responsible for phage single-stranded DNA synthesis. This protein has a molecular weight of about 8,000 daltons. Its precise function in DNA synthesis is not yet known.
Phage proteins are synthesized at nearly normal rates in cells in which replication of phage double-stranded DNA is blocked by gene 2 mutations. This result suggests that the initial double-stranded DNA molecule serves as the principal template, perhaps the only template, for phage messenger RNA synthesis.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRINTON C. C., Jr, GEMSKI P., Jr, CARNAHAN J. A NEW TYPE OF BACTERIAL PILUS GENETICALLY CONTROLLED BY THE FERTILITY FACTOR OF E. COLI K 12 AND ITS ROLE IN CHROMOSOME TRANSFER. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Sep;52:776–783. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.3.776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braunitzer G., Asbeck F., Beyreuther K., Köhler H., von Wettstein G. Die Konstritution des Hüllproteins des Bakteriophagen fd. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1967 Jun;348(6):725–726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggen K., Oeschger M. P., Nathans D. Cell-free protein synthesis directed by colphage MS2 RNA: sequential synthesis of specific phage proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Aug 23;28(4):587–597. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90354-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fareed G., Ippen K. A., Valentine R. C. Active fragments of a filamentous bacteriophage. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Nov 11;25(3):275–284. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90772-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knippers R., Hoffmann-Berling H. A coat protein from bacteriophage fd. I. Hydrodynamic measurements and biological characterization. J Mol Biol. 1966 Nov 14;21(2):281–292. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90099-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathans D., Oeschger M. P., Eggen K., Shimura Y. Bacteriophage-specific proteins in e. Coli infected with an RNA bacteriophage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Dec;56(6):1844–1851. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.6.1844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oeschger M. P., Nathans D. Differential synthesis of bacteriophage-specific proteins in MS2-infected Escherichia coli treated with actinomycin. J Mol Biol. 1966 Dec 28;22(2):235–247. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90129-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt D., Erdahl W. S. Genetic control of bacteriophage M13 DNA synthesis. J Mol Biol. 1968 Oct 14;37(1):181–200. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90082-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt D., Tzagoloff H., Erdahl W. S. Conditional lethal mutants of the small filamentous coliphage M13. I. Isolation, complementation, cell killing, time of cistron action. Virology. 1966 Nov;30(3):397–410. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90118-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. ISOLATION OF THE lambda PHAGE REPRESSOR. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Feb;57(2):306–313. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.2.306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossomando E. F., Zinder N. D. Studies on the bacteriophage fl. I. Alkali-induced disassembly of the phage into DNA and protein. J Mol Biol. 1968 Sep 28;36(3):387–399. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90163-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALIVAR W. O., TZAGOLOFF H., PRATT D. SOME PHYSICAL-CHEMICAL AND BIOLOGICAL PROPERTIES OF THE ROD-SHAPED COLIPHAGE M13. Virology. 1964 Nov;24:359–371. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90173-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SARABHAI A. S., STRETTON A. O., BRENNER S., BOLLE A. CO-LINEARITY OF THE GENE WITH THE POLYPEPTIDE CHAIN. Nature. 1964 Jan 4;201:13–17. doi: 10.1038/201013a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salivar W. O., Henry T. J., Pratt D. Purification and properties of diploid particles of coliphage M13. Virology. 1967 May;32(1):41–51. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90250-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro A. L., Viñuela E., Maizel J. V., Jr Molecular weight estimation of polypeptide chains by electrophoresis in SDS-polyacrylamide gels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Sep 7;28(5):815–820. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90391-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz J. A. Isolation of the A protein from bacteriphage R17. J Mol Biol. 1968 May 14;33(3):937–945. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90329-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers D. F., Maizel J. V., Jr, Darnell J. E., Jr Evidence for virus-specific noncapsid proteins in poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Aug;54(2):505–513. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.2.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



