Abstract
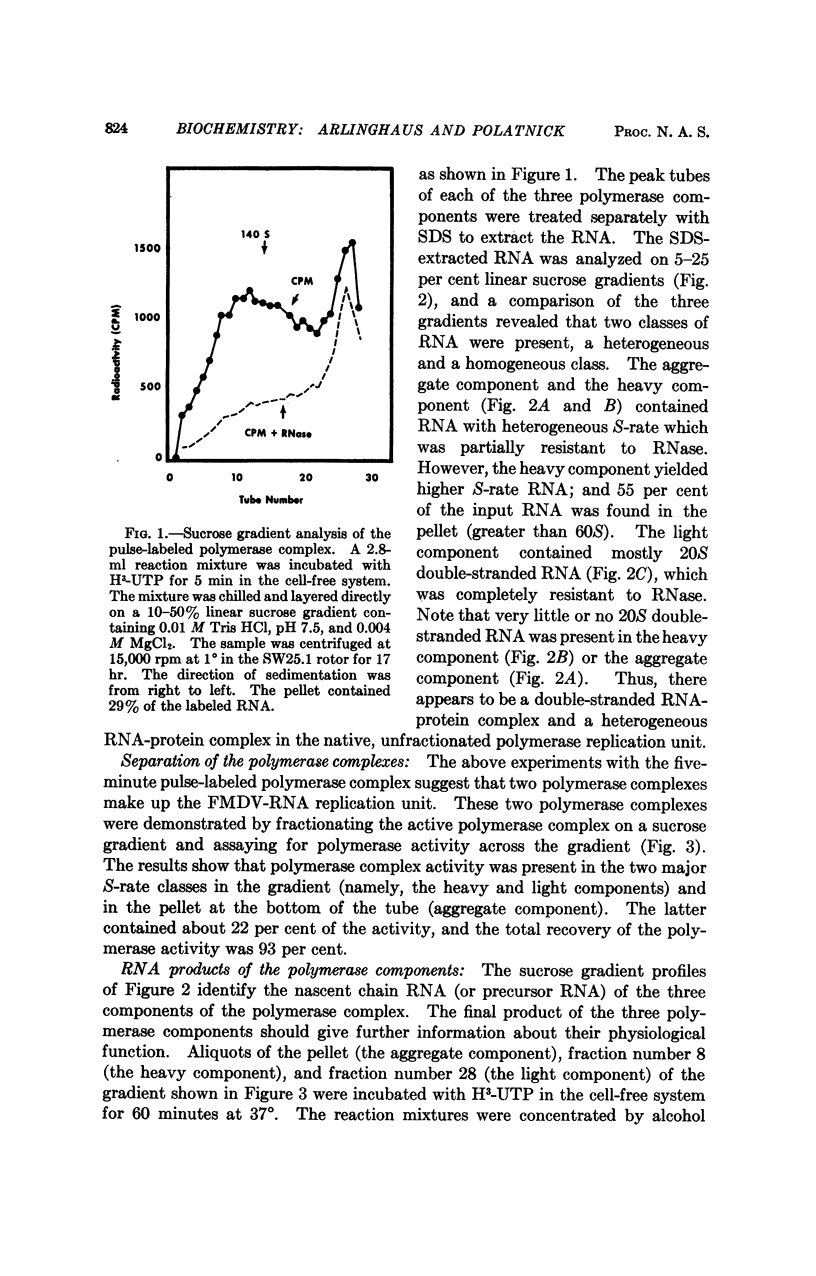
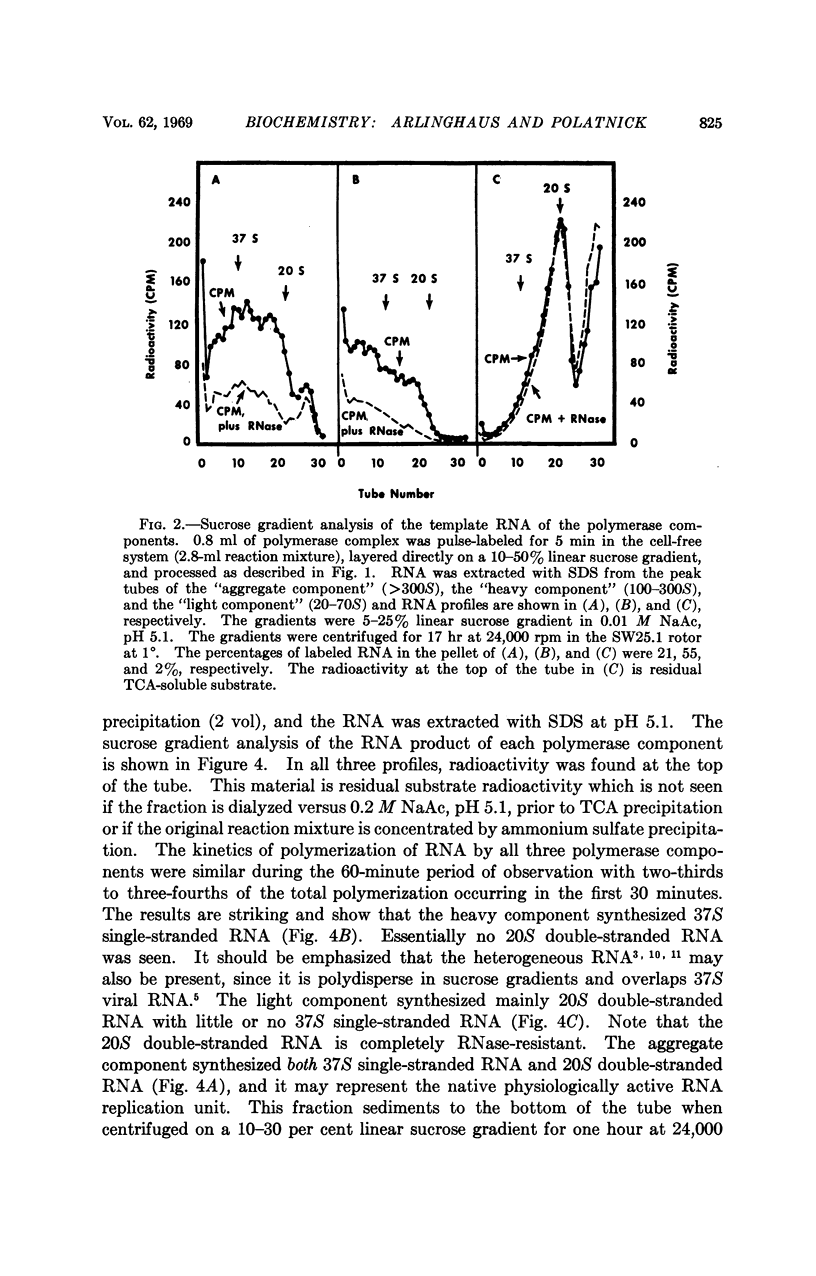
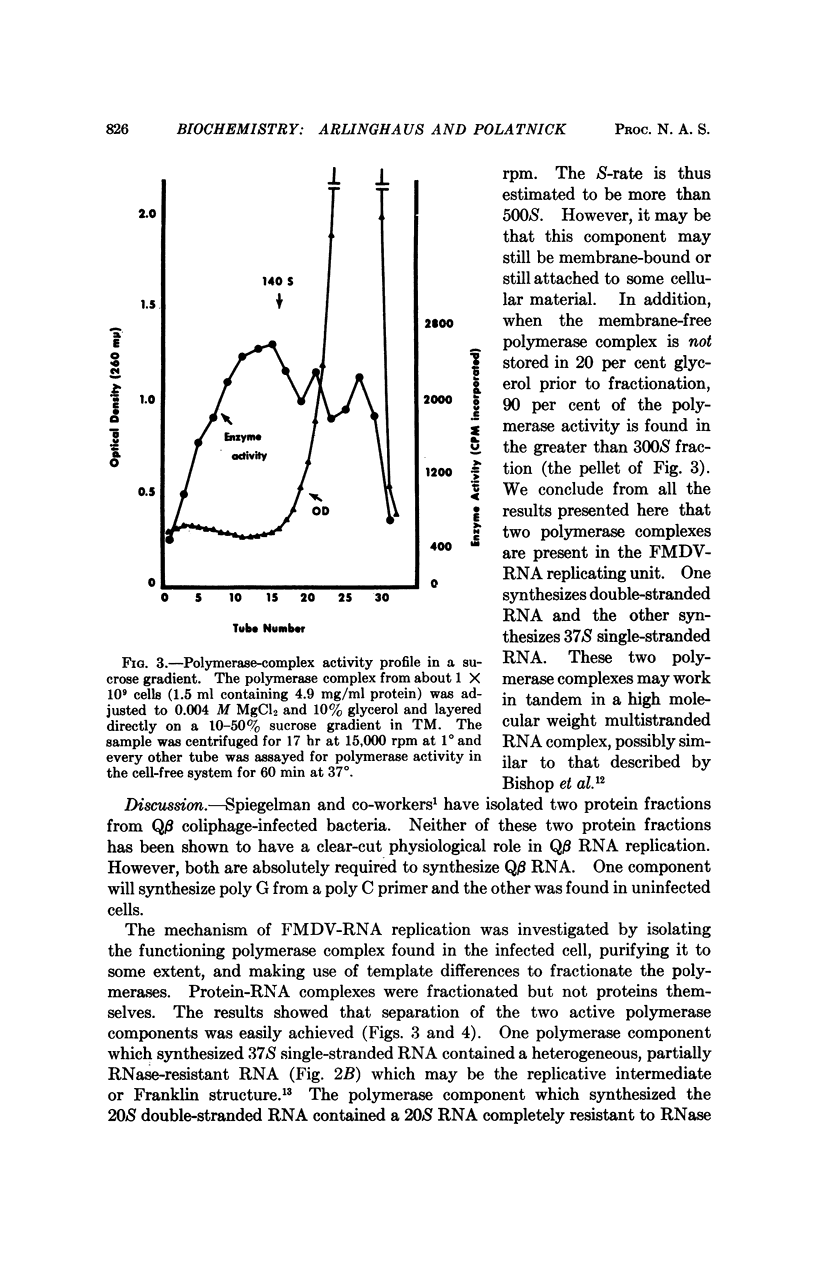
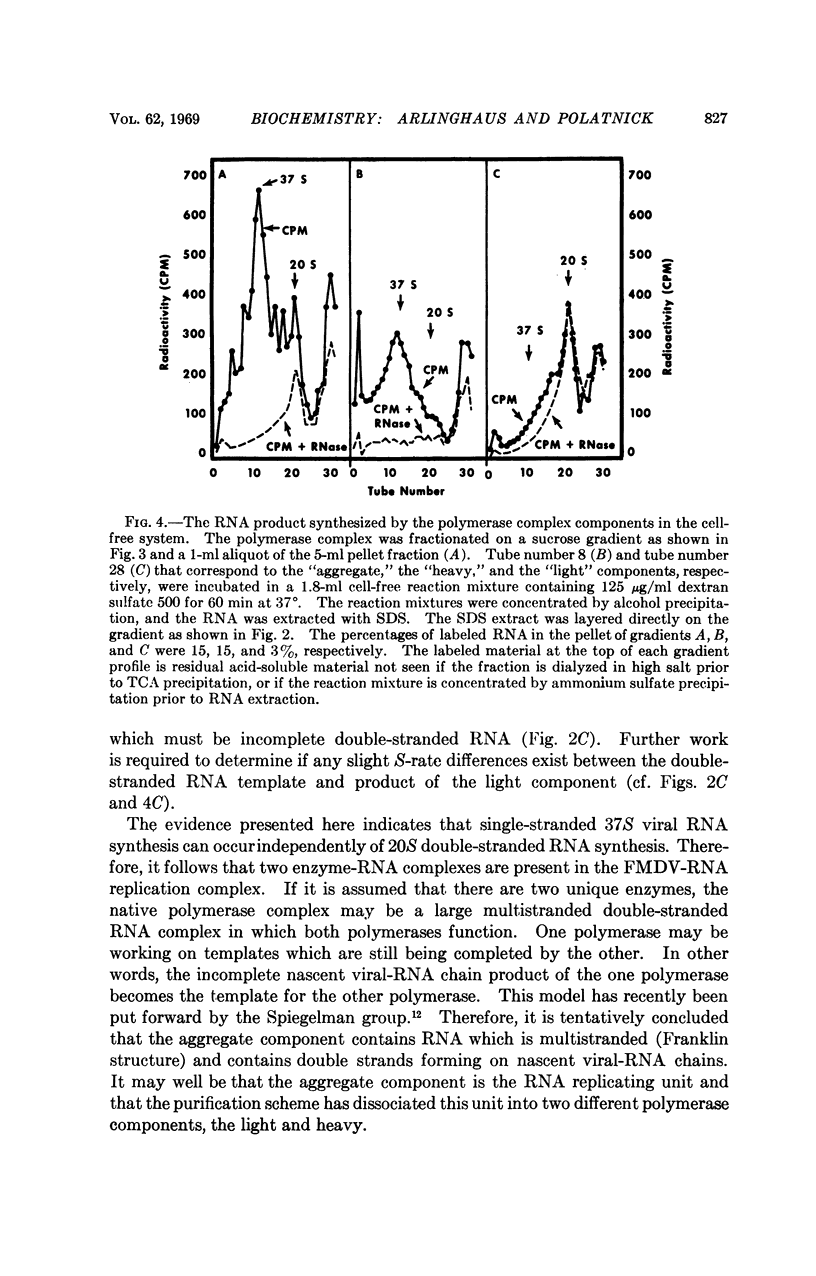
The foot-and-mouth disease virus-RNA polymerase complex was released from membrane particulates present in the cytoplasm of infected baby hamster kidney cells. The soluble polymerase complex was fractionated by zonal centrifugation in sucrose gradients. Two polymerase complexes (RNA and protein complex) active in the cell-free system were isolated and had S-rate ranges of 20-70S and 100-300S, respectively. The light polymerase complex contained 20S double-stranded RNA; and the heavy polymerase complex contained a polydisperse, partially RNase-resistant RNA. The cell-free product of these two polymerase complexes was analyzed by zonal centrifugation in sucrose gradients. The light polymerase complex synthesized only 20S double-stranded RNA. The product of the heavy polymerase complex contained no detectable 20S double-stranded RNA and only a peak of single-stranded RNA with S-rate corresponding to 37S viral RNA. A third polymerase complex was isolated with S-rate greater than 300S, and it contained a polydisperse, partially RNase-resistant RNA. This third polymerase complex synthesized both 37S viral RNA and 20S double-stranded RNA in the cell-free system, and it is probably the native polymerase complex still bound to cellular particulates.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arlinghaus R. B., Bachrach H. L., Polatnick J. Site of foot-and-mouth disease virus-ribonucleic acid synthesis and some properties of its double-stranded ribonucleic acid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jun 18;161(1):170–179. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90306-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arlinghaus R. B., Polatnick J. Detergent-solubilized RNA polymerase from cells infected with foot-and-mouth disease virus. Science. 1967 Dec 8;158(3806):1320–1322. doi: 10.1126/science.158.3806.1320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arlinghaus R. B., Polatnick J. In vitro products of a membrane-free foot-and-mouth disease virus ribonucleic acid polymerase. Virology. 1969 Feb;37(2):252–261. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90205-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arlinghaus R. B., Polatnick J., Vande Woude G. F. Studies on foot-and-mouth disease virus ribonucleic acid synthesis. Virology. 1966 Nov;30(3):541–550. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90129-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BACHRACH H. L., TRAUTMAN R., BREESE S. S., Jr CHEMICAL PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF VIRTUALLY PURE FOOT-AND-MOUTH DISEASE VIRUS. Am J Vet Res. 1964 Mar;25:333–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop D. H., Pace N. R., Spiegelman S. The mechanism of replication: a novel polarity reversal in the in vitro synthesis of Q-beta-RNA and its complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Oct;58(4):1790–1797. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.4.1790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eikhom T. S., Stockley D. J., Spiegelman S. Direct participation of a host protein in the replication of viral RNA in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Feb;59(2):506–512. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.2.506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin R. M. Purification and properties of the replicative intermediate of the RNA bacteriophage R17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jun;55(6):1504–1511. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.6.1504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POLATNICK J., BACHRACH H. L. PRODUCTION AND PURIFICATION OF MILLIGRAM AMOUNTS OF FOOT-AND-MOUTH DISEASE VIRUS FROM BABY HAMSTER KIDNEY CELL CULTURES. Appl Microbiol. 1964 Jul;12:368–373. doi: 10.1128/am.12.4.368-373.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrović S., Petrović J., Bayer M. E. Release of microsomal ribonucleic acids by macromolecular dextran sulfate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Aug 22;145(1):193–195. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(67)90675-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plagemann P. G., Swim H. E. Symposium on replication of viral nucleic acids. 3. Replication of mengovirus ribonucleic acid. Bacteriol Rev. 1966 Jun;30(2):288–308. doi: 10.1128/br.30.2.288-308.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polatnick J., Arlinghaus R. B. Foot-and-mouth disease virus-induced ribonucleic acid polymerase in baby hamster kidney cells. Virology. 1967 Apr;31(4):601–608. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90188-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polatnick J., Vande Woude G. F., Arlinghaus R. B. Changes in protein and nucleic acid metabolism in baby hamster kidney cells infected with foot-and-mouth disease virus. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1968;23(3):218–226. doi: 10.1007/BF01241894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



