Abstract
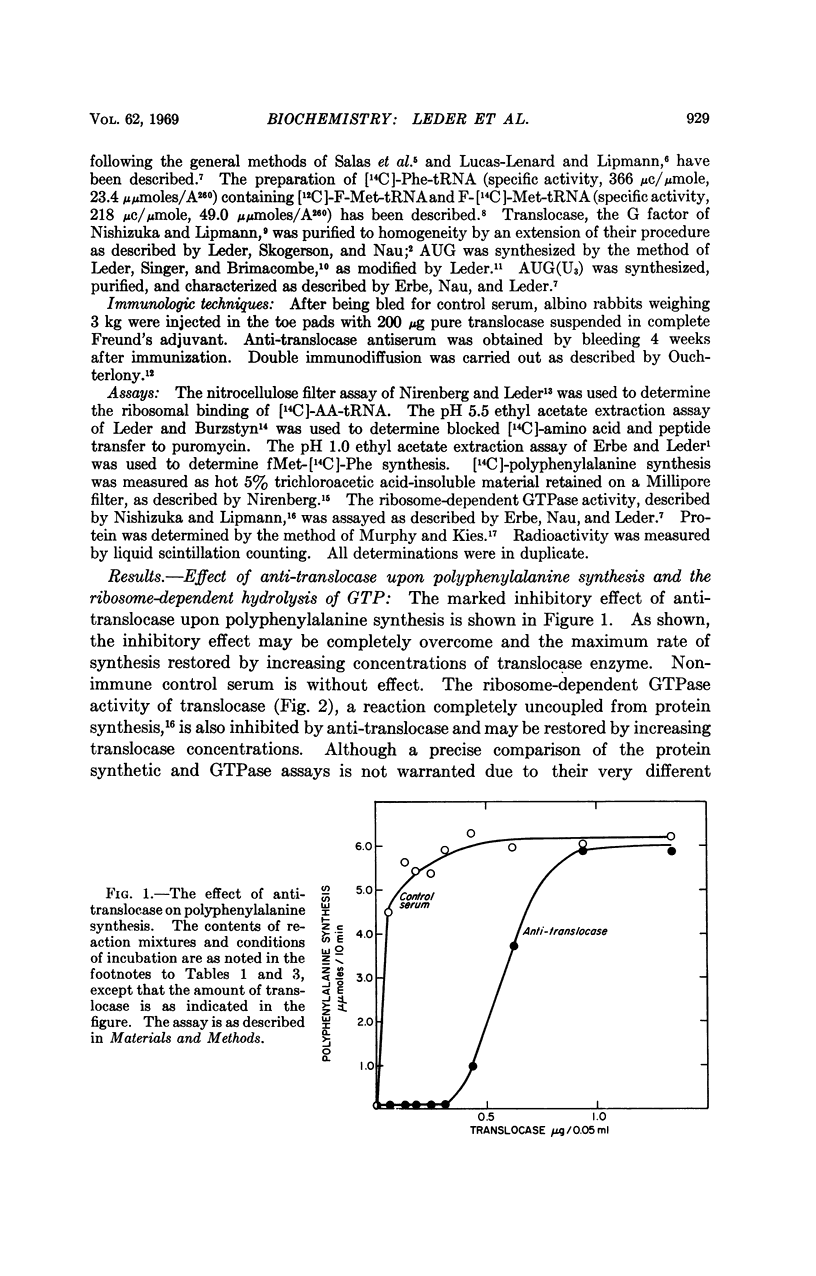
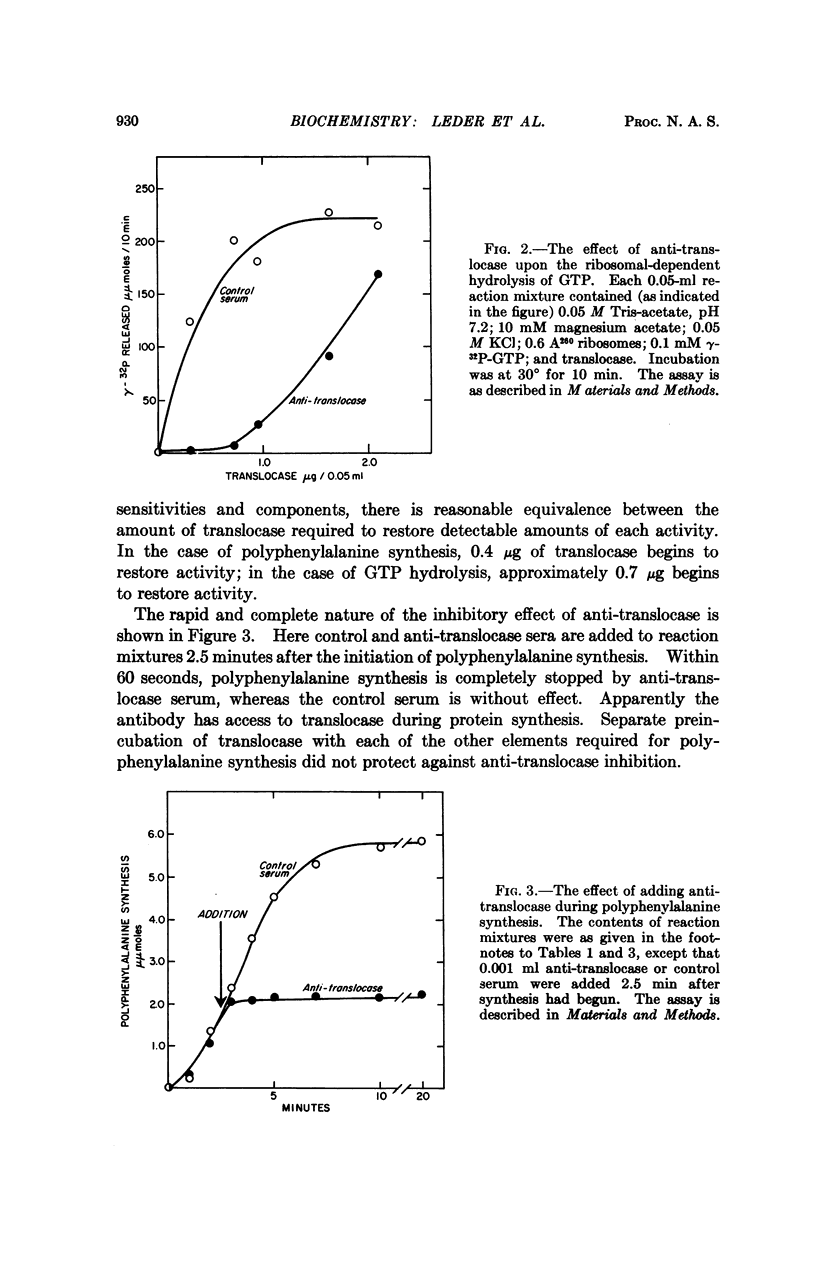
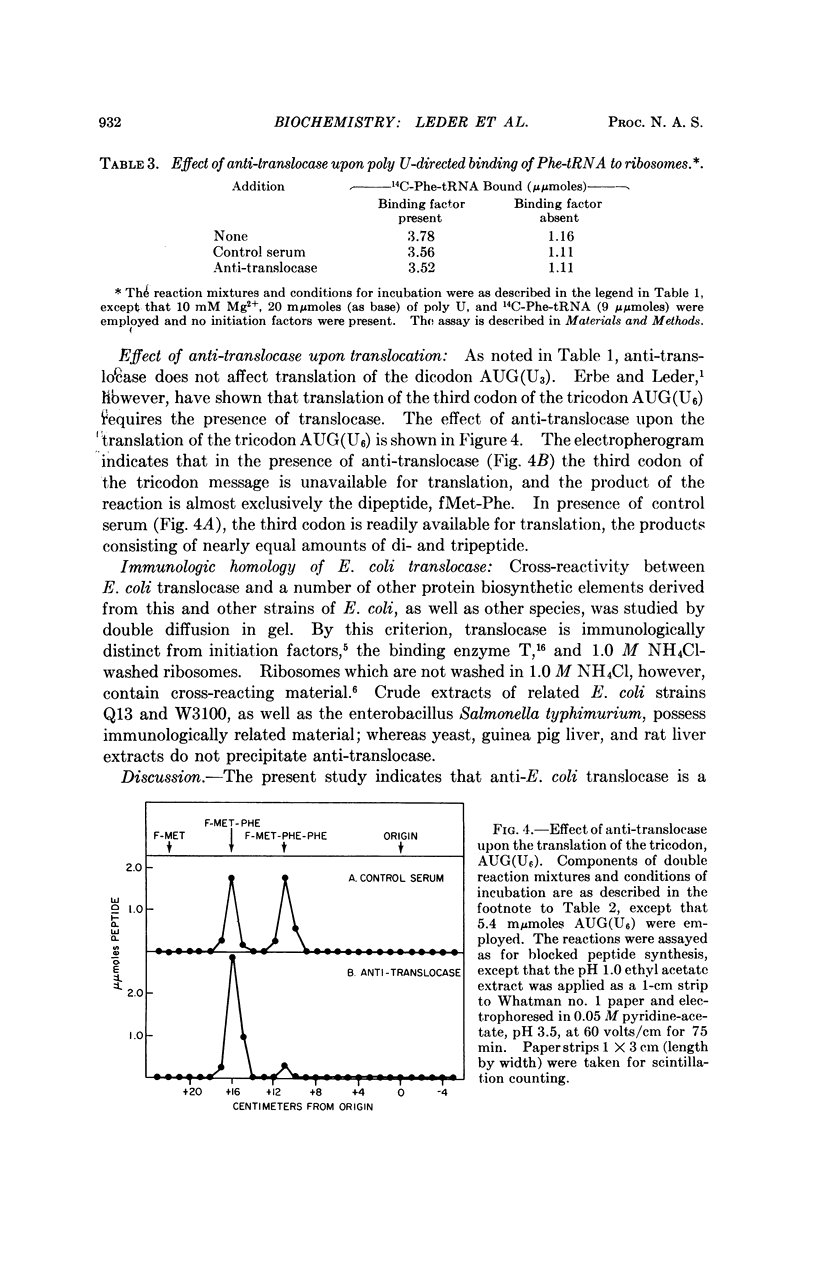
A purified preparation of translocase, one of several enzymes required for protein biosynthesis, has been used to prepare a specific anti-translocase antibody. This antibody provides an extremely useful tool not only for detecting the enzyme independent of its activity, but for inhibiting the translocase-mediated reaction and, thus, protein biosynthesis. Though the antibody very rapidly inhibits elongation of the peptide chain, it fails to effect initiation, binding, or peptide bond formation, which strongly suggests that translocase is not a direct participant in these reactions. It also arrests translation of the defined tricodon AUG(U6) at the second codon, permitting formation only of the dipeptide, fMet-Phe, rather than the tripeptide, fMetPhe-(Phe)2, which is formed in the presence of control serum. We have shown previously that the third codon becomes available only in the presence of translocase, thereby defining the site of action of the antibody. The antibody also has been used to demonstrate that translocase is antigenically distinct from the other proteins required for initiation and protein synthesis in E. coli.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cammack K. A., Wade H. E. The sedimentation behaviour of ribonuclease-active and -inactive ribosomes from bacteria. Biochem J. 1965 Sep;96(3):671–680. doi: 10.1042/bj0960671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erbe R. W., Leder P. Initiation and protein synthesis: translation of di- and tri-codon messengers. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Jun 10;31(5):798–803. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90633-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leder P., Bursztyn H. Initiation of protein synthesis II. A convenient assay for the ribosome-dependent synthesis of N-formyl-C14-methionylpuromycin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Oct 20;25(2):233–238. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90586-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leder P., Singer M. F., Brimacombe R. L. Synthesis of trinucleoside diphosphates with polynucleotide phosphorylase. Biochemistry. 1965 Aug;4(8):1561–1567. doi: 10.1021/bi00884a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leder P., Skogerson L. E., Nau M. M. Translocation of mRNA codons. I. The preparation and characteristics of a homogeneous enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Feb;62(2):454–460. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.2.454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas-Lenard J., Lipmann F. Separation of three microbial amino acid polymerization factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jun;55(6):1562–1566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.6.1562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIRENBERG M., LEDER P. RNA CODEWORDS AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. THE EFFECT OF TRINUCLEOTIDES UPON THE BINDING OF SRNA TO RIBOSOMES. Science. 1964 Sep 25;145(3639):1399–1407. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3639.1399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y., Lipmann F. Comparison of guanosine triphosphate split and polypeptide synthesis with a purified E. coli system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jan;55(1):212–219. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.1.212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y., Lipmann F. The interrelationship between guanosine triphosphatase and amino acid polymerization. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Sep 26;116(1):344–351. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(66)90040-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravel J. M. Demonstration of a guanosine triphosphate-dependent enzymatic binding of aminoacyl-ribonucleic acid to Escherichia coli ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jun;57(6):1811–1816. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.6.1811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salas M., Miller M. J., Wahba A. J., Ochoa S. Translation of the genetic message. V. Effect of Mg++ and formylation of methionine in protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jun;57(6):1865–1869. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.6.1865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweet R., Heintz R. Protein synthesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1966;35:723–758. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.35.070166.003451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



