Abstract
Dosage compensation in mammals occurs by X inactivation, a silencing mechanism regulated in cis by the X inactivation center (Xic). In response to developmental cues, the Xic orchestrates events of X inactivation, including chromosome counting and choice, initiation, spread, and establishment of silencing. It remains unclear what elements make up the Xic. We previously showed that the Xic is contained within a 450-kb sequence that includes Xist, an RNA-encoding gene required for X inactivation. To characterize the Xic further, we performed deletional analysis across the 450-kb region by yeast-artificial-chromosome fragmentation and phage P1 cloning. We tested Xic deletions for cis inactivation potential by using a transgene (Tg)-based approach and found that an 80-kb subregion also enacted somatic X inactivation on autosomes. Xist RNA coated the autosome but skipped the Xic Tg, raising the possibility that X chromosome domains escape inactivation by excluding Xist RNA binding. The autosomes became late-replicating and hypoacetylated on histone H4. A deletion of the Xist 5′ sequence resulted in the loss of somatic X inactivation without abolishing Xist expression in undifferentiated cells. Thus, Xist expression in undifferentiated cells can be separated genetically from somatic silencing. Analysis of multiple Xic constructs and insertion sites indicated that long-range Xic effects can be generalized to different autosomes, thereby supporting the feasibility of a Tg-based approach for studying X inactivation.
In mammals, dosage compensation is carried out by X inactivation in female cells (1). X inactivation is a multistep process that includes X chromosome counting, choice between X chromosomes for inactivation, initiation of silencing on the future inactive X (Xi), propagation of silent chromatin on that X, and establishment of X heterochromatin (2). Dosage compensation ensures that one X is kept active for each diploid autosomal set and all other X chromosomes are converted to heterochromatin. The Xi is hypermethylated (3), late-replicating (4), and hypoacetylated on core histone tails (5). The different steps of X inactivation are controlled by the X inactivation center (Xic), an X linked locus defined by X-to-autosome translocations (6). Xist remains the only Xic gene known to be required for X inactivation. Xist encodes a 15-kb untranslated RNA that is expressed only from the Xi and coats the chromosome in cis (7–9).
Transgene (Tg)-based assays in mouse embryonic stem (ES) cells have facilitated genetic analysis of the Xic. These assays are based on the fact that ES cells also enact X inactivation on induction of differentiation (10) and that autosomes can be inactivated when Xic sequences are present in cis (11, 12). Tg studies showed that the Xic is contained within a 450-kb sequence that includes Xist (11, 12). It has also been shown that a 35-kb cosmid carrying Xist with 9 kb of upstream and 6 kb of downstream sequence could express Xist in differentiating ES cells (13). However, it is not known whether the cosmid was sufficient for Xist expression and cis inactivation in somatic cells. Thus, the question of how much sequence comprises the minimal Xic remains to be addressed. Some suggest that the Xic is Xist itself (13, 14), but knockout studies implicate additional cis elements. Although Xist knockouts destroyed cis silencing, they did not abolish chromosome counting and choice, suggesting that these elements are separately encoded (9, 15). Moreover, deleting a 65-kb sequence downstream of Xist resulted in constitutive Xist expression, suggesting that regulatory elements lie downstream of Xist (16).
For this study, to characterize the Xic, we performed deletional analysis of the 450-kb murine Xic sequence and showed that X inactivation can be recapitulated by an 80-kb multifunction domain.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Construction of Xic Deletions.
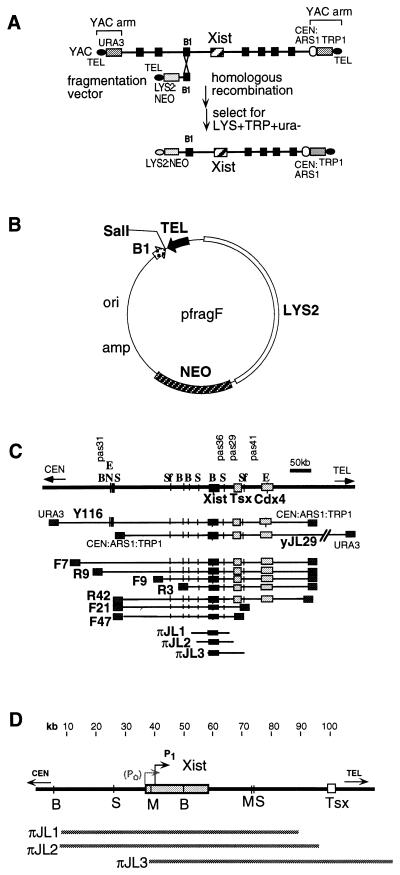
Yeast-artificial-chromosome (YAC) fragmentation (17) was used to create large deletions by homologous recombination at B1 repeats in the 450-kb Xic YAC, Y116 (Fig. 1A; ref. 11). Acentric fragmentation vectors were created with the B1 repeat in two orientations (pfragF and pfragR; Fig. 1B). Homologous targeting of random B1 elements on the YAC created a series of incremental deletions. Y116 (11) was used for deleting sequences upstream of Xist. yJL29 was used for downstream deletions and was derived from a C57BL/6 library (Fig. 1C; ref. 18). Differing from Y116 in insert orientation, yJL29 circumvented the need to construct centric vectors, for which selection is difficult because they yield centric recombinants. Vectors were linearized at SalI and transformed into Y116 and yJL29 cells. Only 7 of >100 Xist-containing recombinants were analyzed further. We also isolated three 80- to 85-kb clones (Fig. 1D) from a phage P1 library (Genome Systems, St. Louis). πJL1 carries 30 kb of sequence upstream of Xist and 30 kb of sequence downstream of Xist; πJL2 carries 30 kb of sequence upstream of Xist and 35 kb of sequence downstream of Xist; πJL3 carries a complete Xist structural gene with 730 bp of upstream sequence and 60 kb of downstream sequence. Thus, πJL3 contains the P1 Xist promoter but lacks P0 (proposed as an alternate Xist promoter; ref. 19). Long-range restriction maps were constructed by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis analysis and PCR mapping with microsatellite markers. Intact clones were used in this study.
Figure 1.
YAC fragmentation scheme (A) and vector (B). (C) Xic deletion panel. E, EagI; N, NotI; B, BssHII; S, SalI; Sf, SfiI. (D) Map of P1 clones.
Generation of Tg ES Cells and Fibroblasts.
YAC DNA was introduced into J1 male ES cells (20) as described (21). P1 DNA was colipofected at a 10-fold molar excess relative to a Neo plasmid, and 10–40 independent Tg lines were generated for each YAC and P1 clone (Table 1). Tg integrity was assessed by Southern blot and densitometric analysis. Clones carrying stoichiometric ratios of vector and Xist sequences were considered intact. Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) was used to identify insertion sites (Table 1). In multicopy integrations, all copies inserted at a single site. The line N1.1 was derived from a fragmented Y116 clone that lacked Xist. Chimeric mice were generated, and mixed fibroblasts were isolated from adults or day 13.5 embryos. Tg fibroblasts were cloned by limiting dilution after simian virus 40-large T immortalization (11) and were identified by PCR.
Table 1.
Characteristics of Xic Tg lines
| Xic derivative, size | Tg ES line | Tg copy no. | Integration site (chromosome) |
|---|---|---|---|
| F7, 400 kb | F7.14 | Med | 4 |
| F7.26 | Med | Med. autosome | |
| F7.32 | Low | 17 | |
| F9, 250 kb | F9.3 | Low | X |
| F9.8 | Low | 8 | |
| F9.18 | Med | Large autosome | |
| R3, 200 kb | R3.1 | Low | Large autosome |
| R3.3 | Low | 8 | |
| R3.6 | Low | 8 | |
| R9, 325 kb | R9.3 | Low | Med. autosome |
| R9.5 | Med | 3 | |
| R9.11 | High | Small autosome | |
| F21, 175 kb | F21.4 | High | ND |
| F21.18 | Med | ND | |
| F21.21 | High | ND | |
| F47, 150 kb | F47.2 | Med | ND |
| F47.4 | Med | ND | |
| F47.5 | Med | ND | |
| R42, 400 kb | R42.5 | Low | ND |
| R42.19 | Low | ND | |
| R42.22 | Low | ND | |
| πJL1, 80 kb | πJL1.3 | High | 13 |
| πJL1.4 | High | 3 | |
| πJL1.5 | Med | 3 | |
| πJL2, 85 kb | πJL2.4 | High | 10 |
| πJL2.5 | High | 8 | |
| πJL2.7 | High | Small autosome | |
| πJL3, 80 kb | πJL3.6 | High | 2 |
| πJL3.8 | High | X | |
| πJL3.10 | High | 10 | |
| N1 | N1.1 | Med | ND |
FISH.
Detailed procedures have been described (22, 23). To detect RNA alone, cells were not denatured before hybridization. For simultaneous RNA/DNA FISH, samples were denatured, and large (100- to 500-kb) probes were used for DNA detection, together with small (2- to 5-kb) probes for RNA detection. Small probes allowed detection of multiple targets (RNA) but not single copy targets (DNA). Xist RNA was detected by exon 6 strand-specific probes (Promega pGEM single-stranded phage DNA system). Mouse chromosome paints were obtained from Oncor. Xic DNA was detected by Y116 or πJL3 probes. The X specific 250-kb bacterial artificial chromosome-Zfx probe has been described (11). Tg-specific hybridization was performed with P1 or YAC vector probes.
Analysis of DNA Replication Timing and Histone H4 Acetylation.
These assays were performed as described (5). Polyclonal antiacetylated H4 antibodies were obtained from Upstate Biotechnology (Lake Placid, NY).
RESULTS
Tests of X Inactivation Potential.
The competence of the Xic deletion clones to carry out different steps of X inactivation was tested in the following ways. (i) Counting was suggested by dual expression of Tg and endogenous Xist RNA during differentiation, a time when Xist becomes repressed in male cells that do not undergo X inactivation. Persistent endogenous Xist expression implied that male cells sensed the presence of additional X chromosomes and could choose the X for inactivation (11). (ii) Initiation and establishment of X inactivation were assessed by the spread of Xist RNA along the chromosome in cis. (iii) Silencing and heterochromatin formation were assessed by delayed DNA replication timing and histone hypoacetylation. A priori, Xic defects could occur in some or all of these steps. Analysis of X inactivation potential showed that the deletions could be grouped into two classes. Only representative clones of each class are shown below. Tg lines derived from each Xic construct behaved similarly, with rare exception as noted below.
Class I.
Class I clones also enacted X inactivation and included Xist-containing clones with 25–35 kb of flanking sequence on both sides. These are F7, F9, R3, R9, R42, F21, F47, πJL1, and πJL2.
Xist Expression, Chromosome Counting, and Choice in Class I Clones.
X inactivation is induced in ES cells by differentiation into embryoid bodies (EB) in culture (24, 25). In both undifferentiated male and female ES cells, Xist is expressed at low levels and can be visualized by FISH as a pinpoint signal localized to the Xic (2). Differentiation in male cells represses Xist expression (Fig. 2 A and B, J1). Differentiation in female cells leads to high expression and spread of Xist RNA over the future Xi and repression of Xist from the active X. This developmentally regulated Xist expression is recapitulated in 116.6, an ES line carrying ≈20 copies of the 450-kb Y116 Tg (Fig. 2 A and B), where differentiation results in choosing between the X and autosome for inactivation (11).
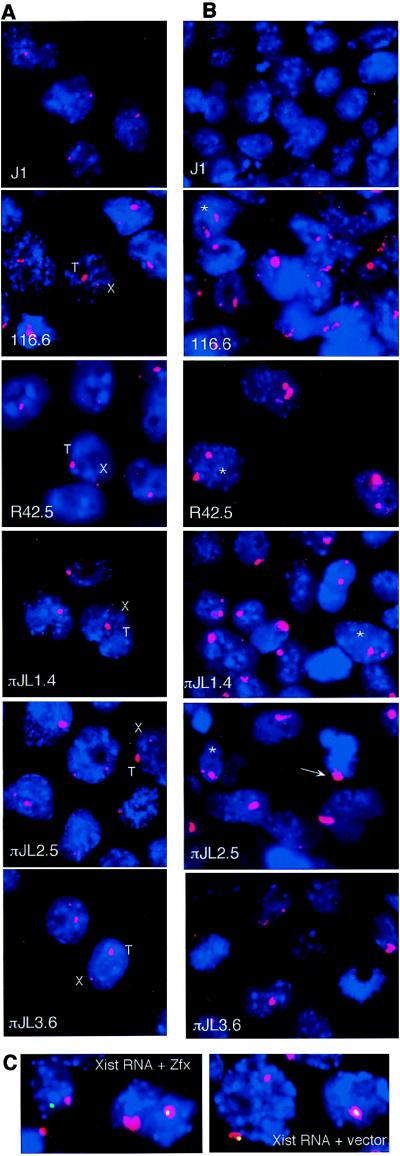
Figure 2.
Xist expression in Tg ES and EB cells. (A) RNA FISH of undifferentiated ES cells with a rhodamine-labeled Xist probe (red). X, endogenous; T, Tg; Blue, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (dapi) staining. (B) RNA FISH of day 9 EB cells (Xist RNA, red). Double Xist expressers are indicated by asterisks; the arrow indicates Xist RNA coat on a πJL2.5 metaphase chromosome. (C) RNA/DNA FISH for Xist RNA (red) and Zfx or vector DNA (FITC, green) was performed for all ES lines to determine Xist RNA origin. πJL2.5 EB is shown. Coincident red and green resulted in white.
The ability of the Xic deletion clones to enact Xist expression and chromosome counting was analyzed by RNA FISH. Fig. 2A depicts Xist RNA patterns in undifferentiated ES cells. In the undifferentiated state, all Tg lines showed Xist expression from endogenous and ectopic loci. RNA/DNA FISH (not shown) indicated that Xist could be expressed from either the X or autosome. As in 116.6, the autosomal Xist signals were reproducibly larger and more intense than the endogenous Xist signals. The signal size directly reflected Tg copy number, consistent with expression from multiple Tg copies.
Differentiation of class I clones showed that they behaved like 116.6 Tg. At a time when J1 and N1.1 cells have lost Xist expression, class I Tg cells showed high Xist expression and transcripts that coated the autosome (Fig. 2B). Xist RNA was observed in 65–100% of all EB cells (Table 2). Consistent with previous observations in 116.6 EB (11), cultures contained both single expressers with only Tg RNA and double expressers with both Tg and endogenous transcripts (Fig. 2 B and C; Table 2). The Tg RNA cluster was large, whereas the endogenous cluster varied in size (though it was usually smaller than Tg RNA). The smaller size of the endogenous cluster may reflect incomplete ES differentiation or selection against cells that have spread Xist RNA along the X.
Table 2.
Pattern of Xist expression in Tg EB cells
| ES line | Double expressors, %
|
Single expressors, %
|
Xist-expressing cells in day 9 EB cultures, % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Endogenous + Tg | Endogenous only | Tg only | ||
| F7.26 | 65 | 0 | 35 | 100 |
| F9.18 | 60 | 0 | 40 | 100 |
| R3.6 | 50 | 0 | 50 | 65 |
| R9.11 | 75 | 0 | 25 | 100 |
| F21.21 | 60 | 0 | 40 | 80 |
| F47.2 | 55 | 0 | 45 | 75 |
| R42.19 | 80 | 0 | 20 | 100 |
| πJL1.4 | 35 | 0 | 65 | 90 |
| πJL2.4 | 50 | 0 | 50 | 80 |
| πJL3.10 | 20 | 0 | 80 | 30 |
| 116.6 | 45 | 0 | 55 | 90 |
| N1.1 | — | — | — | 10 |
| J1 | — | — | — | <10 |
The right column indicates the percentage of Xist-expressing cells in the entire day 9 EB culture. Numbers in column 2, 3, and 4 are the percentages of double or single expressers of all Xist-expressing cells. Percentages are rounded off to nearest fifth percentile and were gathered in three experiments (n > 200 nuclei for each experiment).
The persistent expression of endogenous Xist can be explained in one of two ways. First, the introduction of multiple Xic transgenes may titrate out factors required to repress Xist. Alternatively, the ability to express both endogenous and Tg Xist may reflect the presence of a counting element on the Tg as previously hypothesized (11). In this case, double expressors would account for the majority because each tandem Xic Tg is recognized as a different X chromosome and that the rules of counting require all but one X to express Xist and undergo inactivation. Thus, a Tg clone with four Xic insertions would have simultaneous autosomal and X linked Xist expression in four of five cells. Although double expressers generally accounted for the majority of day 9 EB cells, there was not a direct correlation between Tg copy number and percentage of double expression (Table 2). This lack of correlation may be caused by continuous loss of double expressers as a result of X inactivation. Indeed, increased cell death was seen for class I clones compared with J1 and N1.1 (data not shown), consistent with inactivation of important X linked or autosomal genes during differentiation. Therefore, the number of double expressers counted on day 9 likely reflected only a fraction of the total.
Somatic Xist Expression in Class I Clones: The RNA Skips the Xic.
Fibroblasts were isolated from chimeric Tg mice to determine whether Xist expression was maintained in somatic cells and was accompanied by chromosome inactivation; five independently cloned fibroblast lines for each ES line were examined by RNA FISH (fibroblasts were denoted by an additional number following the ES designation; e.g., πJL2.5.5 was derived from ES πJL2.5). Because cells were immortalized by simian virus 40-large T antigen, each fibroblast clone consisted of diploid and polyploid cells. All showed abundant, highly localized Xist RNA transcripts (Fig. 3A; n > 2,000; >95% of nuclei have Xist signals). As for 116.6 somatic cells, Xist was expressed exclusively from the Tg locus and never from the X. This result is consistent with selection against cells expressing endogenous Xist because of deficiency of X linked gene expression. As in female and 116.6 somatic cells, expression of Xist RNA resulted in coating of the chromosome in cis by Xist RNA. A chromosome-wide coat could be found in >95% of cells in prophase, 40–80% of those in metaphase, and 0% of anaphase cells (n > 100 for each; data not shown). The spread of the Tg-derived RNA was cis-limited (Fig. 3B) with two exceptions. The centromere was skipped on all Tg autosomes as on the female Xi. The Tg themselves were devoid of coating in clones carrying only 80 kb of Xic sequence (Fig. 3C). As shown by DNA hybridization with Tg probes, the skip occurred at the Tg.
Figure 3.
Xist is expressed in class I somatic cells, and the RNA coats the autosome. (A) RNA/DNA FISH of normal female and Tg fibroblasts. Xist RNA is shown in red; Zfx genomic DNA is shown in green. (B) πJL1.4.1 chromosomes were hybridized to Xist probes (red) without chromosome denaturation, then stripped, denatured, and hybridized to chromosome 3 (Ch3)-specific paints (Ch.paint; red) and Tg probes (green). Arrows indicate normal homologues of Ch3. (C) Xist RNA skips the Xic Tg as indicated by the arrows. This experiment was performed as described for B.
DNA Replication Timing in Class I Clones.
The Xi replicates late in S phase (4). The Tg autosome of 116.6 also exhibited delayed replication timing (12). To determine whether this property was retained in the deletion derivatives, we examined replication timing in Tg fibroblasts by differential incorporation of BrdUrd into euchromatic and heterochromatic regions. BrdUrd was added to cell cultures during late S phase, and metaphase chromosomes were prepared after a 6-h incubation. When performed on normal fibroblast lines, this procedure labeled the Xi in female cells and the Y in male cells, both of which have been established as late-replicating chromosomes (26). In class I lines, the Y and Tg autosome were consistently and diffusely labeled by BrdUrd (Fig. 4). In πJL1.3.3, 35 of 48 metaphases showed colabeling of the Ch13 Tg and the Y, whereas 13 of 48 showed labeling only of the Y. In πJL1.4.1, 42 of 45 showed colabeling of both the Ch3 Tg and the Y, whereas 3 of 45 showed labeling of only the Y. In πJL2.5.5, 31 of 40 showed colabeling of the Ch8 Tg and the Y, whereas 9 of 40 showed labeling of only the Y. The consistent labeling of the Y confirmed that we had examined BrdUrd incorporation in late S phase. Thus, these observations indicated that class I sequences induced late replication. The labeling of Tg autosomes varied. In some, the entire autosome was labeled diffusely. In others, regions closest to the Tg were labeled more brightly, suggesting a distance-dependent influence of the autosomally placed Xic on DNA replication. On average, the BrdUrd density on autosomes was less than that for the Xi and Y, suggesting that regions of early replication were interspersed with late-replicating regions. Isolated loci of other chromosomes also were labeled, possibly representing focal heterochromatin.
Figure 4.
Delayed replication timing of the Tg autosome in class I fibroblasts. πJL2.5.5 is shown. Arrows indicate labeling by Ch8-specific paints (Ch.paint) and Tg probes; asterisks indicate Y. BrdU, BrdUrd.
H4 Hypoacetylation in Class I Clones.
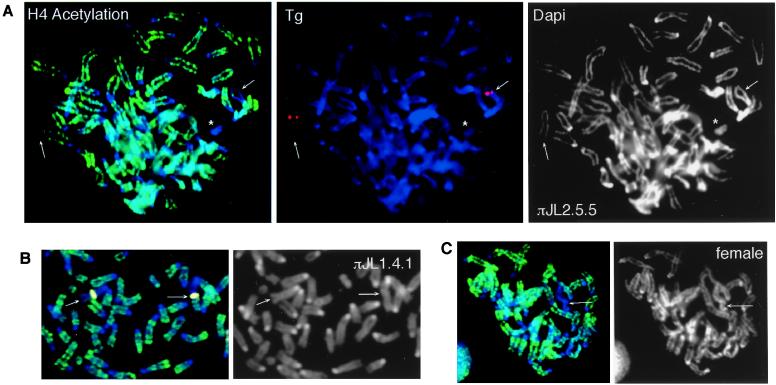
X inactivation has been associated with panchromosomal histone hypoacetylation (Fig. 5C; ref. 5). We previously showed that autosome silencing by the Xic also is correlated with H4 hypoacetylation (12). Here, we tested whether Xic deletion clones retained the ability to induce hypoacetylation. Immunofluorescence with antiacetylated H4 antibodies showed that all class I Tg induced histone deacetylation. In a representative class I clone shown in Fig. 5A, the Ch8 Tg and the Y were hypoacetylated consistently for πJL2.5.5 (n = 33). As on the Xi, hypoacetylation extended bidirectionally from centromere to telomere. Furthermore, like the Xi, the Tg chromosomes reproducibly displayed one to three islands of acetylation, suggesting that sporadic gene clusters escaped heterochromatinization (12). These islands occurred most frequently at the Tg and at distal regions. πJL1.4.1 showed two patterns of hypoacetylation (Fig. 5B; n = 51). In 23 of 51 chromosome spreads, H4 acetylation was low throughout the Ch3 Tg. However, in 28 of 51 spreads, H4 immunofluorescence indicated that acetylation was low on the proximal half of the Ch3 Tg but was higher on the distal half.
Figure 5.
H4 hypoacetylation of Tg autosomes in class I somatic cells. (A) Immunofluorescence of πJL2.5.5 chromosome spreads with antiacetylated H4 antibodies (green). The Ch8 Tg (arrows) and the Y (asterisk) were hypoacetylated. The Tg is shown in red. (B) In πJL1.4.1, some Tg autosomes showed partial deacetylation (arrows). The Tg is pseudocolored yellow. (C) A control female cell showing one hypoacetylated Xi (arrow).
Class II.
πJL3-derived class II clones expressed Tg Xist in undifferentiated cells but are defective for X inactivation in somatic cells. πJL3 carried the P1 promoter of Xist but lacks P0 sequences (19).
Xist Expression, Chromosome Counting, and Choice in Class II Mutants.
In the undifferentiated state, Tg ES cells derived from πJL3 showed Tg Xist expression despite the fact that they lacked the P0 promoter (Fig. 2A). Thus, P0 is not required absolutely for ES cell Xist expression, a result consistent with a prior observation that P1 can act as a minimal Xist promoter in ES cells (27–29). During EB differentiation, Xist expression persisted in a minority of cells in five independent lines (πJL3.1, πJL3.6, πJL3.8, πJL3.9, and πJL3.10; Fig. 2B; Table 2). Loss of expression was unlikely to be caused by position effects, as the five lines have different insertion sites. Interestingly, fewer double expressers were seen in class II lines than in class I Tg (Table 2). These results are consistent with either the loss of a counting element in πJL3 or the deletion of a transcriptional regulator separate from chromosome counting.
Class II Mutants Are Defective in Somatic Xist Expression.
In contrast to class I clones, class II fibroblasts from πJL3.6, πJL3.8, πJL3.9, and πJL3.10 did not show any Xist expression. Thus, somatic Xist expression was compromised in class II clones despite apparently normal expression in ES cells. Together with prior studies (19, 27, 29), these results suggested that separate genetic elements control Xist expression in undifferentiated ES and somatic cells.
Class II Mutants Are Defective in Heterochromatin Formation.
The BrdUrd assay showed that the Tg autosomes of class II clones were not grossly late-replicating. In over 50 metaphases examined for fibroblasts derived from πJL3.6, πJL3.8, and πJL3.10, not one showed diffuse BrdUrd incorporation, whereas nearly all had a brightly stained Y (not shown). Immunofluorescence with antiacetylated H4 antibodies also indicated that fibroblasts from πJL3.6, πJL3.8, and πJL3.10 could not induce H4 hypoacetylation. Although the Y was hypoacetylated consistently, not one Tg chromosome was grossly hypoacetylated (not shown). Thus, πJL3 lacked the sequences to induce late replication and H4 hypoacetylation.
Survival of Mouse Chimeras.
The results presented above suggest that class I deletions retain all important Xic elements, whereas the class II deletion removes essential sequences for the expression of Xist during differentiation and in somatic cells. This conclusion is supported by the reduced viability in vivo of class I relative to class II cells. Chimeric animals were generated easily by class II ES cells despite a high percentage chimerism (70–90%). No phenotype was seen even when the Tg was inserted into the X (πJL3.8). In contrast, class I chimeras were difficult to generate, with most pups dying in utero. In a πJL1.3 chimera, a sixth postaxial digit was evident in the posterior limbs. This extra digit was interesting in light of the fact that the insertion occurred near the telomere of Ch13. The extra toes locus (Xt; Gli3) maps near the centromere of Ch13 and was identified in a mouse with six toes carrying an 80-kb deletion on one allele (30). This identification raises the interesting possibility that the phenotype in πJL1.3 resulted from long-range silencing of the Xt locus.
DISCUSSION
We have created large-scale deletions of the murine Xic and analyzed their effects on X inactivation by using Tg-based assays. The class I deletions showed that more than 80% of the previously defined Xic interval could be removed without obvious effects on initiation, spread, and establishment of cis inactivation. Only an 80-kb domain is required, a region that includes the Xist gene and approximately 30 kb of upstream and 30 kb of downstream sequence. This region includes the 35-kb cosmid sequence identified by Herzing et al. (13).
Our work supports the feasibility of using a Tg approach in studying X inactivation. Because multiple cell lines with different insertion sites were examined for each deletion, this study suggests that long-range cis effects of the 80-kb region can be generalized to many autosomes. Indeed, the Xic Tg could overcome position effects, which had been invoked to explain why other Xic Tg studies had not found cis inactivation of autosomes (31, 32). The different outcomes may be explained by other factors, such as the method used to create Tg lines or Tg copy number. The idea that a high copy number increases Xic efficacy is an interesting one that warrants further investigation.
The data strengthen the hypothesis that the Xic works in a context-independent manner (12). This hypothesis is consistent with the behavior of X-to-autosome translocation chromosomes on which silencing can spread into the autosomal segment (33–35). It has been postulated that its long-range influence is enhanced by “way stations” (36), cis elements that reinforce the inactivation signal as it travels outwards from the Xic. These cis elements may be specific Xist RNA-binding sites. If way stations exist on the X chromosome, related sequences must also occur on autosomes. Such way stations are likely to be qualitatively different from those on the X. Although long-range effects were reproducible among class I Tg, differences from X inactivation were seen with regard to the extent of late DNA replication on the Tg autosome, suggesting that autosomal inactivation is less complete or stable.
The observation that Tg Xist RNA skips the ectopic Xic raises the possibility that the Xic lacks Xist-binding sites and therefore escapes inactivation on the Xi. Interestingly, skipping could be observed only on chromosomes carrying 80-kb P1 Tg and was not evident on those carrying larger YAC inserts (e.g., 116.6). This difference is perhaps because larger Tg carry non-Xic sequences that undergo X inactivation and might be expected to bind Xist RNA, thereby resulting in perceived coating of the Tg. Because a skip is not seen at the endogenous Xic, we believe that the combination of having multicopy Xic insertion and having only the minimal 80-kb Xic sequence enabled us to see the skip region in class I P1 Tg. These observations also raise the possibility that other X linked genes might escape X inactivation by a similar mechanism.
Analysis of class II clones showed that ES cell Xist expression can be separated from later events of X inactivation and that removal of 5′ Xist sequences abolished cis inactivation. Together with other studies (19, 27, 29), our data implicate 5′ sequences in controlling Xist expression. It has been proposed that developmentally specific Xist regulation requires an ES-specific promoter (P0) located 6 kb upstream of P1 and that the switch from P0 to P1 enables high Xist expression (19). Because πJL3 lacks P0 sequences but still expresses Xist in ES cells, P0 is not required absolutely for Xist expression in ES cells. This finding is consistent with prior studies that showed that P1 alone can function as a minimal promoter in both ES and somatic cells (27–29). In the context of other published work, our study also suggests important elements downstream of Xist. It has been proposed that a counting element or repressor of Xist resides in a 65-kb region downstream of Xist (16). Because the 80-kb Xic region identified by our study extends only 30 kb downstream, the combined evidence suggests that the Xist regulator resides in the 30-kb region.
This work shows that somatic X inactivation can be recapitulated by an 80-kb multifunctional domain. By showing that long-range cis effects can be generalized to many autosomes, we have established that Tg-based models for X inactivation serve as reasonable alternatives to mouse knockouts. Future studies will address whether this region is also sufficient for other forms of X inactivation, such as imprinted and male germ-line X inactivation (37, 38). The reduction to 80 kb now makes a detailed and comprehensive mutagenesis of the Xic to identify specific regulatory sequences more feasible.
Acknowledgments
We thank B. Seed for use of the mouse facility, and J. E. Kirby, B. Migeon, N. Stavropoulos, D. Warshawsky, and Y. Ogawa for critical reading of the manuscript. This work was funded by American Cancer Society Award ACS-IRG173H and a Hoechst award to J.T.L.
ABBREVIATIONS
- Chn
chromosome n
- dapi
4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole
- EB
embryoid body
- ES
embryonic stem
- FISH
fluorescence in situ hybridization
- Tg
transgene or transgenic
- Xi
inactive X
- Xic
X inactivation center
- YAC
yeast artificial chromosome
References
- 1.Lyon M F. Nature (London) 1961;190:372–373. doi: 10.1038/190372a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Lee J T, Jaenisch R. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1997;7:274–280. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(97)80138-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Mohandas T, Sparkes R S, Shapiro L J. Science. 1981;211:393–396. doi: 10.1126/science.6164095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Priest J H, Heady J E, Priest R E. J Cell Biol. 1967;35:483–487. doi: 10.1083/jcb.35.2.483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Jeppesen P, Turner B M. Cell. 1993;74:281–289. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90419-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Rastan S, Brown S D M. Genet Res. 1990;56:99–106. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300035163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Brown C J, Ballabio A, Rupert J L, Lafreniere R G, Grompe M, Tonlorenzi R, Willard H. Nature (London) 1991;349:38–44. doi: 10.1038/349038a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Clemson C M, McNeil J A, Willard H, Lawrence J B. J Cell Biol. 1996;132:259–275. doi: 10.1083/jcb.132.3.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Penny G D, Kay G F, Sheardown S A, Rastan S, Brockdorff N. Nature (London) 1996;379:131–137. doi: 10.1038/379131a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Rastan S, Robertson E J. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1985;90:379–388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Lee J T, Strauss W M, Dausman J A, Jaenisch R. Cell. 1996;86:83–94. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80079-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Lee J T, Jaenisch R. Nature (London) 1997;386:275–279. doi: 10.1038/386275a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Herzing L B K, Romer J T, Horn J M, Ashworth A. Nature (London) 1997;386:272–275. doi: 10.1038/386272a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Brockdorff N. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1998;8:328–333. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(98)80090-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Marahrens Y, Panning B, Dausman J, Strauss W, Jaenisch R. Genes Dev. 1997;11:156–166. doi: 10.1101/gad.11.2.156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Clerc P, Avner P. Nat Genet. 1998;19:249–253. doi: 10.1038/924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Pavan W J, Hieter P, Reeves R H. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1990;85:6027–6031. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kusumi K, Smith J S, Segre J A, Koos D S, Lander E S. Mamm Genome. 1993;4:391–392. doi: 10.1007/BF00360591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Johnston C M, Nesterova T B, Formstone E J, Newall A E T, Duthie S M, Sheardown S A, Brockdorff N. Cell. 1998;94:809–817. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81739-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Li E, Bestor T H, Jaenisch R. Cell. 1992;69:915–926. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90611-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Lee J T, Jaenisch R. Nucleic Acids Res. 1996;24:5054–5055. doi: 10.1093/nar/24.24.5054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Lawrence J B, Singer R H, Marselle L M. Cell. 1989;57:493–502. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90924-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Trask B J. Trends Genet. 1991;7:149–154. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90378-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Martin G R, Epstein C J, Travis B, Tucker G, Yatziv S, David W, Martin J, Clift S, Cohen S. Nature (London) 1978;271:329–333. doi: 10.1038/271329a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Kay G F, Penny G D, Patel D, Ashworth A, Brockdorff N, Rastan S. Cell. 1993;72:171–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90658-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Schempp W. In: The Y Chromosome. Sandberg A A, editor. New York: Liss; 1985. pp. 357–371. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Hendrich B D, Plenge R M, Willard H F. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997;25:2661–2671. doi: 10.1093/nar/25.13.2661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Pillet N, Bonny C, Schorderet D F. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1995;92:12515–12519. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.26.12515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Sheardown S A, Newall A E T, Norris D P, Rastan S, Brockdorff N. Gene. 1997;203:159–168. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(97)00507-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Lyon M F, Rastan S, Brown S D M. Genetic Variations and Strains of the Laboratory Mouse. Oxford: Oxford Univ. Press; 1996. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Heard E, Dress C, Mongelard F, Courtier B, Rougeulle C, Ashworth A, Vourch C, Babinet C, Avner P. Hum Mol Genet. 1996;5:441–450. doi: 10.1093/hmg/5.4.441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Matsuura S, Episkopou V, Hamvas R, Brown S D M. Hum Mol Genet. 1996;5:451–459. doi: 10.1093/hmg/5.4.451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Keitges E A, Palmer C G. Hum Genet. 1986;72:230–236. doi: 10.1007/BF00291884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Eicher E M. Adv Genet. 1970;15:175–259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.White W M, Willard H F, Dyke D L V, Wolff D J. Am J Hum Genet. 1998;63:20–28. doi: 10.1086/301922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Gartler S M, Riggs A D. Annu Rev Genet. 1983;17:155–190. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.17.120183.001103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Richardson B J, Czuppon A B, Sharman G B. Nat New Biol. 1971;230:154–155. doi: 10.1038/newbio230154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Monesi V. Exp Cell Res. 1965;39:197–224. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(65)90023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]