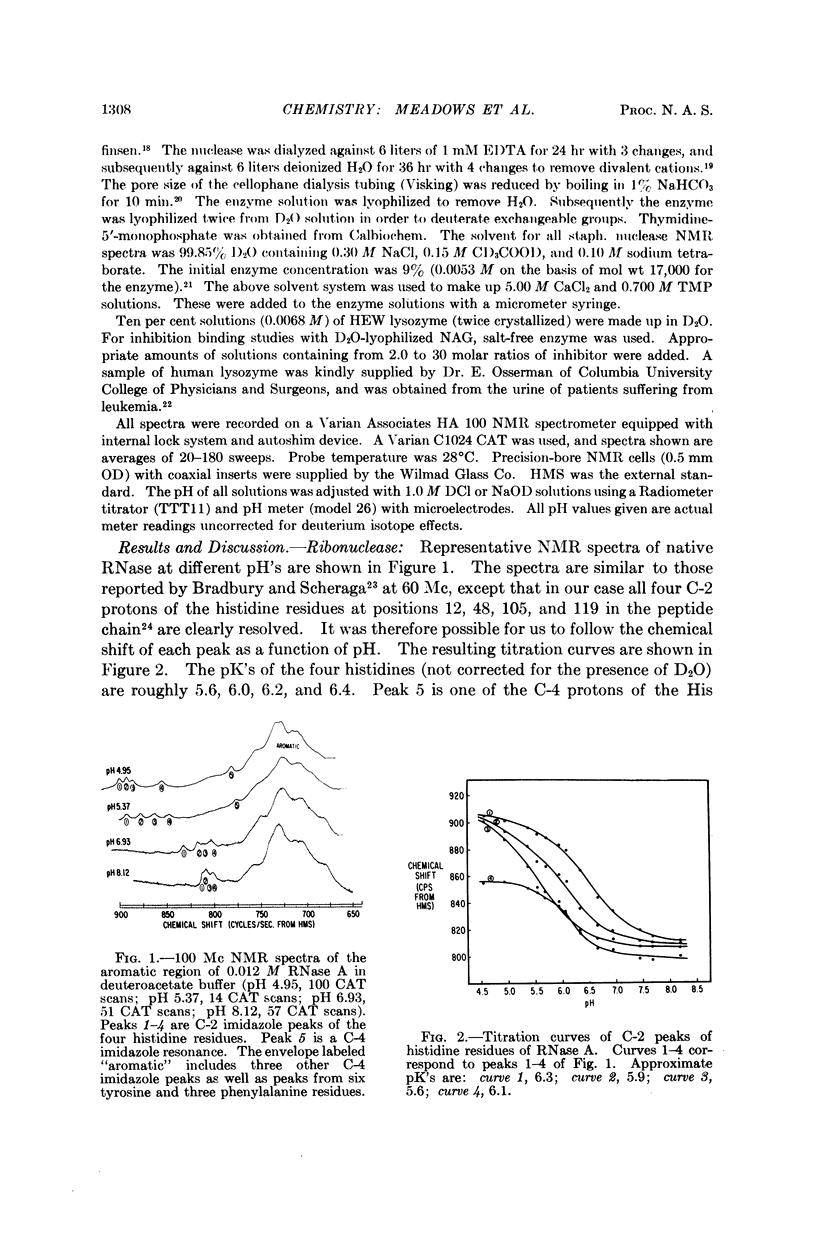
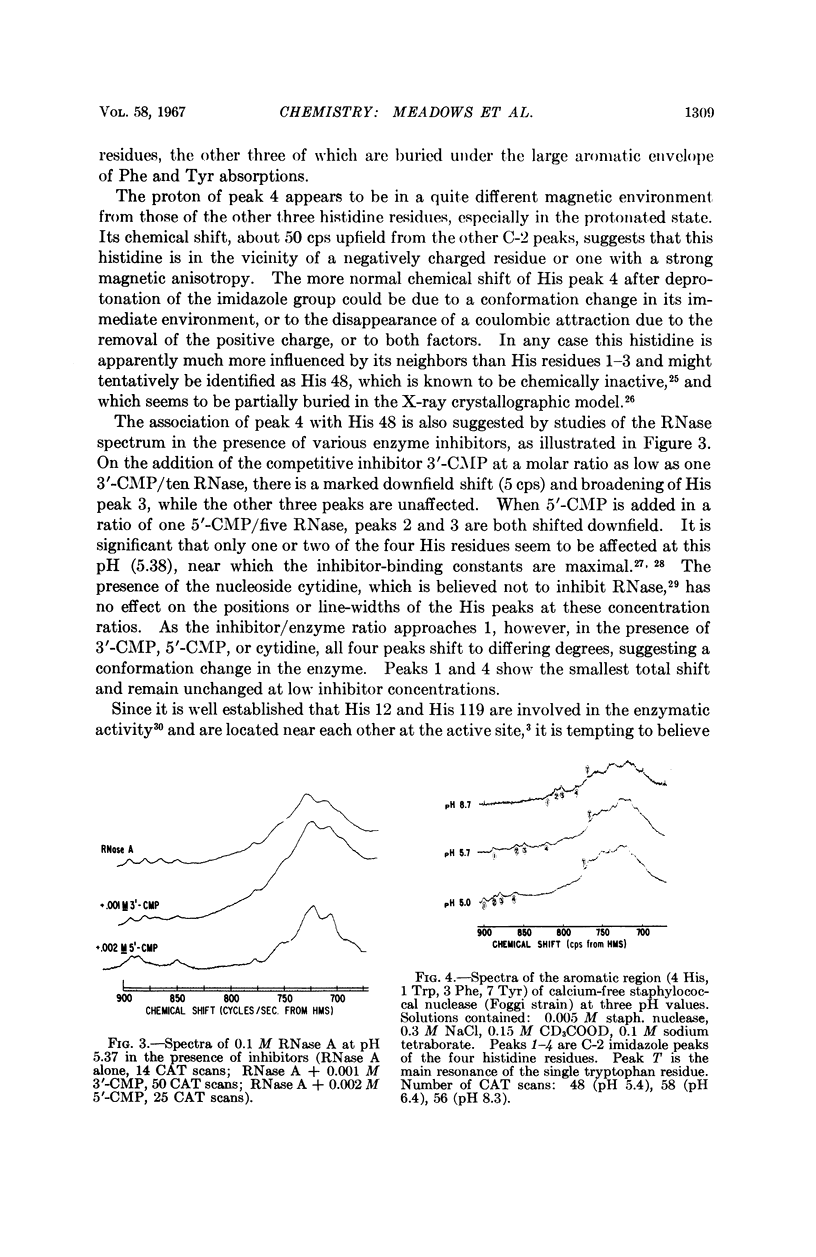
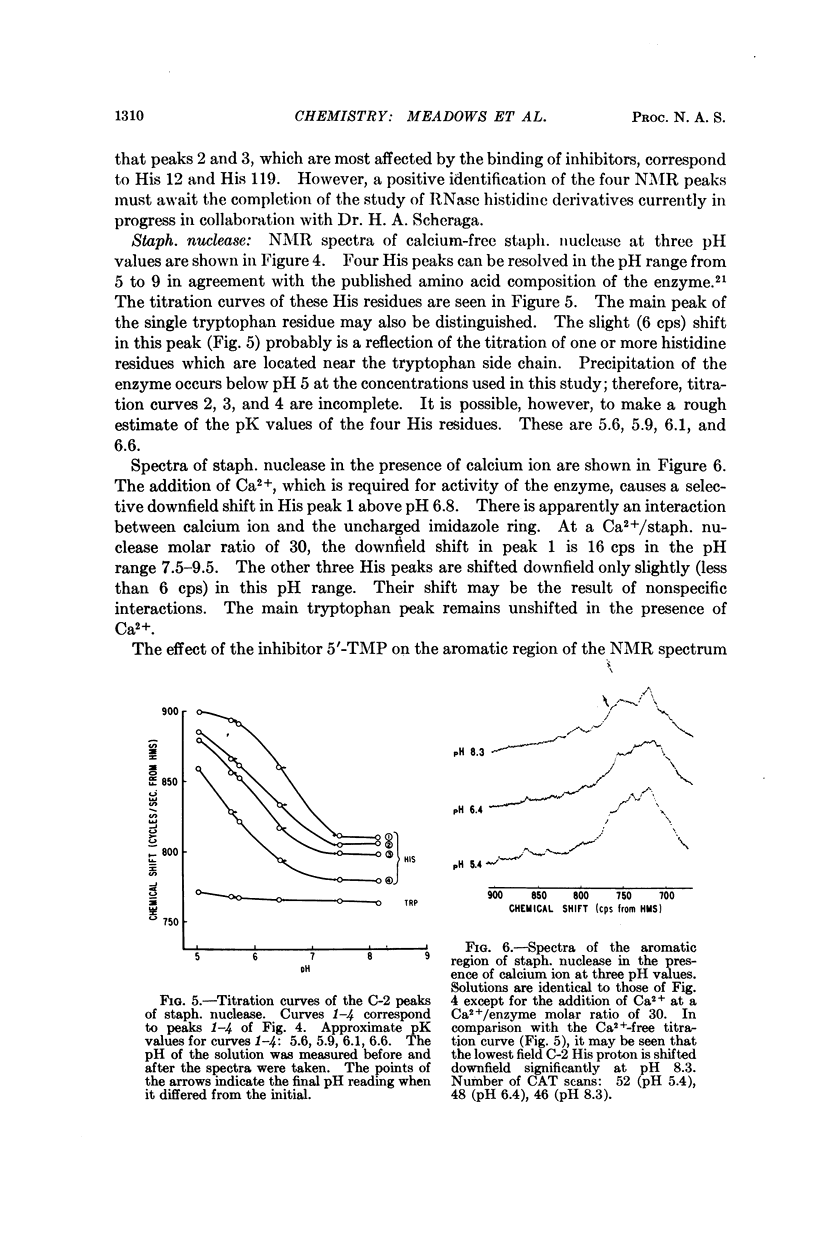
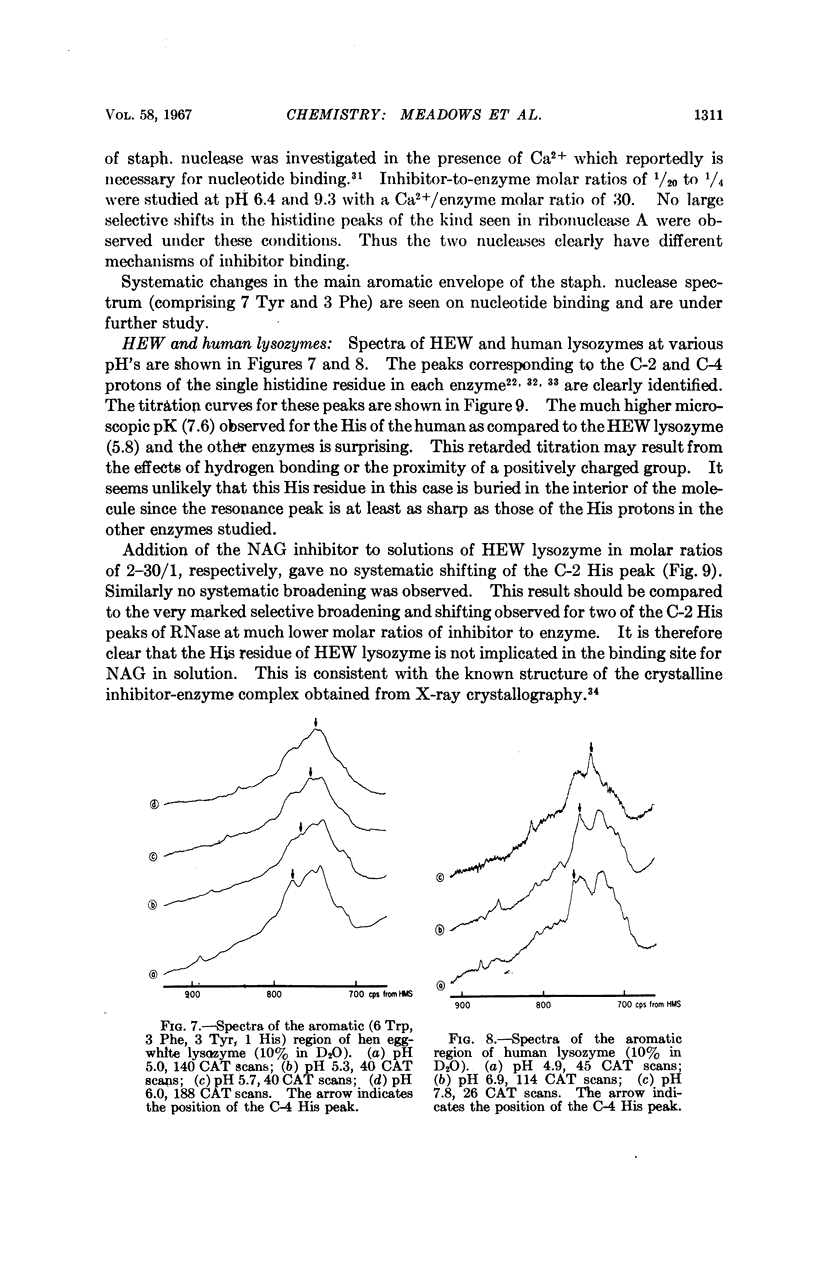
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avey H. P., Boles M. O., Carlisle C. H., Evans S. A., Morris S. J., Palmer R. A., Woolhouse B. A., Shall S. Structure of ribonuclease. Nature. 1967 Feb 11;213(5076):557–562. doi: 10.1038/213557a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bak B., Pedersen E. J., Sundby F. Proton magnetic resonance spectra of porcine and bovine insulin and of the A and B chain of bovine insulin. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jun 10;242(11):2637–2645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake C. C., Koenig D. F., Mair G. A., North A. C., Phillips D. C., Sarma V. R. Structure of hen egg-white lysozyme. A three-dimensional Fourier synthesis at 2 Angstrom resolution. Nature. 1965 May 22;206(4986):757–761. doi: 10.1038/206757a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CANFIELD R. E., LIU A. K. THE DISULFIDE BONDS OF EGG WHITE LYSOZYME (MURAMIDASE). J Biol Chem. 1965 May;240:1997–2002. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRESTFIELD A. M., STEIN W. H., MOORE S. Alkylation and identification of the histidine residues at the active site of ribonuclease. J Biol Chem. 1963 Jul;238:2413–2419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P., Fuchs S., Anfinsen C. B. Catalytic properties and specificity of the extracellular nuclease of Staphylococcus aureus. J Biol Chem. 1967 Apr 10;242(7):1541–1547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISCHER J. J., JARDETZKY O. NUCLEAR MAGNETIC RELAXATION STUDY OF INTERMOLECULAR COMPLEXES. THE MECHANISM OF PENICILLIN BINDING TO SERUM ALBUMIN. J Am Chem Soc. 1965 Jul 20;87:3237–3244. doi: 10.1021/ja01092a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEINRIKSON R. L., STEIN W. H., CRESTFIELD A. M., MOORE S. THE REACTIVITIES OF THE HISTIDINE RESIDUES AT THE ACTIVE SITE OF RIBONUCLEASE TOWARD HALO ACIDS OF DIFFERENT STRUCTURES. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jul;240:2921–2934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUMMEL J. P., VER PLOEG D. A., NELSON C. A. The interaction between ribonuclease and mononucleotides as measured spectrophotometrically. J Biol Chem. 1961 Dec;236:3168–3172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammes G. G., Schimmel P. R. Equilibrium measurements of the binding of cytidine 3'-phosphate to ribonuclease. J Am Chem Soc. 1965 Nov 5;87(21):4665–4669. doi: 10.1021/ja00949a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heins J. N., Suriano J. R., Taniuchi H., Anfinsen C. B. Characterization of a nuclease produced by Staphylococcus aureus. J Biol Chem. 1967 Mar 10;242(5):1016–1020. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jardetzky O., Wade-Jardetzky N. G. On the mechanism of the binding of sulfonamides to bovine serum albumin. Mol Pharmacol. 1965 Nov;1(3):214–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. N., Phillips D. C. Structure of some crystalline lysozyme-inhibitor complexes determined by X-ray analysis at 6 Angstrom resolution. Nature. 1965 May 22;206(4986):761–763. doi: 10.1038/206761a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jollès J., Jollès P. Human tear and human milk lysozymes. Biochemistry. 1967 Feb;6(2):411–417. doi: 10.1021/bi00854a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOWALSKY A. Nuclear magnetic resonance studies of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1962 Jun;237:1807–1819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kartha G., Bello J., Harker D. Tertiary structure of ribonuclease. Nature. 1967 Mar 4;213(5079):862–865. doi: 10.1038/213862a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANDEL M. PROTON MAGNETIC RESONANCE SPECTRA OF SOME PROTEINS. I. RIBONUCLEASE, OXIDIZED RIBONUCLEASE, LYSOZYME, AND CYTOCHROME C. J Biol Chem. 1965 Apr;240:1586–1592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markley J. L., Meadows D. H., Jardetzky O. Nuclear magnetic resonance studies of helix-coil transitions in polyamino acids. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jul 14;27(1):25–40. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90349-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morlino V. J., Martin R. B. Chemical shift nonequivalence in proton magnetic resonance spectra of glycyl peptides. J Am Chem Soc. 1967 Jun 21;89(13):3107–3111. doi: 10.1021/ja00989a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross C. A., Mathias A. P., Rabin B. R. The active site and mechanism of action of bovine pancreatic ribonuclease. 6. Kinetic and spectrophotometric investigation of the interaction of the enzyme with inhibitors and p-nitrophenyl acetate. Biochem J. 1962 Oct;85(1):145–151. doi: 10.1042/bj0850145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMYTH D. G., STEIN W. H., MOORE S. The sequence of amino acid residues in bovine pancreatic ribonuclease: revisions and confirmations. J Biol Chem. 1963 Jan;238:227–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniuchi H., Anfinsen C. B. The amino acid sequence of an extracellular nuclease of Staphylococcus aureus. I. Linear order of the fragments produced by cleavage with cyanogen bromide. J Biol Chem. 1966 Oct 10;241(19):4366–4385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


