Abstract
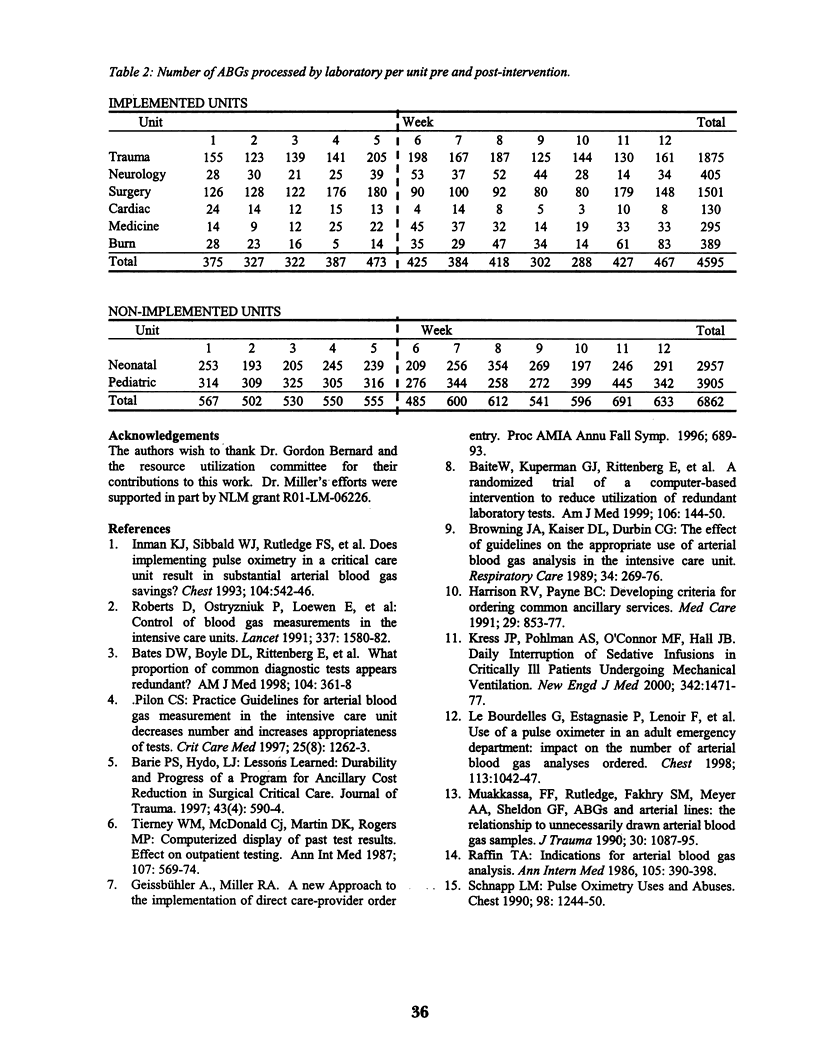
OBJECTIVE: To evaluate impact of a computer-based intervention on arterial blood gas (ABG) usage in an intensive care setting. DESIGN: Retrospectively examined, via mixed group analysis, the effects of the intervention on ABG usage in the intensive care unit (ICU). SUBJECTS: Included all clinicians who placed ABG orders in an ICU using the computerized physician order-entry system, as well as controls in non-order entry units. METHODS: Computer-based intervention presenting ordering clinician with patient s previous ABG values and limiting forward duration of tests ordered. Study spanned 12 weeks, 5 weeks pre-intervention and 7-weeks post-intervention. Of 8 ICUs, intervention implemented in 6, not implemented in 2. Data analyzed using the repeated measure ANOVA. RESULTS: Physicians entered <40% ABG orders. 376 ABGs per week processed pre-intervention, 387 per week post. Results nonsignificant with a p= 0.09. Orders placed declined from 1039 per week, Jan 2000 to 662 per week, April 2001. DISCUSSION: Study did not demonstrate significant change; limited power. Need longer study periods. Impact improved in the future by targeting physician users and tailoring intervention to specific work flow pattern of high utilization units.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barie P. S., Hydo L. J. Lessons learned: durability and progress of a program for ancillary cost reduction in surgical critical care. J Trauma. 1997 Oct;43(4):590–596. doi: 10.1097/00005373-199710000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bates D. W., Boyle D. L., Rittenberg E., Kuperman G. J., Ma'Luf N., Menkin V., Winkelman J. W., Tanasijevic M. J. What proportion of common diagnostic tests appear redundant? Am J Med. 1998 Apr;104(4):361–368. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(98)00063-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bates D. W., Kuperman G. J., Rittenberg E., Teich J. M., Fiskio J., Ma'luf N., Onderdonk A., Wybenga D., Winkelman J., Brennan T. A. A randomized trial of a computer-based intervention to reduce utilization of redundant laboratory tests. Am J Med. 1999 Feb;106(2):144–150. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9343(98)00410-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geissbühler A., Miller R. A. A new approach to the implementation of direct care-provider order entry. Proc AMIA Annu Fall Symp. 1996:689–693. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison R. V., Payne B. C. Developing criteria for ordering common ancillary services. Med Care. 1991 Sep;29(9):853–877. doi: 10.1097/00005650-199109000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inman K. J., Sibbald W. J., Rutledge F. S., Speechley M., Martin C. M., Clark B. J. Does implementing pulse oximetry in a critical care unit result in substantial arterial blood gas savings? Chest. 1993 Aug;104(2):542–546. doi: 10.1378/chest.104.2.542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kress J. P., Pohlman A. S., O'Connor M. F., Hall J. B. Daily interruption of sedative infusions in critically ill patients undergoing mechanical ventilation. N Engl J Med. 2000 May 18;342(20):1471–1477. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200005183422002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Bourdellès G., Estagnasié P., Lenoir F., Brun P., Dreyfuss D. Use of a pulse oximeter in an adult emergency department: impact on the number of arterial blood gas analyses ordered. Chest. 1998 Apr;113(4):1042–1047. doi: 10.1378/chest.113.4.1042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muakkassa F. F., Rutledge R., Fakhry S. M., Meyer A. A., Sheldon G. F. ABGs and arterial lines: the relationship to unnecessarily drawn arterial blood gas samples. J Trauma. 1990 Sep;30(9):1087–1095. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raffin T. A. Indications for arterial blood gas analysis. Ann Intern Med. 1986 Sep;105(3):390–398. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-105-3-390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts D., Ostryzniuk P., Loewen E., Shanks A., Wasyluk T., Pronger L., Hasinoff I., Roberts E., McEwen T. A. Control of blood gas measurements in intensive-care units. Lancet. 1991 Jun 29;337(8757):1580–1582. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)93271-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnapp L. M., Cohen N. H. Pulse oximetry. Uses and abuses. Chest. 1990 Nov;98(5):1244–1250. doi: 10.1378/chest.98.5.1244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tierney W. M., McDonald C. J., Martin D. K., Rogers M. P. Computerized display of past test results. Effect on outpatient testing. Ann Intern Med. 1987 Oct;107(4):569–574. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-107-4-569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


