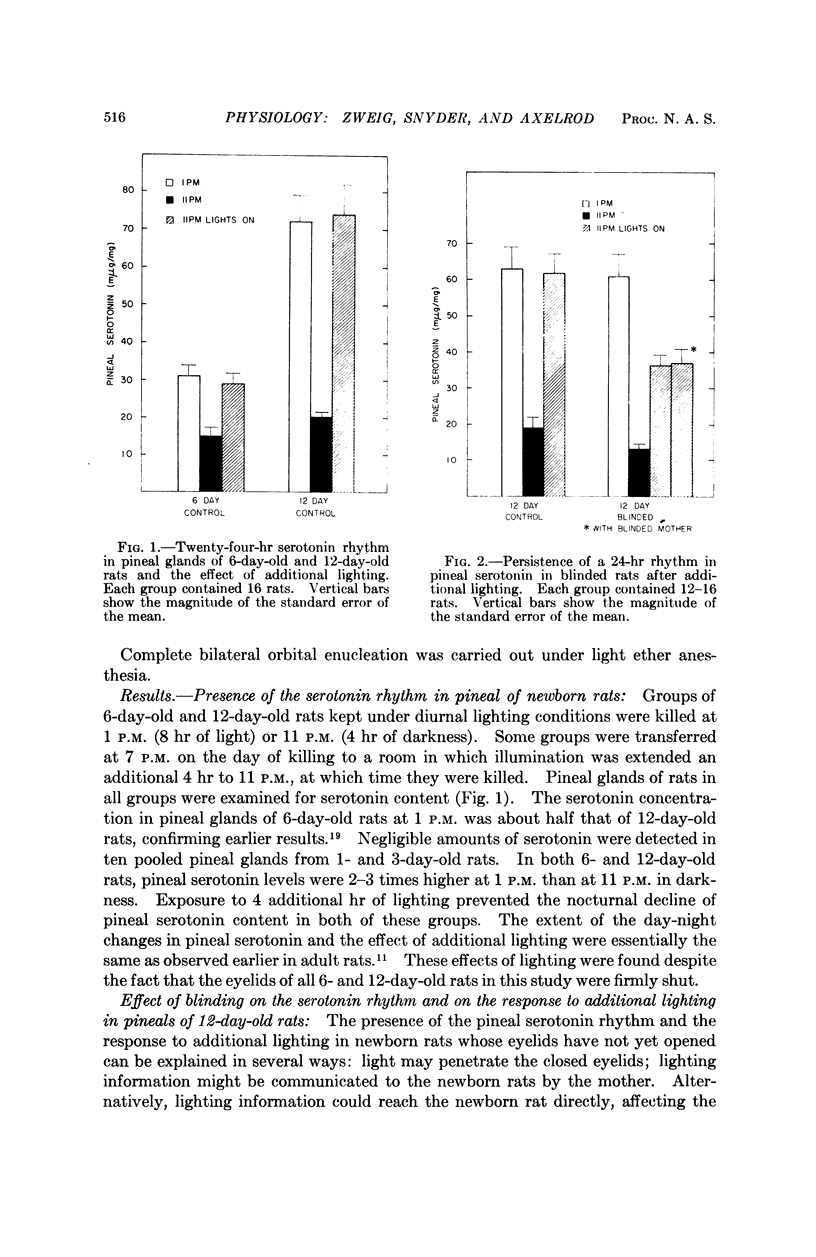
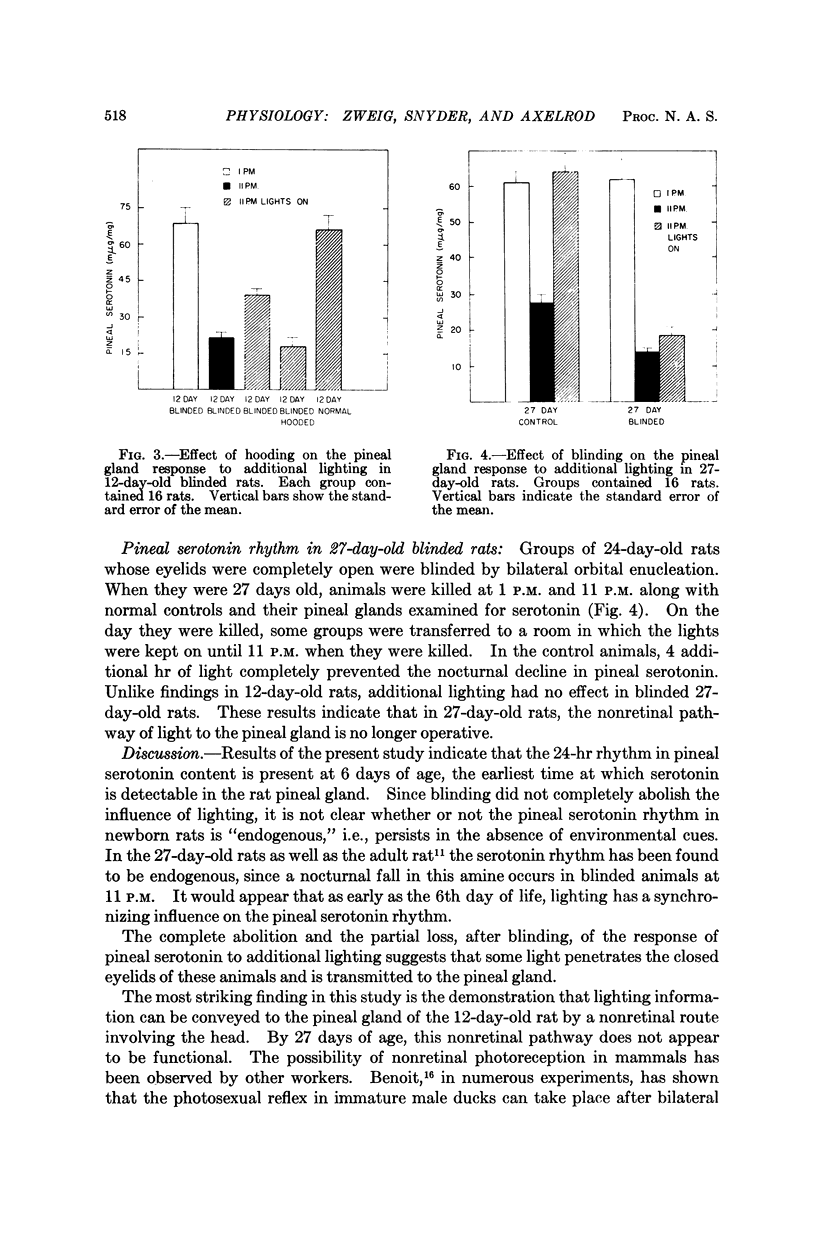
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AXELROD J., WURTMAN R. J., SNYDER S. H. CONTROL OF HYDROXYINDOLE O-METHYLTRANSFERASE ACTIVITY IN THE RAT PINEAL GLAND BY ENVIRONMENTAL LIGHTING. J Biol Chem. 1965 Feb;240:949–954. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENOIT J. THE ROLE OF THE EYE AND OF THE HYPOTHALAMUS IN THE PHOTOSTIMULATION OF GONADS IN THE DUCK. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Sep 10;117:204–216. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb48175.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DODT E., JACOBSON M. PHOTOSENSITIVITY OF A LOCALIZED REGION OF THE FROG DIENCEPHALON. J Neurophysiol. 1963 Sep;26:752–758. doi: 10.1152/jn.1963.26.5.752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GANONG W. F., SHEPHERD M. D., WALL J. R., VAN BRUNT E. E., CLEGG M. T. Penetration of light into the brain of mammals. Endocrinology. 1963 Jun;72:962–963. doi: 10.1210/endo-72-6-962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLWICH F. THE INFLUENCE OF LIGHT VIA THE EYES ON ANIMALS AND MAN. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Sep 10;117:105–131. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb48165.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPPERS J. A. The development, topographical relations and innervation of the epiphysis cerebri in the albino rat. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1960;52:163–215. doi: 10.1007/BF00338980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LISK R. D., KANNWISCHER L. R. LIGHT: EVIDENCE FOR ITS DIRECT EFFECT ON HYPOTHALAMIC NEURONS. Science. 1964 Oct 9;146(3641):272–273. doi: 10.1126/science.146.3641.272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OKSCHE A. SURVEY OF THE DEVELOPMENT AND COMPARATIVE MORPHOLOGY OF THE PINEAL ORGAN. Prog Brain Res. 1965;10:3–29. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)63445-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SNYDER S. H., AXELROD J., FISCHER J. E., WURTMAN R. J. NEURAL AND PHOTIC REGULATION OF 5-HYDROXYTRYPTOPHAN DECARBOXYLASE IN THE RAT PINEAL GLAND. Nature. 1964 Aug 29;203:981–982. doi: 10.1038/203981a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SNYDER S. H., AXELROD J., WURTMAN R. J., FISCHER J. E. CONTROL OF 5-HYDROXYTRYPTOPHAN DECARBOXYLASE ACTIVITY IN THE RAT PINEAL GLAND BY SYMPATHETIC NERVES. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1965 Mar;147:371–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SNYDER S. H., ZWEIG M., AXELROD J. CONTROL OF THE CIRCADIAN RHYTHM IN SEROTONIN CONTENT OF THE RAT PINEAL GLAND. Life Sci. 1964 Oct;3:1175–1179. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(64)90137-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SNYDER S. H., ZWEIG M., AXELROD J., FISCHER J. E. CONTROL OF THE CIRCADIAN RHYTHM IN SEROTONIN CONTENT OF THE RAT PINEAL GLAND. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Feb;53:301–305. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.2.301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder S. H., Axelrod J., Zweig M. A sensitive and specific fluorescence assay for tissue serotonin. Biochem Pharmacol. 1965 May;14(5):831–835. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(65)90102-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WURTMAN R. J., AXELROD J., CHU E. W., FISCHER J. E. MEDIATION OF SOME EFFECT OF ILLUMINATION ON THE RAT ESTROUS CYCLE BY THE SYMPATHETIC NERVOUS SYSTEM. Endocrinology. 1964 Aug;75:266–272. doi: 10.1210/endo-75-2-266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WURTMAN R. J., AXELROD J., PHILLIPS L. S. MELATONIN SYNTHESIS IN THE PINEAL GLAND: CONTROL BY LIGHT. Science. 1963 Nov 22;142(3595):1071–1073. doi: 10.1126/science.142.3595.1071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wurtman R. J., Axelrod J., Fischer J. E. Melatonin Synthesis in the Pineal Gland: Effect of Light Mediated by the Sympathetic Nervous System. Science. 1964 Mar 20;143(3612):1328–1329. doi: 10.1126/science.143.3612.1328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



