Abstract
In the present paper, a multi-agent system is proposed, which can be integrated in the home care telemedicine system that was developed in the context of the Citizen Health System (CHS) European project, functioning as a contact center for diabetic and congestive heart failure patients. The objective of the multi-agent system is to provide a set of alert/notification mechanisms for the clinicians, helping them to classify the clinical condition of each patient. Therefore, despite the huge amount of data managed by the system, due to the daily use of the contact center's services, these alert mechanisms provide the clinician with an overview of the cases that need further examination and save him/her time from the trivial cases. The multi-agent system consists of different types of agents, each one assigned with specific tasks, which communicate with each other, in order to share knowledge.
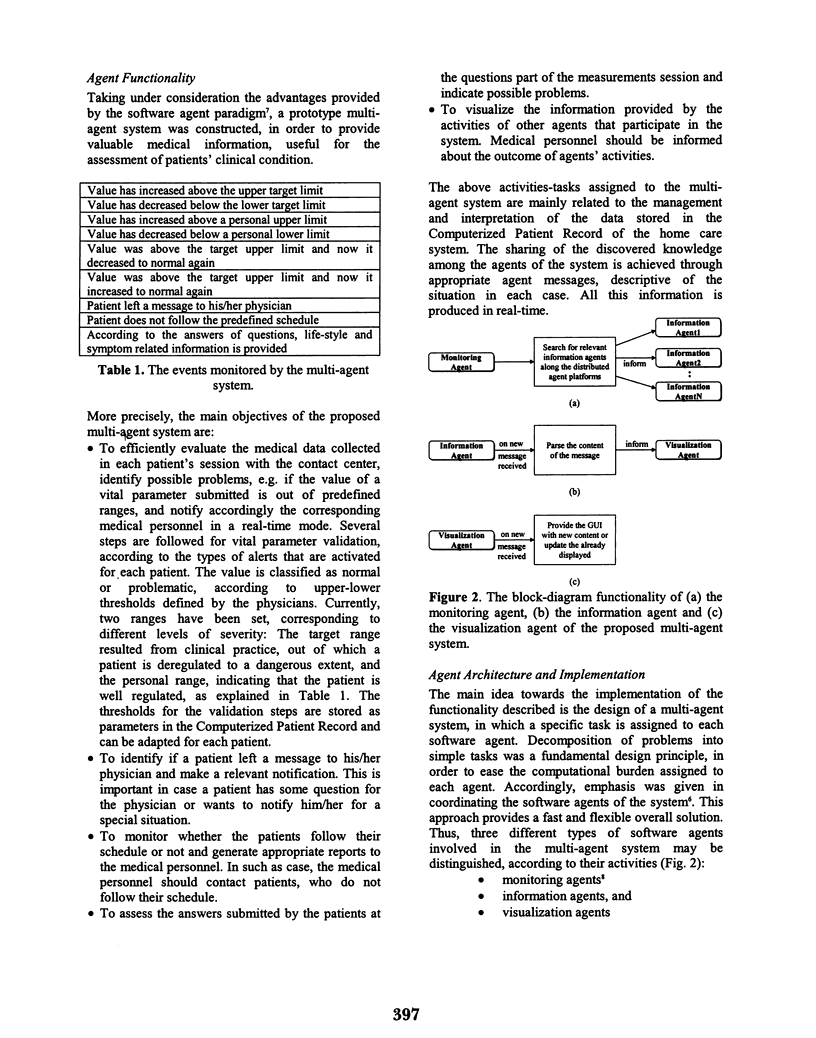
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balas E. A., Iakovidis I. Distance technologies for patient monitoring. Interview by Abi Berger. BMJ. 1999 Nov 13;319(7220):1309–1309. doi: 10.1136/bmj.319.7220.1309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balas E. A., Weingarten S., Garb C. T., Blumenthal D., Boren S. A., Brown G. D. Improving preventive care by prompting physicians. Arch Intern Med. 2000 Feb 14;160(3):301–308. doi: 10.1001/archinte.160.3.301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collen M. F. Historical evolution of preventive medical informatics in the USA. Methods Inf Med. 2000 Aug;39(3):204–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanzola G., Gatti L., Falasconi S., Stefanelli M. A framework for building cooperative software agents in medical applications. Artif Intell Med. 1999 Jul;16(3):223–249. doi: 10.1016/s0933-3657(99)00008-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


