Abstract
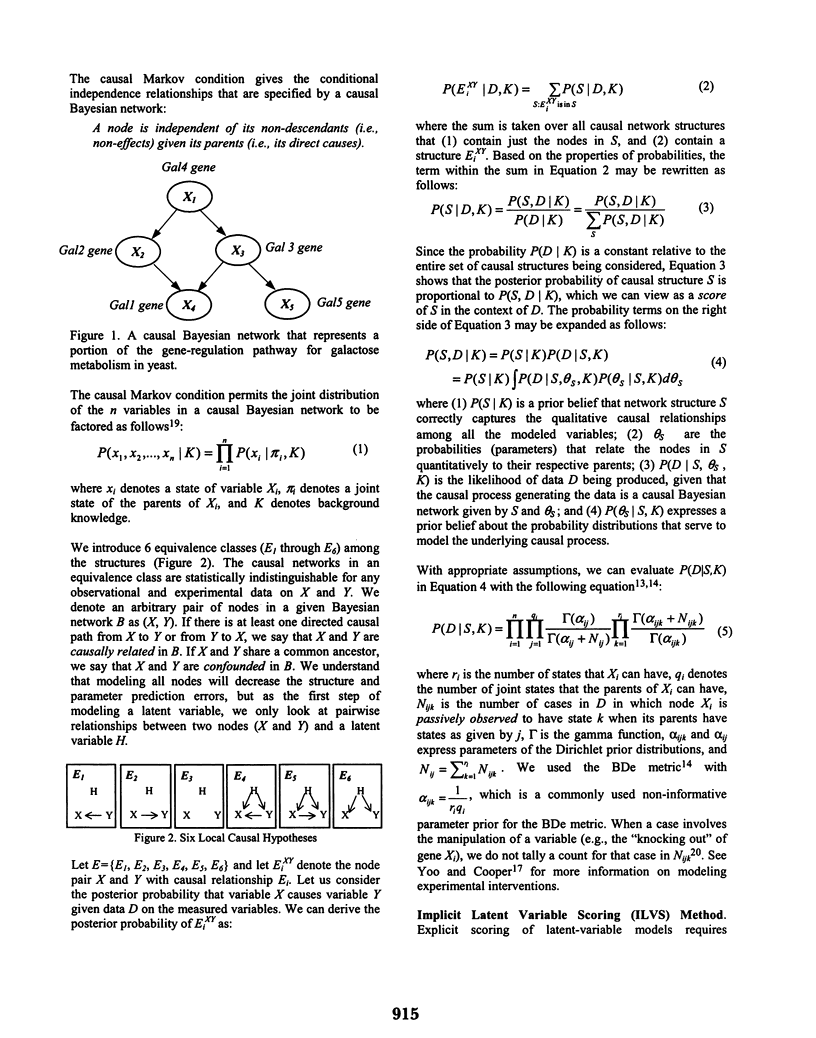
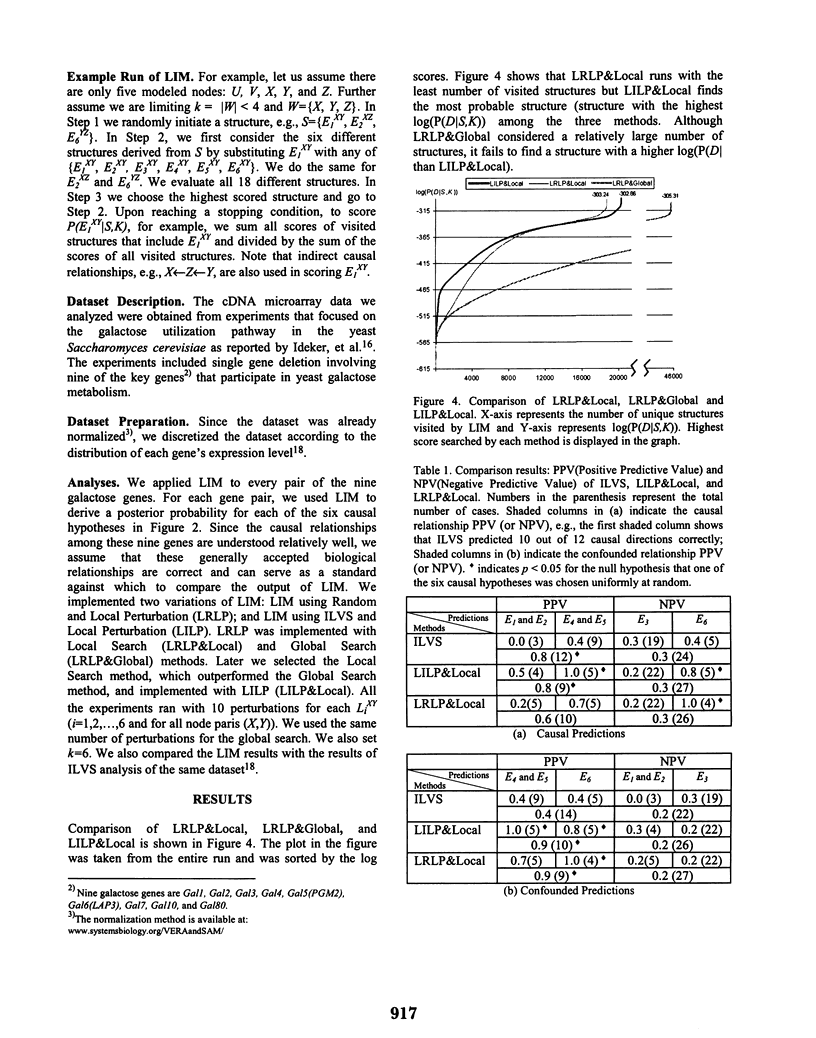
This paper reports the methods and results of a computer-based algorithm that takes as input the expression levels of a set of genes as given by DNA microarray data, and then searches for causal pathways that represent how the genes regulate each other. The algorithm uses local heuristic search and a Bayesian scoring metric. We applied the algorithm to induce causal networks from a mixture of observational and experimental gene-expression data on genes involved in galactose metabolism in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The observational data consisted of gene-expression levels obtained from unmanipulated inverted exclamation mark degrees wild-type inverted exclamation mark +/- cells. The experimental data were produced by deleting ( inverted exclamation mark degrees knocking out inverted exclamation mark +/-) genes and measuring the expression levels of other genes. We used this data to evaluate several variations of the local search method. In each evaluation, causal relationships were predicted for all 36 pairwise combinations of nine key galactose-related genes. These predictions were then compared to the known causal relationships among these genes.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- D'haeseleer P., Liang S., Somogyi R. Genetic network inference: from co-expression clustering to reverse engineering. Bioinformatics. 2000 Aug;16(8):707–726. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/16.8.707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ideker T., Thorsson V., Ranish J. A., Christmas R., Buhler J., Eng J. K., Bumgarner R., Goodlett D. R., Aebersold R., Hood L. Integrated genomic and proteomic analyses of a systematically perturbed metabolic network. Science. 2001 May 4;292(5518):929–934. doi: 10.1126/science.292.5518.929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smolen P., Baxter D. A., Byrne J. H. Modeling transcriptional control in gene networks--methods, recent results, and future directions. Bull Math Biol. 2000 Mar;62(2):247–292. doi: 10.1006/bulm.1999.0155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spellman P. T., Sherlock G., Zhang M. Q., Iyer V. R., Anders K., Eisen M. B., Brown P. O., Botstein D., Futcher B. Comprehensive identification of cell cycle-regulated genes of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae by microarray hybridization. Mol Biol Cell. 1998 Dec;9(12):3273–3297. doi: 10.1091/mbc.9.12.3273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver D. C., Workman C. T., Stormo G. D. Modeling regulatory networks with weight matrices. Pac Symp Biocomput. 1999:112–123. doi: 10.1142/9789814447300_0011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


