Abstract
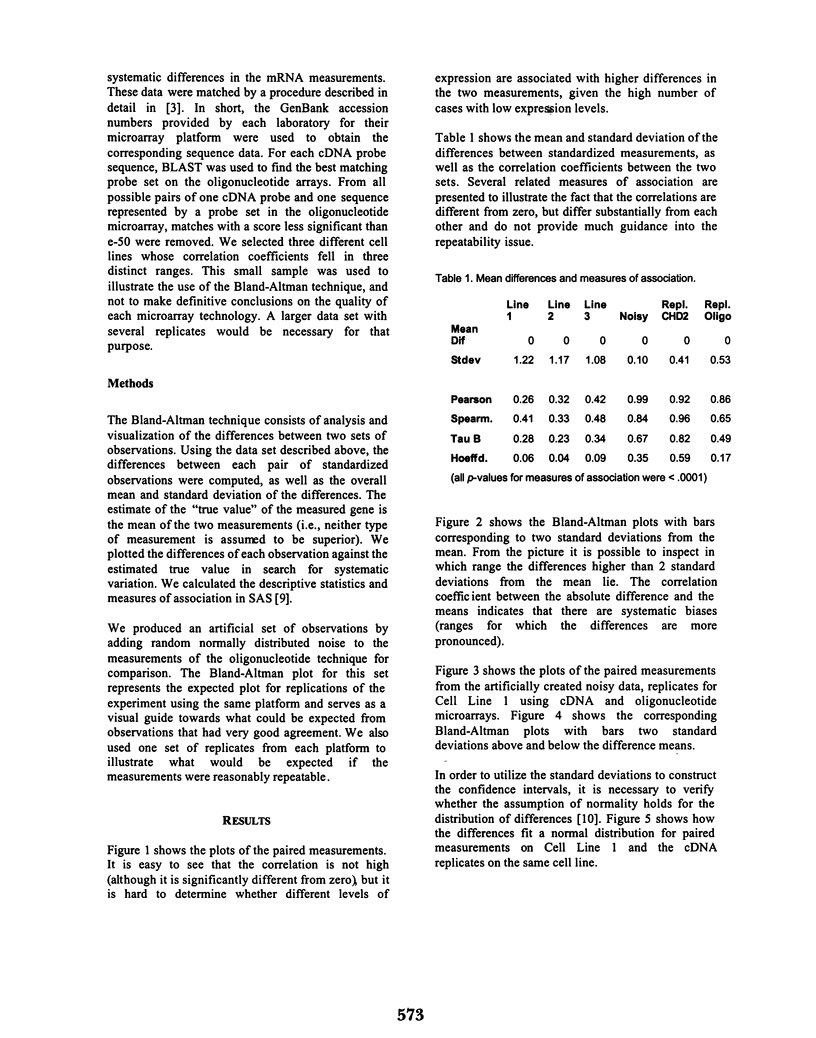
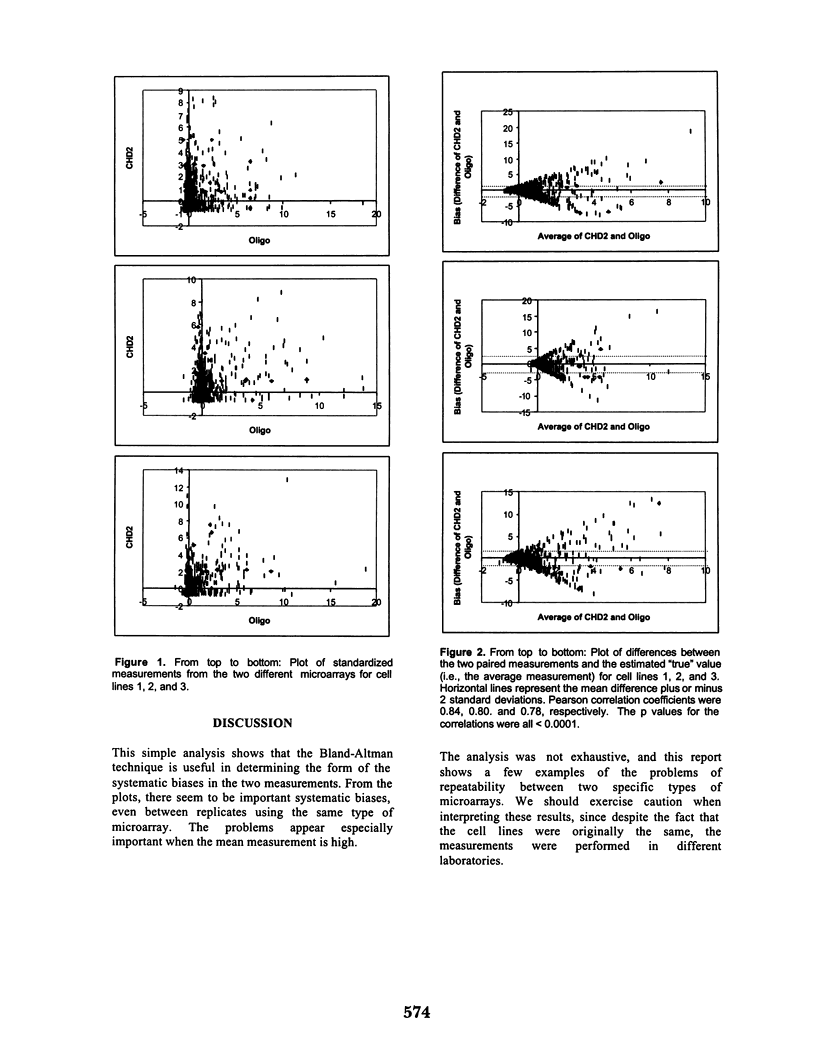
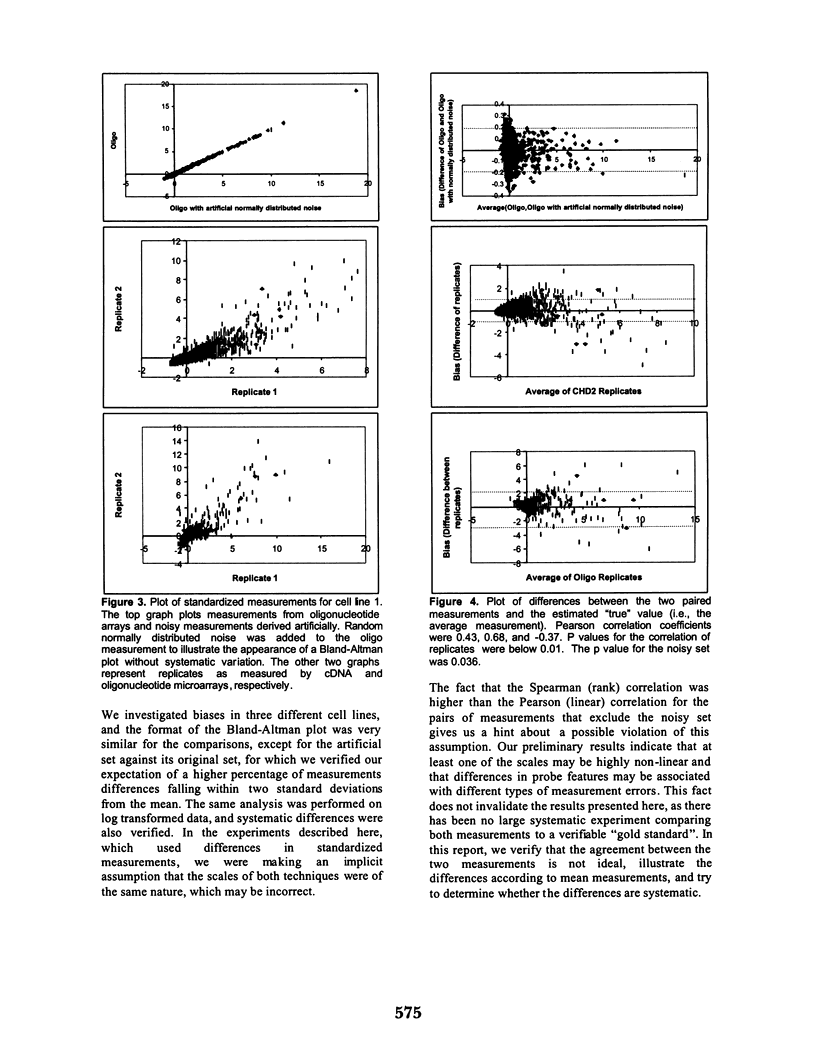
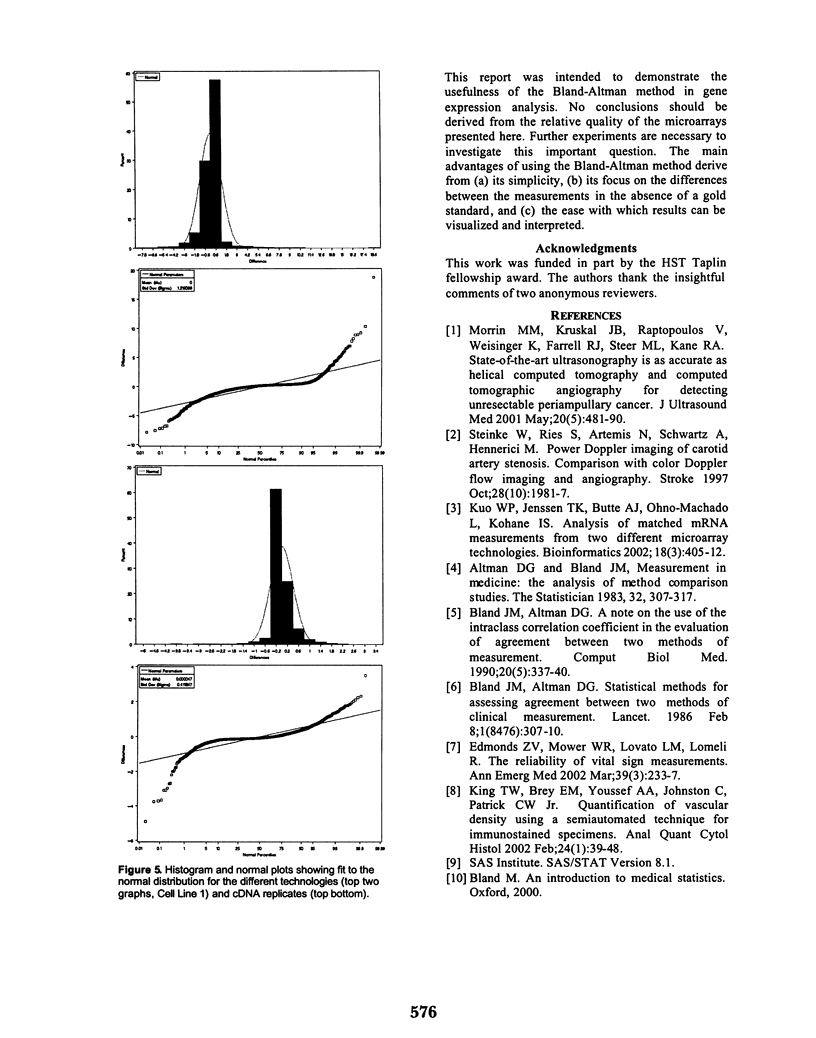
Several problems in medicine and biology involve the comparison of two measurements made on the same set of cases. The problem differs from a calibration problem because no gold standard can be identified. Testing the null hypothesis of no relationship using measures of association is not optimal since the measurements are made on the same cases, and therefore correlation coefficients will tend to be significant. The descriptive Bland-Altman method can be used in exploratory analysis of this problem, allowing the visualization of gross systematic differences between the two sets of measurements. We utilize the method on three sets of matched observations and demonstrate its usefulness in detecting systematic variations between two measurement technologies to assess gene expression.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bland J. M., Altman D. G. A note on the use of the intraclass correlation coefficient in the evaluation of agreement between two methods of measurement. Comput Biol Med. 1990;20(5):337–340. doi: 10.1016/0010-4825(90)90013-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bland J. M., Altman D. G. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet. 1986 Feb 8;1(8476):307–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmonds Zachary V., Mower William R., Lovato Luis M., Lomeli Rosaelva. The reliability of vital sign measurements. Ann Emerg Med. 2002 Mar;39(3):233–237. doi: 10.1067/mem.2002.122017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King Timothy W., Brey Eric M., Youssef Adel A., Johnston Carol, Patrick Charles W., Jr Quantification of vascular density using a semiautomated technique for immunostained specimens. Anal Quant Cytol Histol. 2002 Feb;24(1):39–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo Winston Patrick, Jenssen Tor-Kristian, Butte Atul J., Ohno-Machado Lucila, Kohane Isaac S. Analysis of matched mRNA measurements from two different microarray technologies. Bioinformatics. 2002 Mar;18(3):405–412. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/18.3.405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrin M. M., Kruskal J. B., Raptopoulos V., Weisinger K., Farrell R. J., Steer M. L., Kane R. A. State-of-the-art ultrasonography is as accurate as helical computed tomography and computed tomographic angiography for detecting unresectable periampullary cancer. J Ultrasound Med. 2001 May;20(5):481–490. doi: 10.7863/jum.2001.20.5.481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinke W., Ries S., Artemis N., Schwartz A., Hennerici M. Power Doppler imaging of carotid artery stenosis. Comparison with color Doppler flow imaging and angiography. Stroke. 1997 Oct;28(10):1981–1987. doi: 10.1161/01.str.28.10.1981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


