Abstract
Background
Class I major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules bind, and present to T cells, short peptides derived from intracellular processing of proteins. The peptide repertoire of a specific molecule is to a large extent determined by the molecular structure accommodating so-called main anchor positions of the presented peptide. These receptors are extremely polymorphic, and much of the polymorphism influences the peptide-binding repertoire. However, despite this polymorphism, class I molecules can be clustered into sets of molecules that bind largely overlapping peptide repertoires. Almost a decade ago we introduced this concept of clustering human leukocyte antigen (HLA) alleles and defined nine different groups, denominated as supertypes, on the basis of their main anchor specificity. The utility of this original supertype classification, as well several other subsequent arrangements derived by others, has been demonstrated in a large number of epitope identification studies.
Results
Following our original approach, in the present report we provide an updated classification of HLA-A and -B class I alleles into supertypes. The present analysis incorporates the large amount of class I MHC binding data and sequence information that has become available in the last decade. As a result, over 80% of the 945 different HLA-A and -B alleles examined to date can be assigned to one of the original nine supertypes. A few alleles are expected to be associated with repertoires that overlap multiple supertypes. Interestingly, the current analysis did not identify any additional supertype specificities.
Conclusion
As a result of this updated analysis, HLA supertype associations have been defined for over 750 different HLA-A and -B alleles. This information is expected to facilitate epitope identification and vaccine design studies, as well as investigations into disease association and correlates of immunity. In addition, the approach utilized has been made more transparent, allowing others to utilize the classification approach going forward.
Background
Class I major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules bind short peptides derived from the processing of proteins, and present them on the cell surface for T cell scrutiny. Functional MHC molecules are made of a heavy (α) chain and a β2-microglobulin chain. Peptide binding by class I molecules is accomplished by interaction of the peptide amino acid side chains with discrete pockets within the peptide-binding groove of the MHC molecule formed by the α1 and α2 domains of the heavy chain. Typically, in the case of human leukocyte antigen (HLA) class I, the main binding energy is provided by the interaction of residues in position 2 and the C-terminus of the peptide with the B and F binding pockets of the MHC molecule, respectively [1-8], although side chains throughout the ligand can have a positive or negative influence on binding capacity. The common chemical specificity of the peptide side chains amongst ligands bound by a specific MHC molecule is termed the binding motif [9].
MHC molecules are extremely polymorphic, and over a thousand allelic variants have already been described at the class I A and B loci. Most of the polymorphism is located in the peptide-binding region, and as a result each variant is believed to bind a unique repertoire of peptide ligands. Despite this polymorphism, HLA class I molecules can be clustered into groups, designated as supertypes, representing sets of molecules that share largely overlapping peptide binding specificity. Each supertype can be described by a supermotif that reflects the broad main anchor motif recognized by molecules within the corresponding supertype. For example, molecules of the A2-supertype share specificity for peptides with aliphatic hydrophobic residues in position 2 and at the C-terminus, while A3-supertype molecules recognize peptides with small or aliphatic residues in position 2 and basic residues at the C-terminus.
The first supertypes were described in the mid-1990's by our group [10]. Using motifs derived from binding data or the sequencing of endogenously bound ligands, along with simple structural analyses, nine different supertypes were defined [11,12]. Initial peptide binding studies allowed the identification of several peptides with degenerate binding capacity for the A2- [13-15], A3- [16-18] and B7-supertypes [19,20]. In subsequent years, additional binding data have been published to confirm the B44- [21], A1- and A24-supertypes [22].
Over time, a number of different and more sophisticated computational approaches have been implemented by others to classify HLA class I alleles into clusters or supertypes [23-32]. While in general agreement, additional supertypes, representing either sub-clusters of the original nine or completely novel groupings, have been proposed [23,32]. Despite differences in various classification schemes, the concept of HLA supertypes has been effectively used to characterize and identify promiscuously recognized T cell epitopes from a variety of different disease targets, including measles-mumps-rubella [33], SARS [34], EBV [35,36], HIV [37-41], Kaposi' Sarcoma Associated Human Herpesvirus [42,43], HCV [16,44], HBV [45,46], HPV [47], influenza [48], P. falciparum [49-52], LCMV [53], Lassa virus [54], F. tularensis [55], vaccinia [56-58], and also cancer antigens [59-68]. Supertypes have also been utilized as a component in several approaches and algorithms designed for predicting peptide candidates with degenerate HLA class I binding capacity [69-77]. Finally, supertypes have also been examined as a variable in studies of disease association, rates of susceptibility, and outcome [37,78-86].
The original classification proposed by Sette and Sidney [12] comprised about 100 different class I MHC alleles. However, over the last 10 years, substantially more binding data has been generated, and through the efforts of several seminal MHC-related databases, including SYFPEITHI [87], HLA Ligand [88], FIMM [89] and MHCBN [90], MHC binding motif information is readily accessible. Up-to-date compilations of MHC sequence data are also readily available in the IMGT database [91]. Herein, we analyze the complete list of alleles available through IMGT (release 2.9) using a simple approach largely based on compilation of published motifs, binding data, and analyses of shared repertoires of binding peptides, in conjunction with clustering based on the primary sequence of the B and F peptide binding pockets. As a result, we now provide updated supertype assignments, with new assignments for about 700 different HLA-A and -B alleles. This will permit the use of our original classification scheme based on current data and its comparison to alternative supertype classification methodologies developed since then.
Results
MHC sequences and peptide binding pockets
α1 and 2 chain residues comprising the B and F peptide-binding pockets of 945 HLA A and B class I molecules were extracted and aligned. Based on crystallographic studies [1,4,6,8], residues 7, 9, 24, 34, 45, 63, 66, 67, 70, and 99 were considered as comprising the B pocket, which engages the peptide residue in position 2. The residues comprising the F pocket, which engages the peptide C-terminal residue, were defined as 74, 77, 80, 81, 84, 95, 97, 114, 116, 123, 133, 143, 146, and 147. Further, for the B pocket we defined the subset of residues 9, 45, 63, 66, 67, 70, and 99 as key residues. In the F pocket, the key residues are those in positions 77, 80, 81 and 116.
Pocket chemical specificity
Next, we defined the broad chemical specificity associated with the different B and F pockets. Table 1 summarizes the amino acid residues generally associated with each particular description of binding specificity. The particular set of residues associated with each use of a descriptor may vary with context. While these descriptions largely follow classical textbook definitions, they also consider our own historical use and experience with peptide binding studies. For example, in our analyses we often consider the polar residue Q along with more classically defined aliphatic residues based on observed behavior in MHC peptide binding studies [15,92,93]. It is also important to note that some residues are assigned to multiple categories, as their chemical specificity is compatible with different emphases. For example, L would be considered as both aliphatic and hydrophobic. The chemical specificities defining each supertype are listed in Table 2.
Table 1.
Physiochemical functionality of peptide side chains.
| Pocket specificity | Associated amino acid residues |
| Acidic | DE |
| Aliphatic | LIVMQ |
| Aromatic | FWY |
| Aromatic and aliphatic | FWYLIVMQ |
| Aromatic and basic | YRK |
| Aromatic and large hydrophobic | FWYLIM |
| Basic | RHK |
| Hydrophobic | LIVMFWYA |
| Large hydrophobic | FLIM |
| Proline | P |
| Small | AST |
| Small and aliphatic | ATSVLIMQ |
| Small hydrophobic | AV |
| Small, aliphatic and aromatic | ASTVLIMQFWY |
Table 2.
HLA supertype specificity descriptions.
| Supertype(s) | B pocket specificity | F pocket specificity |
| A01 | Small and aliphatic | Aromatic and large hydrophobic |
| A01 A03 | Small and aliphatic | Aromatic and basic |
| A01 A24 | Small, aliphatic and aromatic | Aromatic and large hydrophobic |
| A02 | Small and aliphatic | Aliphatic and small hydrophobic |
| A03 | Small and aliphatic | Basic |
| A24 | Aromatic and aliphatic | Aromatic, aliphatic and hydrophobic |
| B07 | Proline | Aromatic, aliphatic and hydrophobic |
| B08 | Undefined | Aromatic, aliphatic and hydrophobic |
| B27 | Basic | Aromatic, aliphatic, basic and hydrophobic |
| B44 | Acidic | Aromatic, aliphatic and hydrophobic |
| B58 | Small | Aromatic, aliphatic and hydrophobic |
| B62 | Aliphatic | Aromatic, aliphatic and hydrophobic |
Peptide-binding motif-based supertype assignments
As a starting point, we have largely utilized the nine supertype designations derived previously [11,12], with a few exceptions. These exceptions entail specificities that appear to be compatible with multiple supertypes. More specifically, we recognize that some alleles have repertoires overlapping both the A01 and A03 supertypes (e.g., A*3001; see Hamdahl et al., IEDB submission 1000945 [94-96]), and others with the A01- and A24-supertypes (e.g., A*2902 [22]). Also, because it utilizes a non-canonical main anchor spacing, and as a result appears to have a repertoire that overlaps with other specificities, we have presently separated HLA B*0801 and other alleles sharing sequence and serological antigen similarities, as a separate cluster. While these B*08 alleles utilize a unique mode of peptide binding, it is likely that in most cases their repertoires overlap significantly with other supertypes, especially the B07-supertype (Sidney, Frahm, Brander and Sette, unpublished observations). As a result, we have not defined this a separate supertype.
Next, the available peptide-binding motifs were compiled. In total, 88 different class I motifs were identified. Motif information was derived from our own peptide-binding studies, or from the published scientific literature as compiled in the SYFPEITHI database [87]. The basis for each motif assignment is listed in Tables 3 and 4 for HLA-A and -B alleles, respectively. Corresponding supertype associations were assigned based on the criteria listed in Table 2.
Table 3.
HLA-A motif/structure reference panel alleles.
| Allele | Basis for motif | Supertype association |
| A*0101 | Binding assay | A01 |
| A*0201 | Binding assay | A02 |
| A*0202 | Binding assay | A02 |
| A*0203 | Binding assay | A02 |
| A*0204 | Pool sequencing/ligand elution | A02 |
| A*0205 | Binding assay | A02 |
| A*0206 | Binding assay | A02 |
| A*0207 | Binding assay | A02 |
| A*0214 | Pool sequencing/ligand elution | A02 |
| A*0217 | Pool sequencing/ligand elution | A02 |
| A*0301 | Binding assay | A03 |
| A*1101 | Binding assay | A03 |
| A*2301 | Binding assay | A24 |
| A*2402 | Binding assay | A24 |
| A*2601 | Binding assay | A01 |
| A*2602 | Pool sequencing/ligand elution | A01 |
| A*2603 | Pool sequencing/ligand elution | A01 |
| A*2902 | Binding assay | A01 A24 |
| A*3001 | Binding assay | A01 A03 |
| A*3002 | Binding assay | A01 |
| A*3003 | Pool sequencing/ligand elution | A01 |
| A*3004 | Pool sequencing/ligand elution | A01 |
| A*3101 | Binding assay | A03 |
| A*3201 | Binding assay | A01 |
| A*3301 | Binding assay | A03 |
| A*3303 | Published motif | A03 |
| A*6601 | Pool sequencing/ligand elution | A03 |
| A*6801 | Binding assay | A03 |
| A*6802 | Binding assay | A02 |
| A*6901 | Pool sequencing/ligand elution | A02 |
| A*7401 | Binding assay | A03 |
Table 4.
HLA-B motif/structure reference panel alleles.
| Allele | Basis for motif | Supertype association |
| B*0702 | Binding assay | B07 |
| B*0703 | Pool sequencing/ligand elution | B07 |
| B*0705 | Pool sequencing/ligand elution | B07 |
| B*0801 | Binding assay | B08 |
| B*0802 | Pool sequencing/ligand elution | B08 |
| B*1402 | Pool sequencing/ligand elution | B27 |
| B*1501 | Binding assay | B62 |
| B*1502 | Pool sequencing/ligand elution | B62 |
| B*1503 | Binding assay | B27 |
| B*1508 | Pool sequencing/ligand elution | B07 |
| B*1509 | Pool sequencing/ligand elution | B27 |
| B*1510 | Pool sequencing/ligand elution | B27 |
| B*1512 | Pool sequencing/ligand elution | B62 |
| B*1513 | Pool sequencing/ligand elution | B62 |
| B*1516 | Pool sequencing/ligand elution | B58 |
| B*1517 | Pool sequencing/ligand elution | B58 |
| B*1518 | Pool sequencing/ligand elution | B27 |
| B*1801 | Binding assay | B44 |
| B*2702 | Pool sequencing/ligand elution | B27 |
| B*2703 | Pool sequencing/ligand elution | B27 |
| B*2704 | Pool sequencing/ligand elution | B27 |
| B*2705 | Binding assay | B27 |
| B*2706 | Pool sequencing/ligand elution | B27 |
| B*2707 | Pool sequencing/ligand elution | B27 |
| B*2709 | Pool sequencing/ligand elution | B27 |
| B*3501 | Binding assay | B07 |
| B*3503 | Pool sequencing/ligand elution | B07 |
| B*3701 | Pool sequencing/ligand elution | B44 |
| B*3801 | Pool sequencing/ligand elution | B27 |
| B*3901 | Pool sequencing/ligand elution | B27 |
| B*3902 | Pool sequencing/ligand elution | B27 |
| B*3909 | Pool sequencing/ligand elution | B27 |
| B*4001 | Binding assay | B44 |
| B*4002 | Binding assay | B44 |
| B*4006 | Pool sequencing/ligand elution | B44 |
| B*4201 | Binding assay | B07 |
| B*4402 | Binding assay | B44 |
| B*4403 | Binding assay | B44 |
| B*4501 | Binding assay | B44 |
| B*4601 | Pool sequencing/ligand elution | B62 |
| B*4801 | Pool sequencing/ligand elution | B27 |
| B*5101 | Binding assay | B07 |
| B*5102 | Pool sequencing/ligand elution | B07 |
| B*5103 | Pool sequencing/ligand elution | B07 |
| B*5201 | Pool sequencing/ligand elution | B62 |
| B*5301 | Binding assay | B07 |
| B*5401 | Binding assay | B07 |
| B*5501 | Pool sequencing/ligand elution | B07 |
| B*5502 | Pool sequencing/ligand elution | B07 |
| B*5601 | Pool sequencing/ligand elution | B07 |
| B*5701 | Binding assay | B58 |
| B*5702 | Pool sequencing/ligand elution | B58 |
| B*5801 | Binding assay | B58 |
| B*5802 | Binding assay | B58 |
| B*6701 | Pool sequencing/ligand elution | B07 |
| B*7301 | Pool sequencing/ligand elution | B27 |
| B*7801 | Pool sequencing/ligand elution | B07 |
Pocket analysis and supertype assignments
The amino acids comprising the B and F peptide binding pockets were compiled for all alleles for which complete sequence information was available. The positions of specific MHC residues forming the corresponding pockets are listed above. A reference panel of B and F pockets was generated to include all alleles for which the MHC-peptide binding specificity has been defined (see Tables 3 and 4). These B and F pocket structures, along with the associated alleles and corresponding binding specificity are shown in Tables 5 and 6, respectively.
Table 5.
B pocket structures of reference panel alleles.
| Residues1 | Key residues | Reference panel allele(s) | Associated supertype(s) | Specificity |
| YDSVENIFNY | DENIFNY | B*0801-2 | B08 | Undefined |
| YFAVMEKVHC | FMEKVHC | A*0207 | A02 | Small and aliphatic |
| YFAVMEKVHF | FMEKVHF | A*0217 | A02 | Small and aliphatic |
| YFAVMEKVHY | FMEKVHY | A*0201-4 | A02 | Small and aliphatic |
| YFAVMENMHY | FMENMHY | A*0101 | A01 | Small and aliphatic |
| YFAVMENVHY | FMENVHY | A*3201, A*7401 | A01 A03 | Small and aliphatic |
| YFAVMENVQY | FMENVQY | A*0301 | A03 | Small and aliphatic |
| YHSVTEISNS | HTEISNS | B*3701 | B44 | Acidic |
| YHSVTNISNY | HTNISNY | B*1801 | B44 | Acidic |
| YHTVEEICKY | HEEICKY | B*2702-7, B*2709 | B27 | Basic |
| YHTVENICKY | HENICKY | B*7301 | B27 | Basic |
| YHTVKEISNY | HKEISNY | B*4001-2, B*4006, B*4501 | B44 | Acidic |
| YSAVMEKVHF | SMEKVHF | A*2301, A*2402 | A24 | Aromatic and aliphatic |
| YSAVMENVHY | SMENVHY | A*3002-4 | A01 | Small and aliphatic |
| YSAVMENVQY | SMENVQY | A*3001 | A01 A03 | Small and aliphatic |
| YTAVMENVHY | TMENVHY | A*3101 | A03 | Small and aliphatic |
| YTAVMNNVHY | TMNNVHY | A*3301, A*3303 | A03 | Small and aliphatic |
| YTAVMQNVQY | TMQNVQY | A*2902 | A01 A24 | Small, aliphatic and aromatic |
| YYAVENIYQY | YENIYQY | B*5501-2, B*5601 | B07 | Proline |
| YYAVGNIYQY | YGNIYQY | B*5401 | B07 | Proline |
| YYAVMEISNY | YMEISNY | B*1501, B*1512 | B62 | Aliphatic |
| YYAVMEKVHY | YMEKVHY | A*0205, A*0206, A*0214 | A02 | Small and aliphatic |
| YYAVMEKYQY | YMEKYQY | B*4601 | B62 | Aliphatic |
| YYAVMENMSY | YMENMSY | B*1516-17, B*5701-2 | B58 | Small |
| YYAVMENVQY | YMENVQY | A*1101 | A03 | Small and aliphatic |
| YYAVMNIFNY | YMNIFNY | B*1508 | B07 | Proline |
| YYAVMNISNY | YMNISNY | B*1502, B*1513 | B62 | Aliphatic |
| YYAVMNNVHY | YMNNVHY | A*2601-3 | A01 | Small and aliphatic |
| YYAVMNNVQY | YMNNVQY | A*6601, A*6801-2, A*6901 | A02 A03 | Small and aliphatic |
| YYAVTEISNY | YTEISNY | B*5201 | B62 | Aliphatic |
| YYAVTENMSY | YTENMSY | B*5801-2 | B58 | Small |
| YYAVTNIFNY | YTNIFNY | B*3501, B*3503, B*5101-3, B*5301, B*7801 | B07 | Proline |
| YYSVEEISNY | YEEISNY | B*1503, B*3902, B*4801 | B27 | Basic |
| YYSVENICNS | YENICNS | B*3909 | B27 | Basic |
| YYSVENICNY | YENICNY | B*1402, B*1509-10, B*1518, B*3801, B*3901 | B27 | Basic |
| YYSVENIYNY | YENIYNY | B*0703 | B07 | Proline |
| YYSVENIYQY | YENIYQY | B*0702, B*0705, B*4201, B*6701 | B07 | Proline |
| YYTVKEISNY | YKEISNY | B*4402-3 | B44 | Acidic |
1. Based on data presented in Saper et al, and Madden (see Methods), the MHC residues utilized as constituting the B pocket are: 7, 9, 24, 34, 45, 63, 66, 67, 70, and 99. Key residues are those in positions 9, 45, 63, 66, 67, 70, and 99.
Table 6.
F pocket structures of reference panel alleles.
| Residues1 | Key residues2 | Reference panel allele(s) | Associated supertype(s) | Specificity |
| DDTLYIIEHYWTKW | DTLH | A*3001 | A01 A03 | Aromatic and basic |
| DDTLYIIRDYWTKW | DTLD | A*0301, A*1101 | A03 | Basic |
| DDTLYIMQDYWTKW | DTLD | A*3101, A*3301, A*3303, A*7401 | A03 | Basic |
| DDTLYIMRDYWTKW | DTLD | A*6801 | A03 | Basic |
| DDTLYIRHYYWTKW | DTLY | A*6802 | A02 | Aliphatic |
| DDTLYIRQDYWTKW | DTLD | A*6601 | A03 | Basic |
| DDTLYLNHDYWTKW | DTLD | B*2703, B*2705 | B27 | Hydrophobic and basic |
| DDTLYLNHHYWTKW | DTLH | B*2709 | B27 | Large hydrophobic |
| DDTLYLSNYYWTKW | DTLY | B*2707 | B27 | Large hydrophobic |
| DDTLYVRHYYWTKW | DTLY | A*6901 | A02 | Aliphatic |
| DGNLYWTNFYWTKW | GNLF | B*7301 | B27 | Large hydrophobic |
| DNIAYLMHYYWTKW | NIAY | A*2301, A*2402 | A24 | Large hydrophobic |
| DNIAYLNHDYWTKW | NIAD | B*2702 | B27 | Large hydrophobic |
| DNTAYLSNYYWTKW | NTAY | B*0802 | B08 | Hydrophobic |
| DNTLYIIEHYWTKW | NTLH | A*3002-4 | A01 | Aromatic |
| DNTLYIIRDYWTKW | NTLD | A*0101 | A01 | Aromatic |
| DNTLYIMRDYWTKW | NTLD | A*2902 | A01 A24 | Aromatic and large hydrophobic |
| DNTLYIRQDYWTKW | NTLD | A*2601 | A01 | Aromatic |
| DNTLYIRQNYWTKW | NTLN | A*2602 | A01 | Aromatic |
| DSIAYIMQDYWTKW | SIAD | A*3201 | A01 | Aromatic |
| DSNLYLRDSYWTKW | SNLS | B*4601 | B62 | Large hydrophobic |
| DSNLYLRNFYWTKW | SNLF | B*3901-2, B*3909, B*6701 | B07 B27 | Hydrophobic |
| DSNLYLSDYYWTKW | SNLY | B*0702-3 | B07 | Hydrophobic |
| DSNLYLSNYYWTKW | SNLY | B*0705, B*0801, B*4201 | B07 | Hydrophobic |
| DSNLYLWNFYWTKW | SNLF | B*1402 | B27 | Hydrophobic |
| DSNLYWTNLYWTKW | SNLL | B*5401, B*5501-2, B*5601 | B07 | Small hydrophobic |
| DSNLYWTNYYWTKW | SNLY | B*7801 | B07 | Hydrophobic |
| DSTLYLNDYYWTKW | STLY | B*2706 | B27 | Large hydrophobic |
| DSTLYLNHDYWTKW | STLD | B*2704 | B27 | Large hydrophobic |
| HDTLYIRQDYWTKW | DTLD | A*2603 | A01 | Aromatic |
| HDTLYLMHYYWTKW | DTLY | A*0217 | A02 | Aliphatic |
| HDTLYLRHYYWTKW | DTLY | A*0202, A*0205, A*0214 | A02 | Aliphatic |
| HDTLYVMHYYWTKW | DTLY | A*0204 | A02 | Aliphatic |
| HDTLYVRHYYWTKW | DTLY | A*0201, A*0203, A*0206-7 | A02 | Aliphatic |
| YDTLYIRNFYWTKW | DTLF | B*3701 | B44 | Hydrophobic |
| YNIAYIRDSYWTKW | NIAS | B*1513, B*5301, B*5801 | B07 B58 B62 | Large hydrophobic |
| YNIAYIVDSYWTKW | NIAS | B*5701 | B58 | Large hydrophobic |
| YNIAYIVNYYWTKW | NIAY | B*5702 | B58 | Large hydrophobic |
| YNIAYLRHDYWTKW | NIAD | B*1517 | B58 | Large hydrophobic |
| YNIAYLRNFYWTKW | NIAF | B*3801 | B27 | Large hydrophobic |
| YNIAYLWDSYWTKW | NIAS | B*5802 | B58 | Large hydrophobic |
| YNIAYWRDSYWTKW | NIAS | B*1516 | B58 | Large hydrophobic |
| YNIAYWTNYYWTKW | NIAY | B*5101-3, B*5201 | B07 B62 | Large hydrophobic |
| YNTAYIRDDYWTKW | NTAD | B*4402-3 | B44 | Hydrophobic |
| YSNLYIRDFYWTKW | SNLF | B*3503 | B07 | Hydrophobic |
| YSNLYIRDSYWTKW | SNLS | B*1502, B*3501 | B07 B62 | Hydrophobic |
| YSNLYLRDSYWTKW | SNLS | B*1501, B*1503, B*1508, B*1512, B*1518, B*1801 | B07 B27 B44 B62 | Large hydrophobic |
| YSNLYLRDYYWTKW | SNLY | B*1510 | B27 | Hydrophobic |
| YSNLYLRNYYWSKL | SNLY | B*4001 | B44 | Hydrophobic |
| YSNLYLRNYYWTKW | SNLY | B*1509 | B27 | Hydrophobic |
| YSNLYLSNYYWSKL | SNLY | B*4801 | B27 | Hydrophobic |
| YSNLYLSNYYWTKW | SNLY | B*4002 | B44 | Hydrophobic |
| YSNLYWRNLYWTKW | SNLL | B*4501 | B44 | Small hydrophobic |
| YSNLYWTNYYWTKW | SNLY | B*4006 | B44 | Hydrophobic |
1. Based on data presented in Saper et al, and Madden (see Methods), the MHC residues utilized as constituting the F pocket are: 74, 77, 80, 81, 84, 95, 97, 114, 116, 123, 133, 143, 146, and 147. Key residues are those in positions 77, 80, 81, and 116.
2. The key residue pockets DTLD, DTLH and DTLY are each associated with two different, although overlapping, specificity descriptions. In each case, one description is associated with HLA B27 alleles, and in the other with HLA A alleles. In assigning key residue matches, matches were assigned on the basis of corresponding locus.
Next, the B and F pocket structures of alleles whose peptide binding specificity was unknown were compared against the sequences in the reference panel. For each case, an attempt was made to find an exact match with the full set of residues in the corresponding pocket. If a match was identified, the allele was assigned the associated specificity shown in Tables 5 and 6. If an exact match could not be found, then a match with a key residue sequence was attempted. If no match was identified, the allele was considered unassigned. For each allele where a match for the full or, secondarily, key residue sequence could be identified for both the B and F pockets with any of the alleles indicated in Tables 3 and 4, a corresponding HLA supertype was assigned.
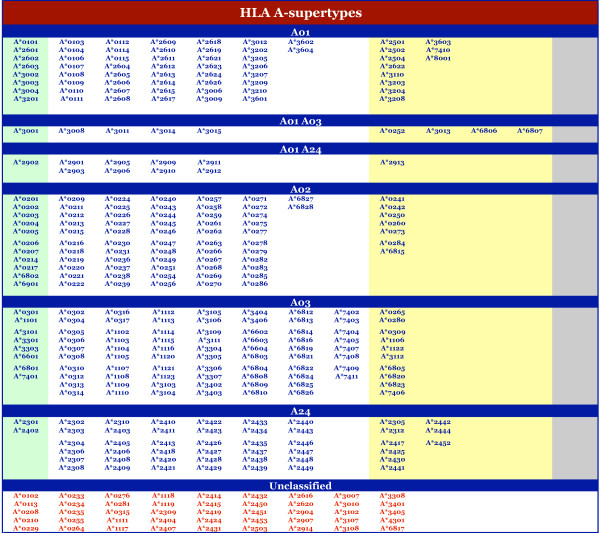
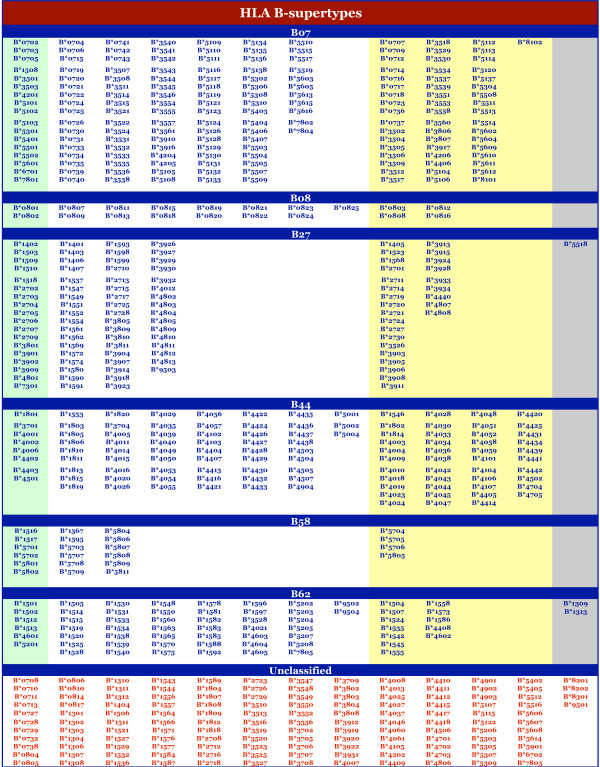
Of the 945 sequences analyzed, matches at both B and F pockets were found for 764 (80.8%) (Table 7). Notably, for the majority (57%) of alleles not in the reference panel full sequence matches were identified at both the B and F pockets. Figures 1 and 2 indicate the alleles associated with each HLA-A or -B supertype, respectively. Conversely, as an index, Additional file 1 provides the supertype assignment for each of the 945 HLA-A and -B alleles examined, along with their respective B and F pocket structures.
Table 7.
Quantification of supertype assignments.
| Classification criteria | ||||||
| Supertype | (n) | Binding assay | Pool sequencing or ligand elution | Full sequence match at B and F | 1 full and 1 key sequence match | Key residue match at B and F |
| A01 | 61 | 4 | 4 | 42 | 11 | 0 |
| A01 A03 | 9 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 4 | 0 |
| A01 A24 | 10 | 1 | 0 | 8 | 1 | 0 |
| A02 | 75 | 7 | 4 | 57 | 7 | 0 |
| A03 | 86 | 6 | 2 | 68 | 10 | 0 |
| A24 | 47 | 2 | 0 | 36 | 9 | 0 |
| B07 | 165 | 6 | 11 | 96 | 52 | 0 |
| B08 | 19 | 1 | 1 | 13 | 4 | 0 |
| B27 | 98 | 2 | 16 | 52 | 27 | 1 |
| B44 | 108 | 6 | 2 | 57 | 43 | 0 |
| B58 | 22 | 3 | 3 | 12 | 4 | 0 |
| B62 | 64 | 1 | 5 | 44 | 12 | 2 |
| Unassigned | 181 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Total | 945 | 40 | 48 | 489 | 184 | 3 |
Figure 1.
Supertype classification of HLA-A alleles. The alleles associated with each HLA-A supertype, multiple supertypes, or that are unclassified, are shown. Under each supertype, alleles are group (by color) on the basis of the stringency of selection: experimentally established motif (i.e., reference panel) (green), exact match(es) in the B and F pockets (white), one exact and one key residue pocket match (yellow), key residue match(es) at B and F pockets (grey). Alleles with no match at one or both pockets are listed with red font.
Figure 2.
Supertype classification of HLA-B alleles. The alleles associated with each HLA-B supertype, multiple supertypes, or that are unclassified, are shown. Under each supertype, alleles are grouped (by color) on the basis of the stringency of selection as described in the legend to Figure 1.
At the HLA-A locus, alleles were fairly evenly distributed amongst the four supertypes we have defined. Considering the alleles with broad, or dual, specificity (i.e., those assigned as A01–A03 or A01–A24), the minimum was 57 alleles for A24, and the maximum was 95 alleles for A03. 75 alleles were assigned to the A02 supertype, and 80 to the A01 supertype. At the HLA-B locus, the B07-supertype is the largest, with 165 members. 19 alleles were associated with the B08 pattern. As noted above, we hypothesize that alleles in this cluster will likely cross-react with other supertypes (especially B07), so we do not consider this group as a distinct supertype. The B58 supertype was assigned only 22 alleles, making it the smallest supertype.
Novel supertypes could not be identified, but several alleles have specificities spanning two different supertypes
From Tables 5 and 6, it is evident that not all possible combinations of B and F pocket specificities are present within the reference panel. For example, there are no alleles associated with a preference for acidic residues in position 2 and basic residues at the C-terminus. Hence, we were interested to see if combinations not found in the original supertype assignments were revealed in the present analysis. Interestingly, we did not identify any new combinations. It is possible that new specificities will be identified from amongst the set of 181 alleles for which pocket matches could not be obtained. However, we also note that in the majority of these cases, matches could be made if one allowed a single conservative residue change (e.g., E to D). Thus, based on the analyses done to date, it would appear that the set of supertype specificities currently identified will cover virtually all HLA-A and -B class I MHC alleles.
In addition to A*2902 and A*3001, the present analysis has identified 17 alleles expected to have a specificity overlapping two supertypes. Nine alleles matched pocket preference patterns that would be compatible with both the A01- and A03-supertypes, and another 10 with the A01- and A24-supertypes. In the former case, the association was established on the basis of pocket matches with A*3001. Not surprisingly, several, but not all, of the alleles assigned the A01–A03 specificity also share the A30 antigen. The A01–A24 cross-reactivity pattern was established on the basis of pocket matches with A*2902. All of the alleles associated with the A01–A24 pattern also shared the A29 antigen.
Unexpected supertype assignments
Typically, the supertype assignment for a particular allele follows the predominant assignment for other alleles sharing the same serological antigen. With this in mind, we did identify several instances where the current classification differed from what was expected based on serology or previous classification (Table 8). Of these, the more striking ones involve alleles for which the assigned supertype represents a non-conservative change in the binding specificity from what would have been expected. For example, A*0265 and A*0280, which are associated with the A02 serological antigen, and thus might be expected to have an F pocket specificity for hydrophobic/aliphatic residues, were found to have an F pocket matching that of A03 supertype alleles, which have a specificity for positively charged residues. Similarly, B*4012 and B*4440 were found to have B27 supertype B pockets, associated with a preference for positively charged residues, when a B44 supertype specificity for acidic residues might have been expected.
Table 8.
Unexpected and/or revised supertype assignments.
| Supertype assignment | ||
| Allele | Expected1or previous | Current |
| A*0252 | A02 | A01 A03 |
| A*0265 | A02 | A03 |
| A*0280 | A02 | A03 |
| A*3001 | A24 | A01 A03 |
| A*3002 | A24 | A01 |
| A*3003 | A24 | A01 |
| A*3110 | A03 | A01 |
| A*7410 | A03 | A01 |
| B*3528 | B07 | B62 |
| B*3806 | B27 | B07 |
| B*3807 | B27 | B07 |
| B*3910 | B27 | B07 |
| B*3916 | B27 | B07 |
| B*3917 | B27 | B07 |
| B*4012 | B44 | B27 |
| B*4021 | B44 | B62 |
| B*4406 | B44 | B07 |
| B*4408 | B44 | B62 |
| B*4440 | B44 | B27 |
| B*5518 | B07 | B27 |
1. Expected based on serological association.
As noted above, in the present analysis, and contrary to what was done in the original analysis, we did not make supertype assignments for alleles without an exact or key match by considering conservative substitutions. As a result of this more conservative approach, we now no longer assign supertypes to some alleles previously given a supertype designation (Table 9). In the majority of these cases, however, the original designation would still seem to be a reasonable assumption.
Table 9.
Alleles reclassified as "unassigned".
| Allele | Previous assignment | B pocket match | F pocket match | Comments |
| A*0102 | A01 | - | A01 full | Single difference with A*0101 (F to S) at position 9 in B pocket is non-conservative. |
| A*2404 | A24 | A24 full | - | F pocket key sequence is similar to A02 and B27 (hydrophobic), so A24 is still likely. |
| A*3401 | A03 | - | A03 full | N/K in 63/66 are relatively unique, otherwise similar to A03 in the B pocket. |
| A*4301 | A01 | - | A01 full | Q to N in 63 is only difference with A*2601, so A01 is still likely. |
| B*1301 | B62 | B62 key | - | Unusual F pocket. |
| B*1302 | B62 | B62 key | - | Unusual F pocket. |
| B*1506 | B62 | - | B07 B27 B44 B62 full | Single conservative change (Y to F) at position 99 of B pocket, comapred to B*1501; B62 still likely. |
| B*1521 | B62 | - | B07 B62 full | S to C change in position 67 is the onlyB pocket difference with B*1501, so B62 is still likely. |
| B*2708 | B27 | B27 full | - | Position 77 T to N change is only difference with b*2704, so B27 is still likely. |
| B*3802 | B27 | B27 full | - | I to T in position 80 of the F pocket is the only difference with B*3801, so B27 is still likely. |
| B*4701 | B44 | - | B27 key | Y to F at position 99 is the only difference with B*4402-3 in the B pocket, so B44 is still likely. |
| B*4901 | B44 | B44 full | - | F full pocket is similar to B*3801 (hydrophobic), so B44 is still likely. |
Discussion
In the present study we have attempted to classify almost 1000 HLA-A and -B class I alleles into supertypes. This is nearly a 10-fold increase in the number of alleles compared to our original classification done about a decade ago [12]. Besides providing supertype assignments for considerably more alleles, the present report has attempted to make more transparent how the original "phenomenological" classifications were done. About 80% of the 945 alleles examined were classified into one of the nine supertypes identified previously. Analysis of B and F pocket specificity patterns did not suggest the existence of any novel supertypes.
HLA supertypes do not necessarily demarcate groups of alleles with completely non-overlapping repertoires. A binding repertoire overlapping multiple supertypes has been demonstrated previously, for example, in the cases of A*2902 [22] and A*3001 (see Hamdahl et al., IEDB submission 1000945 [94-96]). In the present study we have identified 17 other alleles that would appear to have specificities that bridge either the A01 and A03 supertypes, or the A01 and A24 supertypes. At the same time, individual peptides can be readily identified that bear a particular supermotif, but that do not bind individual HLA allele members of the supertype, or that bind alleles of other supertypes, even supertypes associated with a different locus. Typically, in the first case, these phenomena result from differences in motif compatibility, perhaps at secondary positions. The second case likely reflects overlap(s) between the supertypes in terms of specificity, although in rare cases binding can be accomplished when no main anchor motif compatibility is apparent.
These observations are exemplified by a large scale analysis of the capacity of a non-redundant set of 252 known EBV and HIV derived epitopes to bind a panel of 30 different HLA class I A and B molecules (Sidney, Frahm, Brander and Sette, unpublished observations). It was found that about 21% of the peptides bearing a specific supermotif bound a given allele in the corresponding supertype with an affinity of 100 nM, or better. By contrast, only in 1% of the cases considered did an allele bind a peptide that did not have the corresponding supermotif. At the same time, it was noted that in the set of peptides utilized 62% (155/252) have motifs associated with 2 or more supertypes. The pattern of binding also followed this general promiscuity. It is also significant to note that when the same library of peptides was examined for recognition in HIV/EBV patients, it was found that ~95% of the epitopes were recognized in individuals not expressing the allele the epitope was originally reported to be restricted by, and the promiscuity more often than not involved an allele outside of the supertype associated with originally described restricting allele [97]. Thus, it is apparent that the lines of demarcation between supertypes can be fuzzy from the perspective of both the allelic specificity and the peptide motif.
Restriction outside or across supertypes can also originate from overlaps in supermotifs (e.g., A02 and B62), or for alleles such as B*0801 which do not utilize the typical P2/Cterminus anchor spacing. B*0801 utilizes P3 and P5, not P2, and as such may be compatible with several supertypes and alleles. Thus, an A02- or A24-supertype epitope cross-reacting with B*0801 is not an example of a motif "failure", but merely reflects the fact that the specific peptide has both motifs.
It is important to emphasize that supertypes are based on MHC binding, and that MHC binding alone is not sufficient criteria for T cell recognition. Indeed, hundreds of examples of peptides that bind with remarkably high affinity, but that are not recognized by T cells, have been reported in the literature. We note that even in the best affinity ranges (i.e., IC50 <10 nM), rarely more than 10% of the peptides can be expected to be recognized [98]. Similarly, binding affinity is not necessarily correlative of frequency of recognition [99]. It is true that the trend is towards the most frequently recognized peptides being also the highest affinity binders [38,50,100], but that is not always the case, and there are clearly cases where the dominant epitope has an IC50 of ~100 nM, while several other non-recognized peptides have affinities in the <10 nM range.
It must also be emphasized that membership of an epitope in a supertype is not sufficient to guarantee its recognition by T cells in the context of different MHC alleles. Peptide binding to MHC is an absolute requirement for an epitope to be recognized by T cells. At the same time, many other factors, including protein expression and processing, as well as T cell repertoire and the specific MHC context, come into play in determining whether a peptide will be an epitope or not, or whether an epitope will be promiscuously recognized within a specific supertype. For example, Goulder and co-workers, studying B7-supertype epitopes, found that differential selection pressure exerted on HIV by CTL targeting identical epitopes, but restricted by distinct HLA alleles from the same supertype, can result in significant functional differences [101]. Macdonald et al., looking at two B44 subtypes described as members of the HLA B44-supertype, reported that a naturally selected dimorphism between the two molecules alters class I structure, peptide repertoire, and T cell recognition [102].
The intent of the current study was to derive an updated classification of HLA class I MHC alleles on the basis of primary anchor specificity. For the vast majority of HLA class I molecules whose binding specificity have been described by crystal structure, pool sequencing or peptide binding studies, the main anchor interactions of the peptide almost invariably involve the MHC B and F pockets, while other pockets likely dictate secondary interactions. This pattern also appears to be true for most macaque and chimpanzee class I alleles studied to date.
There are exceptions, however, and indeed we have not assigned B*08 alleles to a specific supertype in recognition of the fact that these alleles appear to utilize pockets other than the B pocket as a primary anchor contact. For HLA class I molecules in general, the B and F pockets are the most likely main anchor contacts, while other pockets likely dictate secondary interactions. High levels of crossreactivity have been experimentally demonstrated in the case of 6 supertypes for alleles that vary at secondary pockets [15,17,20-22].
By contrast, in the murine system it is well recognized that other pockets are often the important primary peptide contacts [103-109]. Thus, to utilize the classification approach described here in the context of other species, additional pockets may need to be considered. It is also likely that the further parsing or sub-classifying of supertypes on the basis of secondary interactions can be accomplished.
In the case of HLA-B alleles, F pocket specificity is difficult to correlate with a specific sequence, as a diverse pattern of residues appears to be associated with similar binding specificity. Independent of the residues in the F pocket, most HLA-B alleles seem to bind hydrophobic residues. Thus, assignment of B alleles was primarily driven by the specificity exhibited by the B pocket. On the other hand, it is also possible that greater resolution in the F pocket could be achieved as more data become available to discriminate different preference patterns. For example, in the B7 supertype it is apparent that some alleles, like B*3501, prefer large hydrophobic residues, such as Y. Conversely, other B7 supertype alleles, such as B*5401, seem to prefer small hydrophobic residues, such as A, at the C-terminus. While we have noted these subtle differences in preference [20], in practice we have not found that they significantly impact cross-reactivity between the alleles. This perhaps suggests that the C-terminal anchor in some contexts is less important, and that shared secondary preferences can have a stronger influence on degenerate binding capacity than in other cases. At the same time, it may be necessary to consider additional key residues in the analysis of the F pocket. This is exemplified in the cases of A*2603 and A*0301 which have the same key F pocket residues, but which are associated with much different specificity.
The vast majority of HLA-A and -B alleles fall into one of the 9 supertypes we have described. There are likely reasons for this [110], which include evolutionary relationships, but also constraints and limitations inherent in the epitope processing infrastructure. For example, no allele has been identified to date that binds peptides with D, E, Q or P at the C-terminus, which is in congruence with the preferences of both proteasomal cleavage and TAP transport [111], and an observation that has been applied in the rational design of an in vitro test reagent tool (PeptGen) offered as a tool by the Los Alamos HIV Sequence Database [112].
Supertype classification should not be taken to necessarily imply an evolutionary relationship. In some cases this is largely true, as for example in the case of the A2-supertype, where most alleles are associated with the A2 serological antigen. In other cases the relationship is more complicated, such as the gene conversion relationship between the A2, A3 and A68 antigens. This latter example is somewhat of the exception that proves the rule. Supertype associations are based on shared binding specificity, which may result from both common ancestry and convergent evolution [110]. Thus, while alleles within a supertype may have a close evolutionary relationship, that is not a given. Also, alleles (supertypes) sharing specificity at one anchor position may be associated with very disparate specificities at the other.
Other groups have also utilized various methodologies to define supertypes. In general, our classification is in agreement with those derived by other approaches, as compiled by Hertz [32], Lund [23] and Tong [31]. This is not surprising given the good agreement observed between our initial dataset and other classifications, and that the methodology utilized here is not different from the one utilized to derive the original assignments. If there are variations, they usually represent the splitting of a supertype, or reassignment of individual alleles. As in any classification problem of this kind, there is no absolute truth in supertype assignments. The practical application of supertype classification schemes to identify degenerately binding peptides will ultimately show what classification scheme has the most practical value.
Conclusion
The present study represents an update to the HLA class I supertype classification originally described almost a decade ago. Using MHC peptide binding motif data and MHC sequence information that has since become available, supertype associations have now been provided for over 750 HLA-A and -B alleles. In addition, the approach utilized has been made more transparent, allowing others to utilize the classification approach going forward.
Methods
MHC sequences
The sequences of HLA A and B class I alleles were obtained from the IMGT/HLA Database [91,113], release 2.9. Alleles with incomplete sequences were removed from further analysis. The residues forming the B and F peptide binding pockets were aligned as described in the Results section.
Peptide binding motif reference panel
The main anchor peptide binding motifs recognized by HLA-A and -B molecules were compiled from our own data, or as reported at the SYFPEITHI database [87]. The HLA supertype associated with each motif was assigned as defined previously [11,12], and/or on the basis of the broad chemical specificity of each supertype indicated in Tables 1 and 2.
Pocket analysis
The residues forming the B and F pockets of each allele in the motif reference panel were compiled as a lookup table in Microsoft Excel. Pockets were defined more stringently by considering all residues forming the pocket, or less stringently by considering only a subset of residues, denominated as key residues, hypothesized to be most directly involved in peptide binding. To assign a B and F pocket specificity for each of the remaining alleles, the reference panel was scanned to identify exact pocket sequence matches. If an exact match could be identified, the allele was assigned the corresponding B or F pocket specificity. Supertype assignments were then made by matching the B and F pocket specificity pattern with the supertype descriptions indicated in Table 2. If an exact match for either the full pocket sequence or key residue sequence could not be made at both the B and F pockets, the allele was considered unassigned.
Abbreviations
EBV (Epstein-Barr virus); HBV (hepatitis B virus); HCV (hepatitis C virus); HIV (human immunodeficiency virus); HLA (human leukocyte antigen); HPV (human papilloma virus); IEDB (Immune Epitope Database); LCMV (lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus); MHC (major histocompatibility complex); SARS (severe acute respiratory syndrome).
Authors' contributions
JS performed the sequence analyses, determined the supertype assignments and drafted the manuscript. BP participated in the conceptualization and design of the study, and assisted in the preparation of the manuscript. NF and CB assisted in the study design and data interpretation. AS participated in conceptualization of the study and its design, provided interpretation of the data, and helped to draft the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Supplementary Material
HLA supertype classification of HLA A and B class I alleles. This table provides a complete listing of the HLA A and B alleles examined in the present study. The table is sorted in alphanumeric order to facilitate searching for a specific allele. For each allele, the supertype assignment is indicated, and it's corresponding B and F pocket sequences are shown.
Acknowledgments
Acknowledgements
Efforts for this study were supported by funds from NIH-NIAID contracts N01-AI-40023, NO1-AI-40024 and HHSN266200400006C to AS.
Contributor Information
John Sidney, Email: jsidney@liai.org.
Bjoern Peters, Email: bpeters@liai.org.
Nicole Frahm, Email: nfrahm@partners.org.
Christian Brander, Email: brander@helix.mgh.harvard.edu.
Alessandro Sette, Email: alex@liai.org.
References
- Guo HC, Jardetzky TS, Garrett TP, Lane WS, Strominger JL, Wiley DC. Different length peptides bind to HLA-Aw68 similarly at their ends but bulge out in the middle. Nature. 1992;360:364–6. doi: 10.1038/360364a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver ML, Guo HC, Strominger JL, Wiley DC. Atomic structure of a human MHC molecule presenting an influenza virus peptide. Nature. 1992;360:367–9. doi: 10.1038/360367a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorga JC, Madden DR, Prendergast JK, Wiley DC, Strominger JL. Crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction studies of the human major histocompatibility antigen HLA-B27. Proteins. 1992;12:87–90. doi: 10.1002/prot.340120110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madden DR. The three-dimensional structure of peptide-MHC complexes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1995;13:587–622. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.13.040195.003103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madden DR, Garboczi DN, Wiley DC. The antigenic identity of peptide-MHC complexes: a comparison of the conformations of five viral peptides presented by HLA-A2. Cell. 1993;75:693–708. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90490-H. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madden DR, Gorga JC, Strominger JL, Wiley DC. The three-dimensional structure of HLA-B27 at 2.1 A resolution suggests a general mechanism for tight peptide binding to MHC. Cell. 1992;70:1035–48. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90252-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorkman PJ, Saper MA, Samraoui B, Bennett WS, Strominger JL, Wiley DC. The foreign antigen binding site and T cell recognition regions of class I histocompatibility antigens. Nature. 1987;329:512–8. doi: 10.1038/329512a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saper MA, Bjorkman PJ, Wiley DC. Refined structure of the human histocompatibility antigen HLA-A2 at 2.6 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1991;219:277–319. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90567-P. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk K, Rotzschke O, Stevanovic S, Jung G, Rammensee HG. Allele-specific motifs revealed by sequencing of self-peptides eluted from MHC molecules. Nature. 1991;351:290–6. doi: 10.1038/351290a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidney J, Grey HM, Kubo RT, Sette A. Practical, biochemical and evolutionary implications of the discovery of HLA class I supermotifs. Immunol Today. 1996;17:261–6. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(96)80542-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sette A, Sidney J. HLA supertypes and supermotifs: a functional perspective on HLA polymorphism. Curr Opin Immunol. 1998;10:478–82. doi: 10.1016/S0952-7915(98)80124-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sette A, Sidney J. Nine major HLA class I supertypes account for the vast preponderance of HLA-A and -B polymorphism. Immunogenetics. 1999;50:201–12. doi: 10.1007/s002510050594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- del Guercio MF, Sidney J, Hermanson G, Perez C, Grey HM, Kubo RT, Sette A. Binding of a peptide antigen to multiple HLA alleles allows definition of an A2-like supertype. J Immunol. 1995;154:685–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidney J, del Guercio MF, Southwood S, Hermanson G, Maewal A, Appella E, Sette A. The HLA-A*0207 peptide binding repertoire is limited to a subset of the A*0201 repertoire. Hum Immunol. 1997;58:12–20. doi: 10.1016/S0198-8859(97)00206-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidney J, Southwood S, Mann DL, Fernandez-Vina MA, Newman MJ, Sette A. Majority of peptides binding HLA-A*0201 with high affinity crossreact with other A2-supertype molecules. Hum Immunol. 2001;62:1200–16. doi: 10.1016/S0198-8859(01)00319-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang KM, Gruener NH, Southwood S, Sidney J, Pape GR, Chisari FV, Sette A. Identification of HLA-A3 and -B7-restricted CTL response to hepatitis C virus in patients with acute and chronic hepatitis C. J Immunol. 1999;162:1156–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidney J, Grey HM, Southwood S, Celis E, Wentworth PA, delGuercio MF, Kubo RT, Chesnut RW, Sette A. Definition of an HLA-A3-like supermotif demonstrates the overlapping peptide-binding repertoires of common HLA molecules. Hum Immunol. 1996;45:79–93. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(95)00173-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Threlkeld SC, Wentworth PA, Kalams SA, Wilkes BM, Ruhl DJ, Keogh E, Sidney J, Southwood S, Walker BD, Sette A. Degenerate and promiscuous recognition by CTL of peptides presented by the MHC class I A3-like superfamily: implications for vaccine development. J Immunol. 1997;159:1648–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidney J, del Guercio MF, Southwood S, Engelhard VH, Appella E, Rammensee HG, Falk K, Rotzschke O, Takiguchi M, Kubo RT, et al. Several HLA alleles share overlapping peptide specificities. J Immunol. 1995;154:247–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidney J, Southwood S, del Guercio MF, Grey HM, Chesnut RW, Kubo RT, Sette A. Specificity and degeneracy in peptide binding to HLA-B7-like class I molecules. J Immunol. 1996;157:3480–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidney J, Southwood S, Pasquetto V, Sette A. Simultaneous prediction of binding capacity for multiple molecules of the HLA B44-supertype. J Immunol. 2003;171:5964–5974. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.171.11.5964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidney J, Southwood S, Sette A. Classification of A1- and A24-supertype molecules by analysis of their MHC-peptide binding repertoires. Immunogenetics. 2005;57:393–408. doi: 10.1007/s00251-005-0004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund O, Nielsen M, Kesmir C, Petersen AG, Lundegaard C, Worning P, Sylvester-Hvid C, Lamberth K, Roder G, Justesen S, et al. Definition of supertypes for HLA molecules using clustering of specificity matrices. Immunogenetics. 2004;55:797–810. doi: 10.1007/s00251-004-0647-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang C, Anderson A, DeLisi C. Structural principles that govern the peptide-binding motifs of class I MHC molecules. J Mol Biol. 1998;281:929–47. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1998.1982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cano P, Fan B, Stass S. A geometric study of the amino acid sequence of class I HLA molecules. Immunogenetics. 1998;48:324–34. doi: 10.1007/s002510050439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doytchinova IA, Guan P, Flower DR. Identifiying human MHC supertypes using bioinformatic methods. J Immunol. 2004;172:4314–23. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.172.7.4314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reche PA, Reinherz EL. Definition of MHC supertypes through clustering of MHC peptide binding repertoires. LNCS, ICARIS. 2004;3239:189–196. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60327-118-9_11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chelvanayagam G. A roadmap for HLA-A, HLA-B, and HLA-C peptide binding specificities. Immunogenetics. 1996;45:15–26. doi: 10.1007/s002510050162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kangueane P, Sakharkar MK, Rajaseger G, Bolisetty S, Sivasekari B, Zhao B, Ravichandran M, Shapshak P, Subbiah S. A framework to sub-type HLA supertypes. Front Biosci. 2005;10:879–86. doi: 10.2741/1582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao B, Png AE, Ren EC, Kolatkar PR, Mathura VS, Sakharkar MK, Kangueane P. Compression of functional space in HLA-A sequence diversity. Hum Immunol. 2003;64:718–28. doi: 10.1016/S0198-8859(03)00078-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tong JC, Tan TW, Ranganathan S. In silico grouping of peptide/HLA class I complexes using structural interaction characteristics. Bioinformatics. 2007;23:177–83. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btl563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertz T, Yanover C. Identifying HLA supertypes by learning distance functions. Bioinformatics. 2007;23:e148–55. doi: 10.1093/Bioinformatics/btl324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovsyannikova IG, Jacobson RM, Vierkant RA, Pankratz VS, Poland GA. HLA supertypes and immune responses to measles-mumps-rubella viral vaccine: findings and implications for vaccine design. Vaccine. 2007;25:3090–100. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2007.01.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sylvester-Hvid C, Nielsen M, Lamberth K, Roder G, Justesen S, Lundegaard C, Worning P, Thomadsen H, Lund O, Brunak S, et al. SARS CTL vaccine candidates; HLA supertype-, genome-wide scanning and biochemical validation. Tissue Antigens. 2004;63:395–400. doi: 10.1111/j.0001-2815.2004.00221.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrows SR, Elkington RA, Miles JJ, Green KJ, Walker S, Haryana SM, Moss DJ, Dunckley H, Burrows JM, Khanna R. Promiscuous CTL recognition of viral epitopes on multiple human leukocyte antigens: biological validation of the proposed HLA A24 supertype. J Immunol. 2003;171:1407–12. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.171.3.1407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khanna R, Burrows SR, Nicholls J, Poulsen LM. Identification of cytotoxic T cell epitopes within Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) oncogene latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1): evidence for HLA A2 supertype-restricted immune recognition of EBV-infected cells by LMP1-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1998;28:451–8. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1521-4141(199802)28:02<451::AID-IMMU451>3.0.CO;2-U. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trachtenberg E, Korber B, Sollars C, Kepler TB, Hraber PT, Hayes E, Funkhouser R, Fugate M, Theiler J, Hsu YS, et al. Advantage of rare HLA supertype in HIV disease progression. Nat Med. 2003;9:928–35. doi: 10.1038/nm893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson CC, McKinney D, Anders M, MaWhinney S, Forster J, Crimi C, Southwood S, Sette A, Chesnut R, Newman MJ, et al. Development of a DNA vaccine designed to induce cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses to Multiple conserved epitopes in HIV-1. J Immunol. 2003;171:5611–23. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.171.10.5611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altfeld MA, Livingston B, Reshamwala N, Nguyen PT, Addo MM, Shea A, Newman M, Fikes J, Sidney J, Wentworth P, et al. Identification of novel HLA-A2-restricted human immunodeficiency virus type 1-specific cytotoxic T-lymphocyte epitopes predicted by the HLA-A2 supertype peptide-binding motif. J Virol. 2001;75:1301–11. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.3.1301-1311.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichterfeld KL, Williams M, Mui SK, Shah SS, Mothe BR, Sette A, Kim A, Johnston MN, Burgett N, Frahm N, et al. T cell receptor cross-recognition of an HIV-1 CD8+ T cell epitope presented by closely related alleles from the HLA-A3 superfamily. Int Immunol. 2006;18:1179–88. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxl052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honeyborne I, Rathod A, Buchli R, Ramduth D, Moodley E, Rathnavalu P, Chetty S, Day C, Brander C, Hildebrand W, et al. Motif inference reveals optimal CTL epitopes presented by HLA class I alleles highly prevalent in southern Africa. J Immunol. 2006;176:4699–705. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.176.8.4699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bihl F, Narayan M, Chisholm JV, 3rd, Henry LM, Suscovich TJ, Brown EE, Welzel TM, Kaufmann DE, Zaman TM, Dollard S, et al. Lytic and latent antigens of the human gammaherpesviruses Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus and Epstein-Barr virus induce T-cell responses with similar functional properties and memory phenotypes. J Virol. 2007;81:4904–8. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02509-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brander C, O'Connor P, Suscovich T, Jones NG, Lee Y, Kedes D, Ganem D, Martin J, Osmond D, Southwood S, et al. Definition of an optimal cytotoxic T lymphocyte epitope in the latently expressed Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus kaposin protein. J Infect Dis. 2001;184:119–26. doi: 10.1086/322003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wentworth PA, Sette A, Celis E, Sidney J, Southwood S, Crimi C, Stitely S, Keogh E, Wong NC, Livingston B, et al. Identification of A2-restricted hepatitis C virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocyte epitopes from conserved regions of the viral genome. Int Immunol. 1996;8:651–9. doi: 10.1093/intimm/8.5.651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertoni R, Sidney J, Fowler P, Chesnut RW, Chisari FV, Sette A. Human histocompatibility leukocyte antigen-binding supermotifs predict broadly cross-reactive cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses in patients with acute hepatitis. J Clin Invest. 1997;100:503–13. doi: 10.1172/JCI119559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingston BD, Crimi C, Fikes J, Chesnut RW, Sidney J, Sette A. Immunization with the HBV core 18-27 epitope elicits CTL responses in humans expressing different HLA-A2 supertype molecules. Hum Immunol. 1999;60:1013–7. doi: 10.1016/S0198-8859(99)00103-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ressing ME, de Jong JH, Brandt RM, Drijfhout JW, Benckhuijsen WE, Schreuder GM, Offringa R, Kast WM, Melief CJ. Differential binding of viral peptides to HLA-A2 alleles. Implications for human papillomavirus type 16 E7 peptide-based vaccination against cervical carcinoma. Eur J Immunol. 1999;29:1292–303. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1521-4141(199904)29:04<1292::AID-IMMU1292>3.0.CO;2-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang HG, Pang XW, Shang XY, Xing Q, Chen WF. Functional supertype of HLA-A2 in the presentation of Flu matrix p58-66 to induce CD8+ T-cell response in a Northern Chinese population. Tissue Antigens. 2003;62:285–95. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-0039.2003.00102.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyke KE, Burges RB, Cissoko Y, Sangare L, Kone A, Dao M, Diarra I, Fernandez-Vina MA, Plowe CV, Doumbo OK, et al. HLA-A2 supertype-restricted cell-mediated immunity by peripheral blood mononuclear cells derived from Malian children with severe or uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria and healthy controls. Infect Immun. 2005;73:5799–808. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.9.5799-5808.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolan DL, Hoffman SL, Southwood S, Wentworth PA, Sidney J, Chesnut RW, Keogh E, Appella E, Nutman TB, Lal AA, et al. Degenerate cytotoxic T cell epitopes from P. falciparum restricted by multiple HLA-A and HLA-B supertype alleles. Immunity. 1997;7:97–112. doi: 10.1016/S1074-7613(00)80513-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolan DL, Southwood S, Freilich DA, Sidney J, Graber NL, Shatney L, Bebris L, Florens L, Dobano C, Witney AA, et al. Identification of Plasmodium falciparum antigens by antigenic analysis of genomic and proteomic data. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100:9952–7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1633254100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang Y, Lin Y, Mao Y, Dong M, Wang H. Cross-binding between Plasmodium falciparum CTL epitopes and HLA class I molecules. Immunol Invest. 2003;32:31–41. doi: 10.1081/IMM-120019206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botten J, Whitton JL, Barrowman P, Sidney J, Whitmire JK, Alexander J, Ting JP, Bui HH, Sette A, Buchmeier MJ. HLA-A2-restricted protection against lethal lymphocytic choriomeningitis. J Virol. 2007;81:2307–17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02063-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botten J, Alexander J, Pasquetto V, Sidney J, Barrowman P, Ting J, Peters B, Southwood S, Stewart B, Rodriguez-Carreno MP, et al. Identification of protective Lassa virus epitopes that are restricted by HLA-A2. J Virol. 2006;80:8351–61. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00896-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMurry JA, Gregory SH, Moise L, Rivera D, Buus S, De Groot AS. Diversity of Francisella tularensis Schu4 antigens recognized by T lymphocytes after natural infections in humans: identification of candidate epitopes for inclusion in a rationally designed tularemia vaccine. Vaccine. 2007;25:3179–91. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2007.01.039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostrout ND, McHugh MM, Tisch DJ, Moormann AM, Brusic V, Kazura JW. Long-term T cell memory to human leucocyte antigen-A2 supertype epitopes in humans vaccinated against smallpox. Clin Exp Immunol. 2007 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2007.03401.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oseroff C, Kos F, Bui HH, Peters B, Pasquetto V, Glenn J, Palmore T, Sidney J, Tscharke DC, Bennink JR, et al. HLA class I-restricted responses to vaccinia recognize a broad array of proteins mainly involved in virulence and viral gene regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102:13980–5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0506768102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasquetto V, Bui HH, Giannino R, Mirza F, Sidney J, Oseroff C, Tscharke DC, Irvine K, Bennink JR, Peters B, et al. HLA-A* HLA-A*1101, and HLA-B*0702 Transgenic Mice Recognize Numerous Poxvirus Determinants from a Wide Variety of Viral Gene Products. J Immunol. 2001;175:5504–15. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.175.8.5504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fikes JD, Sette A. Design of multi-epitope, analogue-based cancer vaccines. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2003;3:985–93. doi: 10.1517/14712598.3.6.985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawashima I, Hudson SJ, Tsai V, Southwood S, Takesako K, Appella E, Sette A, Celis E. The multi-epitope approach for immunotherapy for cancer: identification of several CTL epitopes from various tumor-associated antigens expressed on solid epithelial tumors. Hum Immunol. 1998;59:1–14. doi: 10.1016/S0198-8859(97)00255-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawashima I, Tsai V, Southwood S, Takesako K, Celis E, Sette A. Identification of gp100-derived, melanoma-specific cytotoxic T-lymphocyte epitopes restricted by HLA-A3 supertype molecules by primary in vitro immunization with peptide-pulsed dendritic cells. Int J Cancer. 1998;78:518–24. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0215(19981109)78:4<518::AID-IJC20>3.0.CO;2-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keogh E, Fikes J, Southwood S, Celis E, Chesnut R, Sette A. Identification of new epitopes from four different tumor-associated antigens: recognition of naturally processed epitopes correlates with HLA-A*0201-binding affinity. J Immunol. 2001;167:787–96. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.167.2.787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang RF, Johnston SL, Southwood S, Sette A, Rosenberg SA. Recognition of an antigenic peptide derived from tyrosinase-related protein-2 by CTL in the context of HLA-A31 and -A33. J Immunol. 1998;160:890–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawashima I, Tsai V, Southwood S, Takesako K, Sette A, Celis E. Identification of HLA-A3-restricted cytotoxic T lymphocyte epitopes from carcinoembryonic antigen and HER-2/neu by primary in vitro immunization with peptide-pulsed dendritic cells. Cancer Res. 1999;59:431–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsueda S, Takedatsu H, Sasada T, Azuma K, Ishihara Y, Komohara Y, Noguchi M, Shichijo S, Itoh K, Harada M. New peptide vaccine candidates for epithelial cancer patients with HLA-A3 supertype alleles. J Immunother (1997) 2007;30:274–81. doi: 10.1097/01.cji.0000211340.88835.e7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minami T, Matsueda S, Takedatsu H, Tanaka M, Noguchi M, Uemura H, Itoh K, Harada M. Identification of SART3-derived peptides having the potential to induce cancer-reactive cytotoxic T lymphocytes from prostate cancer patients with HLA-A3 supertype alleles. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2007;56:689–98. doi: 10.1007/s00262-006-0216-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takedatsu H, Shichijo S, Katagiri K, Sawamizu H, Sata M, Itoh K. Identification of peptide vaccine candidates sharing among HLA-A3+, -A11+, -A31+, and -A33+ cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10:1112–20. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-0797-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsueda S, Takedatsu H, Yao A, Tanaka M, Noguchi M, Itoh K, Harada M. Identification of peptide vaccine candidates for prostate cancer patients with HLA-A3 supertype alleles. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:6933–43. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-0682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brusic V, Petrovsky N, Zhang G, Bajic VB. Prediction of promiscuous peptides that bind HLA class I molecules. Immunol Cell Biol. 2002;80:280–5. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1711.2002.01088.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan AM, Miotto O, Heiny AT, Salmon J, Srinivasan KN, Nascimento EJ, Marques ET, Jr, Brusic V, Tan TW, August JT. A systematic bioinformatics approach for selection of epitope-based vaccine targets. Cell Immunol. 2006;244:141–7. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2007.02.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reche PA, Reinherz EL. PEPVAC: a web server for multi-epitope vaccine development based on the prediction of supertypic MHC ligands. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005;33:W138–42. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu S, Udaka K, Sidney J, Sette A, Aoki-Kinoshita KF, Mamitsuka H. Improving MHC binding peptide prediction by incorporating binding data of auxiliary MHC molecules. Bioinformatics. 2006;22:1648–55. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btl141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang GL, Khan AM, Srinivasan KN, August JT, Brusic V. MULTIPRED: a computational system for prediction of promiscuous HLA binding peptides. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005;33:W172–9. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogan KT, Sutton JN, Chu KU, Busby JA, Shabanowitz J, Hunt DF, Slingluff CL., Jr Use of selected reaction monitoring mass spectrometry for the detection of specific MHC class I peptide antigens on A3 supertype family members. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2005;54:359–71. doi: 10.1007/s00262-004-0592-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doytchinova I, Flower D. The HLA-A2-supermotif: a QSAR definition. Org Biomol Chem. 2003;1:2648–54. doi: 10.1039/b300707c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan P, Doytchinova IA, Flower DR. A comparative molecular similarity indices (CoMSIA) study of peptide binding to the HLA-A3 superfamily. Bioorg Med Chem. 2003;11:2307–11. doi: 10.1016/S0968-0896(03)00109-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan P, Doytchinova IA, Flower DR. HLA-A3 supermotif defined by quantitative structure-activity relationship analysis. Protein Eng. 2003;16:11–8. doi: 10.1093/proeng/gzg005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald KS, Fowke KR, Kimani J, Dunand VA, Nagelkerke NJ, Ball TB, Oyugi J, Njagi E, Gaur LK, Brunham RC, et al. Influence of HLA supertypes on susceptibility and resistance to human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. J Infect Dis. 2000;181:1581–9. doi: 10.1086/315472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald KS, Embree JE, Nagelkerke NJ, Castillo J, Ramhadin S, Njenga S, Oyug J, Ndinya-Achola J, Barber BH, Bwayo JJ, et al. The HLA A2/6802 supertype is associated with reduced risk of perinatal human immunodeficiency virus type 1 transmission. J Infect Dis. 2001;183:503–6. doi: 10.1086/318092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald KS, Matukas L, Embree JE, Fowke K, Kimani J, Nagelkerke NJ, Oyugi J, Kiama P, Kaul R, Luscher MA, et al. Human leucocyte antigen supertypes and immune susceptibility to HIV-1, implications for vaccine design. Immunol Lett. 2001;79:151–7. doi: 10.1016/S0165-2478(01)00277-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens HA. HIV-1 diversity versus HLA class I polymorphism. Trends Immunol. 2005;26:41–7. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2004.11.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balamurugan A, Sharma SK, Mehra NK. Human leukocyte antigen class I supertypes influence susceptibility and severity of tuberculosis. J Infect Dis. 2004;189:805–11. doi: 10.1086/381689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Vazquez A, Mina-Blanco A, Martinez-Borra J, Njobvu PD, Suarez-Alvarez B, Blanco-Gelaz MA, Gonzalez S, Rodrigo L, Lopez-Larrea C. Interaction between KIR3DL1 and HLA-B*57 supertype alleles influences the progression of HIV-1 infection in a Zambian population. Hum Immunol. 2005;66:285–9. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2005.01.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Larrea C, Mijiyawa M, Gonzalez S, Fernandez-Morera JL, Blanco-Gelaz MA, Martinez-Borra J, Lopez-Vazquez A. Association of ankylosing spondylitis with HLA-B*1403 in a West African population. Arthritis Rheum. 2002;46:2968–71. doi: 10.1002/art.10584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novitsky V, Gilbert P, Peter T, McLane MF, Gaolekwe S, Rybak N, Thior I, Ndung'u T, Marlink R, Lee TH, et al. Association between virus-specific T-cell responses and plasma viral load in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 subtype C infection. J Virol. 2003;77:882–90. doi: 10.1128/JVI.77.2.882-890.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer A, Frater J, Oxenius A, Agudelo J, Price DA, Gunthard HF, Barnardo M, Perrin L, Hirschel B, Phillips RE, et al. Quantifiable cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses and HLA-related risk of progression to AIDS. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:12266–70. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0404091101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rammensee H, Bachmann J, Emmerich NP, Bachor OA, Stevanovic S. SYFPEITHI: database for MHC ligands and peptide motifs. Immunogenetics. 1999;50:213–9. doi: 10.1007/s002510050595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sathiamurthy M, Hickman HD, Cavett JW, Zahoor A, Prilliman K, Metcalf S, Fernandez Vina M, Hildebrand WH. Population of the HLA ligand database. Tissue Antigens. 2003;61:12–9. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-0039.2003.610102.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schonbach C, Koh JL, Flower DR, Wong L, Brusic V. FIMM, a database of functional molecular immunology: update 2002. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002;30:226–9. doi: 10.1093/nar/30.1.226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhasin M, Singh H, Raghava GP. MHCBN: a comprehensive database of MHC binding and non-binding peptides. Bioinformatics. 2003;19:665–6. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btg055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J, Waller MJ, Parham P, de Groot N, Bontrop R, Kennedy LJ, Stoehr P, Marsh SG. IMGT/HLA and IMGT/MHC: sequence databases for the study of the major histocompatibility complex. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003;31:311–4. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk K, Rotzschke O, Takiguchi M, Gnau V, Stevanovic S, Jung G, Rammensee HG. Peptide motifs of HLA-B58, B60, B61, and B62 molecules. Immunogenetics. 1995;41:165–8. doi: 10.1007/BF00182333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prilliman KR, Jackson KW, Lindsey M, Wang J, Crawford D, Hildebrand WH. HLA-B15 peptide ligands are preferentially anchored at their C termini. J Immunol. 1999;162:7277–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- The Immune epitope database and analysis resource http://www.immuneepitope.org
- Peters B, Sette A. Integrating epitope data into the emerging web of biomedical knowledge resources. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7:485–90. doi: 10.1038/nri2092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters B, Sidney J, Bourne P, Bui HH, Buus S, Doh G, Fleri W, Kronenberg M, Kubo R, Lund O, et al. The immune epitope database and analysis resource: from vision to blueprint. PLoS Biol. 2005;3:e91. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0030091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frahm N, Yusim K, Suscovich TJ, Adams S, Sidney J, Hraber P, Hewitt HS, Linde CH, Kavanagh DG, Woodberry T, et al. Extensive HLA class I allele promiscuity among viral CTL epitopes. Eur J Immunol. 2007;37:2419–33. doi: 10.1002/eji.200737365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Assarsson E, Sidney J, Oseroff C, Pasquetto V, Bui HH, Frahm N, Brander C, Peters B, Grey H, Sette A. A quantitative analysis of the variables affecting the repertoire of T cell specificities recognized after vaccinia virus infection. J Immunol. 2007;178:7890–901. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.178.12.7890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bihl F, Frahm N, Di Giammarino L, Sidney J, John M, Yusim K, Woodberry T, Sango K, Hewitt HS, Henry L, et al. Impact of HLA-B alleles, epitope binding affinity, functional avidity, and viral coinfection on the immunodominance of virus-specific CTL responses. J Immunol. 2006;176:4094–101. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.176.7.4094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altfeld M, Allen TM, Kalife ET, Frahm N, Addo MM, Mothe BR, Rathod A, Reyor LL, Harlow J, Yu XG, et al. The majority of currently circulating human immunodeficiency virus type 1 clade B viruses fail to prime cytotoxic T-lymphocyte responses against an otherwise immunodominant HLA-A2-restricted epitope: implications for vaccine design. J Virol. 2005;79:5000–5. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.8.5000-5005.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leslie A, Price DA, Mkhize P, Bishop K, Rathod A, Day C, Crawford H, Honeyborne I, Asher TE, Luzzi G, et al. Differential selection pressure exerted on HIV by CTL targeting identical epitopes but restricted by distinct HLA alleles from the same HLA supertype. J Immunol. 2006;177:4699–708. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.177.7.4699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald WA, Purcell AW, Mifsud NA, Ely LK, Williams DS, Chang L, Gorman JJ, Clements CS, Kjer-Nielsen L, Koelle DM, et al. A naturally selected dimorphism within the HLA-B44 supertype alters class I structure, peptide repertoire, and T cell recognition. J Exp Med. 2003;198:679–91. doi: 10.1084/jem.20030066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apostolopoulos V, Yu M, Corper AL, Li W, McKenzie IF, Teyton L, Wilson IA, Plebanski M. Crystal structure of a non-canonical high affinity peptide complexed with MHC class I: a novel use of alternative anchors. J Mol Biol. 2002;318:1307–16. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(02)00198-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apostolopoulos V, Yu M, Corper AL, Teyton L, Pietersz GA, McKenzie IF, Wilson IA, Plebanski M. Crystal structure of a non-canonical low-affinity peptide complexed with MHC class I: a new approach for vaccine design. J Mol Biol. 2002;318:1293–305. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(02)00196-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fremont DH, Stura EA, Matsumura M, Peterson PA, Wilson IA. Crystal structure of an H-2Kb-ovalbumin peptide complex reveals the interplay of primary and secondary anchor positions in the major histocompatibility complex binding groove. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1995;92:2479–83. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.7.2479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hengel H, Burke K, Kyburz D, Zinkernagel RM, Koszinowski UH. Peptides control the gain and loss of allele specificity by mutated MHC class I molecules. J Immunol. 1995;154:4557–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H, Natarajan K, Malchiodi EL, Margulies DH, Mariuzza RA. Three-dimensional structure of H-2Dd complexed with an immunodominant peptide from human immunodeficiency virus envelope glycoprotein 120. J Mol Biol. 1998;283:179–91. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1998.2091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mata M, Travers PJ, Liu Q, Frankel FR, Paterson Y. The MHC class I-restricted immune response to HIV-gag in BALB/c mice selects a single epitope that does not have a predictable MHC-binding motif and binds to Kd through interactions between a glutamine at P3 and pocket D. J Immunol. 1998;161:2985–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitaksov V, Fremont DH. Structural definition of the H-2Kd peptide-binding motif. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:10618–25. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M510511200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sette A, Sidney J, Livingston B, Dzuris J, Crimi C, Walker CM, Southwood S, Collins EJ, Hughes A. Class I molecules with similar peptide binding specificities are the result of both common ancestry and convergent evolution. Immunogenetics. 2003;54:830–841. doi: 10.1007/s00251-002-0530-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenzer S, Peters B, Bulik S, Schoor O, Lemmel C, Schatz MM, Kloetzel PM, Rammensee HG, Schild H, Holzhutter HG. Modeling the MHC class I pathway by combining predictions of proteasomal cleavage, TAP transport and MHC class I binding. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2005;62:1025–37. doi: 10.1007/s00018-005-4528-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Los Alamos HIV Sequence Database http://www.hiv.lanl.gov
- IMGT/HLA Database http://www.ebi.ac.uk/imgt/hla/
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
HLA supertype classification of HLA A and B class I alleles. This table provides a complete listing of the HLA A and B alleles examined in the present study. The table is sorted in alphanumeric order to facilitate searching for a specific allele. For each allele, the supertype assignment is indicated, and it's corresponding B and F pocket sequences are shown.