Abstract
The c-erbB-2 gene codes for a putative transmembrane protein, similar in structure to the epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor. Amplification of the gene has been described in a variety of human adenocarcinomas and is particularly well documented in breast carcinoma. It has been suggested that amplification is indicative of poor prognosis and, as such, is comparable with lymph node status as a predictor of clinical outcome. This study examines the suggestion indirectly by an immunohistochemical technique. Archival tissue from 195 patients with primary breast carcinoma was stained with the polyclonal antibody 21N, raised to amino acids 1243-1255, the C-terminus of the predicted amino acid sequence of the c-erbB-2 protein. Up to 10 year verified follow-up data were available on all patients. Staining compatible with significant amplification was observed in 17 patients. Using the chi-squared test for trend a significant correlation was found between staining and grade (P = 0.04) but not with either node or receptor status. No significant association was found between staining and clinical outcome although there was a tendency for patients with stained tumours to have a worse prognosis. A Cox regression analysis was used to adjust for node status and grade and still no correlation was revealed between staining and prognosis. However a study of this size in which only a small number of patients have been found to have stained tumours does have wide confidence limits. Comparable staining observed in in situ and infiltrating components of tumours suggests that amplification is an early event in carcinogenesis. Similar staining in primary and subsequent metastatic lesions was also noted. It is considered that further studies at both the DNA/mRNA and protein levels are required to confirm the significance of c-erbB-2 amplification in human breast carcinoma.
Full text
PDF


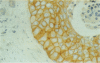
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akiyama T., Sudo C., Ogawara H., Toyoshima K., Yamamoto T. The product of the human c-erbB-2 gene: a 185-kilodalton glycoprotein with tyrosine kinase activity. Science. 1986 Jun 27;232(4758):1644–1646. doi: 10.1126/science.3012781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLOOM H. J., RICHARDSON W. W. Histological grading and prognosis in breast cancer; a study of 1409 cases of which 359 have been followed for 15 years. Br J Cancer. 1957 Sep;11(3):359–377. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1957.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bargmann C. I., Hung M. C., Weinberg R. A. The neu oncogene encodes an epidermal growth factor receptor-related protein. Nature. 1986 Jan 16;319(6050):226–230. doi: 10.1038/319226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M. The molecular genetics of cancer. Science. 1987 Jan 16;235(4786):305–311. doi: 10.1126/science.3541204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan V. T., McGee J. O. Cellular oncogenes in neoplasia. J Clin Pathol. 1987 Sep;40(9):1055–1063. doi: 10.1136/jcp.40.9.1055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Fiore P. P., Pierce J. H., Kraus M. H., Segatto O., King C. R., Aaronson S. A. erbB-2 is a potent oncogene when overexpressed in NIH/3T3 cells. Science. 1987 Jul 10;237(4811):178–182. doi: 10.1126/science.2885917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escot C., Theillet C., Lidereau R., Spyratos F., Champeme M. H., Gest J., Callahan R. Genetic alteration of the c-myc protooncogene (MYC) in human primary breast carcinomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4834–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gullick W. J., Berger M. S., Bennett P. L., Rothbard J. B., Waterfield M. D. Expression of the c-erbB-2 protein in normal and transformed cells. Int J Cancer. 1987 Aug 15;40(2):246–254. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910400221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward J. L., Meakin J. W., Stewart H. J. Assessment of response and recurrence in breast cancer. Semin Oncol. 1978 Dec;5(4):445–449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King R. J., Hayward J. L., Kumaoka S., Yamamoto H. Comparison of soluble oestrogen and progestin receptor content of primary breast tumours from Japan and Britain. Eur J Cancer. 1977 Sep;13(9):967–970. doi: 10.1016/0014-2964(77)90174-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubens R. D., Hayward J. L., Knight R. K., Bulbrook R. D., Fentiman I. S., Chaudary M., Howell A., Bush H., Crowther D., Sellwood R. A. Controlled trial of adjuvant chemotherapy with melphalan for breast cancer. Lancet. 1983 Apr 16;1(8329):839–843. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91385-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter A. L., Stern D. F., Vaidyanathan L., Decker S. J., Drebin J. A., Greene M. I., Weinberg R. A. The neu oncogene: an erb-B-related gene encoding a 185,000-Mr tumour antigen. Nature. 1984 Dec 6;312(5994):513–516. doi: 10.1038/312513a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeger R. C., Brodeur G. M., Sather H., Dalton A., Siegel S. E., Wong K. Y., Hammond D. Association of multiple copies of the N-myc oncogene with rapid progression of neuroblastomas. N Engl J Med. 1985 Oct 31;313(18):1111–1116. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198510313131802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semba K., Kamata N., Toyoshima K., Yamamoto T. A v-erbB-related protooncogene, c-erbB-2, is distinct from the c-erbB-1/epidermal growth factor-receptor gene and is amplified in a human salivary gland adenocarcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6497–6501. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
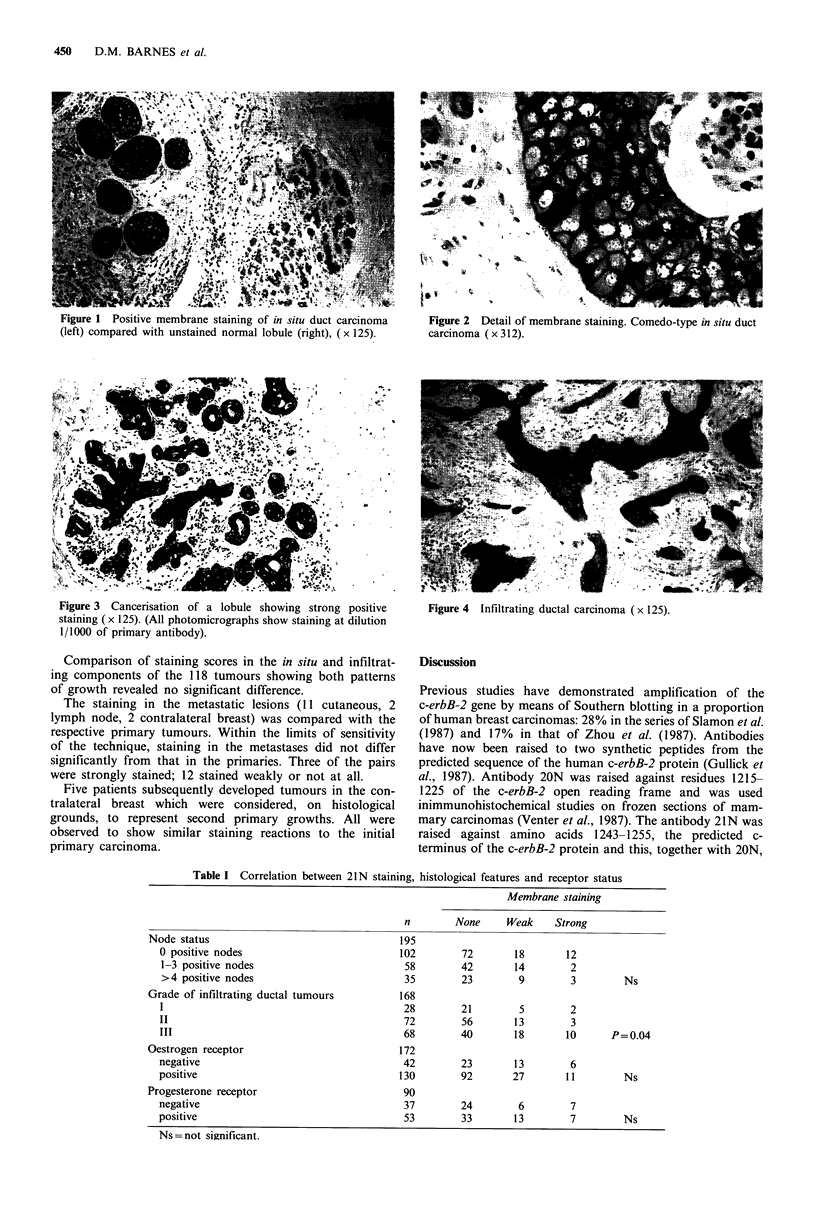
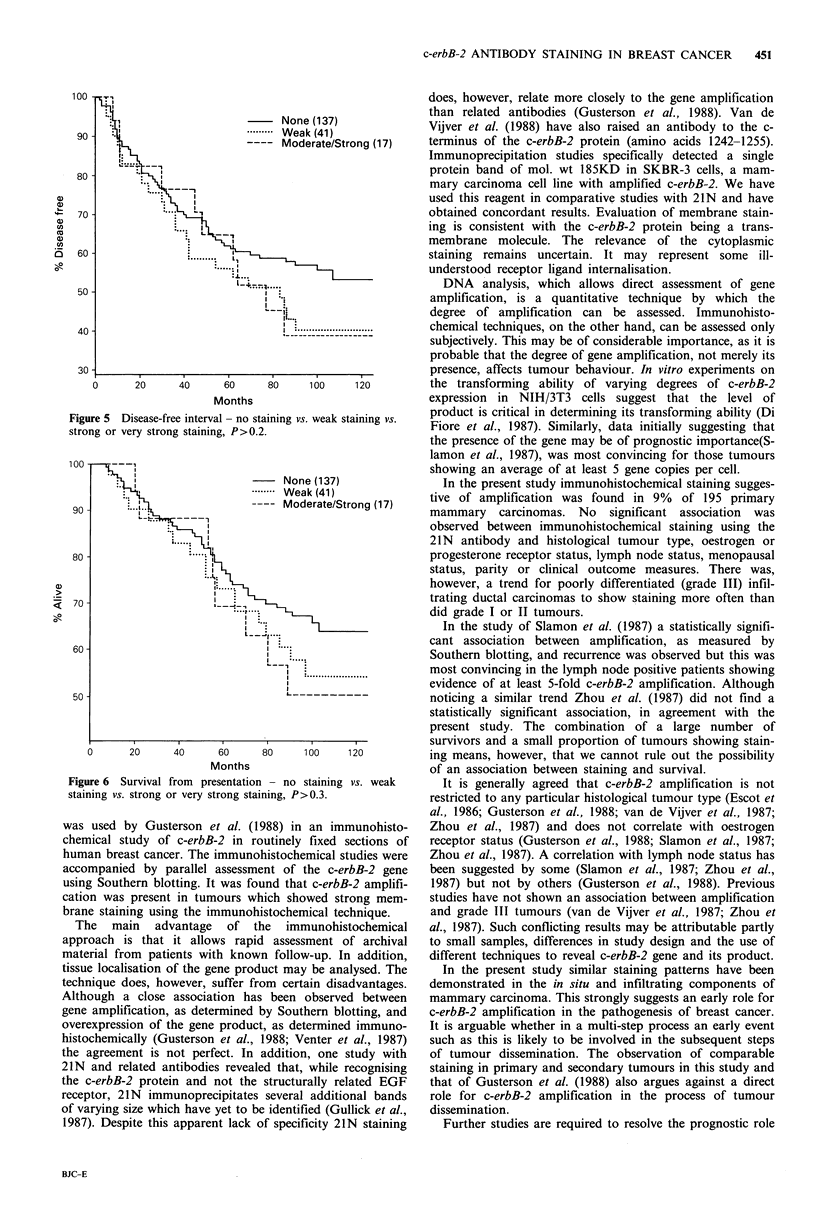
- Slamon D. J., Clark G. M., Wong S. G., Levin W. J., Ullrich A., McGuire W. L. Human breast cancer: correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene. Science. 1987 Jan 9;235(4785):177–182. doi: 10.1126/science.3798106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venter D. J., Tuzi N. L., Kumar S., Gullick W. J. Overexpression of the c-erbB-2 oncoprotein in human breast carcinomas: immunohistological assessment correlates with gene amplification. Lancet. 1987 Jul 11;2(8550):69–72. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)92736-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Ikawa S., Akiyama T., Semba K., Nomura N., Miyajima N., Saito T., Toyoshima K. Similarity of protein encoded by the human c-erb-B-2 gene to epidermal growth factor receptor. Nature. 1986 Jan 16;319(6050):230–234. doi: 10.1038/319230a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokota J., Yamamoto T., Toyoshima K., Terada M., Sugimura T., Battifora H., Cline M. J. Amplification of c-erbB-2 oncogene in human adenocarcinomas in vivo. Lancet. 1986 Apr 5;1(8484):765–767. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)91782-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou D., Battifora H., Yokota J., Yamamoto T., Cline M. J. Association of multiple copies of the c-erbB-2 oncogene with spread of breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1987 Nov 15;47(22):6123–6125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Vijver M. J., Mooi W. J., Wisman P., Peterse J. L., Nusse R. Immunohistochemical detection of the neu protein in tissue sections of human breast tumors with amplified neu DNA. Oncogene. 1988 Feb;2(2):175–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Vijver M., van de Bersselaar R., Devilee P., Cornelisse C., Peterse J., Nusse R. Amplification of the neu (c-erbB-2) oncogene in human mammmary tumors is relatively frequent and is often accompanied by amplification of the linked c-erbA oncogene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):2019–2023. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.2019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]