Abstract
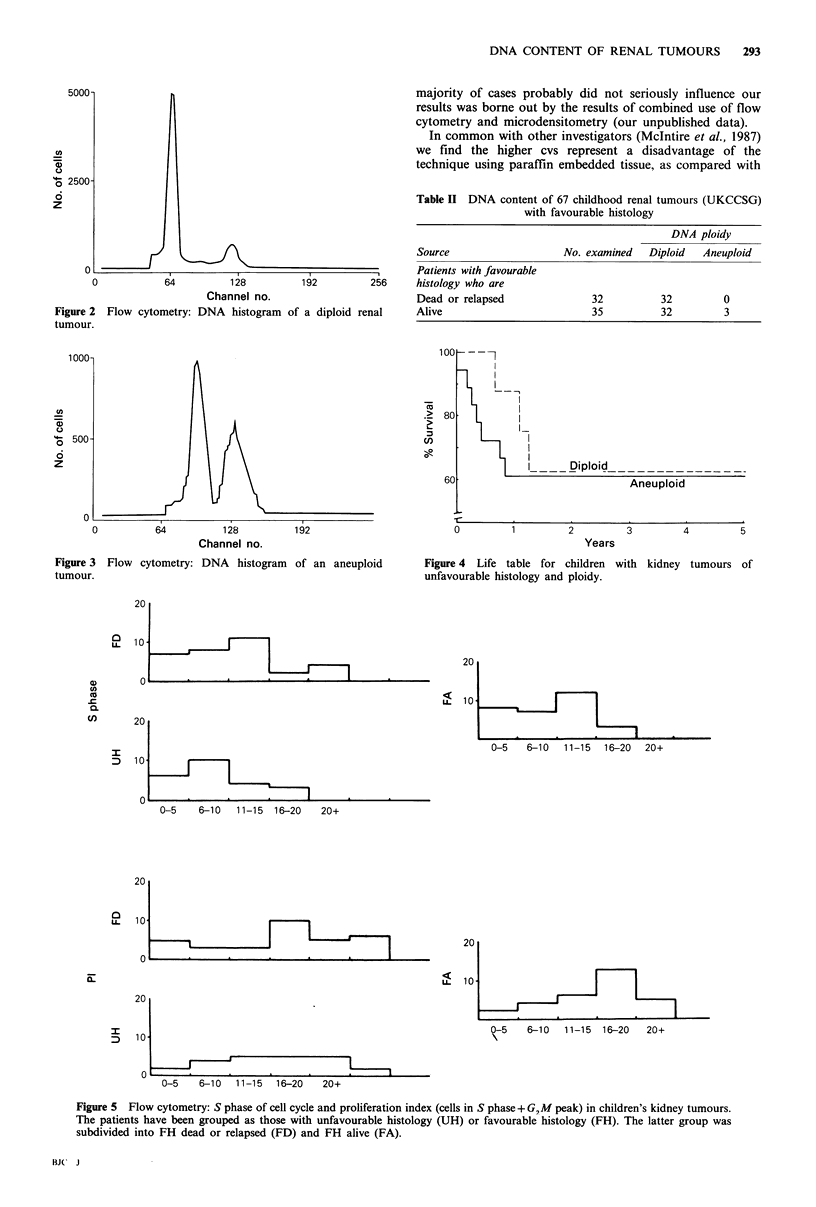
The DNA content of paraffin embedded tumour specimens from 100 children with kidney tumours was studied by flow cytometry. Data of adequate quality were obtained from 93 cases comprising 67 Wilms' tumours with a favourable histology (FH), 12 Wilms' tumours with unfavourable histology (UH) (pleomorphic), 8 bone-metastasising renal tumours of childhood (BMRTC) and 6 rhabdoid renal tumours. Only 4.5% FH compared with 75% UH Wilms' were aneuploid (P less than 0.001). Although BMRTC and rhabdoid tumours are associated with poor prognosis, there were no examples of aneuploidy in these tumours. The proliferation index was found to be of no prognostic value. Staging and ploidy were not correlated with each other in any of the various histological types of renal tumours studied.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkin N. B. Modal deoxyribonucleic acid value and survival in carcinoma of the breast. Br Med J. 1972 Jan 29;1(5795):271–272. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5795.271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auer G., Eriksson E., Azavedo E., Caspersson T., Wallgren A. Prognostic significance of nuclear DNA content in mammary adenocarcinomas in humans. Cancer Res. 1984 Jan;44(1):394–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baildam A. D., Zaloudik J., Howell A., Barnes D. M., Turnbull L., Swindell R., Moore M., Sellwood R. A. DNA analysis by flow cytometry, response to endocrine treatment and prognosis in advanced carcinoma of the breast. Br J Cancer. 1987 May;55(5):553–559. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1987.113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckwith J. B., Palmer N. F. Histopathology and prognosis of Wilms tumors: results from the First National Wilms' Tumor Study. Cancer. 1978 May;41(5):1937–1948. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197805)41:5<1937::aid-cncr2820410538>3.0.co;2-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckwith J. B. Wilms' tumor and other renal tumors of childhood: a selective review from the National Wilms' Tumor Study Pathology Center. Hum Pathol. 1983 Jun;14(6):481–492. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(83)80003-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilateral anaplastic Wilms' tumors: change in ploidy following treatment. Med Pediatr Oncol. 1987;15(1):28–30. doi: 10.1002/mpo.2950150107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coon J. S., Landay A. L., Weinstein R. S. Flow cytometric analysis of paraffin-embedded tumors: implications for diagnostic pathology. Hum Pathol. 1986 May;17(5):435–437. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(86)80029-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelisse C. J., de Koning H. R., Moolenaar A. J., van de Velde C. J., Ploem J. S. Image and flow cytometric analysis of DNA content in breast cancer. Relation to estrogen receptor content and lymph node involvement. Anal Quant Cytol. 1984 Mar;6(1):9–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danova M., Riccardi A., Mazzini G., Ucci G., Montecucco C. M., Gaetani P., Silvani V., Knerich R., Butti G., Ascari E. Proliferative characteristics and ploidy of human brain tumors by DNA flow cytometry. Basic Appl Histochem. 1986;30(2):175–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglass E. C., Look A. T., Webber B., Parham D., Wilimas J. A., Green A. A., Roberson P. K. Hyperdiploidy and chromosomal rearrangements define the anaplastic variant of Wilms' tumor. J Clin Oncol. 1986 Jun;4(6):975–981. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1986.4.6.975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak H. F. Tumors: wounds that do not heal. Similarities between tumor stroma generation and wound healing. N Engl J Med. 1986 Dec 25;315(26):1650–1659. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198612253152606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedlander M. L., Russell P., Taylor I. W., Hedley D. W., Tattersall M. H. Flow cytometric analysis of cellular DNA content as an adjunct to the diagnosis of ovarian tumours of borderline malignancy. Pathology. 1984 Jul;16(3):301–306. doi: 10.3109/00313028409068541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gansler T., Chatten J., Varello M., Bunin G. R., Atkinson B. Flow cytometric DNA analysis of neuroblastoma. Correlation with histology and clinical outcome. Cancer. 1986 Dec 1;58(11):2453–2458. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19861201)58:11<2453::aid-cncr2820581117>3.0.co;2-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedley D. W., Friedlander M. L., Taylor I. W. Application of DNA flow cytometry to paraffin-embedded archival material for the study of aneuploidy and its clinical significance. Cytometry. 1985 Jul;6(4):327–333. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990060409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedley D. W., Friedlander M. L., Taylor I. W., Rugg C. A., Musgrove E. A. Method for analysis of cellular DNA content of paraffin-embedded pathological material using flow cytometry. J Histochem Cytochem. 1983 Nov;31(11):1333–1335. doi: 10.1177/31.11.6619538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedley D. W., Rugg C. A., Ng A. B., Taylor I. W. Influence of cellular DNA content on disease-free survival of Stage II breast cancer patients. Cancer Res. 1984 Nov;44(11):5395–5398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiddemann W., Schumann J., Andreef M., Barlogie B., Herman C. J., Leif R. C., Mayall B. H., Murphy R. F., Sandberg A. A. Convention on nomenclature for DNA cytometry. Committee on Nomenclature, Society for Analytical Cytology. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1984 Oct;13(2):181–183. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(84)90059-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain R. K. Transport of molecules in the tumor interstitium: a review. Cancer Res. 1987 Jun 15;47(12):3039–3051. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreicbergs A., Tribukait B., Willems J., Bauer H. C. DNA flow analysis of soft tissue tumors. Cancer. 1987 Jan 1;59(1):128–133. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19870101)59:1<128::aid-cncr2820590126>3.0.co;2-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar S., Marsden H. B., Calabuig M. C. Childhood kidney tumours: in vitro studies and natural history. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1984;405(1):95–111. doi: 10.1007/BF00694928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawler W., Marsden H. B., Palmer M. K. Wilms' tumor--histologic variation and prognosis. Cancer. 1975 Sep;36(3):1122–1126. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197509)36:3<1122::aid-cncr2820360343>3.0.co;2-#. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Look A. T., Hayes F. A., Nitschke R., McWilliams N. B., Green A. A. Cellular DNA content as a predictor of response to chemotherapy in infants with unresectable neuroblastoma. N Engl J Med. 1984 Jul 26;311(4):231–235. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198407263110405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann D. M., Yates P. O. A quantitative study of the glia of the Purkinje cell layer of the cerebellum in mammals. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1979 Jan-Feb;5(1):71–76. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1979.tb00615.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden H. B., Lawler W., Carr T., Kumar S. A scoring system for Wilms' tumour: pathological study of the second Medical Research Council (MRC) trial. Int J Cancer. 1984 Mar 15;33(3):365–368. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910330314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntire T. L., Goldey S. H., Benson N. A., Braylan R. C. Flow cytometric analysis of DNA in cells obtained from deparaffinized formalin-fixed lymphoid tissues. Cytometry. 1987 Sep;8(5):474–478. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990080507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran R. E., Black M. M., Alpert L., Straus M. J. Correlation of cell-cycle kinetics, hormone receptors, histopathology, and nodal status in human breast cancer. Cancer. 1984 Oct 15;54(8):1586–1590. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19841015)54:8<1586::aid-cncr2820540820>3.0.co;2-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rainwater L. M., Hosaka Y., Farrow G. M., Lieber M. M. Well differentiated clear cell renal carcinoma: significance of nuclear deoxyribonucleic acid patterns studied by flow cytometry. J Urol. 1987 Jan;137(1):15–20. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)43857-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandstad E., Hartveit F. Stromal metachromasia: a marker for areas of incipient invasion in ductal carcinoma of the breast? Histopathology. 1987 Jan;11(1):73–80. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1987.tb02610.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt D., Wiedemann B., Keil W., Sprenger E., Harms D. Flow cytometric analysis of nephroblastomas and related neoplasms. Cancer. 1986 Dec 1;58(11):2494–2500. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19861201)58:11<2494::aid-cncr2820581124>3.0.co;2-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



