Abstract
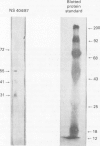
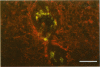
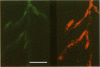
The distribution of tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA) has been studied in a series of 38 human brain tumours and two specimens of cerebral cortex, using the monoclonal antibody ESP6. t-PA was localised in vascular endothelium in the majority of tumours and both the cortical specimens, confirmed by double staining with Ulex europaeus lectin (Uel) and Factor 8-related antigen. Nineteen out of 22 high grade astrocytomas showed strong endothelial staining whereas staining was weak or absent in the four low grade astrocytomas studied. No consistent relationship was found between the pattern of staining and tumour grade in the other tumours, although strong staining of the three metastatic lesions with Uel was observed. Among the astroglial tumours only one glioblastoma showed any tumour cell staining for t-PA, which raises questions concerning the origin of t-PA producing cells derived from human gliomas in vitro. Studies of t-PA in brain tumours should take account of this vascular localisation before concluding that the activity is derived from neoplastic cells.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALI S. Y., LACK C. H. STUDIES ON THE TISSUE ACTIVATOR OF PLASMINOGEN. DISTRIBUTION OF ACTIVATOR AND PROTEOLYTIC ACTIVITY IN THE SUBCELLULAR FRACTIONS OF RABBIT KIDNEY. Biochem J. 1965 Jul;96:63–74. doi: 10.1042/bj0960063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohadon F., Aouad N., Rougier A., Vital C., Rivel J., Dartigues J. F. Histologic and non-histologic factors correlated with survival time in supratentorial astrocytic tumors. J Neurooncol. 1985;3(2):105–111. doi: 10.1007/BF02228885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenlon S., Ellis I. O., Bell J., Todd J. H., Elston C. W., Blamey R. W. Helix pomatia and Ulex europeus lectin binding in human breast carcinoma. J Pathol. 1987 Jul;152(3):169–176. doi: 10.1002/path.1711520305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frame M. C., Freshney R. I., Vaughan P. F., Graham D. I., Shaw R. Interrelationship between differentiation and malignancy-associated properties in glioma. Br J Cancer. 1984 Mar;49(3):269–280. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1984.44. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franks A. J., Burrow H. M. In vitro heterogeneity in human gliomas. Are all transformed cells of glial origin? Anticancer Res. 1986 Jul-Aug;6(4):625–629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulling K. H., Garcia D. M. Anaplastic astrocytoma of the adult cerebrum. Prognostic value of histologic features. Cancer. 1985 Mar 1;55(5):928–931. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19850301)55:5<928::aid-cncr2820550503>3.0.co;2-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen P. F., Jenkyn D. J., Papadimitriou J. M. Four permanent cell lines established from human malignant gliomas: three exhibiting striated muscle differentiation. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1987 Jul;46(4):431–450. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198707000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy P. G., Watkins B. A., Thomas D. G., Noble M. D. Antigenic expression by cells derived from human gliomas does not correlate with morphological classification. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1987 Sep-Oct;13(5):327–347. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.1987.tb00190.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohga S., Harvey S. R., Weaver R. M., Markus G. Localization of plasminogen activators in human colon cancer by immunoperoxidase staining. Cancer Res. 1985 Apr;45(4):1787–1796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laug W. E., Tokes Z. A., Benedict W. F., Sorgente N. Anchorage independent growth and plasminogen activator production by bovine endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1980 Feb;84(2):281–293. doi: 10.1083/jcb.84.2.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lolait S. J., Harmer J. H., Auteri G., Pedersen J. S., Toh B. H. Expression of glial fibrillary acidic protein, actin, fibronectin and factor VIII antigen in human astrocytomas. Pathology. 1983 Oct;15(4):373–378. doi: 10.3109/00313028309085162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markus G., Kohga S., Camiolo S. M., Madeja J. M., Ambrus J. L., Karakousis C. Plasminogen activators in human malignant melanoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1984 Jun;72(6):1213–1222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maunoury R. Establishment and characterization of 5 human cell lines derived from a series of 50 primary intracranial tumors. Acta Neuropathol. 1977 Jul 15;39(1):33–41. doi: 10.1007/BF00690383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAuslan B. R., Hannan G. N., Reilly W., Stewart F. H. Variant endothelial cells. Fibronectin as a transducer of signals for migration and neovascularisation. J Cell Physiol. 1980 Aug;104(2):177–186. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041040207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeever P. E., Smith B. H., Taren J. A., Wahl R. L., Kornblith P. L., Chronwall B. M. Products of cells cultured from gliomas. VI. Immunofluorescent, morphometric, and ultrastructural characterization of two different cell types growing from explants of human gliomas. Am J Pathol. 1987 May;127(2):358–372. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean J. S., Frame M. C., Freshney R. I., Vaughan P. F., Mackie A. E., Singer I. Phenotypic modification of human glioma and non-small cell lung carcinoma by glucocorticoids and other agents. Anticancer Res. 1986 Sep-Oct;6(5):1101–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullins D. E., Rohrlich S. T. The role of proteinases in cellular invasiveness. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Dec 29;695(3-4):177–214. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(83)90011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paetau A. Glial fibrillary acidic protein, vimentin and fibronectin in primary cultures of human glioma and fetal brain. Acta Neuropathol. 1988;75(5):448–455. doi: 10.1007/BF00687131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Presta M., Moscatelli D., Joseph-Silverstein J., Rifkin D. B. Purification from a human hepatoma cell line of a basic fibroblast growth factor-like molecule that stimulates capillary endothelial cell plasminogen activator production, DNA synthesis, and migration. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):4060–4066. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.4060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quigley J. P. Association of a protease (plasminogen activator) with a specific membrane fraction isolated from transformed cells. J Cell Biol. 1976 Nov;71(2):472–486. doi: 10.1083/jcb.71.2.472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quindlen E. A., Bucher A. P. Correlation of tumor plasminogen activator with peritumoral cerebral edema. A CT and biochemical study. J Neurosurg. 1987 May;66(5):729–733. doi: 10.3171/jns.1987.66.5.0729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijken D. C., Collen D. Purification and characterization of the plasminogen activator secreted by human melanoma cells in culture. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):7035–7041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijken D. C., Wijngaards G., Welbergen J. Relationship between tissue plasminogen activator and the activators in blood and vascular wall. Thromb Res. 1980 Jun 15;18(6):815–830. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(80)90204-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijken D. C., Wijngaards G., Zaal-de Jong M., Welbergen J. Purification and partial characterization of plasminogen activator from human uterine tissue. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Sep 29;580(1):140–153. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(79)90205-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TODD A. S. The histological localisation of fibrinolysin activator. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1959 Jul;78:281–283. doi: 10.1002/path.1700780131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takashima S., Koga M., Tanaka K. Fibrinolytic activity of human brain and cerebrospinal fluid. Br J Exp Pathol. 1969 Dec;50(6):533–539. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiku M. L., Tomasi T. B. Enhancement of endothelial plasminogen activator synthesis by lymphokines. Transplantation. 1985 Sep;40(3):293–298. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198509000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tripathi B. J., Geanon J. D., Tripathi R. C. Distribution of tissue plasminogen activator in human and monkey eyes. An immunohistochemical study. Ophthalmology. 1987 Nov;94(11):1434–1438. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(87)33278-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker W. S., Kirsch W. M., Martinez-Hernandez A., Fink L. M. In vitro plasminogen activator activity in human brain tumors. Cancer Res. 1978 Feb;38(2):297–302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unkeless J. C., Gordon S., Reich E. Secretion of plasminogen activator by stimulated macrophages. J Exp Med. 1974 Apr 1;139(4):834–850. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.4.834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]