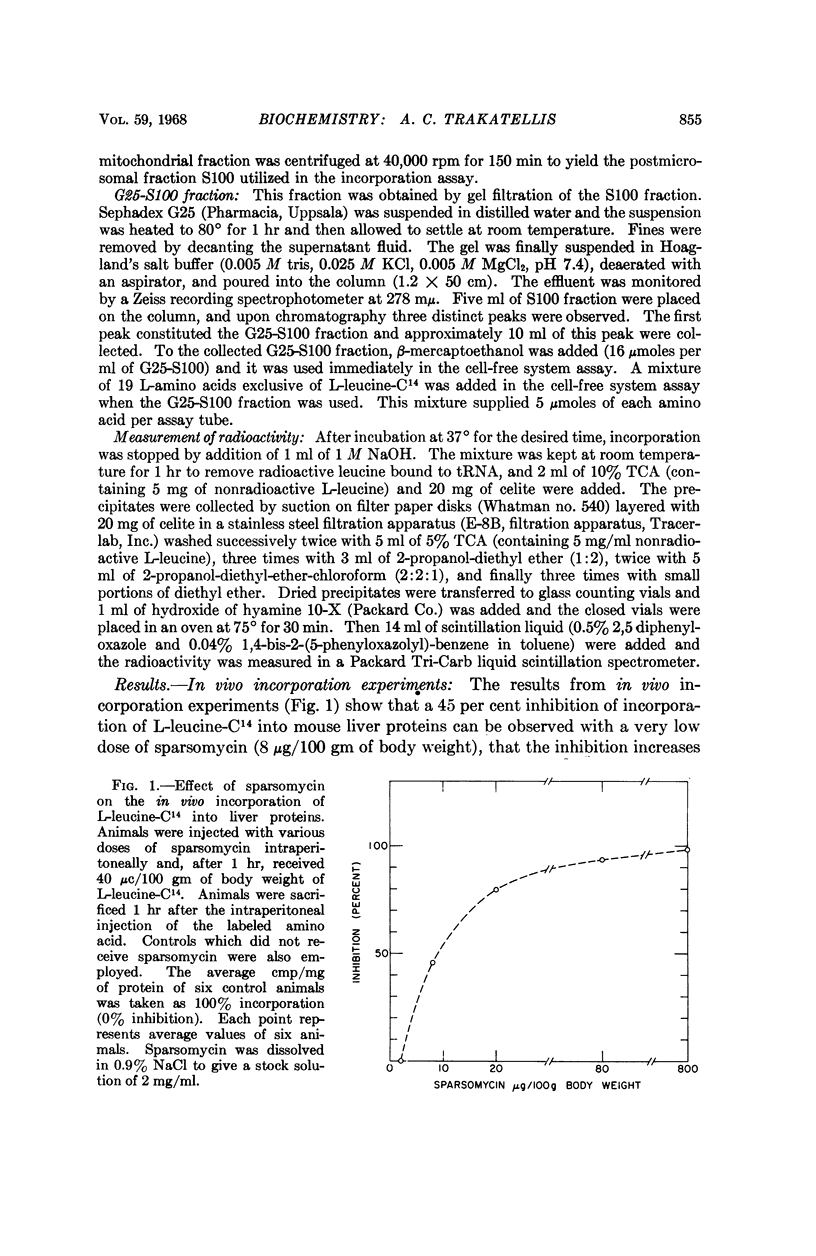
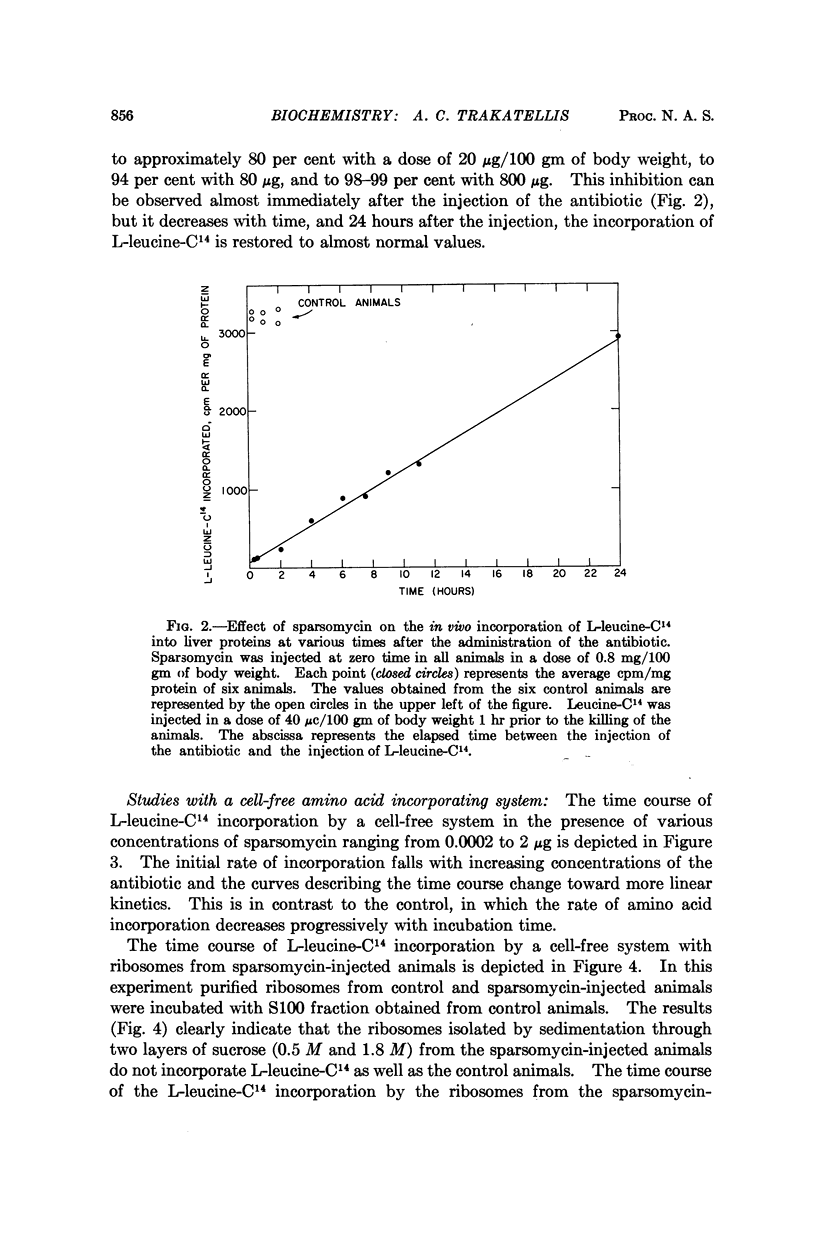
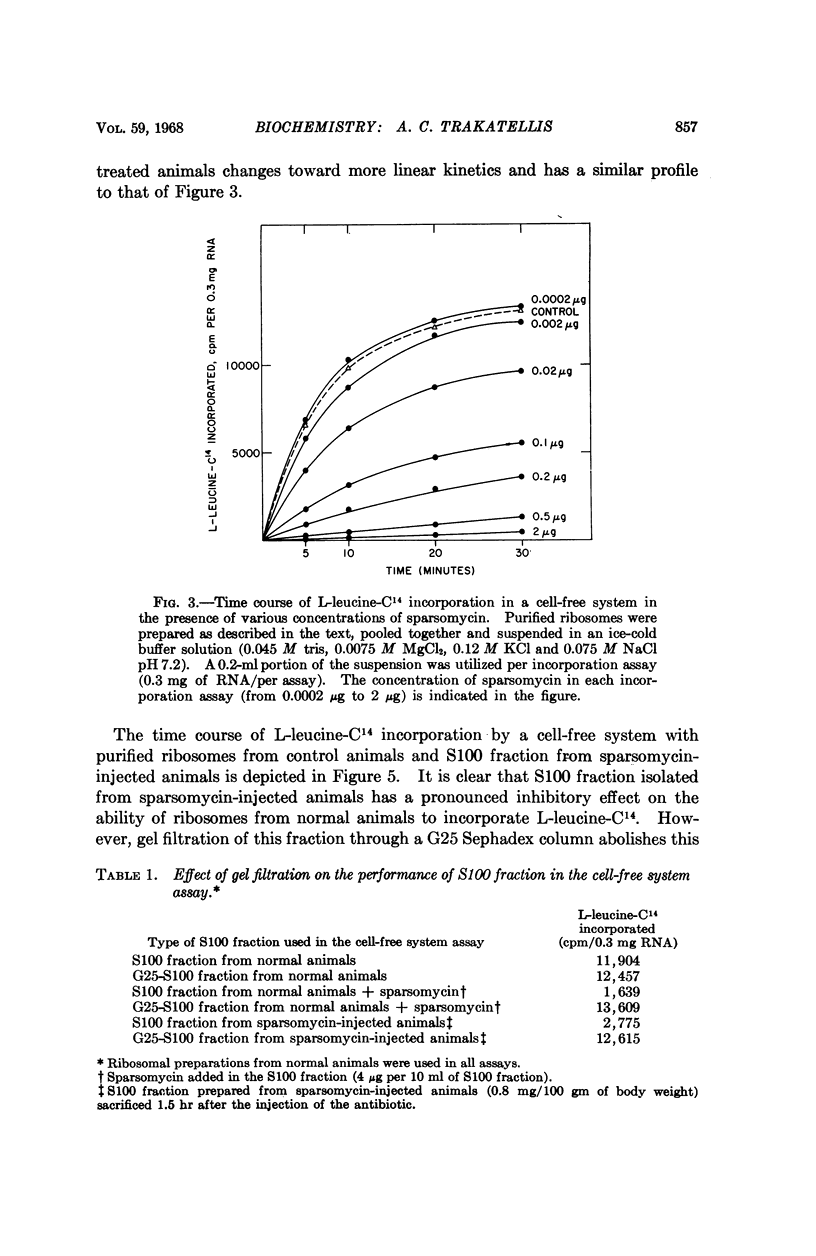
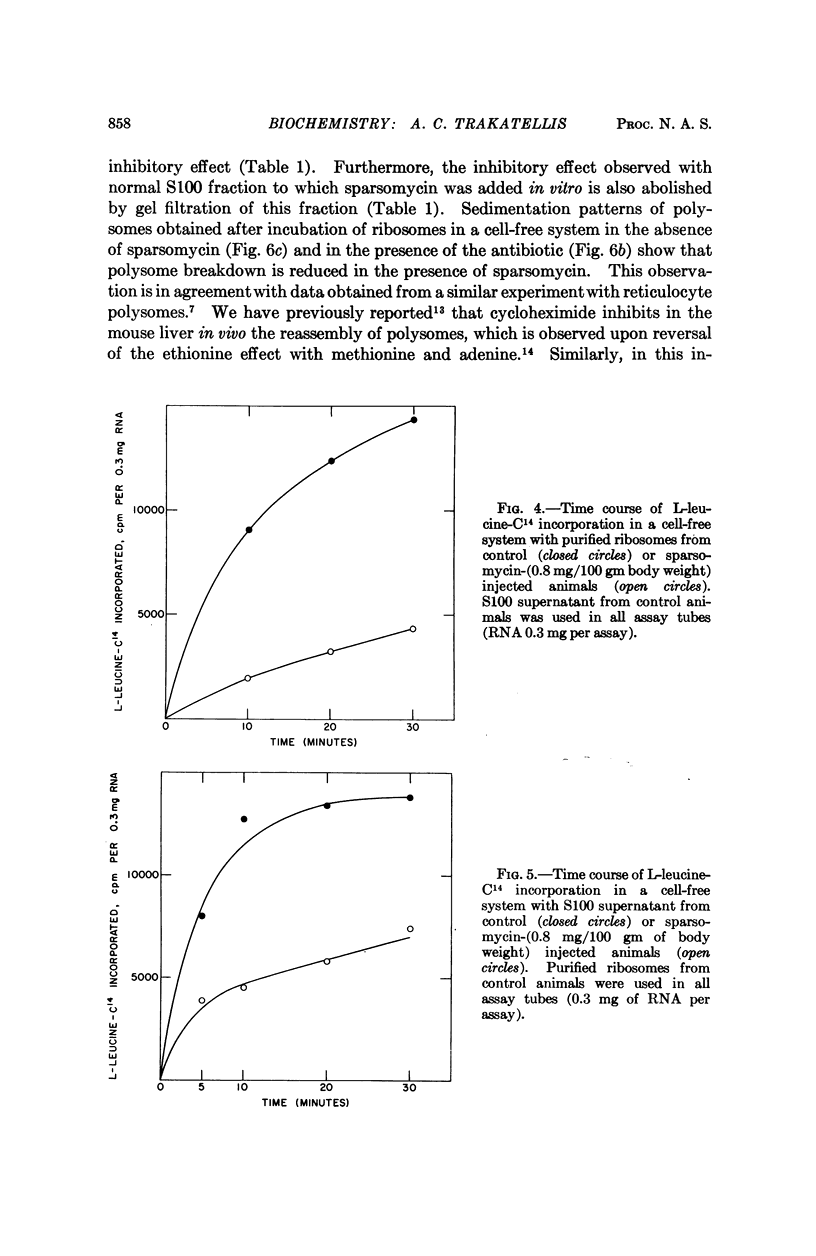
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLENDE J. E., MONRO R., LIPMANN F. RESOLUTION OF THE E. COLI AMINO ACYL SRNA TRANSFER FACTOR INTO TWO COMPLEMENTARY FRACTIONS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Jun;51:1211–1216. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.6.1211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baglioni C. Inhibition of protein synthesis in reticulocytes by antibiotics. 3. Mechanism of action of sparsomycin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Dec 21;129(3):642–645. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90085-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONWAY T. W., LIPMANN F. CHARACTERIZATION OF A RIBOSOME-LINKED GUANOSINE TRIPHOSPHATASE IN ESCHERICHIA COLI EXTRACTS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Dec;52:1462–1469. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.6.1462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colombo B., Felicetti L., Baglioni C. Inhibition of protein synthesis in reticulocytes by antibiotics. I. Effects on polysomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Apr 18;119(1):109–119. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90043-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg I. H., Mitsugi K. Inhibition by sparsomycin and other antibiotics of the puromycin-induced release of polypeptide from ribosomes. Biochemistry. 1967 Feb;6(2):383–391. doi: 10.1021/bi00854a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg I. H., Mitsugi K. Sparsomycin inhibition of polypeptide synthesis promoted by synthetic and natural polynucleotides. Biochemistry. 1967 Feb;6(2):372–382. doi: 10.1021/bi00854a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg I. H., Mitsugi K. Sparsomycin, an inhibitor of aminoacyl transfer to polypeptide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 May 25;23(4):453–459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIHO Y., RICH A. INDUCED ENZYME FORMED ON BACTERIAL POLYRIBOSOMES. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Jan;51:111–118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.1.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y., Lipmann F. Comparison of guanosine triphosphate split and polypeptide synthesis with a purified E. coli system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jan;55(1):212–219. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.1.212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slechta L. Mode of action of sparsomycin in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1965;5:326–333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trakatellis A. C., Montjar M., Axelrod A. E. Turnover of messenger ribonucleic acid and protein biosynthesis in the mouse mammary adenocarcinoma H2712. Biochemistry. 1965 Aug;4(8):1678–1686. doi: 10.1021/bi00884a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VILLA-TREVINO S., FARBER E., STAEHELIN T., WETTSTEIN F. O., NOLL H. BREAKDOWN AND REASSEMBLY OF RAT LIVER ERGOSOMES AFTER ADMINISTRATION OF ETHIONINE OR PUROMYCIN. J Biol Chem. 1964 Nov;239:3826–3833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WETTSTEIN F. O., STAEHELIN T., NOLL H. Ribosomal aggregate engaged in protein synthesis: characterization of the ergosome. Nature. 1963 Feb 2;197:430–435. doi: 10.1038/197430a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



