Abstract
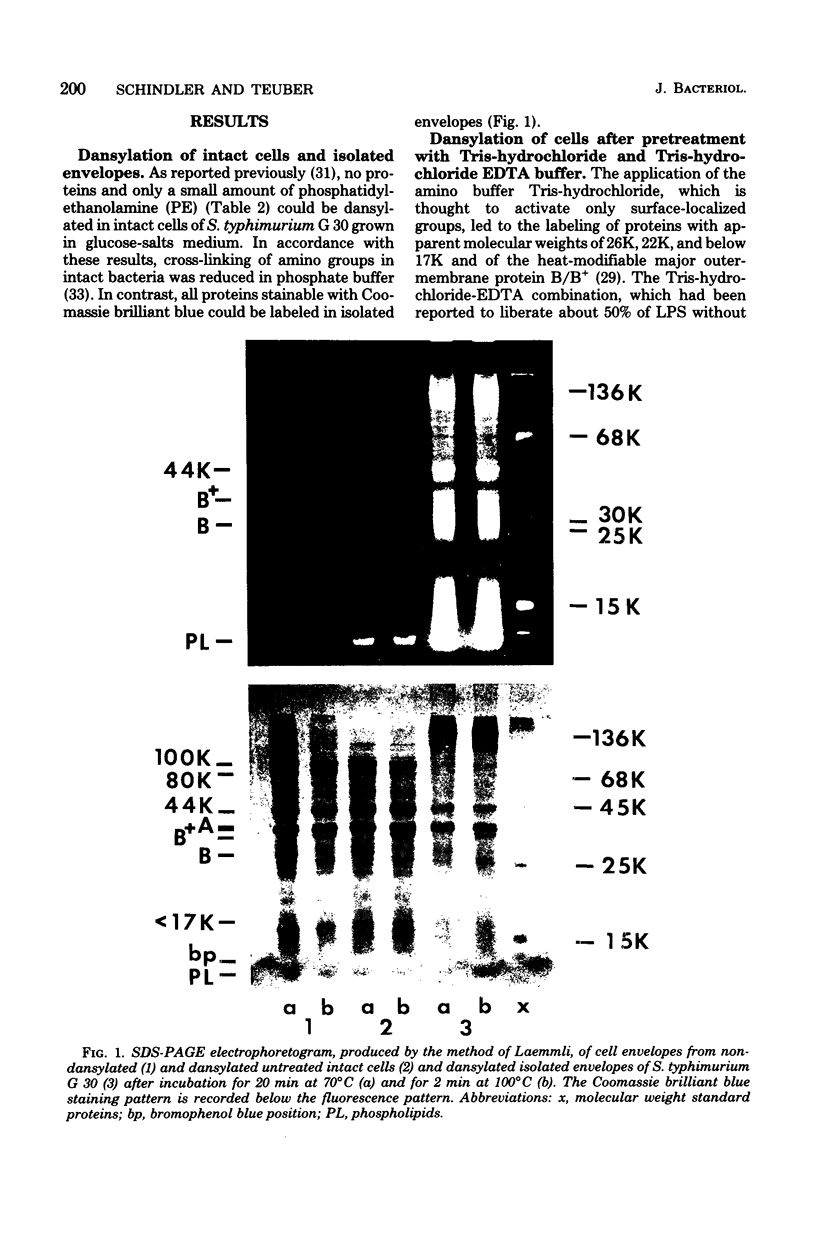
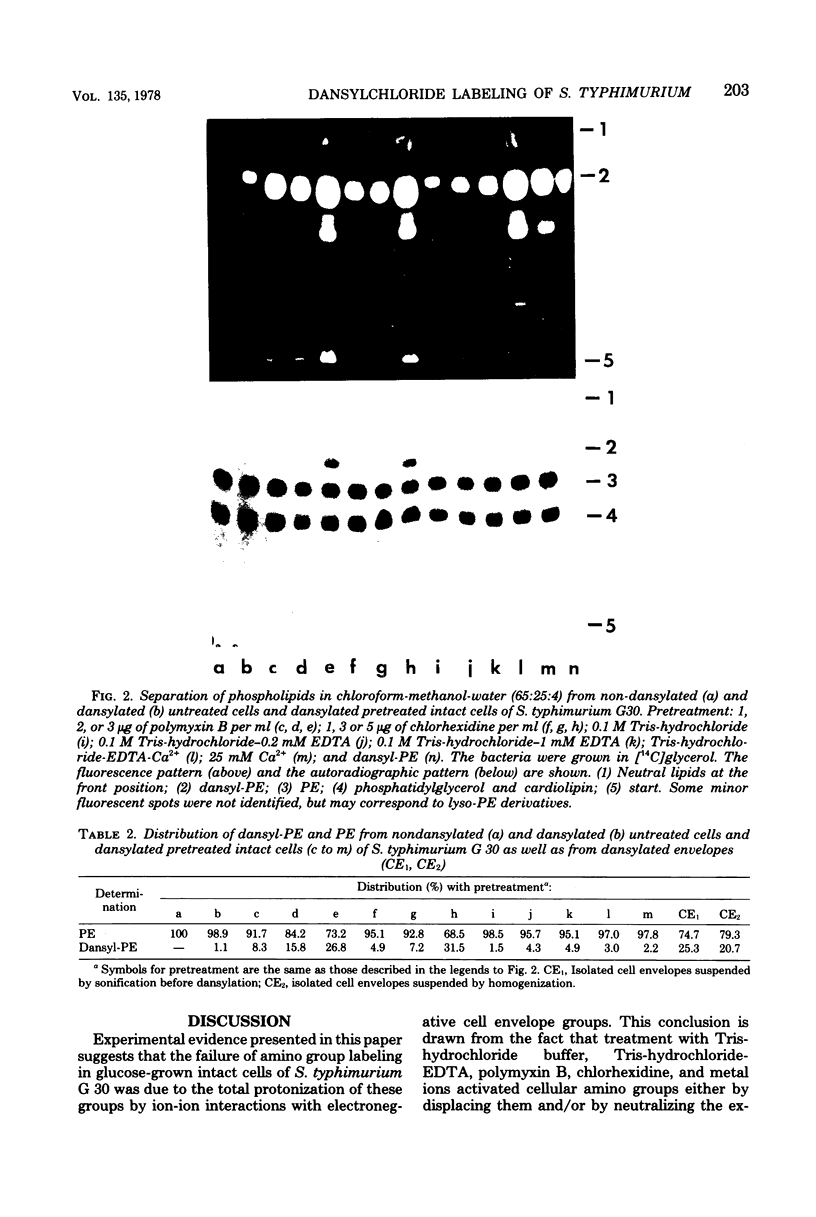
Amino groups of cell envelope proteins, lipids, and lipopolysaccharides cannot be labeled in intact cells of Salmonella typhimurium G 30 by using 5-dimethylaminonaphthalene-1-sulfonylchloride incorporated in lecithin-cholesterol vesicles. However, application of membrane-interacting agents like tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane (Tris)-hydrochloride, ethylenediaminetetraacetate (Na salt) (EDTA), divalent cations, and sublethal doses of the cationic antibacterial agents polymyxin B and chlorhexidine induced specific fluorescent labeling of envelope proteins and lipids but not of cytoplasmic compounds, with the exception of a soluble protein with a molecular weight of 46,000 in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Treatment with Tris-hydrochloride buffer produced labeling of the heat-modifiable protein B/B+ and of proteins with molecular weights of 26,000, 22,000, and below 17,000. A combination of Tris-hydrochloride and EDTA induced additional dansylation of the major protein A and of proteins of molecular weights 80,000, 60,000, and 44,000. Polymyxin B and chlorhexidine caused similar labeling patterns. In every case, except with divalent cation treatment, protein B/B+ was the most prominently labeled species. Phosphatidylethanolamine was dansylated up to 30%. Lipopolysaccharide was not reactive under any condition or treatment. In addition, the peptidoglycan-bound lipoprotein did not react with dansylchloride in either intact or Tris-hydrochloride-treated cells. The results are discussed with regard to a possible localization of labeled and unlabeled compounds of the cell envelope on the basis of a model placing cell envelope amino groups into ion-ion interactions with anionic components of other envelope compounds like phosphate and carboxyl groups.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames G. F., Spudich E. N., Nikaido H. Protein composition of the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium: effect of lipopolysaccharide mutations. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):406–416. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.406-416.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bader J., Teuber M. Action of polymyxin B on bacterial membranes. 1. Binding to the O-antigenic lipopolysaccharide of Salmonella typhimurium. Z Naturforsch C. 1973 Jul-Aug;28(7):422–430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun V., Bosch V., Klumpp E. R., Neff I., Mayer H., Schlecht S. Antigenic determinants of murein lipoprotein and its exposure at the surface of Enterobacteriaceae. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Mar 1;62(3):555–566. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10190.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun V. Covalent lipoprotein from the outer membrane of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Oct 31;415(3):335–377. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90013-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosloy S. D., Oishi M. Genetic transformation in Escherichia coli K12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jan;70(1):84–87. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.1.84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costerton J. W., Ingram J. M., Cheng K. J. Structure and function of the cell envelope of gram-negative bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1974 Mar;38(1):87–110. doi: 10.1128/br.38.1.87-110.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duckworth D. H., Bevers E. M., Verkleij A. J., Op den Kamp J. A., van Deenen L. L. Action of phospholipase A2 and phospholipase C on Escherichia coli. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Nov;165(1):379–387. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROLLMAN A. P., OSBORN M. J. O-PHOSPHORYLETHANOLAMINE: A COMPONENT OF LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDE IN CERTAIN GRAM-NEGATIVE BACTERIA. Biochemistry. 1964 Oct;3:1571–1574. doi: 10.1021/bi00898a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grefrath S. P., Reynolds J. A. The molecular weight of the major glycoprotein from the human erythrocyte membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):3913–3916. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.3913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halegoua S., Hirashima A., Inouye M. Existence of a free form of a specific membrane lipoprotein in gram-negative bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1974 Dec;120(3):1204–1208. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.3.1204-1208.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henning U., Haller I. Mutants of Escherichia coli K12 lacking all 'major' proteins of the outer cell envelope membrane. FEBS Lett. 1975 Jul 15;55(1):161–164. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80983-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juliano R. L., Behar-Bannelier M. An evaluation of techniques for labelling the surface proteins of cultured mammalian cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jan 28;375(2):249–267. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90193-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamio Y., Nikaido H. Outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium. Identification of proteins exposed on cell surface. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Feb 4;464(3):589–601. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90033-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koplow J., Goldfine H. Alterations in the outer membrane of the cell envelope of heptose-deficient mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):527–543. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.527-543.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leive L. The barrier function of the gram-negative envelope. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 May 10;235(0):109–129. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb43261.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machtiger N. A., Fox C. F. Biochemistry of bacterial membranes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1973;42:575–600. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.42.070173.003043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel M., Higa A. Calcium-dependent bacteriophage DNA infection. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mühlradt P. F., Menzel J., Golecki J. R., Speth V. Lateral mobility and surface density of lipopolysaccharide in the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Apr 16;43(3):533–539. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03440.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neihof R., Echols W. H. Physicochemical studies of microbial cell walls. I. Comparative electrophoretic behavior of intact cells and isolated cell walls. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Aug 9;318(1):23–32. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90332-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurminen M., Lounatmaa K., Sarvas M., Mäkelä P. H., Nakae T. Bacteriophage-resistant mutants of Salmonella typhimurium deficient in two major outer membrane proteins. J Bacteriol. 1976 Aug;127(2):941–955. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.2.941-955.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M. J., Gander J. E., Parisi E., Carson J. Mechanism of assembly of the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium. Isolation and characterization of cytoplasmic and outer membrane. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):3962–3972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prehm P., Stirm S., Jann B., Jann K. Cell-wall lipopolysaccharide from Escherichia coli B. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 1;56(1):41–55. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02205.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reithmeier R. A., Bragg P. D. Purification and characterization of heat-modifiable protein from the outer membrane of Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1974 May 1;41(2):195–198. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)81210-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler P. R., Teuber M. Action of polymyxin B on bacterial membranes: morphological changes in the cytoplasm and in the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli B. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Jul;8(1):95–104. doi: 10.1128/aac.8.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler P. R., Teuber M. Differential fluorescence labelling with 5-dimethyl-aminonaphthalene-1-sulfonyl chloride of intact cells and isolated membranes in Salmonella typhimurium and Acholeplasma laidlawii. Arch Microbiol. 1975;102(1):29–33. doi: 10.1007/BF00428341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmalreck A. F., Teuber M. Effect of chemical modification by (di)imidoesters on cells and cell envelope components of Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. Microbios. 1976;17(68-69):93–131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt-Ullrich R., Knüfermann H., Wallach D. F. The reaction of 1-dimethylaminonaphthalene-5-sulfonyl chloride (DANSC1) with erythrocyte membranes. A new look at "vectorial" membrane probes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 May 11;307(2):353–365. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90101-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaitman C. A. Effect of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, Triton X-100, and lysozyme on the morphology and chemical composition of isolate cell walls of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):553–563. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.553-563.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zanetta J. P., Vincendon G., Mandel P., Gombos G. The utilisation of I-dimethylaminonaphthalene-5-sulphonyl chloride for quantitative determination of free amino acids and partial analysis of primary structure of proteins. J Chromatogr. 1970 Sep 23;51(3):441–458. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)96893-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]