Abstract
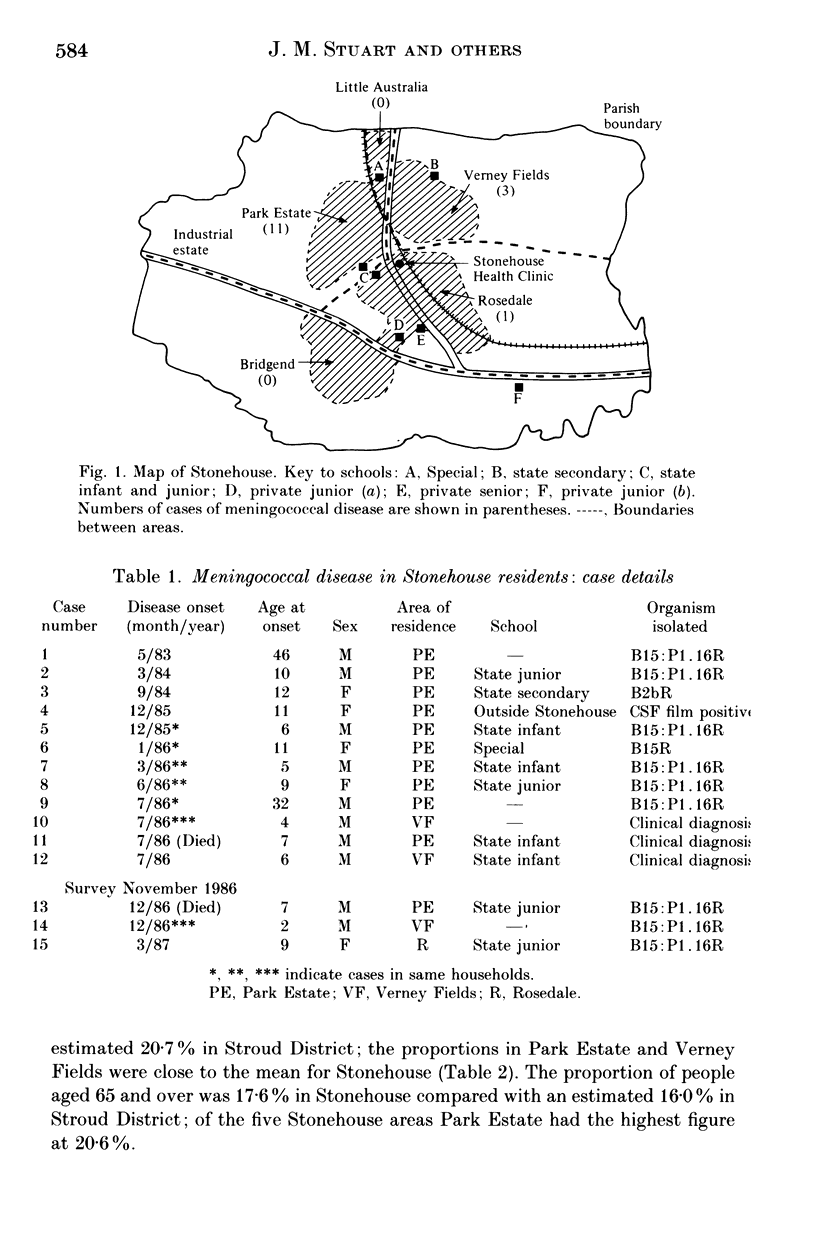
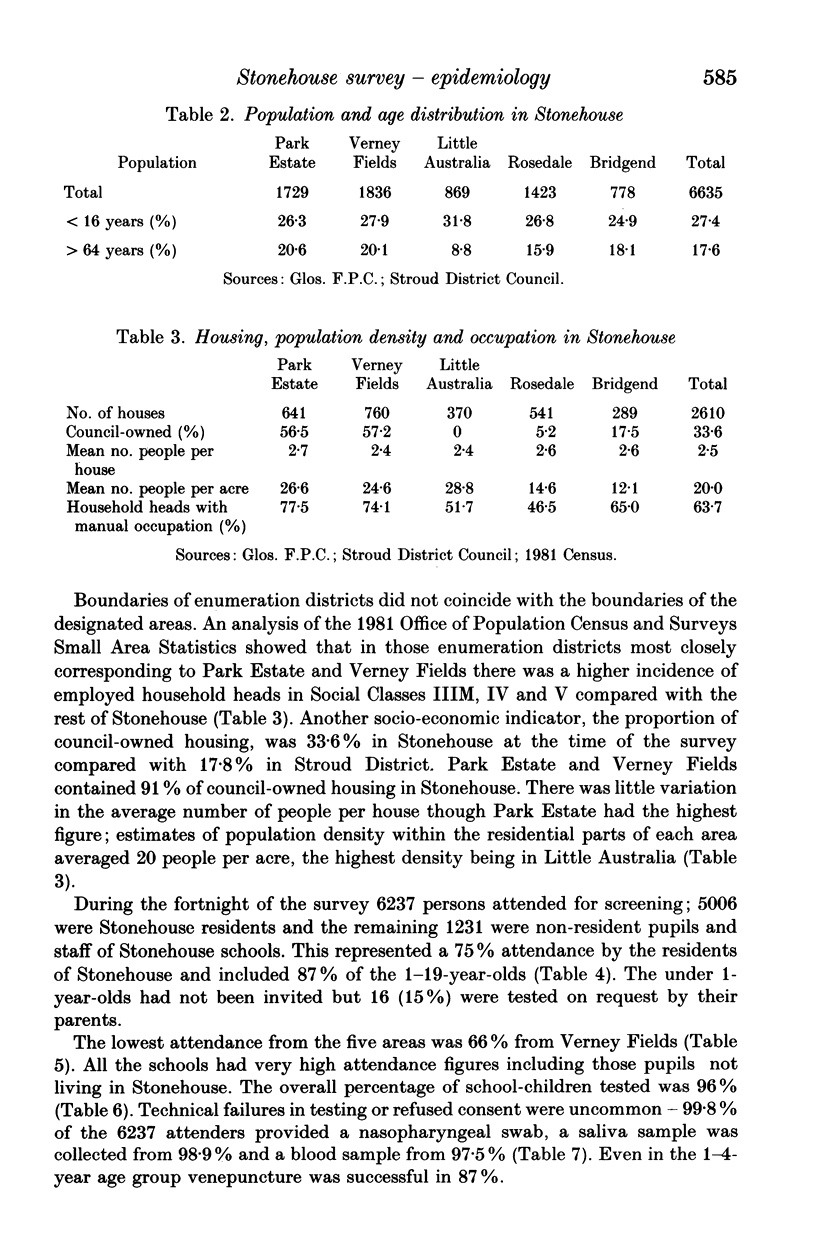
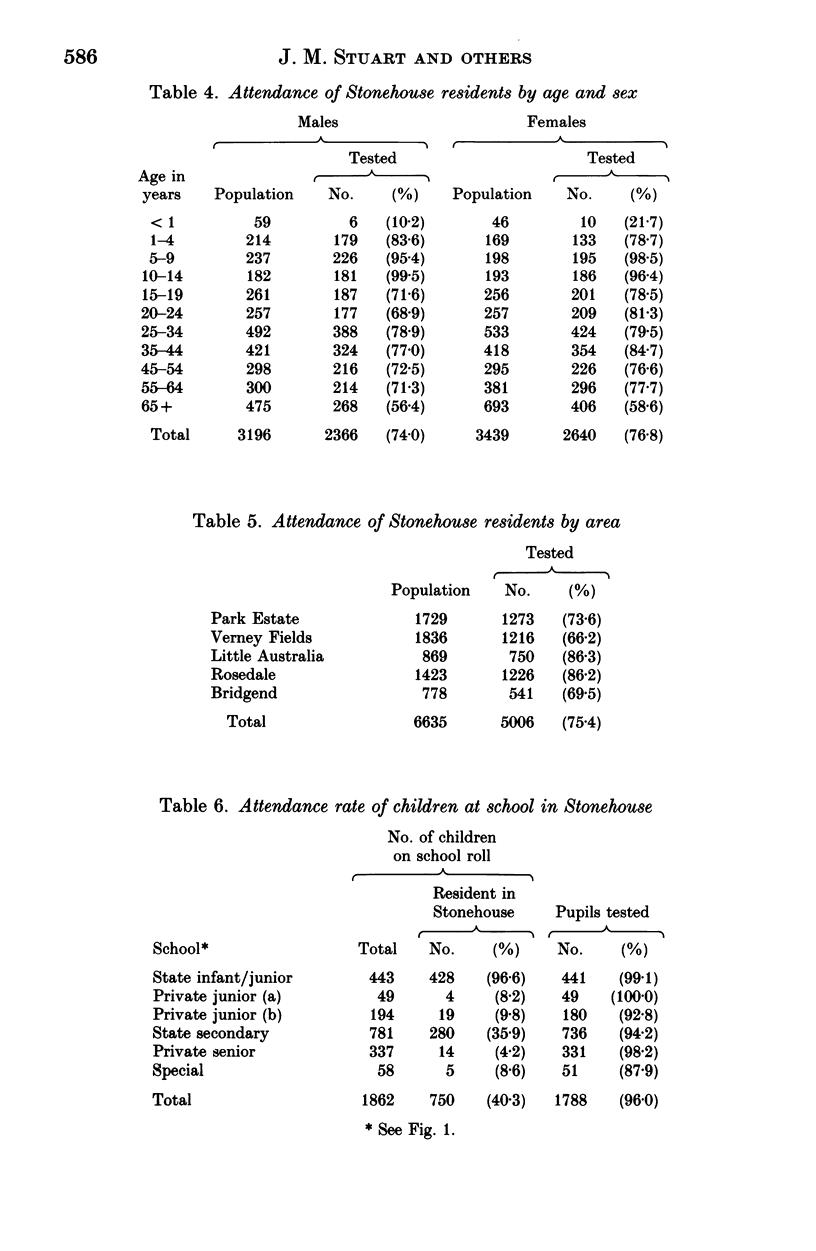
In November 1986 a large-scale survey was undertaken in the Gloucestershire town of Stonehouse during an outbreak of meningococcal disease due to group B type 15 subtype P1.16 sulphonamide-resistant strains. There were 15 cases in Stonehouse residents during the 4 years from April 1983, an annual attack rate of 56.5 per 100,000. Four secondary cases occurred despite rifampicin prophylaxis. The objectives of this community survey were to investigate patterns of meningococcal carriage, transmission and immunity and to determine the proportion of non-secretors of blood group antigens in the Stonehouse population and amongst meningococcal carriers. A total of 6237 subjects participated including 75% of the 6635 Stonehouse residents. Over 97% of the participants provided all three of the requested specimens-nasopharyngeal swabs, saliva and blood samples. The co-operation between the many organizations involved in the detailed preliminary planning was instrumental in the success of the survey; in particular the value of effective collaboration between Departments of Community Medicine and Microbiology and of the Public Health Laboratory Service network of laboratories in undertaking investigations of this size and type was clearly demonstrated.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blackwell C. C., Jónsdóttir K., Hanson M., Todd W. T., Chaudhuri A. K., Mathew B., Brettle R. P., Weir D. M. Non-secretion of ABO antigens predisposing to infection by Neisseria meningitidis and Streptococcus pneumoniae. Lancet. 1986 Aug 2;2(8501):284–285. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92103-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright K. A., Stuart J. M., Jones D. M., Noah N. D. The Stonehouse survey: nasopharyngeal carriage of meningococci and Neisseria lactamica. Epidemiol Infect. 1987 Dec;99(3):591–601. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800066449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright K. A., Stuart J. M., Noah N. D. An outbreak of meningococcal disease in Gloucestershire. Lancet. 1986 Sep 6;2(8506):558–561. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90124-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Centers for Disease Control (CDC) Meningococcal disease--United States, 1981. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1981 Mar 20;30(10):113–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farries J. S., Dickson W., Greenwood E., Malhotra T. R., Abbott J. D., Jones D. M. Meningococcal infections in Bolton, 1971-74. Lancet. 1975 Jul 19;2(7925):118–120. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)90016-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschneider I., Gotschlich E. C., Artenstein M. S. Human immunity to the meningococcus. I. The role of humoral antibodies. J Exp Med. 1969 Jun 1;129(6):1307–1326. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.6.1307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meningococcal disease in south-west of England. Lancet. 1986 Oct 4;2(8510):806–807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poolman J. T., Lind I., Jónsdóttir K., Frøholm L. O., Jones D. M., Zanen H. C. Meningococcal serotypes and serogroup B disease in north-west Europe. Lancet. 1986 Sep 6;2(8506):555–558. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90123-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



