Abstract
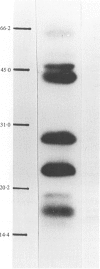
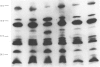
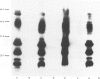
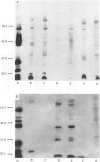
Twenty-one strains of Haemophilus ducreyi were analysed by Western blotting using two antisera produced in mice. Common antigens of molecular weights 58, 46, 41, 28, 22 and 16 kDa were detected in all the strains. The antigens were protein in nature, since they could not be detected in whole-cell lysates which had been treated with proteinase K. The H. ducreyi strains showed antigenic cross-reactivity with strains of H. influenzae and H. parainfluenzae, but showed minimal or no cross-reactivity with seven other species of bacteria.
Full text
PDF

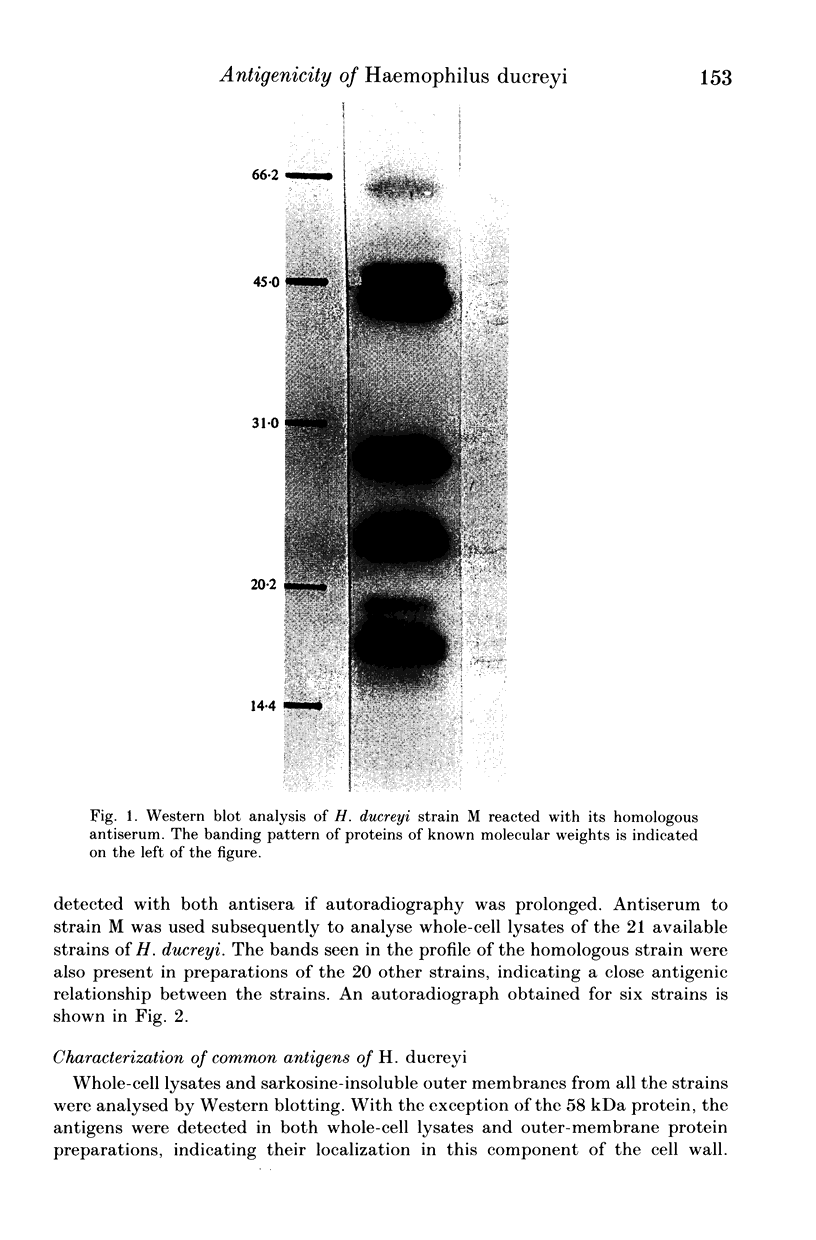
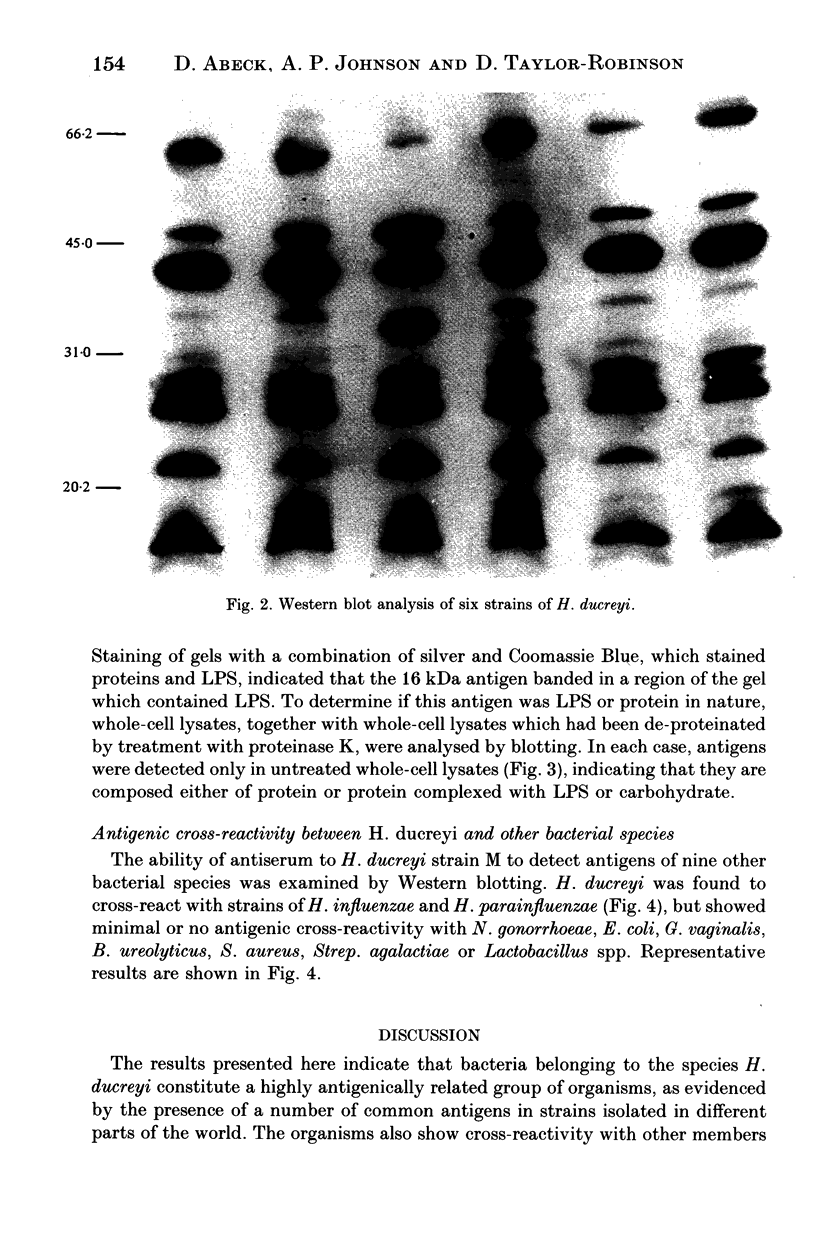
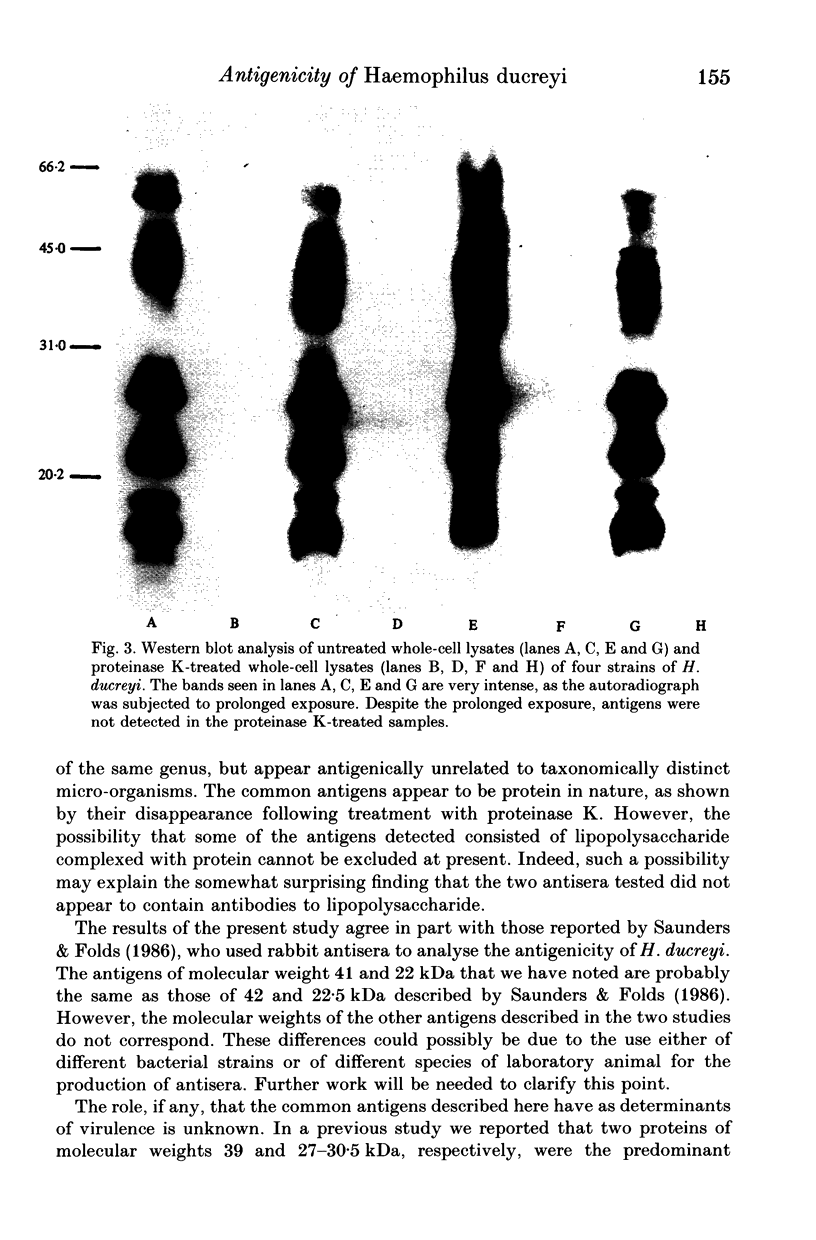
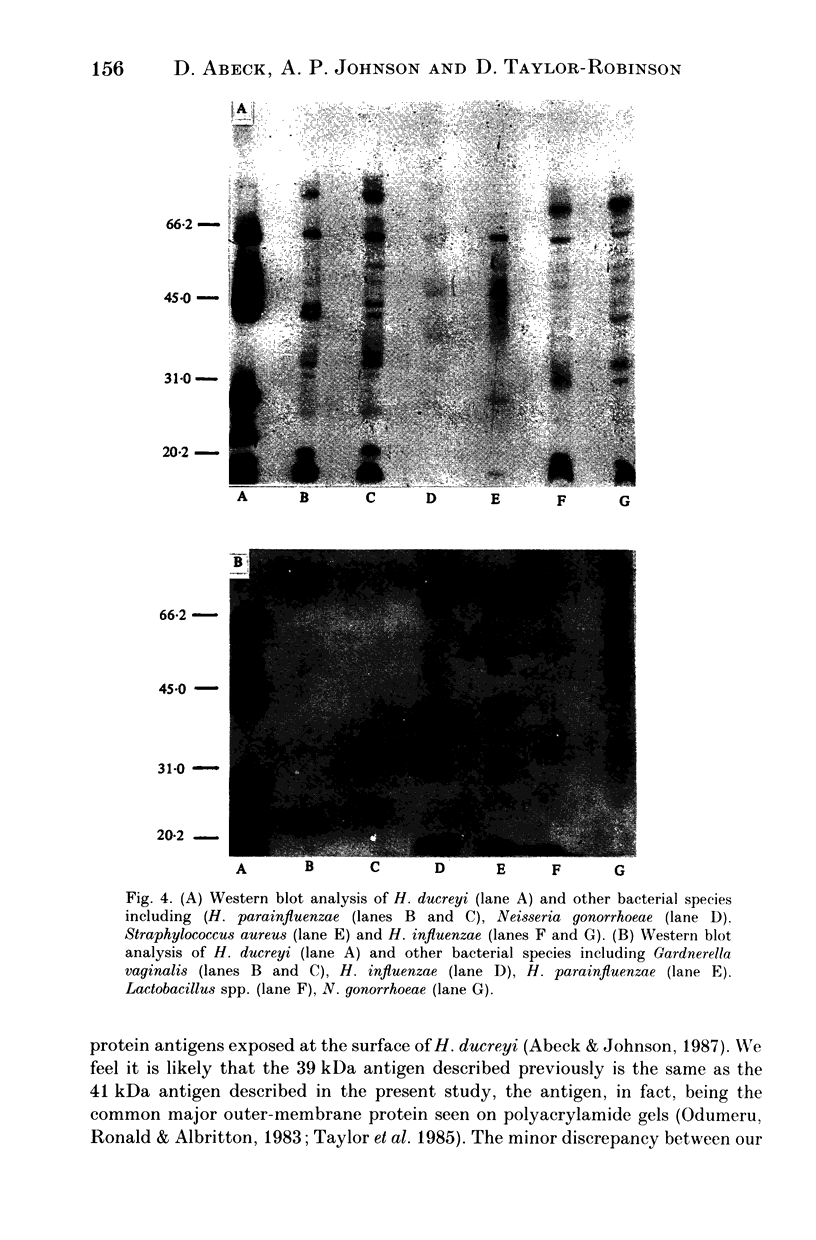

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boustouller Y. L., Johnson A. P., Taylor-Robinson D. T. Detection of a species-specific antigen of Gardnerella vaginalis by Western blot analysis. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Jul;132(7):1969–1973. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-7-1969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond G. W., Lian C. J., Wilt J. C., Ronald A. R. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Haemophilus ducreyi. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Apr;13(4):608–612. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.4.608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock P. J., Brown T. M. Morphological heterogeneity among Salmonella lipopolysaccharide chemotypes in silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):269–277. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.269-277.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odumeru J. A., Ronald A. R., Albritton W. L. Characterization of cell proteins of Haemophilus ducreyi by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Infect Dis. 1983 Oct;148(4):710–714. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.4.710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders J. M., Folds J. D. Immunoblot analysis of antigens associated with Haemophilus ducreyi using serum from immunised rabbits. Genitourin Med. 1986 Oct;62(5):321–328. doi: 10.1136/sti.62.5.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. Microbial surfaces in relation to pathogenicity. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Jun;41(2):475–500. doi: 10.1128/br.41.2.475-500.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. N., Echeverria P., Hanchalay S., Pitarangsi C., Slootmans L., Piot P. Antimicrobial susceptibility and characterization of outer membrane proteins of Haemophilus ducreyi isolated in Thailand. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Mar;21(3):442–444. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.3.442-444.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]