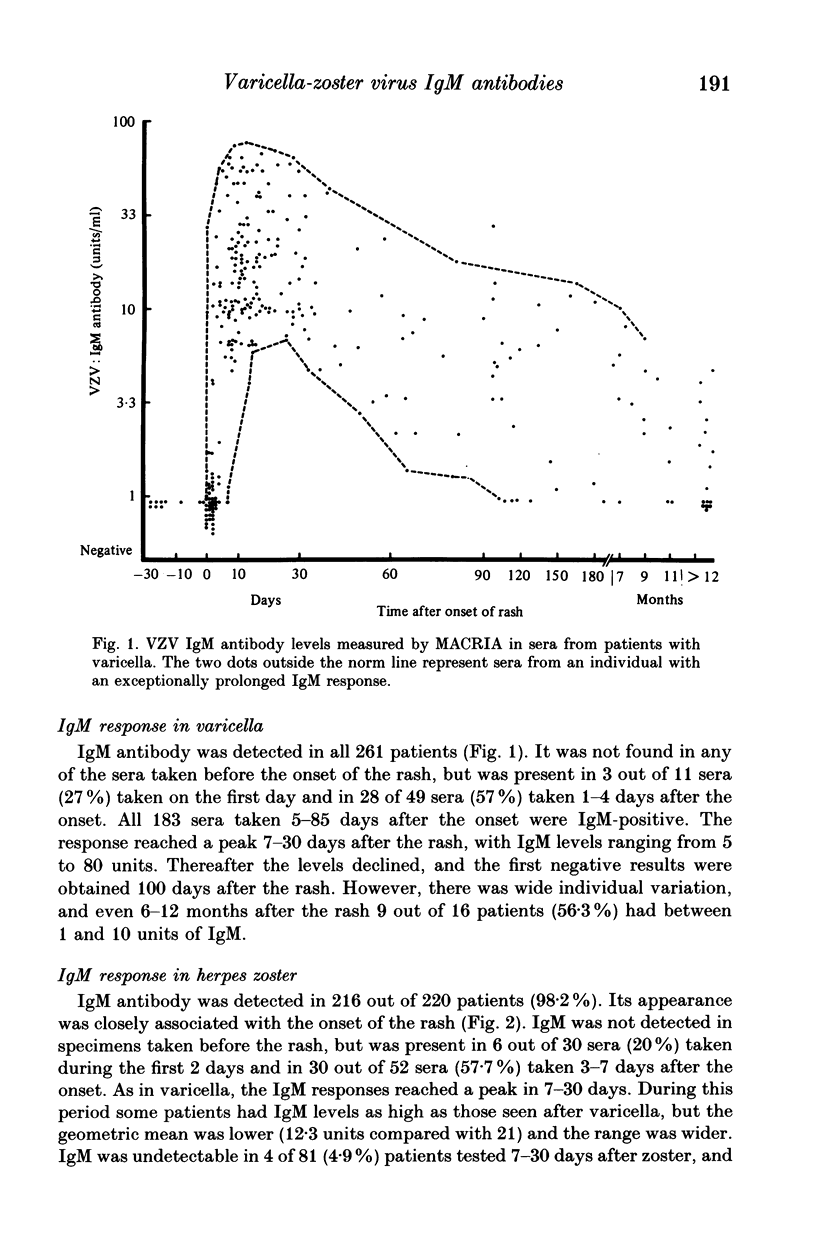
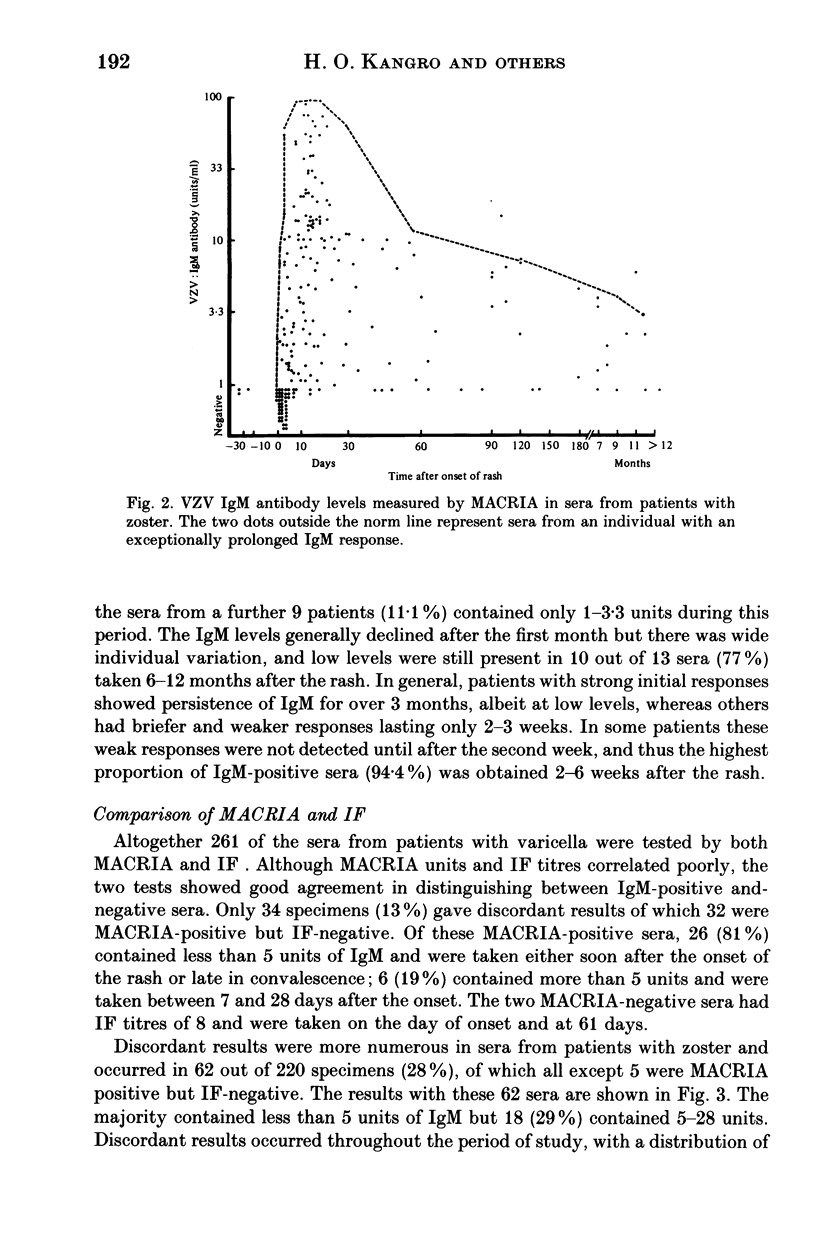
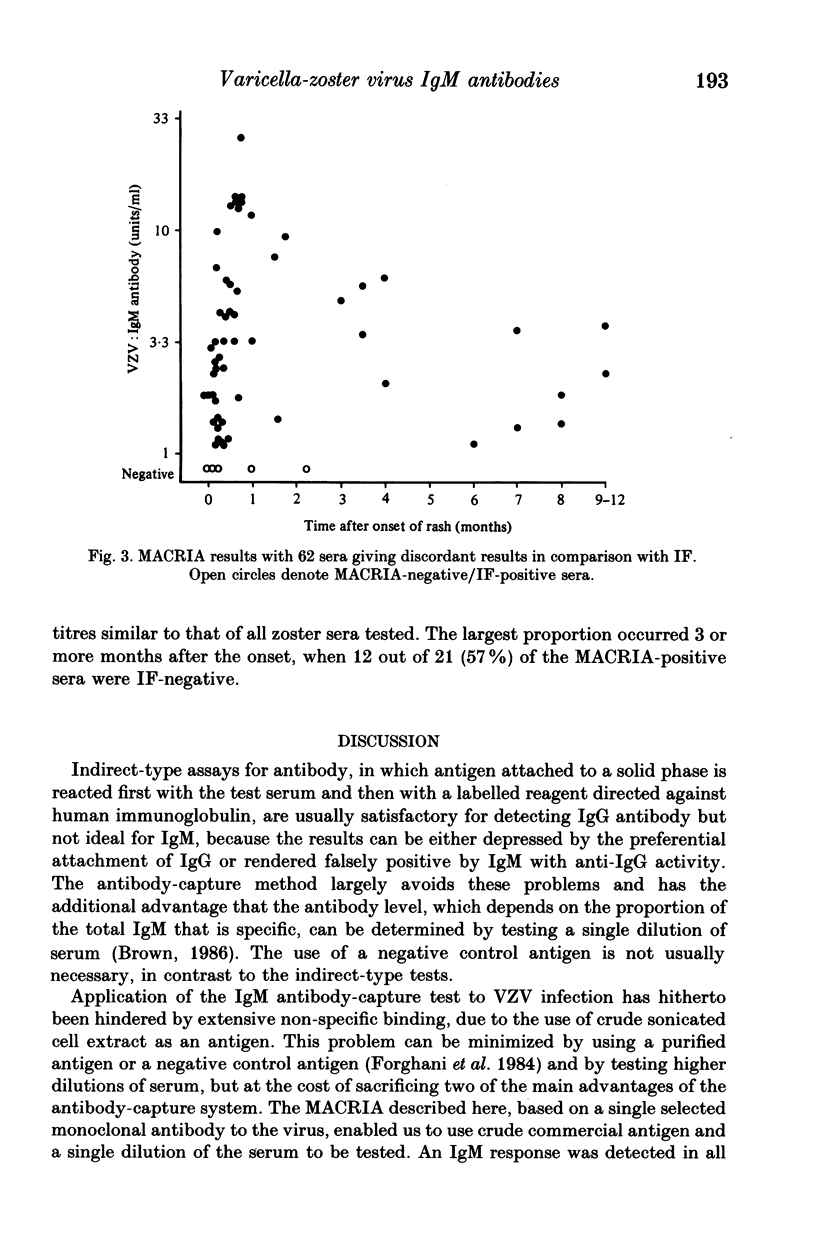
Abstract
A simple and sensitive M antibody-capture radioimmunoassay (MACRIA) is described which utilizes crude commercial VZV antigen and a single monoclonal anti-VZV antibody. This was compared to the immunofluorescence (IF) test for IgM antibody and was used to study IgM responses in sera from 261 patients with varicella and 220 patients with herpes zoster. With MACRIA, IgM antibodies were detected in all patients with varicella. The IgM antibodies appeared shortly after onset of rash, reached peak levels between 1 and 4 weeks after onset and then declined to low or undetectable levels in most, though not all, patients after 3 months. IgM antibodies were also detected in 98.2% of patients with herpes zoster, but the levels of IgM were significantly lower than after varicella and there was wider individual variation both in magnitude and duration of the IgM responses, in some cases only lasting 2-3 weeks. Comparison between MACRIA and IF showed good agreement in the detection of IgM antibodies following varicella. Discordant results were obtained with 13% of sera, of which 81% were taken either early or late after onset of rash and contained very low IgM levels. In contrast, 62 (28%) of the 220 sera from patients with zoster gave discordant results in the two tests, all except five being MACRIA-positive but IF-negative. The largest proportion of discordant results were obtained with sera taken more than 3 months after onset of rash, but 18 (29%) contained high IgM levels and were taken during the period of peak IgM responses. The diagnostic applications of the VZV MACRIA are discussed.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arvin A. M., Koropchak C. M. Immunoglobulins M and G to varicella-zoster virus measured by solid-phase radioimmunoassay: antibody responses to varicella and herpes zoster infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Sep;12(3):367–374. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.3.367-374.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell-Benzie A., Kangro H. O., Heath R. B. The development and evaluation of a solid-phase radioimmunoassay (RIA) procedure for the determination of susceptibility to varicella. J Virol Methods. 1981 Feb;2(3):149–158. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(81)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke J. R., Ronalds C. J., Kangro H. O., Heath R. B. Improving the varicella-zoster virus: IgG radioimmunoassay procedure by the use of purified antigen. J Virol Methods. 1984 Feb;8(1-2):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(84)90035-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cradock-Watson J. E., Ridehalgh M. K., Bourne M. S. Specific immunoglobulin responses after varicella and herpes zoster. J Hyg (Lond) 1979 Apr;82(2):319–336. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400025730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forghani B., Myoraku C. K., Dupuis K. W., Schmidt N. J. Antibody class capture assays for varicella-zoster virus. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 May;19(5):606–609. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.5.606-609.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershon A. A., Steinberg S. P., Borkowsky W., Lennette D., Lennette E. IgM to varicella-zoster virus: demonstration in patients with and without clinical zoster. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1982 May-Jun;1(3):164–167. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198205000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luqman W. A., Matej L. A., Smith M. L. Comparison of prolactin levels in human semen and seminal plasma. J Endocrinol. 1979 Apr;81(1):131–133. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0810131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross C. A., McDaid R. Specific IgM antibody in serum of patients with herpes zoster infections. Br Med J. 1972 Dec 2;4(5839):522–523. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5839.522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt N. J., Lennette E. H. Neutralizing antibody responses to varicella-zoster virus. Infect Immun. 1975 Sep;12(3):606–613. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.3.606-613.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tedder R. S., Mortimer P. P., Lord R. B. Detection of antibody to varicella-zoster virus by competitive and IgM-antibody capture immunoassay. J Med Virol. 1981;8(2):89–101. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890080203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



