Abstract
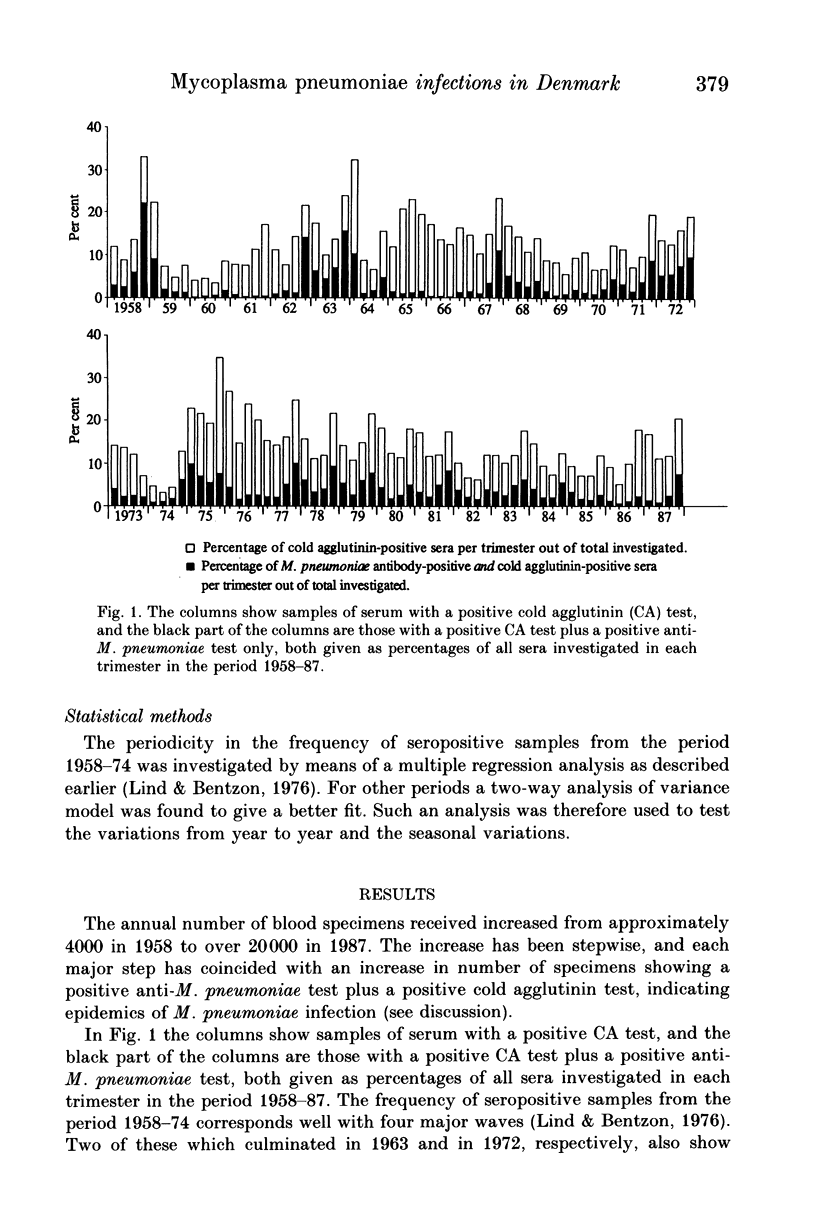
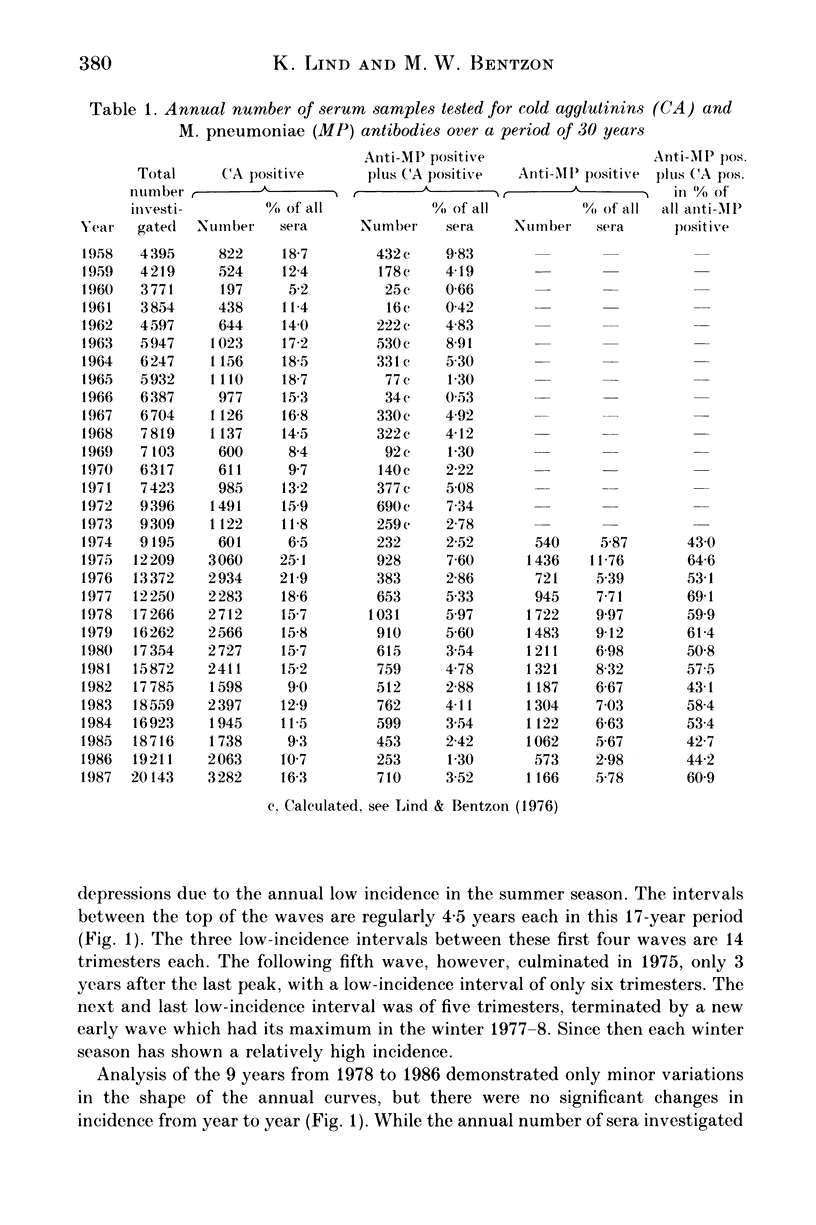
A seroepidemiological survey has shown a remarkable shift in the previously reported regular cyclic pattern of Mycoplasma pneumoniae epidemics which culminated every 4.5 years during the period 1958-74. The last of four regular epidemics occurred in 1972. It was followed by 'premature' epidemics in 1975 and 1977/8 which inaugurated a change from an epidemic to an endemic pattern of the infection in Denmark. Over the following 9 years (1978-86) there has been an irregular but significant decrease in the annual number of seropositive samples with the usual high incidence during winter seasons. This endemic period terminated in the fourth trimester of 1987 with the development of a new epidemic. The hypothesis is advanced that a sixfold increase of children in day care may have influenced the change from an epidemic to an endemic situation which after 9 years led to a new epidemic of M. pneumoniae infection.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CHANOCK R. M., MUFSON M. A., BLOOM H. H., JAMES W. D., FOX H. H., KINGSTON J. R. Eaton agent pneumonia. JAMA. 1961 Jan 21;175:213–220. doi: 10.1001/jama.1961.03040030037007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chanock R. M., Fox H. H., James W. D., Gutekunst R. R., White R. J., Senterfit L. B. Epidemiology of M. pneumoniae infection in military recruits. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):484–496. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27692.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denny F. W., Clyde W. A., Jr, Glezen W. P. Mycoplasma pneumoniae disease: clinical spectrum, pathophysiology, epidemiology, and control. J Infect Dis. 1971 Jan;123(1):74–92. doi: 10.1093/infdis/123.1.74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENNY G. E., GRAYSTON J. T. EATON PLEUROPNEUMONIA-LIKE ORGANISM (MYCOPLASMA PNEUMONIAE) COMPLEMENT-FIXING ANTIGEN: EXTRACTION WITH ORGANIC SOLVENTS. J Immunol. 1965 Jul;95:19–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans A. S., Allen V., Sueltmann S. Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections in University of Wisconsin students. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1967 Aug;96(2):237–244. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1967.96.2.237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernald G. W., Clyde W. A., Jr, Denny F. W. Nature of the immune response to Mycoplasma pneumoniae. J Immunol. 1967 May;98(5):1028–1038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernald G. W., Collier A. M., Clyde W. A., Jr Respiratory infections due to Mycoplasma pneumoniae in infants and children. Pediatrics. 1975 Mar;55(3):327–335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foy H. M., Cooney M. K., Allan I., Kenny G. E. Rates of pneumonia during influenza epidemics in Seattle, 1964 to 1975. JAMA. 1979 Jan 19;241(3):253–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foy H. M., Kenny G. E., Sefi R., Ochs H. D., Allan I. D. Second attacks of pneumonia due to Mycoplasma pneumoniae. J Infect Dis. 1977 Apr;135(4):673–677. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.4.673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glezen W. P., Loda F. A., Clyde W. A., Jr, Senior R. J., Sheaffer C. I., Conley W. G., Denny F. W. Epidemiologic patterns of acute lower respiratory disease of children in a pediatric group practice. J Pediatr. 1971 Mar;78(3):397–406. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(71)80218-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handrick W., Heinze M., Winter R., Lange R., Rudolf D. Uber Infektionen durch Mycoplasma pneumoniae bei Kindern und Jugendlichen. Z Erkr Atmungsorgane. 1987;168(1):59–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hers J. F., Masurel N. Infection with Mycoplasma pneumoniae in civilians in the Netherlands. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):447–460. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27689.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansson E., von Essen R., Tuuri S. Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in Helsinki 1962-1970. Epidemic pattern and autoimmune manifestations. Scand J Infect Dis. 1971;3(1):51–54. doi: 10.3109/inf.1971.3.issue-1.09. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joosting A. C., Harwin R. M., Coppin A., Battaglia P., van der Hoef P. A serological investigation of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection on the Witwatersrand. S Afr Med J. 1976 Dec 18;50(54):2134–2135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIND K., MANSA B., OLESEN H. Penicillamine treatment in the cold-haemagglutinin syndrome. Acta Med Scand. 1963 May;173:647–660. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1963.tb17449.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lind K., Bentzon M. W. Epidemics of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection in Denmark from 1958 to 1974. Int J Epidemiol. 1976 Sep;5(3):267–277. doi: 10.1093/ije/5.3.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lind K. Immunological relationships between Mycoplasma pneumoniae and Streptococcus MG. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1968;73(2):237–244. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1968.tb00497.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lind K. Incidence of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection in Denmark from 1958 to 1969. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1971;79(2):239–247. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1971.tb02151.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lind K., Ravn T. J., Moller J. Occurrence of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection in patients hospitalized with acute respiratory illness. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1970;78(1):6–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1970.tb04265.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUFSON M. A., BLOOM H. H., MANKO M. A., KINGSTON J. R., CHANOCK R. M. Acute respiratory diseases of viral etiology. V. Eaton agent: a review. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1962 Jun;52:925–932. doi: 10.2105/ajph.52.6.925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martelli A., Vegis D., Milanino T., Monteverde A. Il ruolo del "mycoplasma pneumoniae" nelle affezioni pleuro-polmonari. Indagine sierologica. Ann Sclavo. 1976 Mar-Apr;18(2):260–267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortel S., Hermsdorf S., Bender U. Erfahrungen mit einem Messstellenprogramm zur Uberwachung akuter respiratorischer Erkrankungen (ARE). Z Gesamte Hyg. 1979 Aug;25(8):608–612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RYTEL M. W. PRIMARY ATYPICAL PNEUMONIA: CURRENT CONCEPTS. Am J Med Sci. 1964 Jan;247:84–104. doi: 10.1097/00000441-196401000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritter E., Nicklisch W., Lange A. Studie über Mycoplasma pneumoniae-Infektionen ambulant behandelter Patienten mit respiratorischen Infektionen. Z Gesamte Hyg. 1983 Aug;29(8):435–438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobeslavský O., Brücková M., Kunzová L., Syrücek L., Vojtechovský K. Adenovirus, RS virus and M. pneumoniae infections in young population of Prague in 1962-1967. J Hyg Epidemiol Microbiol Immunol. 1970;14(3):350–359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vu A. C., Foy H. M., Cartwright F. D., Kenny G. E. The principal protein antigens of isolates of Mycoplasma pneumoniae as measured by levels of immunoglobulin G in human serum are stable in strains collected over a 10-year period. Infect Immun. 1987 Aug;55(8):1830–1836. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.8.1830-1836.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


