Abstract
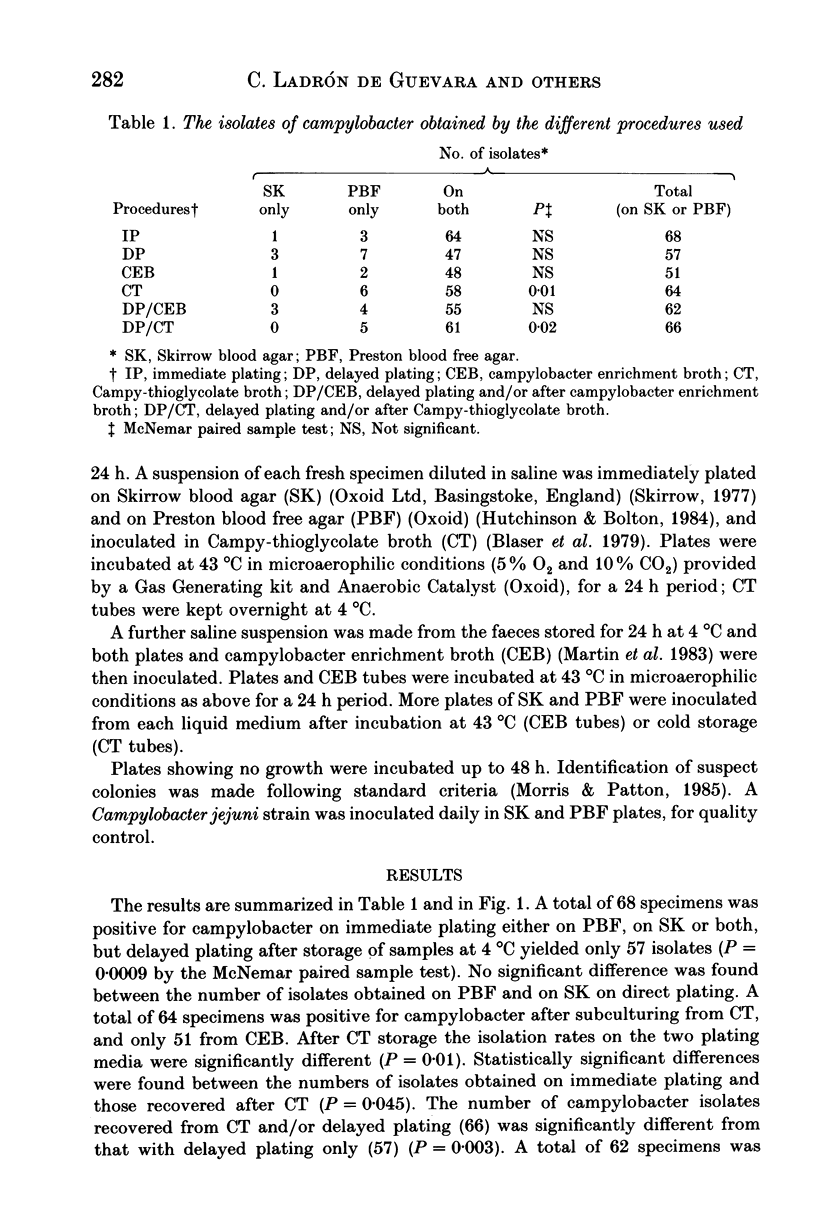
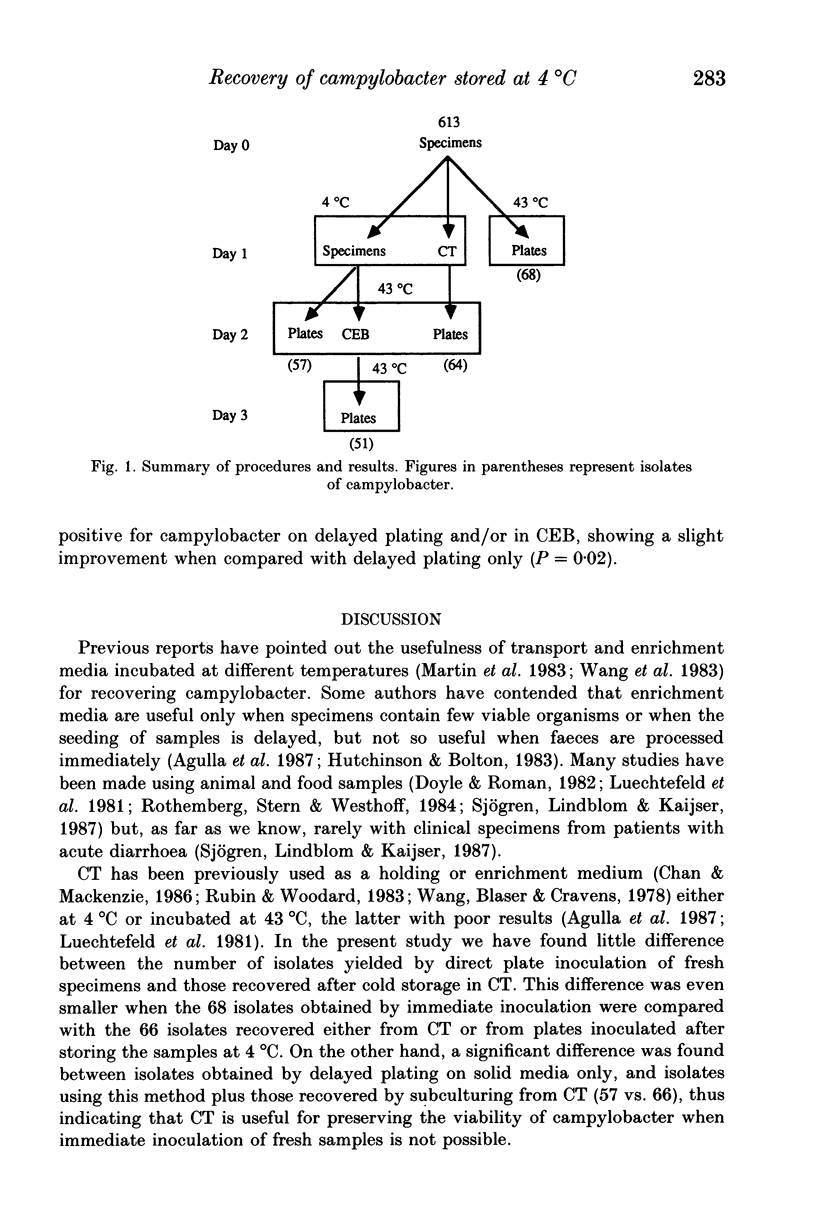
Six hundred and thirteen fresh diarrhoeal faeces were inoculated on Skirrow blood agar (SK), on Preston blood free agar (PBF), and in Campy-thioglycolate broth (CT). After 24 h of storage at 4 degrees C, specimens were again inoculated on SK and PBF, and in Campylobacter enrichment broth (CEB). CT tubes were placed overnight at 4 degrees C. Plates and CEB tubes were incubated at 43 degrees C in microaerophilic conditions. A total of 68 specimens was positive for campylobacter on direct plating. Sixty-four of them were also recovered after subculturing from CT, and only 51 from CEB. Delayed inoculation of plates after storage of samples at 4 degrees C yielded 57 isolates. The storage of faeces at 4 degrees C for 24 h significantly reduces the number of campylobacter isolates. When samples are not plated immediately we recommend inoculating a CT tube maintained at 4 degrees C overnight as a holding medium.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agulla A., Merino F. J., Villasante P. A., Saz J. V., Díaz A., Velasco A. C. Evaluation of four enrichment media for isolation of Campylobacter jejuni. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jan;25(1):174–175. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.1.174-175.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blankenship L. C., Craven S. E. Campylobacter jejuni survival in chicken meat as a function of temperature. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jul;44(1):88–92. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.1.88-92.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Berkowitz I. D., LaForce F. M., Cravens J., Reller L. B., Wang W. L. Campylobacter enteritis: clinical and epidemiologic features. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Aug;91(2):179–185. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-2-179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Hardesty H. L., Powers B., Wang W. L. Survival of Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni in biological milieus. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Apr;11(4):309–313. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.4.309-313.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan F. T., Mackenzie A. M. Evaluation of primary selective media and enrichment methods for Campylobacter species isolation. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Apr;5(2):162–164. doi: 10.1007/BF02013974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle M. P., Roman D. J. Recovery of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli from inoculated foods by selective enrichment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jun;43(6):1343–1353. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.6.1343-1353.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant I. H., Richardson N. J., Bokkenheuser V. D. Broiler chickens as potential source of Campylobacter infections in humans. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 May;11(5):508–510. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.5.508-510.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey T. J., Cruickshank J. G. Antibiotic and deoxycholate resistance in Campylobacter jejuni following freezing or heating. J Appl Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;59(1):65–71. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1985.tb01777.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey T. J. Techniques for the optimum recovery of cold injured Campylobacter jejuni from milk or water. J Appl Bacteriol. 1986 Aug;61(2):125–132. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1986.tb04265.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson D. N., Bolton F. J. Improved blood free selective medium for the isolation of campylobacter jejuni from faecal specimens. J Clin Pathol. 1984 Aug;37(8):956–957. doi: 10.1136/jcp.37.8.956-b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson D. N., Bolton F. J. Is enrichment culture necessary for the isolation of Campylobacter jejuni from faeces? J Clin Pathol. 1983 Dec;36(12):1350–1352. doi: 10.1136/jcp.36.12.1350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luechtefeld N. W., Wang W. L., Blaser M. J., Reller L. B. Evaluation of transport and storage techniques for isolation of Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni from turkey cecal specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Mar;13(3):438–443. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.3.438-443.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W. T., Patton C. M., Morris G. K., Potter M. E., Puhr N. D. Selective enrichment broth medium for isolation of Campylobacter jejuni. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 May;17(5):853–855. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.5.853-855.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merino F. J., Agulla A., Villasante P. A., Díaz A., Saz J. V., Velasco A. C. Comparative efficacy of seven selective media for isolating Campylobacter jejuni. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Sep;24(3):451–452. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.3.451-452.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng L. K., Stiles M. E., Taylor D. E. Inhibition of Campylobacter coli and Campylobacter jejuni by antibiotics used in selective growth media. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Oct;22(4):510–514. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.4.510-514.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothenberg P. J., Stern N. J., Westhoff D. C. Selected enrichment broths for recovery of Campylobacter jejuni from foods. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Jul;48(1):78–80. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.1.78-80.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin S. J., Woodard M. Enhanced isolation of Campylobacter jejuni by cold enrichment in Campy-thio broth. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Oct;18(4):1008–1010. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.4.1008-1010.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjögren E., Lindblom G. B., Kaijser B. Comparison of different procedures, transport media, and enrichment media for isolation of Campylobacter species from healthy laying hens and humans with diarrhea. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Oct;25(10):1966–1968. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.10.1966-1968.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skirrow M. B. Campylobacter enteritis: a "new" disease. Br Med J. 1977 Jul 2;2(6078):9–11. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6078.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svedhem A., Kaijser B., Sjögren E. The occurrence of Campylobacter jejuni in fresh food and survival under different conditions. J Hyg (Lond) 1981 Dec;87(3):421–425. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400069667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner E. I., Bullin C. H. Campylobacter enteritis. Br Med J. 1977 Aug 27;2(6086):579–579. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6086.579-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velasco A. C., Mateos M. L., Más G., Pedraza A., Díez M., Gutiérrez A. Three-year prospective study of intestinal pathogens in Madrid, Spain. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Aug;20(2):290–292. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.2.290-292.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walder M. Epidemiology of campylobacter enteritis. Scand J Infect Dis. 1982;14(1):27–33. doi: 10.3109/inf.1982.14.issue-1.06. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang W. L., Blaser M., Cravens J. Isolation of campylobacter. Br Med J. 1978 Jul 1;2(6129):57–57. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6129.57-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang W. L., Reller L. B., Smallwood B., Luechtefeld N. W., Blaser M. J. Evaluation of transport media for Campylobacter jejuni in human fecal specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Oct;18(4):803–807. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.4.803-807.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



