Abstract
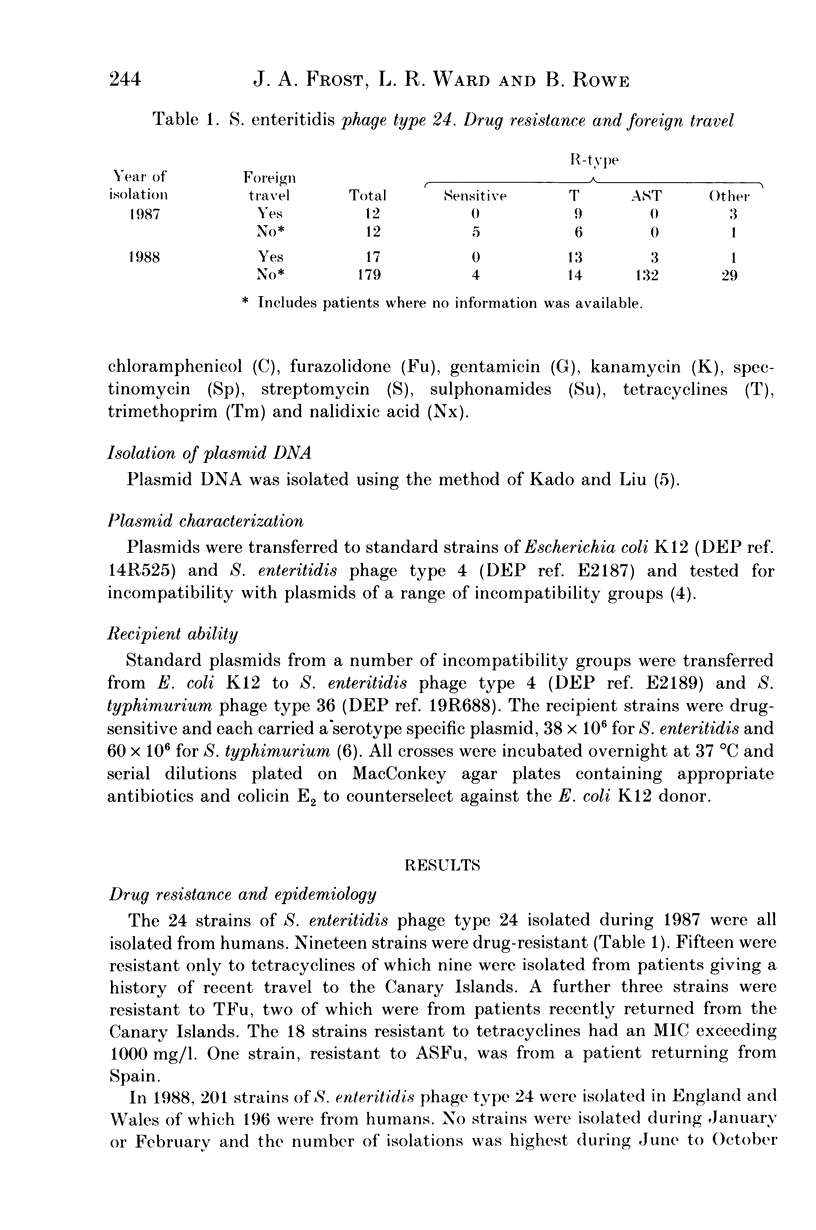
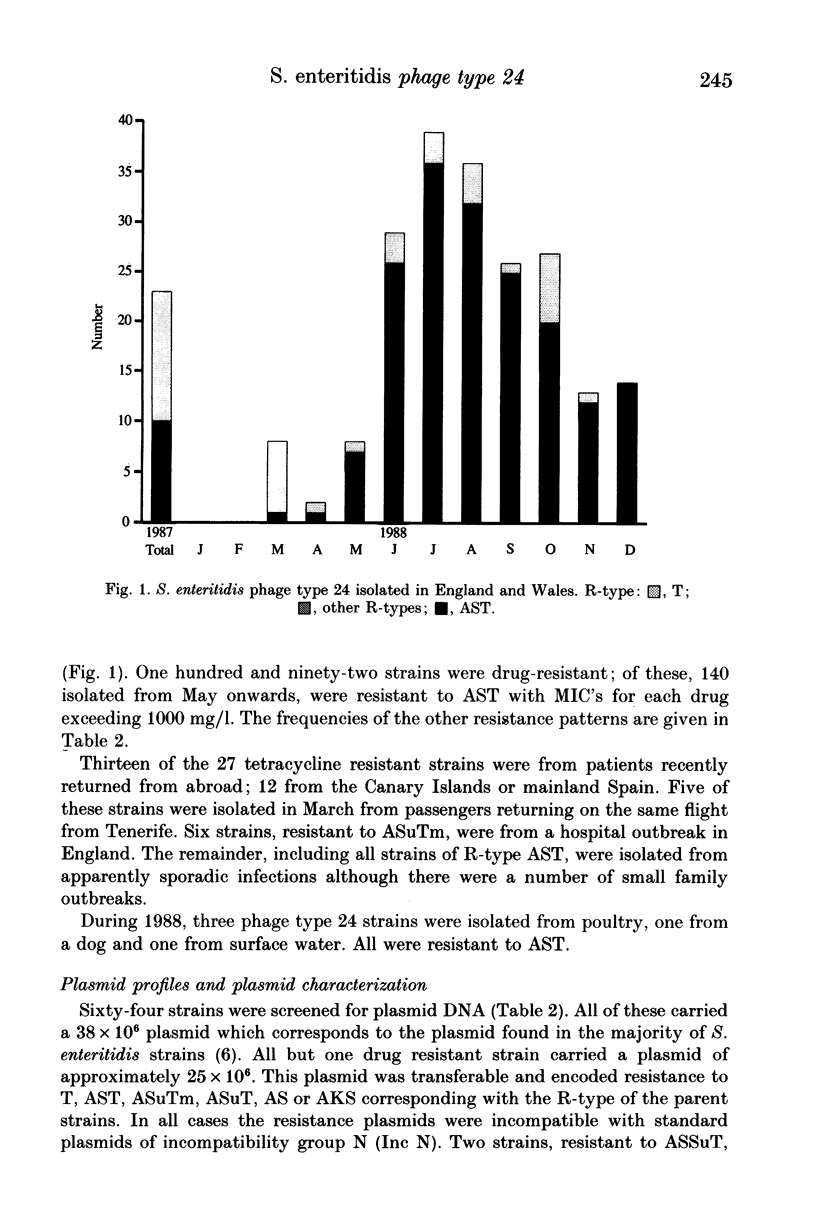
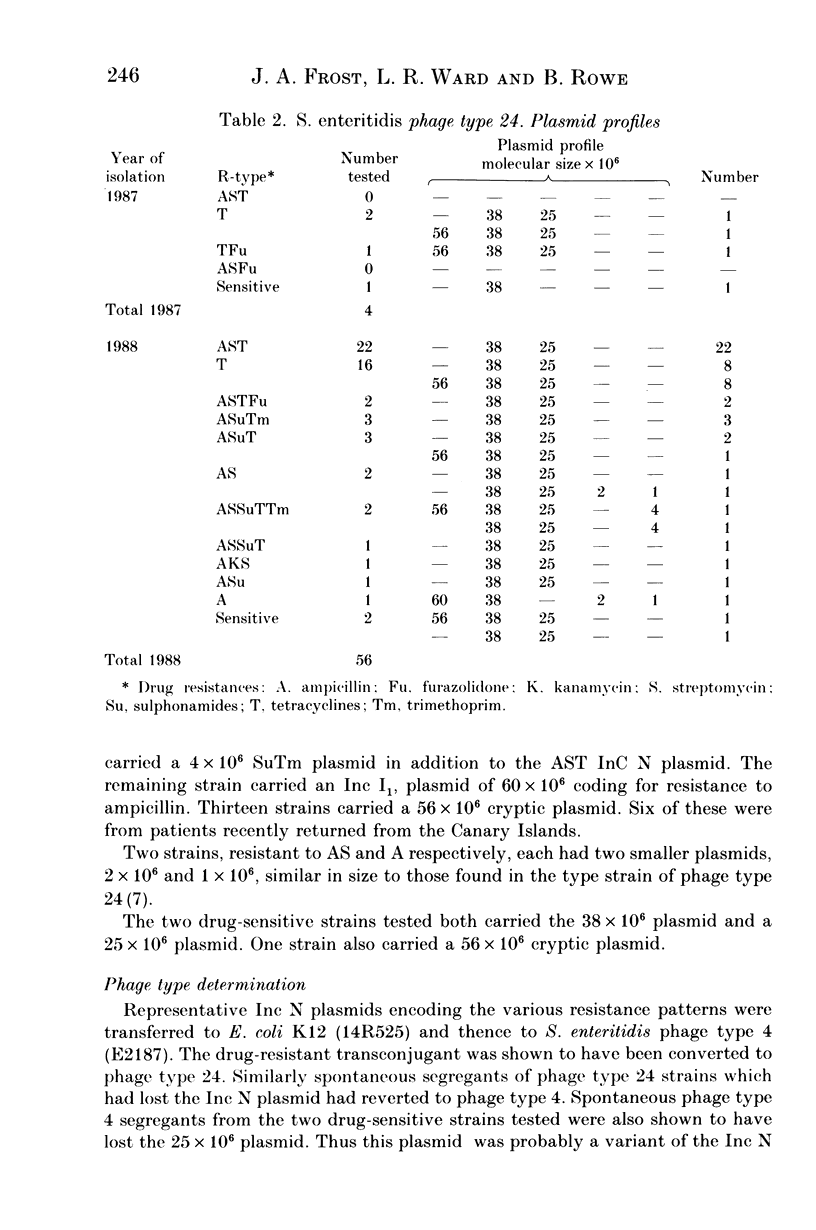
Salmonella enteritidis accounted for 55% of the 27,478 salmonellae isolated from humans in England and Wales during 1988. Within this serotype phage type 24 has increased from 24 isolations in 1987 to 201 in 1988. The high frequency of drug resistance in this phage type has been shown to be due to the presence of plasmids belonging to Inc N and coding for resistance to a range of antimicrobial drugs among which resistance to ampicillin, streptomycin, tetracycline (AST) and T predominate. These plasmids are phage-type determining and convert strains of phage type 4 to phage type 24.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson E. S., Threlfall E. J., Carr J. M., Savoy L. G. Bacteriophage restriction in Salmonella typhimurium by R factors and transfer factors. J Hyg (Lond) 1973 Sep;71(3):619–631. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400046611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson E. S., Threlfall E. J. Change of host range in a resistance factor. Genet Res. 1970 Oct 2;16(2):207–214. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300002421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta N., Richards H., Datta C. Salmonella typhi in vivo acquires resistance to both chloramphenicol and co-trimoxazole. Lancet. 1981 May 30;1(8231):1181–1183. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92350-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmuth R., Stephan R., Bunge C., Hoog B., Steinbeck A., Bulling E. Epidemiology of virulence-associated plasmids and outer membrane protein patterns within seven common Salmonella serotypes. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):175–182. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.175-182.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kado C. I., Liu S. T. Rapid procedure for detection and isolation of large and small plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1365–1373. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1365-1373.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Threlfall E. J., Rowe B., Ward L. R. Subdivision of Salmonella enteritidis phage types by plasmid profile typing. Epidemiol Infect. 1989 Jun;102(3):459–465. doi: 10.1017/s095026880003017x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward L. R., de Sa J. D., Rowe B. A phage-typing scheme for Salmonella enteritidis. Epidemiol Infect. 1987 Oct;99(2):291–294. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800067765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


