Abstract
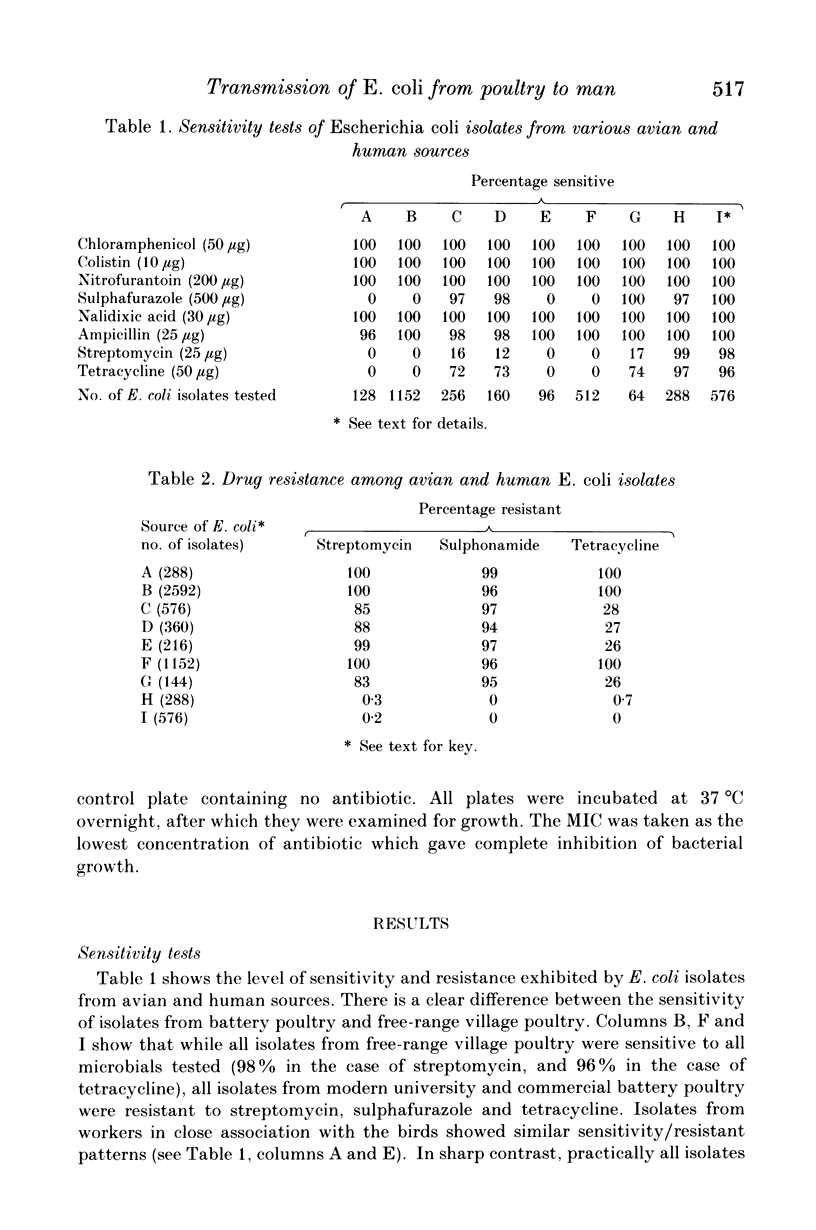
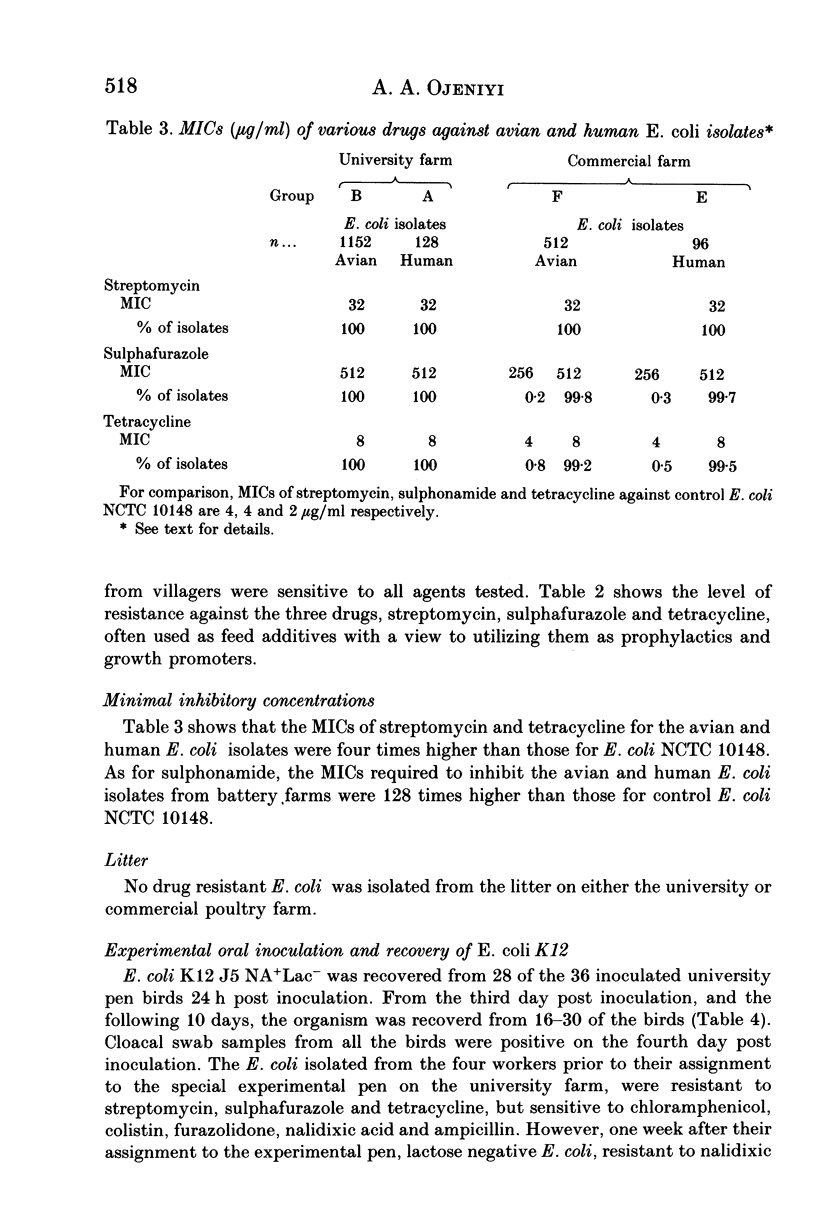
Eight hundred and sixty-four Escherichia coli isolates from workers at the University of Ibadan Teaching and Research Poultry Farm, and 216 isolates from poultry attendants at a commercial poultry farm in the city were found to be resistant to streptomycin, sulphafurazole and tetracycline. In contrast, all 576 and 288 E. coli isolates from village fowls and from villagers respectively were sensitive to these drugs. Isolates from birds in a modern university poultry unit (3744) exhibited the same resistance patterns as those isolated from workers who were in direct contact with the birds. No nalidixic acid-resistant E. coli was isolated from farm workers prior to their assignment to the experimental pen. Following experimental oral infection of birds with E. coli K12 J5 NA+ Lac-, the organism was recovered from the workers who manned the experimental pen. Neither before nor after the experimental infection was any nalidixic acid-resistant E. coli isolated from workers who manned the pen from which birds used in the experiment were selected. Similarly, no drug resistant organisms were isolated from workers outside the poultry unit of the university or commercial farm. The MIC of the drugs against the avian and human E. coli isolates at the university and commercial poultry farms were similar.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Fein D., Burton G., Tsutakawa R., Blenden D. Matching of antibiotic resistance patterns of Escherichia coli of farm families and their animals. J Infect Dis. 1974 Sep;130(3):274–279. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.3.274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guinée P. A. Prevalence of extrachromosomal drug resistance. Bacterial drug resistance in animals. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1971 Jun 11;182:40–51. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1971.tb30641.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg S. D., Osterholm M. T., Senger K. A., Cohen M. L. Drug-resistant Salmonella from animals fed antimicrobials. N Engl J Med. 1984 Sep 6;311(10):617–622. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198409063111001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg S. D., Wells J. G., Cohen M. L. Animal-to-man transmission of antimicrobial-resistant Salmonella: investigations of U.S. outbreaks, 1971-1983. Science. 1984 Aug 24;225(4664):833–835. doi: 10.1126/science.6382605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe K., Linton A. H., Osborne A. D. The effect of tetracycline on the coliform gut flora of broiler chickens with special reference to antibiotic resistance and O-serotypes of Escherichia coli. J Appl Bacteriol. 1976 Dec;41(3):453–464. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1976.tb00658.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson G. A survey of antibiotic resistance of Escherichia Coli isolated from farm animals in Great Britain from 1971 to 1977. Vet Rec. 1981 Apr 11;108(15):325–328. doi: 10.1136/vr.108.15.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen J. L., Nielsen N. C. Indflydelse af restriktiv antibiotika-anvendelse på Escherichia coli floraens resistensforhold i svinebasaetninger. Nord Vet Med. 1975 Jul-Aug;27(7-8):353–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy S. B., FitzGerald G. B., Macone A. B. Spread of antibiotic-resistant plasmids from chicken to chicken and from chicken to man. Nature. 1976 Mar 4;260(5546):40–42. doi: 10.1038/260040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linton A. H. Antibiotic resistance: the present situation reviewed. Vet Rec. 1977 Apr 23;100(17):354–360. doi: 10.1136/vr.100.17.354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linton A. H. Has Swann failed? Vet Rec. 1981 Apr 11;108(15):328–331. doi: 10.1136/vr.108.15.328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linton A. H., Howe K., Hartley C. L., Clements H. M., Richmond M. H., Osborne A. D. Antibiotic resistance among Escherichia coli O-serotypes from the gut and carcases of commercially slaughtered broiler chickens: a potential public health hazard. J Appl Bacteriol. 1977 Jun;42(3):365–378. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1977.tb00704.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linton A. H., Howe K., Osborne A. D. The effects of feeding tetracycline, nitrovin and quindoxin on the drug-resistance of coli-aerogenes bacteria from calves and pigs. J Appl Bacteriol. 1975 Jun;38(3):255–275. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1975.tb00530.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsik F. J., Parisi J. T., Blenden D. C. Transmissible drug resistance of Escherichia coli and Salmonella from humans, animals, and their rural environments. J Infect Dis. 1975 Sep;132(3):296–302. doi: 10.1093/infdis/132.3.296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray B. E., Moellering R. C., Jr Patterns and mechanisms of antibiotic resistance. Med Clin North Am. 1978 Sep;62(5):899–923. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)31746-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel D., Huber W. G., Drysdale S. Human therapeutic and agricultural uses of antibacterial drugs and resistance of the enteric flora of humans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Nov;8(5):538–543. doi: 10.1128/aac.8.5.538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W. Clinical problems of preventive medicine. Antibiotic-resistant bacteria in animals: the dangers to human health. Br Vet J. 1974 Mar-Apr;130(0):110–119. doi: 10.1016/s0007-1935(17)35933-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snoeyenbos G. H. An approach to identifying and maintaining salmonella-free chickens. Avian Dis. 1971 Jan-Mar;15(1):28–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe T. The problems of drug-resistant pathogenic bacteria. The origin of R factors. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1971 Jun 11;182:126–140. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1971.tb30652.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells D. M., James O. B. Transmission of infectious drug resistance from animals to man. J Hyg (Lond) 1973 Mar;71(1):209–215. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400046374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


