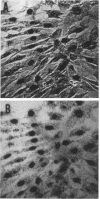
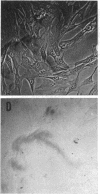
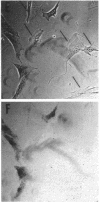
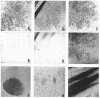
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barr M. L. The significance of the sex chromatin. Int Rev Cytol. 1966;19:35–95. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60564-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIDSON R. G., NITOWSKY H. M., CHILDS B. DEMONSTRATION OF TWO POPULATIONS OF CELLS IN THE HUMAN FEMALE HETEROZYGOUS FOR GLUCOSE-6-PHOSPHATE DEHYDROGENASE VARIANTS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Sep;50:481–485. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.3.481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danes B. S., Bearn A. G. Hurler's syndrome: a genetic study of clones in cell culture with particular reference to the Lyon hypothesis. J Exp Med. 1967 Sep 1;126(3):509–522. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.3.509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMars R. The single-active-X: functional differentiation at the chromosome level. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1967 Sep;26:327–351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grüneberg H. Sex-linked genes in man and Lyon hypothesis. Ann Hum Genet. 1967 Jan;30(3):239–257. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1967.tb00025.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOEFNAGEL D., ANDREW E. D., MIREAULT N. G., BERNDT W. O. HEREDITARY CHOREOATHETOSIS, SELF-MUTILATION AND HYPERURICEMIA IN YOUNG MALES. N Engl J Med. 1965 Jul 15;273:130–135. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196507152730303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley W. N., Rosenbloom F. M., Henderson J. F., Seegmiller J. E. A specific enzyme defect in gout associated with overproduction of uric acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jun;57(6):1735–1739. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.6.1735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LESCH M., NYHAN W. L. A FAMILIAL DISORDER OF URIC ACID METABOLISM AND CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM FUNCTION. Am J Med. 1964 Apr;36:561–570. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(64)90104-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LYON M. F. Gene action in the X-chromosome of the mouse (Mus musculus L.). Nature. 1961 Apr 22;190:372–373. doi: 10.1038/190372a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NANCE W. E. GENETIC TESTS WITH A SEX-LINKED MARKER: GLUCOSE-6-PHOSPHATE DEHYDROGENASE. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1964;29:415–425. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1964.029.01.043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUSSELL L. B. Mammalian X-chromosome action: inactivation limited in spread and region of origin. Science. 1963 May 31;140(3570):976–978. doi: 10.1126/science.140.3570.976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seegmiller J. E., Rosenbloom F. M., Kelley W. N. Enzyme defect associated with a sex-linked human neurological disorder and excessive purine synthesis. Science. 1967 Mar 31;155(3770):1682–1684. doi: 10.1126/science.155.3770.1682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro S. L., Sheppard G. L., Jr, Dreifuss F. E., Newcombe D. S. X-linked recessive inheritance of a syndrome of mental retardation with hyperuricemia. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Jun;122(2):609–611. doi: 10.3181/00379727-122-31204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wajntal A., DeMars R. A tetrazolium method for distinguishing between cultured human fibroblasts having eiter normal or deficient levels of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Biochem Genet. 1967 Jun;1(1):61–64. doi: 10.1007/BF00487737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]