Abstract
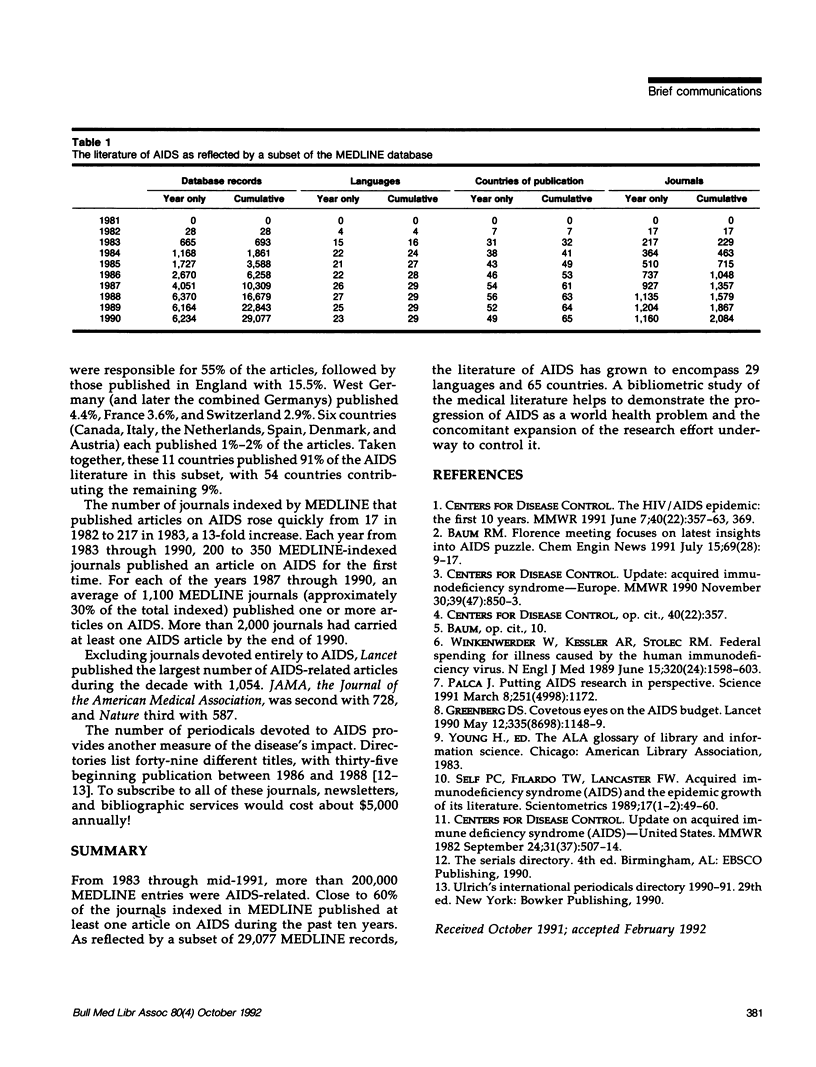
From 1983 through mid-1991, more than 200,000 MEDLINE entries were AIDS-related. Close to 60% of the journals indexed in MEDLINE published at least one article on AIDS during the past ten years. As reflected by a subset of 29,077 MEDLINE records, the literature of AIDS has grown to encompass 29 languages and 65 countries. A bibliometric study of the medical literature helps to demonstrate the progression of AIDS as a world health problem and the concomitant expansion of the research effort underway to control it.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Centers for Disease Control (CDC) Update on acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS)--United States. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1982 Sep 24;31(37):507-8, 513-4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Centers for Disease Control (CDC) Update: acquired immunodeficiency syndrome--Europe. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1990 Nov 30;39(47):850–853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg D. S. Covetous eyes on the AIDS budget. Lancet. 1990 May 12;335(8698):1148–1149. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91141-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palca J. Putting AIDS research in perspective. Science. 1991 Mar 8;251(4998):1172–1172. doi: 10.1126/science.2006406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose A. O., Rose C. A DICEPHALOUS FOETUS. Can Med Assoc J. 1927 Feb;17(2):217–217. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkenwerder W., Kessler A. R., Stolec R. M. Federal spending for illness caused by the human immunodeficiency virus. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jun 15;320(24):1598–1603. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198906153202406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



