Abstract
Background
The analysis of expressed sequence tags (EST) offers a rapid and cost effective approach to elucidate the transcriptome of an organism, but requires several computational methods for assembly and annotation. Researchers frequently analyse each step manually, which is laborious and time consuming. We have recently developed ESTExplorer, a semi-automated computational workflow system, in order to achieve the rapid analysis of EST datasets. In this study, we evaluated EST data analysis for the parasitic nematode Trichostrongylus vitrinus (order Strongylida) using ESTExplorer, compared with database matching alone.
Results
We functionally annotated 1776 ESTs obtained via suppressive-subtractive hybridisation from T. vitrinus, an important parasitic trichostrongylid of small ruminants. Cluster and comparative genomic analyses of the transcripts using ESTExplorer indicated that 290 (41%) sequences had homologues in Caenorhabditis elegans, 329 (42%) in parasitic nematodes, 202 (28%) in organisms other than nematodes, and 218 (31%) had no significant match to any sequence in the current databases. Of the C. elegans homologues, 90 were associated with 'non-wildtype' double-stranded RNA interference (RNAi) phenotypes, including embryonic lethality, maternal sterility, sterile progeny, larval arrest and slow growth. We could functionally classify 267 (38%) sequences using the Gene Ontologies (GO) and establish pathway associations for 230 (33%) sequences using the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG). Further examination of this EST dataset revealed a number of signalling molecules, proteases, protease inhibitors, enzymes, ion channels and immune-related genes. In addition, we identified 40 putative secreted proteins that could represent potential candidates for developing novel anthelmintics or vaccines. We further compared the automated EST sequence annotations, using ESTExplorer, with database search results for individual T. vitrinus ESTs. ESTExplorer reliably and rapidly annotated 301 ESTs, with pathway and GO information, eliminating 60 low quality hits from database searches.
Conclusion
We evaluated the efficacy of ESTExplorer in analysing EST data, and demonstrate that computational tools can be used to accelerate the process of gene discovery in EST sequencing projects. The present study has elucidated sets of relatively conserved and potentially novel genes for biological investigation, and the annotated EST set provides further insight into the molecular biology of T. vitrinus, towards the identification of novel drug targets.
Background
Many parasitic worms, including roundworms (nematodes), cause diseases in humans, animals and plants, which have substantial socio-economic impact throughout the world [1]. Investigating the molecular biology of such parasitic nematodes is not only of fundamental significance but could also lead to the discovery of novel methods for their control. In spite of the importance of parasitic nematodes [2], little is known and understood about them at the molecular level [3-5]. Clearly, molecular biological research, including whole genome and expressed sequence tag (EST) sequencing of key parasitic nematodes, provides a critically important foundation for a wide range of fundamental areas (including functional genomics, genetics, proteomics, systems biology, molecular biology, physiology, biochemistry, ecology, epidemiology, pathology and many more), underpinning many applied areas. Importantly, genomic technologies employed in an integrated way also have considerable potential for the identification of new drug targets linked to key biological pathways in parasitic nematodes of major socio-economic importance. This is of particular relevance, given the current problems with resistance against nematocidal drugs [6,7].
Genome sequencing of parasitic nematodes has focused predominantly on the use of a "global" EST approach [8,9]. Besides 'house-keeping' and structural genes isolated employing this approach, some genes that relate to drug target candidates have been identified in EST data sets. These include genes encoding antioxidant and de-toxifying enzymes, proteinases, proteinase inhibitors, cyclophilins, neurotransmitter receptors, transporters and nuclear hormone receptors [10]. Other studies [4,11] have used a much more "targeted" approach for exploring gender-enriched genes in Trichostrongylus vitrinus (an important trichostrongylid nematode of small ruminants) and Oesophagostomum dentatum, a nodule worm of pigs. For example, Nisbet and Gasser [4] investigated gender-enriched transcription in T. vitrinus via the construction of male- and female-enriched cDNA archives using suppressive-subtractive hybridization (SSH), sequencing of ESTs from these archives, comparison with genes of the free-living nematode, Caenorhabditis elegans and other organisms, and transcription profiling of a representative ESTs by array analysis. In the latter study, an emphasis was placed on a comparative analysis with data available for C. elegans, as it is currently the best-characterized nematode, (see WormBase [12]).
The whole genome sequencing approach is unlikely to be applied extensively to all organisms, irrespective of their commercial or scientific significance in human and animal health, agriculture and ecology. In contrast, expressed sequence tags (ESTs) offer a rapid and cost effective method to explore the transcriptome of an organism, leading to data representing short, unedited, single-pass sequence reads. ESTs are error prone and require several computational methods for pre-processing, clustering, assembly and annotation to yield biological information. As ESTs are usually generated in large numbers, it is crucial to be able to store, organize and annotate them using an automated analysis pipeline. A procedure is required to transfer data efficiently between programs without human intervention, based on carefully parameterized threshold criteria.
The analyses of EST data sets obtained [4,11] can take weeks or months if conducted manually, and the quality of analysis depends very much on the selection of software programs and packages employed. In order to address this limitation, we recently appraised current methods adopted for each step of EST analysis, compiled software tools considered most suited for EST pre-processing, clustering and assembly, database similarity searches and functional annotation, and proposed a "road map" to significantly accelerate the analyses of EST data sets [13]. After a detailed investigation of four current EST analysis platforms, ESTannotator [14], ESTAP [15], PartiGene [16], and EGassembler [17], a comprehensive workflow approach for gene and protein annotations was yet to be incorporated. Among the existing platforms, EGassembler terminates at the assembly level, providing contigs and singletons as output, whereas ESTSAP, ESTannotator and PartiGene provide predominantly an annotation at the nucleotide level. We have developed a semi-automated, user-definable computational workflow system, ESTExplorer [18], as a comprehensive workflow system for species-specific EST data assembly and annotation at both the DNA and protein levels.
In the present study, using a well-defined data set generated previously and analysed manually from the adult stage of a parasitic nematode, T. vitrinus [4], we evaluated the efficacy of ESTExplorer to assemble and correctly annotate ESTs. Compared with the previous study [4], which was limited to the annotation of ESTs via similarity searches (BLAST) for assigning putative function, we have added annotations to the EST data and identified important genes for further investigation. Firstly, we have included functional identification, in terms of mapping to protein domains and metabolic pathways. Secondly, we have categorised the T. vitirnus ESTs based on comparison with three databases (Wormpep [12], parasitic nematodes database and non-nematodes database (parasitic nematodes database and non-nematodes database are locally built databases) and used the Java tool SimiTri [19] to visualize the data comparison. Thirdly, we have related ESTs to molecules in C. elegans which can be silenced by double-stranded RNA interference (RNAi). For comparison purposes, we have repeated the earlier EST analysis [4] by running BLAST against the current databases, in order to minimize any database bias in the results, and compared these results with the automated EST sequence annotations for T. vitrinus data. We showed that ESTExplorer provides a comprehensive, but controlled functional annotation for EST datasets, which leads to a deeper understanding of the annotated molecules. Finally, we have identified 40 putative secreted proteins which represent potential candidates for developing novel anthelmintics or vaccines, using a procedure developed for the EST analysis for the bovine lungworm Dictyocaulus viviparus [20].
Results and discussion
Overall EST analysis
In total, 1776 sequences (866 female and 910 male) were obtained from 2112 clones selected from the gender-specific libraries [4]. The pre-processed male ESTs ranged from 101–585 bp in length (with a mean of 328 bp), and 103–695 bp (with a mean of 340 bp) for female ESTs. After clustering, the mean length of the contigs (or consensus sequences) increased to 412 (+/- 84) bp and 430 (+/-102) bp for the male-specific and female-specific datasets, respectively. The G+C contents of the coding sequences for male and female ESTs were 45.9% and 46.2%, respectively, which is consistent with other related ("clade V") nematodes [21], and higher than for C. elegans (37%) and C. briggsae (38%) [22].
We provided T. vitrinus male and female EST sequences separately as input to ESTExplorer for analyses, using all three phases. The CPU time taken for the processing of all of the programs (Phases I to III) in ESTExplorer is given in Table 1. All programs were run on a 16 CPU Linux cluster. It took 5158 sec (1 h 43 min) to process 910 male ESTs and 3861 seconds (1 h 07 min) to process 866 ESTs from female dataset. The time taken to assemble and annotate EST data was substantially reduced compared with previous manual analysis [4], for which individual ESTs were submitted for BLAST analysis, taking weeks to perform.
Table 1.
Time taken for Trichostrongylus vitrinus EST data analysis carried out on 16 CPU Linux cluster (CPU time in seconds).
| Category | Number of ESTs | Sequential BLASTX alone (s) | ESTExplorer (s) | |||||||
| PHASE I | PHASE II | PHASE III | ||||||||
| SeqClean | RepeatMasker | CAP3 | BLASTX + BLAST2GO | ESTScan | InterProScan (12 programs) | KOBAS | Total time taken in seconds | |||
| Male | 910 | 981 | 8 | 52 | 48 | 1218 | 4 | 2461 | 1367 | 5158 |
| Female | 866 | 729 | 7 | 47 | 45 | 918 | 3 | 1867 | 974 | 3861 |
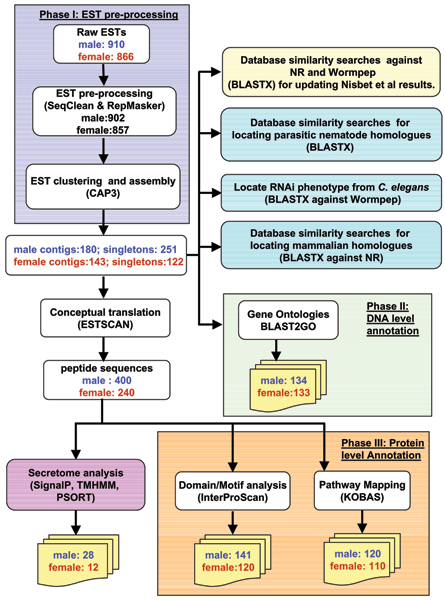
The cluster analysis of the 902 male and 857 female ESTs from T. vitrinus yielded 431 male and 265 female representative ESTs (rESTs; 180 male contigs and 251 singleton sequences; female 143 contigs and 122 singleton sequences; see Figure 1), of which 400 (92.8%) male and 240 (90.1%) female sequences had open reading frames (ORFs). Of a total of 640 peptides obtained by conceptual translation, 161 peptides could be mapped to either a protein domain or a motif. Figure 1 shows the detailed schema of all the programs used during the analysis, together with the mapping results for male and female EST datasets.
Figure 1.
Bioinformatics analysis schema for T. vitrinus ESTs.
Male-specific protein kinases and protein phosphatases, major sperm proteins and enzymes involved in carbohydrate metabolism were abundant in the male EST dataset. Female-specific vitellogenins, heat-shock proteins and chaperonins were also highly represented. Genes involved in a number of cellular processes, such as ubiquitination and proteasome function, gene transcription, cell signaling, protein-protein interactions and chromatin assembly and function were also transcribed in a gender-specific manner. The gender-specific or gender-enriched transcription of many of the genes in the analyses is likely to reflect their roles in energy provision, gametogenesis, embryogenesis and reproduction, as discussed previously [4,11].
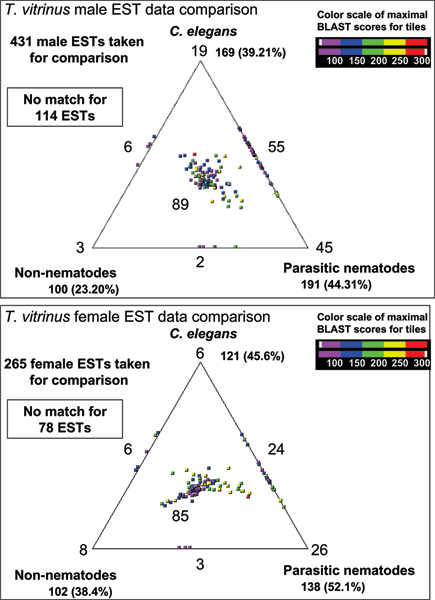
Representative ESTs (rESTs) were also queried against three databases containing protein sequences from different organisms, in order to categorize the molecules from the T. vitrinus. Data were compared with protein sequences available for (i) C. elegans (from WORMPEP v.167 [12]), (ii) parasitic nematodes (available protein sequences and peptides from conceptually translated ESTs) and (iii) organisms other than nematodes (from NCBI non-redundant protein database) [23]. A three-way comparison of male and female T. vitrinus rESTs with homologues from C. elegans, WORMPEP and parasitic nematodes has been figuratively presented using SimiTri [19] (Figure 2). A total of 696 rESTs from male and female T. vitrinus were taken for this comparison. For the male, we found 169 (39.21%) homologues to C. elegans, 191 (44.31%) to those from other parasitic nematodes, including some strongylids, 100 (23.20%) homologues in organisms other than nematodes, and 114 (36.5%) with no significant similarity to any other organism (cut-off of <0.00001 [10-5]) for which sequence data are currently available (Figure 2).
Figure 2.
Comparison of male Trichostrongylus vitrinus ESTs with Caenorhabditis elegans, parasitic nematodes and non-nematodes protein sequence databases. Quantitative analysis of degree of similarity between T. vitrinus sequences homologous to those from C. elegans, other nematodes and non-nematode sequences, visualized by SimiTri. These comparisons demonstrate that the sampled transcriptome from male and female T. vitrinus has a closer relationship to molecules in parasitic nematodes and C. elegans than to non-nematodes.
From the comparative analysis of 265 female rESTs, we found 121 (45.6%) homologues to C. elegans, 138 (52.1%) to those from other parasitic nematodes, including some strongylids, 102 (38.4%) homologues in organisms other than nematodes and 78 (29.4%) with no significant similarity to any other organism for which sequence data are currently available. The SimiTri plot (Figures 2) shows, using the current archive, that the transcriptome subset from T. vitrinus has a closer relationship to that of other parasitic nematode and C. elegans than to that of non-nematodes.
The comparative analysis to identify homologues in C. elegans is important because T. vitrinus and this free-living nematode are both considered to belong to clade V of the Nematoda [24], and because C. elegans also represents the best characterized nematode in many respects, particularly in terms of its genome, genetics, biology, physiology, biochemistry, and the localization and function of molecules [12,25]. Specifically, the comparative analysis (at the amino acid level) of all rESTs with the C. elegans data revealed 169 (39.21%) sequences in male and 121 (45.6%) sequences in female to be key, well-characterized molecules associated with a range of important biological processes (male n = 80 and female n = 88), including development, regulation of biological processes, metabolic process, response to abiotic and biotic stimuli and reproduction. 'Non-wildtype' RNAi phenotypes in C. elegans homologues, such as Bmd (body morphology defect), Clr (clear), Emb (embryonic lethal), Gro (slow growth), Muv (multivulva), Mlt (molt defect), Slu (sluggish), Stp (sterile progeny), Sck (sick), Let (larval lethal), Lvl (larval lethal), Lva (larval arrest) and Unc (uncoordinated); (see WormBase [26] for details) were characterized for 30 and 60 molecules from male and female T. vitrinus, respectively (Additional File 1).
Of all 696 rESTs, the functions for 267 (62%) sequences could be predicted using descriptions from Gene Ontology (GO) [27], with 230 (33%) sequences mapping to key biological pathways (including signal transduction mechanisms, antigen processing and presentation, and/or the regulation of actin cytoskeleton, ribosomal proteins and translation factors). Overall, the functional classification revealed that approximately half of the rESTs had homologues in C. elegans and parasitic nematodes, nearly half of the sequences had homologues in other parasitic nematodes and one third of the rESTs did not have significant similarity to any of the sequences in current databases, including those with known functional domains, thus possibly representing novel genes.
RNAi phenotypes in C. elegans
The use of genomic approaches, such as RNAi, transgenesis and microarray technologies, can considerably accelerate the characterisation of novel genes [9]. C. elegans (non-wild-type) RNAi phenotypes can provide an indication of the relevance and functions of orthologous genes in other nematodes, particularly in parasitic nematodes of clade V, for which the complexity of an obligate parasitic life cycle and the lack of an effective (long-term) laboratory culture system make high-throughput functional screening impractical [28].
We retrieved the C. elegans RNAi data representing T. vitrinus orthologues. Of 431 male and 265 female T. vitrinus rESTs, 30 (18.3%) male and 60 (49.5%) female sequences had homologues in C. elegans which have been silenced by RNAi (see Additional File 1). The RNAi phenotypes (as listed in Wormbase) included Adl (adult lethal), Age (ageing alteration), Bmd (body morphology defect), Dpy (dumpy), Egl (egg laying defect), Emb (embryonic lethal), Gro (slow growth), Let (larval lethal), Lvl (larval lethal), Lva (larval arrest) and Unc (uncoordinated).
In parasitic nematodes, successful RNAi has been reported in some plant parasites, such as Heterodera glycines and Globodera pallida, and in the animal parasites, Nippostrongylus brasiliensis, Brugia malayi, Onchocerca volvulus, Ascaris suum and Trichostrongylus colubriformis [29-34]. Geldhof et al. [35] have described that, under certain conditions, it is possible to silence some genes in Haemonchus contortus by RNAi. From the present study, we have predicted 90 rESTs from T. vitrinus to have homologues in C. elegans which can be silenced by RNAi. Possible targets for intervention are molecules with the phenotypes adult lethal, embryonic lethal, larval lethal and/or larval arrest. With drug resistance in strongylid parasites increasing, the development of an effective RNAi approach in parasitic nematodes could provide a powerful tool for the functional characterization of molecules involved in development, reproduction and survival, and could potentially lead to identification of novel therapeutic targets. Nonetheless, significant efforts are still required to develop a reliable and reproducible RNAi approach for a number of species [28,36].
Gene Ontologies
GO has been used widely to predict gene function and classification [27]. It provides a dynamic vocabulary and hierarchy that unifies descriptions of biological, cellular and molecular functions across genomes. We used BLAST2GO [37], a sequence-based tool, to assign GO terms, extracting them for each BLAST hit obtained by mapping to extant annotation associations. We found that GO terms could be functionally assigned to 134 (31%) male and 133 50(%) female sequences of 696 (both male and female) rESTs. In summary, we found the following GO terms for male and female sequences: male, biological processes (n = 80), cellular components (n = 45) and molecular functions (n = 77) and female, biological processes (n = 88), cellular components (n = 62) and molecular functions (n = 83). A summary GO representation of the T. vitrinus rESTs is given in Additional File 2.
Gene Ontologies for male T. vitrinus sequences
Amongst the most common GO categories in biological processes were developmental process (GO: 0032502), metabolic process (GO: 0008152), reproduction (GO: 0000003) and growth (GO: 0040007). Binding (GO: 0005488), catalytic activity (GO: 0003824) and structural molecule activity (GO: 0005198) were most common GO categories representing molecular function. The largest number of GO terms in cellular components was for cell part (GO: 0044464), membrane-bound organelle (GO: 0043227) and non-membrane-bound organelle (GO: 0043228). A complete listing of male GO mappings assigned to rESTs is given in Additional File 2.
Gene Ontologies for female T. vitrinus sequences
We found similar GO categories in female sequences, including developmental process (GO: 0032502), metabolic process (GO: 0008152), reproduction (GO: 0000003), growth (GO: 0040007) and multicellular organismal process (GO: 0032501) for biological processes. The category, GO: 00032501, is not found in the male ESTs analysed in this study. Binding (GO: 0005488), catalytic activity (GO: 0003824) and structural molecule activity (GO: 0005198) were the most common GO categories representing molecular function. The largest number of GO terms in cellular components was for cell part (GO: 0044464), membrane-bound organelle (GO: 0043227) and non-membrane-bound organelle (GO: 0043228). A complete listing of female GO mappings assigned to rESTs is given in Additional File 2.
Pathway analysis using KEGG assignments
Biochemical functionality was predicted by mapping male (431) and female (265) molecules to pathways, using KOBAS implemented within ESTExplorer [38], with an E-value cut-off of 1.0 e-5. After mapping sets of rESTs to pathways, we have then collected the enzymes (including EC numbers) within each pathway for possible biochemical assays. In the case of male molecules, a total of 120 (28%) sequences were mapped to 53 KEGG pathways, with 100 sequences representing metabolic enzymes characterized by unique EC numbers. A higher percentage of female molecules could be mapped. Out of 265 female molecules, a total of 110 (41%) sequences were mapped to 57 KEGG pathways, with 78 sequences representing metabolic enzymes characterized by unique EC numbers. KEGG biochemical pathway mapping data for male and female are listed in Additional File 3.
Amongst the rESTs mapped to KEGG pathways, molecules involved in glycolysis/gluconeogenesis, pyruvate metabolism and the proteasome had the highest representation amongst the male sequences, whereas members of ribosomal subunits were highly represented in female sequences as well as pyruvate metabolism and aminosugar metabolism. We identified seven putative proteins with potential roles in host-parasite interactions, such as molecules predicted to be involved in antigen processing and/or presentation, T-cell receptor signalling pathway and CD molecules. We found nine pathways considered functionally crucial for the organisms, such as signal transduction mechanisms, apoptosis and ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis.
Secretome analysis
Important in the identification of potential novel drug or vaccine candidates in parasites is the prediction of molecules that are secreted or excreted in or around the host parasite interface [39-41]. Examples of such proteins are the aspartyl protease inhibitor API-1 [42], mi-msp-1 (similar to the venom allergen antigen AG5-like protein) [43] and the Ancylostoma-secreted protein (ASP) [44].
From the present data set (431 male and 265 female ESTs), we predicted 40 secreted proteins representing a non-redundant catalogue of T. vitrinus molecules (Table 2). Of these, 24 (60%) had homologues in nematodes, with 14 (35%) homologues in C. elegans and/or C. briggsae and 5 (12%) in various other parasitic nematodes, including the trichostrongylids Haemonchus contortus and Trichostrongylus colubriformis as well as the filarioid Brugia malayi. Of the 40 proteins inferred to be secreted, 16 (40%) were novel (sequences with no significant similarity to any sequence in current databases), making them intriguing candidates for further characterization, because they may relate specifically to parasitism. The secretome analysis revealed some very interesting molecules. For example, the protein predicted from TvmContig101 (from male) has homology to an astacin 13 in C. elegans [45]. The astacins are zinc metalloproteases present in prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms and serve a variety of physiological functions, such digestion, hatching, peptide processing and morphogenesis [45]. TVmContig96 is predicted to code a protein which has homology to RPN-1, a non-ATPase subunit of the 19S regulatory particle (RP) of the 26S proteasome. RPN-1 is required for embryonic, larval and germline development and by homology, is predicted to function in unfolding and recognition of protein substrates and/or recycling of ubiquitin moieties during protein degradation [46].
Table 2.
Identification and analysis of secreted proteins from Trichostrongylus vitrinus ESTs.
| Number | EST sequence ID | Seq Length (aa) | Start | Signal Peptide length (aa) | Description (top hit from non-redundant protein database) | E-value | % Identity (aa) | RNAi phenotype in C. elegans |
| 1 | TvmContig8 | 102 | - | 19 | No significant hits | - | - | - |
| 2 | TVmContig11 | 148 | - | 24 | No significant hits | - | - | - |
| 3 | TVmContig20 | 121 | - | 25 | 24 kDa excretory/secretory protein [Haemonchus contortus] | 3.00E-028 | 63/109 (57%) | |
| 4 | TvmContig28 | 167 | - | 19 | No significant hits | - | - | - |
| 5 | TVmContig35 | 120 | M | 17 | 30 kDa antigenic glycoprotein precursor [Trichostrongylus colubriformis] | 4.00E-006 | 27/65 (41%) | No observed phenotype is found. |
| 6 | TVmContig39 | 208 | - | 18 | Weakly similar to PhosphoDiEsterase family member (pde-2) [Caenorhabditis elegans] | 4.00E-028 | 22/72 (30%) | No observed phenotype is found. |
| 7 | TvmContig68 | 131 | - | 26 | Weakly similar to SaPosin-like Protein family member (spp-19) [Caenorhabditis elegans] | 0.016 | 23/82 (28%) | No observed phenotype is found. |
| 8 | TVmContig75 | 239 | - | 26 | Weakly similar to Na/Ca eXchangers family member (ncx-4) [Caenorhabditis elegans] | 0.3 | 15/39 (38%) | No observed phenotype is found. |
| 9 | TVmContig96 | 120 | - | 15 | Non-ATPase-like family member (rpn-1) [Caenorhabditis elegans] | 2.00E-047 | 94/119 (78%) | EMB, LET embryonic_lethal, maternal_sterile, sick (Sck) |
| 10 | TvmContig101 | 156 | M | 18 | Zinc metalloproteinase nas-13 precursor (Nematode astacin 13) [Caenorhabditis elegans] | 2.00E-008 | 30/96 (31%) | No observed phenotype is found. |
| 11 | TVmContig107 | 85 | - | 27 | No significant hits | - | - | - |
| 12 | TVmContig134 | 190 | - | 26 | No significant hits | - | - | - |
| 13 | TvmContig135 | 116 | - | 19 | Late Embryo Abundant (LEA) related family member (lea-1) [Caenorhabditis elegans] | 4.00E-004 | 22/86 (25%) | No observed phenotype is found. |
| 14 | TVmContig150 | 137 | - | 24 | No significant hits | - | - | - |
| 15 | TVmContig164 | 122 | - | 20 | Weakly similar to Human xnp gene related protein 1 [Caenorhabditis elegans] | 0.18 | 18/57 (31%) | None |
| 16 | TVmContig170 | 85 | M | 19 | No significant hits | - | - | - |
| 17 | TVmContig171 | 131 | M | 15 | No significant hits | - | - | - |
| 18 | TVmContig172 | 129 | - | 26 | Weakly similar to abnormal NUClease family member (nuc-1) [Caenorhabditis elegans] | 0.016 | 12/30 (40%) | life span abnormal (Age) |
| 19 | TvmContig178 | 146 | - | 17 | Weakly similar to Maternal Effect Sterile family member (mes-3) [Caenorhabditis elegans] | 0.047 | 13/26 (50%) | STP sterile_progeny |
| 20 | TVm01_A12 | 91 | - | 18 | No significant hits | - | - | - |
| 21 | TVm02_D11 | 86 | M | 24 | No significant hits | - | - | - |
| 22 | TVm03_G11 | 108 | - | 20 | No significant hits | - | - | - |
| 23 | TVm04_F02 | 97 | - | 19 | No significant hits | - | - | - |
| 24 | TVm06_F08 | 72 | - | 25 | No significant hits | - | - | - |
| 25 | TVm07_A07 | 78 | - | 26 | No significant hits | - | - | - |
| 26 | TVm07_G02 | 124 | - | 16 | putative calcium-binding mitochondrial carrier protein [Brugia malayi] | 1.00E-036 | 75/116 (64%) | GRO slow_growth |Unclassified |
| 27 | TVm08_D01 | 64 | M | 19 | Hypothetical protein MGG_00752 [Magnaporthe grisea 70-15] | 8.00E-006 | 25/52 (48%) | None |
| 28 | TVm08_H01 | 120 | - | 19 | Pyruvate kinase [Caenorhabditis elegans] | 6.00E-025 | 42/87 (48%) | EMB, LET embryonic_lethal |
| 29 | TvfContig1 | 152 | - | 22 | No significant hits | - | - | - |
| 30 | TvfContig3 | 143 | - | 23 | C-type LECtin family member (clec-88) [Caenorhabditis elegans] | 5.00E-021 | 55/132 (41%) | No observed phenotype is found. |
| 31 | TvfContig5 | 134 | M | 22 | Hypothetical protein K06A9.1c [Caenorhabditis elegans] | 0.004 | 28/98 (28%) | None |
| 32 | TvfContig78 | 161 | - | 20 | MSH (MutS Homolog) family member (msh-2) [Caenorhabditis elegans] | 2.00E-027 | 70/167 (41%) | spontaneous mutation rate increased |
| 33 | TvfContig84 | 104 | M | 18 | No significant hits | - | - | - |
| 34 | TvfContig88 | 145 | M | 22 | similar to TPRXL protein [Pan troglodytes] | 0.002 | 31/122 (25%) | None |
| 35 | TvfContig122 | 97 | - | 24 | No significant hits | - | - | - |
| 36 | TvfContig132 | 214 | M | 13 | Vitellogenin-6 precursor [Caenorhabditis elegans] | GRO slow_growth |EMB, LET embryonic_lethal | ||
| 37 | TVf03_C08 | 132 | - | 20 | No significant hits | - | - | - |
| 38 | TVf04_D01 | 162 | - | 16 | putative serine-threonine kinase PAR-4 [Caenorhabditis elegans] | 0.027 | 16/35 (45%) | No observed phenotype is found. |
| 39 | TVf06_A07 | 145 | - | 22 | 15 kDa excretory/secretory protein [Haemonchus contortus] | 6.00E-004 | 39/118 (33%) | No observed phenotype is found. |
| 40 | TVf07_A05 | 146 | - | 23 | No significant hits | - | - | - |
Comparison of individual EST analysis with ensemble annotation by ESTExplorer
Previously, Nisbet and Gasser [4] carried out an individual BLAST analysis of the 1776 gender-enriched ESTs from T. vitrinus and categorised the molecules into different functional classes. This conventional analysis took ~16 weeks to perform compared with an enhanced analysis of the same data set using ESTExplorer (with the exception of the secretome, SimiTri and RNAi phenotype analyses) which took less than 3 h. A total of 301 ESTs representing 31 functional categories were defined and compared. Male T. vitrinus was represented predominantly by major sperm protein-like, protein kinases/phosphatases, transcription factors, nucleic acid synthesis and other categories (Table 3), whereas female T. vitrinus was represented by vitellogenins, protein kinases/phosphatases and transcription factor and molecules involved in carbohydrate metabolism and modification and the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway (Table 3).
Table 3.
Comparision of annotations for T. vitrinus ESTs: EST annotations performed by Nisbet and Gasser [4] based on BLAST similarity results in first three columns and annotations obtained from ESTExplorer are shown in next columns. Example catagories selected for male ESTs are major sperm protein-like, protein kinases and protein phosphatases, transcription factors and related and nucleic acid synthesis and function and for female ESTs, vitellogenins, carbohydrate metabolism and modification, ubiquitin-proteasome pathway, protein kinases/phosphatases and transcription factors and related proteins
| Manual annotation using BLAST | Annotations obtained automatically from ESTExplorer | ||||||
| MALE: Protein kinases and protein phosphatases | |||||||
| EST ID | E-value | BLAST results | BLAST results | E-value | Gene Ontologies | Metabolic Pathway Mapping | Domain/Motif data |
| TVm02_C07 | 2.00E-37 | PP1-gamma serine/threonine protein phosphatase | protein phosphatasecatalyticgamma isoform isoform 1 | 1.00E-36 | chromatin modification, protein amino acid dephosphorylation, embryonic cleavage, cytokinesis, meiosis, oviposition, manganese ion binding, protein phosphatase type 1 activity, mitochondrial outer membrane, protein binding, mitosis, glycogen metabolic process, iron ion binding, nucleus | Long-term potentiation, Regulation of actin cytoskeleton, Focal adhesion, Insulin signaling pathway | Metallophosphoesterase, Serine/threonine-specific protein phosphatase and bis(5-nucleosyl)-tetraphosphatase |
| TVm02_F11 | 2.00E-45 | Serine/threonine protein kinase of the casein kinase I subfamily | tau tubulin kinase | 1.00E-44 | protein kinase activity, ATP binding, protein amino acid phosphorylation, locomotory behavior, growth, larval development (sensu Nematoda) | Nicotinate and nicotinamide metabolism, Inositol phosphate metabolism, Benzoate degradation via CoA ligation | Protein kinase |
| TVm08_H06 | 5.00E-60 | Member of the protein phosphatase protein family | serine threonine protein phosphatase pp1 | 1.00E-64 | phosphoprotein phosphatase activity, protein amino acid dephosphorylation, iron ion binding, manganese ion binding | None | Metallophosphoesterase, Serine/threonine-specific protein phosphatase and bis(5-nucleosyl)-tetraphosphatase |
| TVm09_B11 | 8.00E-34 | Protein phosphatase-1 (PP1) | phosphoprotein phosphatase 1 | 1.00E-33 | growth, larval development (sensu Nematoda), embryonic development ending in birth or egg hatching, hydrolase activity | None | Metallophosphoesterase, Serine/threonine-specific protein phosphatase and bis(5-nucleosyl)-tetraphosphatase |
| MALE: Transcription factors and related | |||||||
| EST ID | E-value | BLAST results | BLAST results | E-value | Gene Ontologies | Metabolic Pathway Mapping | Domain/Motif data |
| TVm01_F11 | 8.00E-10 | Transcription elongation factor (testes specific homologue in mouse) | transcription elongation factor a1 | 1.00E-19 | regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent, RNA elongation, translation elongation factor activity, zinc ion binding, RNA polymerase II transcription factor activity, nucleus, DNA binding, defense response, transcription regulator activity, transcription, regulation of transcription, transcription factor activity, transcription elongation factor complex, protein binding, transcriptional elongation regulator activity, erythrocyte differentiation, positive regulation of transcription, DNA-dependent, general RNA polymerase II transcription factor activity, metal ion binding, nucleoplasm | None | None |
| TVm09_B03 | 1.00E-09 | Protein containing six kelch motifs and one BTB/POZ domain | klhl10 protein | 1.00E-10 | larval development (sensu Nematoda), growth, protein binding | None | Kelch repeat |
| FEMALE: Vitellogenins | |||||||
| EST ID | E-value | BLAST results | BLAST results | E-value | Gene Ontologies | Metabolic Pathway Mapping | Domain/Motif data |
| TVf01_C08 | 4.00E-25 | Vitellogenin 6 precursor | vitellogenin structural genes (yolk protein genes) family member (vit-6) | 1.00E-24 | embryonic development ending in birth or egg hatching;P:determination of adult life span, lipid transporter activity | None | Lipid transport protein, N-terminal |
| TVf01_C11 | 7.00E-14 | Vitellogenin 5 precursor | vitellogenin structural genes (yolk protein genes) family member (vit-6) | 1.00E-25 | embryonic development ending in birth or egg hatching;P:determination of adult life span, lipid transporter activity | None | Lipid transport protein, N-terminal |
| FEMALE: Carbohydrate metabolism and modification | |||||||
| EST ID | E-value | BLAST results | BLAST results | E-value | Gene Ontologies | Metabolic Pathway Mapping | Domain/Motif data |
| TVf02_G06 | 7.70E-15 | glyceraldehyde 3 phosphate dehydrogenase gpd-3C | glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase | 1.00E-18 | cell wall chitin biosynthetic process, glutamine-fructose-6-phosphate transaminase (isomerizing) activity | None | Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase, Lipocalin |
| TVf02_H12 | 6.80E-24 | glucosamine-fructose-6-phosphate aminotransferase | glutamine-fructose-6-phosphate transaminase 2 | 1.00E-32 | fructose 6-phosphate metabolic process, glutamine-fructose-6-phosphate transaminase (isomerizing) activity | Aminosugars metabolism, Glutamate metabolism | Glutamine amidotransferase, class-II |
| TVf03_B07 | 5.80E-28 | Pyruvate dehydrogenase alpha subunit | pyruvate dehydrogenase e1 alpha subunit | 1.00E-62 | oxidoreductase activity, acting on the aldehyde or oxo group of donors, disulfide as acceptor, metabolic process, C:mitochondrion | Pyruvate metabolism, Glycolysis/Gluconeogenesis, Valine leucine and isoleucine biosynthesis, Butanoate metabolism | Dehydrogenase, E1 component |
| TVf03_E01 | 2.80E-35 | Pyruvate dehydrogenase | dihydrolipoamide acetyltransferase | 1.00E-53 | oxidoreductase activity | Pyruvate metabolism, Glycolysis/Gluconeogenesis, Valine leucine and isoleucine biosynthesis, Butanoate metabolism | Transketolase, central region |
| TVf06_E11 | 3.80E-49 | gei-7 isocitrate lyase | malate synthase a | 1.00E-50 | embryonic development, F:acyltransferase activity, tricarboxylic acid cycle, isocitrate lyase activity, determination of adult life span, glyoxylate cycle | Pyruvate metabolism, Glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism | Malate synthase |
| TVf09_D01 | 3.20E-08 | Ribulose-phosphate 3 epimerase | ribulose-phosphate 3-epimerase | 1.00E-17 | metabolic process, catalytic activity | Pentose phosphate pathway | Ribulose-phosphate 3-epimerase |
| FEMALE: Ubiquitin-proteasome pathway | |||||||
| EST ID | E-value | BLAST results | BLAST results | E-value | Gene Ontologies | Metabolic Pathway Mapping | Domain/Motif data |
| TVf02_H07 | 3.00E-28 | Ubiquitin-like | ubiquitin family member (ubq-1) | 1.00E-27 | ribosome, larval development (sensu Nematoda), structural constituent of ribosome, reproduction, growth translation, protein modification process | Ribosome | Ubiquitin |
| TVf06_D11 | 1.30E-12 | pbs-2 Proteasome A-type and B-type | 20s proteasome beta subunit pbb2 | 1.00E-22 | threonine endopeptidase activity, ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolism, proteasome core complex (sensu Eukaryota) | Proteasome | 20S proteasome, A and B subunits |
| TVf10_F06 | 5.20E-07 | ubiquitin activating enzyme related (uba-1) | ubiquitin-activating enzyme e1 | 1.00E-12 | ATP binding, ubiquitin-protein ligase activity, ubiquitin activating enzyme activity | Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis | Ubiquitin-activating enzyme repeat |
| FEMALE: Protein kinases/phosphatases | |||||||
| EST ID | E-value | BLAST results | BLAST results | E-value | Gene Ontologies | Metabolic Pathway Mapping | Domain/Motif data |
| TVf06_F11 | 1.40E-49 | lin-2 erythrocyte membrane like protein | calcium calmodulin-dependent serine protein kinase (maguk family) | 1.00E-51 | synapse, guanylate kinase activity, cell adhesion, positive regulation of vulval development (sensu Nematoda), actin cytoskeleton, protein-tyrosine kinase activity, synaptosome, nucleotide binding, basolateral plasma membrane, protein amino acid phosphorylation, cytosol, cell junction, calmodulin binding, protein serine/threonine kinase activity, positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter | Tight junction, Neurodegenerative Disorders | Pkinase_Tyr, Guanylate_kin |
| FEMALE: Transcription factors and related | |||||||
| EST ID | E-value | BLAST results | BLAST results | E-value | Gene Ontologies | Metabolic Pathway Mapping | Domain/Motif data |
| TVf01_C02 | 3.80E-18 | ama-1 RNA polymerase II | rna polymerase ii largest subunit | 1.00E-30 | DNA-directed RNA polymerase activity, DNA binding, transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter, DNA-directed RNA polymerase II, core complex | Purine metabolism, Pyrimidine metabolism, RNA polymerase | RNA polymerase Rpb1, domain 1 |
| TVf03_A03 | 9.70E-25 | btf-1 helicase | tbp associated factor | 1.00E-63 | nucleic acid binding, helicase activity, ATP binding | Purine metabolism | Helicase, C-terminal |
| TVf04_E07 | 2.00E-09 | ceh-5 Homeobox domain | similarity to lim-homeobox protein lmx1_mesau | 1.00E-15 | metal ion binding, sequence-specific DNA binding, transcription factor activity, regulation of transcription, multicellular organismal development DNA-dependent, nucleus | None | None |
We showed that ESTExplorer provides a comprehensive "functional" annotation for EST datasets which leads to an enhanced characterization and understanding of the annotated molecules. When a gene has multiple predicted functions, it is possible to list them in advanced annotation protocols, such as GO and pathway mapping, which provides a comprehensive prediction for the molecule to underpin any further molecular, biochemical and/or biological investigations. For instance, the EST TVm02_C07, which is homologous to a serine/threonine protein phosphatase, has revealed the following GO terms: "chromatin modification, protein amino acid dephosphorylation, embryonic cleavage, cytokinesis, meiosis, oviposition, manganese ion binding, protein phosphatase type 1 activity, protein binding, mitosis, glycogen metabolic process, iron ion binding, mitochondrial outer membrane, nucleus," and has been predicted to be involved in three pathways, "long-term potentiation, regulation of actin cytoskeleton, focal adhesion and insulin signaling pathway". Other findings indicated that this gene can be silenced in C. elegans, leading to progeny with Egl (egg laying deficit), Emb (embryonic lethal) and/or Sck (sick) phenotypes. Being able to achieve silencing in C. elegans showed that this gene is central to the development, reproduction and/or survival of this free-living nematode. This information provided a basis for the detailed molecular characterization and transcriptional analysis of the full-length gene (Tv-stp-1) encoding this serine/threonine protein phosphatase (Tv-STP-1) from T. vitrinus. The findings of this study [47] indicated that there is relative conservation in features and function of the serine/threonine protein phosphatase characterized among T. vitrinus, O. dentatum and C. elegans, likely to have significant implications for exploring molecular reproductive and developmental processes in strongylid nematodes of socio-economic importance.
Using ESTExplorer, we also showed that is possible to directly visualise the GO output according to the class of molecule. Blast2GO [37] (a part of Phase II) allows a data file to be generated which summarizes different classes of molecules with their representations (See Additional File 4). This facility is particularly useful when large EST data sets are being subjected to annotation. By using the online B2GO Java tool [48], statistical analyses (e.g., enrichment analysis using the Fisher's exact test) of particular classes of molecules can be conducted and hierarchical gene ontology graphs produced. Furthermore, EST Explorer applies several filtration steps for the removal of possible false positive predictions, by setting relatively high homology threshold values. We showed that 39 (male) and 21 (female) ESTs were not annotated by ESTExplorer in comparison with manual annotation. We examined the BLAST results for these ESTs and found that most of them indeed represented alignments with relatively low homology and incomplete sequence coverage. Thus, these ESTs did not meet the E-value threshold, set at 1.0E-05 as the default in ESTExplorer. For example, TVf02_D08 (3.40E-04) was annotated as a vitellogenin 3 precursor by individual BLAST search alone. Even when the E-value threshold (1.0E-05) was exceeded, the length of the alignment and its coverage were used to eliminate low homology matches. This issue was observed more frequently in categories, such as hypothetical, uncharacterised proteins and other proteins whose function has not yet been ascribed. A detailed comparison of all of the categories is given in Additional File 5. In addition, as users can modify the E-value thresholds and the overlap (percent identity) cut-offs during the assembly of ESTs in ESTExplorer, there is control over the way in which a particular EST dataset is annotated, which can range from "stringent" to "less stringent" parameters. This point is particularly important when investigating "lesser known" species, such as T. vitrinus, for which no genome sequence or functional data are available. Taken together, we demonstrate that ESTExplorer provides reliable, detailed and in-depth annotations, such as Gene Ontologies, mapped pathways and protein domain/motif annotations compared to BLAST-based annotations, with one such prediction (TVm02_C07) validated by experimentation.
Conclusion and future directions
In this study, we critically evaluated a semi-automated EST analysis platform, ESTExplorer and compared the results obtained using this platform with those of a previous individual BLAST search approach. We have demonstrated that ESTExplorer is capable of rapidly analysing data, and also show the accuracy of the annotation using test datasets for the nematode T. vitrinus (Strongylida).
In the present study, among all test ESTs (n = 1776), we identified 192 novel sequences (27.5%), with high confidence, with no known homologue to any nematode or mammalian sequence currently available in public databases. These molecules are particularly interesting, as they may represent genes that relate to the parasitic mode of existence or to the species (T. vitrinus). However, such molecules are currently difficult to investigate, as their functions cannot be predicted using current bioinformatics approaches. Nonetheless, there is huge scope for studying such molecules in the future, using a combination of genomic and proteomic approaches. Insights into such molecules and/or their interplay with the ruminant host could provide opportunities for developing novel methods of parasite intervention. Opportunities will be enhanced when the complete genome of T. vitrinus and a detailed characterization of the transcriptome become available. Having available the whole genome sequence for T. vitrinus, will also underpin meaningful proteomic analyses of differentially expressed proteins. Importantly, the future application of an integrated bioinformatic-genomic-phenomic-proteomic ("systems biology") approach, focusing on molecular processes, will enhance our understanding of the molecular biology of moulting, invasion of and establishment in the host, hypobiosis (arrested development), and sexual differentiation, maturation and behaviour of T. vitrinus. Clearly, progress in such fundamental areas could lead to the development of new ways of controlling parasitic nematode, by blocking or disrupting key biological pathways in them.
Extending the present study, we are in the process of developing a user-definable workflow system specifically for the analysis of EST data from parasitic nematodes. We plan to integrate additional functionalities to the current version of ESTExplorer. For instance, the query sequence comparison with data available in three databases and generation of a SimiTri triangle to visualize homologous data. The BLAST searches against C. elegans protein sequences (Wormpep) and automatic retrieval of RNAi phenotypic data. With 454 Life Science GS20 sequencing technology [49,50], providing an unprecedented rate of genomic and EST data at substantially lower costs than incurred in conventional sequencers, ESTExplorer facilitates the timely analysis of high throughput data, providing "high confidence annotation" at the DNA and protein levels, enriched with gene ontology, protein domain and pathway information.
Materials and methods
The EST data set representing molecules from T. vitrinus was obtained previously via the sequencing of gender-enriched cDNA from archives generated using suppressive-subtractive hybridisation (SSH) [4]. These EST data were initially analysed and annotated using the automated EST analysis platform ESTExplorer [38], available at http://estexplorer.biolinfo.org. In brief, the analyses comprised three phases. In phase I, all ESTs were pre-processed (SeqClean, RepeatMasker), aligned/clustered using the Contig Assembly Program CAP3, employing a minimum sequence overlap length "cut-off" of 30 bases and an identity threshold of 95% (in Phase I) for the removal of flanking vector and adapter sequences, followed by assembly. Phase II of the ESTExplorer led to GO inference, at the DNA-level annotation, using BLAST2GO [37]. In Phase III, rESTs were then conceptually translated into peptides using ESTScan. The ESTScan program requires a matrix, known as the "smat" file, generated from available mRNA data for a specific organism, for conceptual translation. When the smat file for a specific organism is not available in ESTScan, the nearest well-studied organism using NCBI Taxonomy is selected as a reference and its smat file is used for conceptual translation. As T. vitrinus mRNA data are very scanty, we have selected C. elegans as the nearest reference organism for generating a smat file, based on available 25,481 (as on 15 February 2007) cDNA sequences from C. elegans was used for comparative analysis. C. elegans was selected because it belongs to the same clade (V) of the Nematoda [24,51] as T. vitrinus. We validated this approach by taking 56 untranslated sequences (contigs and singletons) and attempted to look for homologous proteins using BLASTX. We found that 36 entries did not return any hits from the BLASTX output (Additional file 6), with 12 sequences showing no matches to nematode sequences. Of the eight sequences with nematode matches, only two could be considered significant. Thus, the use of C. elegans smat is considered to be ~96% accurate (54/56 sequences). The peptides were mapped via InterProScan (domain/motifs) and to respective pathways in C. elegans using KOBAS (KEGG Orthology-Based Annotation System). Peptides were also compared, using BLASTP, with the non-redundant protein sequence database from National Centre for Biotechnology Information (NCBI), as part of the generic ESTExplorer pipeline for systematic EST analysis and annotation.
Protein databases for 'parasitic nematodes' and 'non-nematodes' were built in-house for similarity searches. The former group contains all available protein sequences for parasitic nematodes and ESTs from GenBank (17th May 2007), translated into peptide sequences whereas the latter database comprises amino acid sequences from the complete non-redundant protein database NR (17th May 2007) excluding any from nematodes. Additionally, homologues to peptides inferred from rESTs were identified via comparisons against WormBase using BLASTX. Each EST of T. vitrinus was assigned a 'statistically significant' gene homologue if the E-value from the BLAST output of the sequence alignment was <0.00001 (10-5). Comparison (at the amino acid sequence level) of T. vitrinus rESTs with C. elegans, parasitic nematode and non-nematode protein sequence databases using SimiTri [19]. SimiTri provides a two-dimensional display and an analysis of relative similarity relationships of the dataset of interest to three different databases.
Secreted proteins were predicted from the inferred peptides using a combination of three programs, in order to minimize the number of false positive predictions. Firstly, SignalP 3.0 [52] was used to predict the presence of secretory signal peptides and signal anchors for each predicted protein. A signal sequence was considered present if predicted both by the artificial neural network and the hidden Markov model prediction approaches (SignalPNN and SignalP-HMM, available as options within SignalP). In order to exclude the erroneous prediction of putative transmembrane (TM) sequences as signal sequences, TMHMM [53], a membrane topology prediction program, was then applied. We further validated the list of secreted proteins, using extracellular localization, using PSORT [54]. The performance of this semi-automated approach was evaluated and compared with the previous, manual analysis [4] in terms of effectiveness, efficiency, detail and time.
Comparison of individual EST analysis with ensemble annotation by ESTExplorer
In 2003, Nisbet and Gasser [4] carried out their analysis on an EST-by-EST basis, using BLASTX against the non-redundant protein and WormPep databases. We have employed the same dataset using BLASTX [55] searches (30 April 2007), to update the original BLAST results with current databases. We then subjected the same EST dataset, separately for male and female data, to a systematic analysis using Phase I (pre-processing, assembly and consensus generation), Phase II (nucleotide level annotation) and Phase III (protein level annotation) in the ESTExplorer pipeline [19] (with all underlying databases updated to 30 April 2007). The individual EST analysis results, using BLASTX alone, were compared with the output obtained via the automated ESTExplorer pipeline.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors' contributions
SHN, RBG and SR conceived and designed the research plan and participated in all aspects of data collection and analysis. SHN conducted the analysis and SHN, RBG, AJN and SR interpreted the data. All authors contributed towards writing of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final version.
Supplementary Material
Comparison of 696 rESTs from Trichostrongylus vitrinus with Caenorhabditis elegans proteome (Wormpep v 167). The table also provides corresponding RNAi phenotypic information.
Gene Ontology mappings for Trichostrongylus vitrinus rESTs.
Metabolic pathways in Trichostrongylus vitrinus mapped by Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG).
An example output for functional classification of ESTs generated using the Blast2GO component of ESTEXplorer's Phase II – Nucleotide-level Analysis.
Comparison of individual EST analysis via BLAST searches and ensemble annotation by ESTExplorer.
Validation of Caenorhabditis elegans smat file used for ESTScan by BLASTX results for untranslated EST sequences.
Acknowledgments
Acknowledgements
We thank Michael Baxter and Doan Le, Macquarie University, and Gary Cobon, Genetic Technologies Limited, for their invaluable help and support. This work was supported by grants from the Australian Research Council (LP0667795), Genetic Technologies Limited and Meat and Livestock Australia and the Macquarie University External Research Collaboration Scheme. SHN is grateful to Macquarie University for the award of iMURS research scholarships and an MUPGR travel grant. Open Access publication charges for this article were covered by Macquarie University.
This article has been published as part of BMC Bioinformatics Volume 9 Supplement 1, 2008: Asia Pacific Bioinformatics Network (APBioNet) Sixth International Conference on Bioinformatics (InCoB2007). The full contents of the supplement are available online at http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2105/9?issue=S1.
Contributor Information
Shivashankar H Nagaraj, Email: snagaraj@els.mq.edu.au.
Robin B Gasser, Email: robinbg@unimelb.edu.au.
Alasdair J Nisbet, Email: Alasdair.Nisbet@moredun.ac.uk.
Shoba Ranganathan, Email: shoba.ranganathan@mq.edu.au.
References
- Platt HM. In: The phylogenetic systematics of free-living nematodes. Lorenzen S, editor. The Ray Society, London; 1994. pp. i–ii. [Google Scholar]
- Gasser RB, Newton SE. Genomic and genetic research on bursate nematodes: significance, implications and prospects. Int J Parasitol. 2000;30:509–534. doi: 10.1016/s0020-7519(00)00021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boag PR, Newton SE, Gasser RB. Molecular aspects of sexual development and reproduction in nematodes and schistosomes. Adv Parasitol. 2001;50:153–198. doi: 10.1016/s0065-308x(01)50031-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nisbet AJ, Gasser RB. Profiling of gender-specific gene expression for Trichostrongylus vitrinus (Nematoda: Strongylida) by microarray analysis of expressed sequence tag libraries constructed by suppressive-subtractive hybridisation. Int J Parasitol. 2004;34:633–643. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2003.12.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikolaou S, Gasser RB. Extending from PARs in Caenorhabditis elegans to homologues in Haemonchus contortus and other parasitic nematodes. Parasitology. 2006. pp. 1–22. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Coles GC, Jackson F, Taylor MA, Wolstenholme AJ. Collaborating to tackle the problem of anthelmintic resistance. Vet Rec. 2004;155:253–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolstenholme AJ, Fairweather I, Prichard R, von Samson-Himmelstjerna G, Sangster NC. Drug resistance in veterinary helminths. Trends Parasitol. 2004;20:469–476. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2004.07.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks DR, Isaac RE. Functional genomics of parasitic worms: the dawn of a new era. Parasitol Int. 2002;51:319–325. doi: 10.1016/s1383-5769(02)00063-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitreva M, Blaxter ML, Bird DM, McCarter JP. Comparative genomics of nematodes. Trends Genet. 2005;21:573–581. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2005.08.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashmi S, Tawe W, Lustigman S. Caenorhabditis elegans and the study of gene function in parasites. Trends Parasitol. 2001;17:387–393. doi: 10.1016/s1471-4922(01)01986-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cottee PA, Nisbet AJ, Abs El-Osta YG, Webster TL, Gasser RB. Construction of gender-enriched cDNA archives for adult Oesophagostomum dentatum by suppressive-subtractive hybridization and a microarray analysis of expressed sequence tags. Parasitology. 2006;132:691–708. doi: 10.1017/S0031182005009728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wombase http://wormbase.org/
- Nagaraj SH, Gasser RB, Ranganathan S. A hitchhiker's guide to expressed sequence tag (EST) analysis. Brief Bioinform. 2007;8:6–21. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbl015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hotz-Wagenblatt A, Hankeln T, Ernst P, Glatting KH, Schmidt ER, Suhai S. ESTAnnotator: A tool for high throughput EST annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003;31:3716–3719. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao C, Cushman JC, May GD, Weller JW. ESTAP – an automated system for the analysis of EST data. Bioinformatics. 2003;19:1720–1722. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btg205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J, Anthony A, Wasmuth J, Schmid R, Hedley A, Blaxter M. PartiGene – constructing partial genomes. Bioinformatics. 2004;20:1398–1404. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bth101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masoudi-Nejad A, Tonomura K, Kawashima S, Moriya Y, Suzuki M, Itoh M, Kanehisa M, Endo T, Goto S. EGassembler: online bioinformatics service for large-scale processing, clustering and assembling ESTs and genomic DNA fragments. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006:W459–462. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagaraj S, Deshpande N, Gasser R, Ranganathan S. ESTExplorer: an expressed sequence tag (EST) assembly and annotation platform. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007 doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J, Blaxter M. SimiTri – visualizing similarity relationships for groups of sequences. Bioinformatics. 2003;19:390–395. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btf870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranganathan S, Nagaraj SH, Hu M, Strube C, Schnieder T, Gasser RB. A transcriptomic analysis of the adult stage of the bovine lungworm, Dictyocaulus viviparus. BMC Genomics. 2007;8:311. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-8-311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaxter ML, De Ley P, Garey JR, Liu LX, Scheldeman P, Vierstraete A, Vanfleteren JR, Mackey LY, Dorris M, Frisse LM, et al. A molecular evolutionary framework for the phylum Nematoda. Nature. 1998;392:71–75. doi: 10.1038/32160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein LD, Bao Z, Blasiar D, Blumenthal T, Brent MR, Chen N, Chinwalla A, Clarke L, Clee C, Coghlan A, et al. The genome sequence of Caenorhabditis briggsae: a platform for comparative genomics. PLoS Biol. 2003;1:E45. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0000045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson DA, Karsch-Mizrachi I, Lipman DJ, Ostell J, Wheeler DL. GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006:D16–20. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkj157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaxter M. Caenorhabditis elegans is a nematode. Science. 1998;282:2041–2046. doi: 10.1126/science.282.5396.2041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wormbook http://www.wormbook.org/
- Schwarz EM, Antoshechkin I, Bastiani C, Bieri T, Blasiar D, Canaran P, Chan J, Chen N, Chen WJ, Davis P, et al. WormBase: better software, richer content. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006:D475–478. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkj061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT, et al. Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. The Gene Ontology Consortium. Nat Genet. 2000;25:25–29. doi: 10.1038/75556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geldhof P, Visser A, Clark D, Saunders G, Britton C, Gilleard J, Berriman M, Knox D. RNA interference in parasitic helminths: current situation, potential pitfalls and future prospects. Parasitology. 2007. pp. 1–11. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Issa Z, Grant WN, Stasiuk S, Shoemaker CB. Development of methods for RNA interference in the sheep gastrointestinal parasite, Trichostrongylus colubriformis. Int J Parasitol. 2005;35:935–940. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2005.06.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Islam MK, Miyoshi T, Yamada M, Tsuji N. Pyrophosphatase of the roundworm Ascaris suum plays an essential role in the worm's molting and development. Infect Immun. 2005;73:1995–2004. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.4.1995-2004.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lustigman S, Zhang J, Liu J, Oksov Y, Hashmi S. RNA interference targeting cathepsin L and Z-like cysteine proteases of Onchocerca volvulus confirmed their essential function during L3 molting. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2004;138:165–170. doi: 10.1016/j.molbiopara.2004.08.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aboobaker AA, Blaxter ML. Use of RNA interference to investigate gene function in the human filarial nematode parasite Brugia malayi. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2003;129:41–51. doi: 10.1016/s0166-6851(03)00092-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urwin PE, Lilley CJ, Atkinson HJ. Ingestion of double-stranded RNA by preparasitic juvenile cyst nematodes leads to RNA interference. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2002;15:747–752. doi: 10.1094/MPMI.2002.15.8.747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hussein AS, Kichenin K, Selkirk ME. Suppression of secreted acetylcholinesterase expression in Nippostrongylus brasiliensis by RNA interference. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2002;122:91–94. doi: 10.1016/s0166-6851(02)00068-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geldhof P, Murray L, Couthier A, Gilleard JS, McLauchlan G, Knox DP, Britton C. Testing the efficacy of RNA interference in Haemonchus contortus. Int J Parasitol. 2006;36:801–810. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2005.12.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zawadzki JL, Presidente PJ, Meeusen EN, De Veer MJ. RNAi in Haemonchus contortus: a potential method for target validation. Trends Parasitol. 2006;22:495–499. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2006.08.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conesa A, Gotz S, Garcia-Gomez JM, Terol J, Talon M, Robles M. Blast2GO: a universal tool for annotation, visualization and analysis in functional genomics research. Bioinformatics. 2005;21:3674–3676. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bti610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagaraj S, Deshpande N, Gasser R, Ranganathan S. ESTExplorer: an expressed sequence tag (EST) assembly and annotation platform. 2007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Harcus YM, Parkinson J, Fernandez C, Daub J, Selkirk ME, Blaxter ML, Maizels RM. Signal sequence analysis of expressed sequence tags from the nematode Nippostrongylus brasiliensis and the evolution of secreted proteins in parasites. Genome Biol. 2004;5:R39. doi: 10.1186/gb-2004-5-6-r39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews JB, Davidson AJ, Beynon RJ. The application of mass spectrometry to identify immunogenic components of excretory/secretory products from adult Dictyocaulus viviparus. Parasitology. 2004;128:S43–47. doi: 10.1017/S0031182004006808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanholme B, De Meutter J, Tytgat T, Van Montagu M, Coomans A, Gheysen G. Secretions of plant-parasitic nematodes: a molecular update. Gene. 2004;332:13–27. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2004.02.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delaney A, Williamson A, Brand A, Ashcom J, Varghese G, Goud GN, Hawdon JM. Cloning and characterisation of an aspartyl protease inhibitor (API-1) from Ancylostoma hookworms. Int J Parasitol. 2005;35:303–313. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2004.11.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ding X, Shields J, Allen R, Hussey RS. A secretory cellulose-binding protein cDNA cloned from the root-knot nematode (Meloidogyne incognita) Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 1998;11:952–959. doi: 10.1094/MPMI.1998.11.10.952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhan B, Liu Y, Badamchian M, Williamson A, Feng J, Loukas A, Hawdon JM, Hotez PJ. Molecular characterisation of the Ancylostoma-secreted protein family from the adult stage of Ancylostoma caninum. Int J Parasitol. 2003;33:897–907. doi: 10.1016/s0020-7519(03)00111-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohrlen F, Hutter H, Zwilling R. The astacin protein family in Caenorhabditis elegans. Eur J Biochem. 2003;270:4909–4920. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1033.2003.03891.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M, Iwasaki H, Inoue H, Takahashi K. Reverse genetic analysis of the Caenorhabditis elegans 26S proteasome subunits by RNA interference. Biol Chem. 2002;383:1263–1266. doi: 10.1515/BC.2002.140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu M, Abs El-Osta YG, Campbell BE, Boag PR, Nisbet AJ, Beveridge I, Gasser RB. Trichostrongylus vitrinus (Nematoda: Strongylida): Molecular characterization and transcriptional analysis of Tv-stp-1, a serine/threonine phosphatase gene. Exp Parasitol. 2007. [DOI] [PubMed]
- BLAST2GO http://www.blast2go.de/
- Cheung F, Haas BJ, Goldberg SM, May GD, Xiao Y, Town CD. Sequencing Medicago truncatula expressed sequenced tags using 454 Life Sciences technology. BMC Genomics. 2006;7:272. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-7-272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margulies M, Egholm M, Altman WE, Attiya S, Bader JS, Bemben LA, Berka J, Braverman MS, Chen YJ, Chen Z, et al. Genome sequencing in microfabricated high-density picolitre reactors. Nature. 2005;437:376–380. doi: 10.1038/nature03959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J, Mitreva M, Whitton C, Thomson M, Daub J, Martin J, Schmid R, Hall N, Barrell B, Waterston RH, et al. A transcriptomic analysis of the phylum Nematoda. Nat Genet. 2004;36:1259–1267. doi: 10.1038/ng1472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendtsen JD, Nielsen H, von Heijne G, Brunak S. Improved prediction of signal peptides: SignalP 3.0. J Mol Biol. 2004;340:783–795. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2004.05.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krogh A, Larsson B, von Heijne G, Sonnhammer EL. Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden Markov model: application to complete genomes. J Mol Biol. 2001;305:567–580. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2000.4315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakai K, Horton P. PSORT: a program for detecting sorting signals in proteins and predicting their subcellular localization. Trends Biochem Sci. 1999;24:34–36. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(98)01336-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997;25:3389–3402. doi: 10.1093/nar/25.17.3389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Comparison of 696 rESTs from Trichostrongylus vitrinus with Caenorhabditis elegans proteome (Wormpep v 167). The table also provides corresponding RNAi phenotypic information.
Gene Ontology mappings for Trichostrongylus vitrinus rESTs.
Metabolic pathways in Trichostrongylus vitrinus mapped by Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG).
An example output for functional classification of ESTs generated using the Blast2GO component of ESTEXplorer's Phase II – Nucleotide-level Analysis.
Comparison of individual EST analysis via BLAST searches and ensemble annotation by ESTExplorer.
Validation of Caenorhabditis elegans smat file used for ESTScan by BLASTX results for untranslated EST sequences.