Abstract
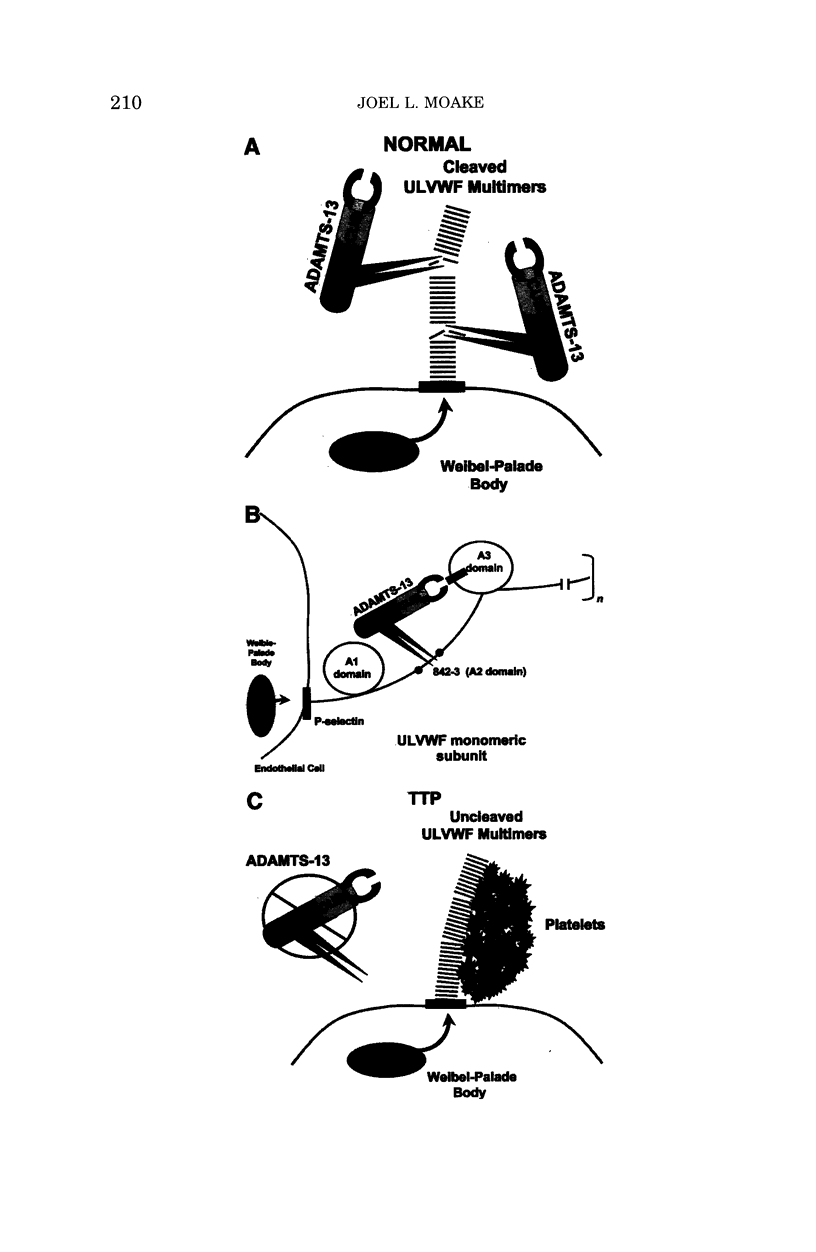
A teenager died suddenly in 1923 of systemic microvascular thrombosis. Dr. Eli Moschcowitz attributed the "hitherto undescribed disease" (now "thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura," or "TTP") to "some powerful poison" with "both agglutinative and hemolytic properties." In 1982, TTP was found to be a defect in the "processing" of unusually large (UL) von Willebrand factor (VWF) multimers. By 1998, the cause of TTP was known to be either familial absence or acquired inhibition (by autoantibody) of plasma VWF-cleaving metalloprotease. This enzyme, the 13th member of a disintegrin and metalloprotease family with thrombospondin domains (ADAMTS-13), circulates in normal plasma waiting to cleave the long strings of ULVWF multimers emerging from stimulated endothelial cells. Uncleaved ULVWF multimers in TTP induce platelet adhesion and aggregation in the rapidly flowing blood of microvessels. Episodes of TTP are treated by "giving A DAM" (TS-13, that is) contained in normal plasma, either by infusion alone or in combination with plasmapheresis.
Full text
PDF




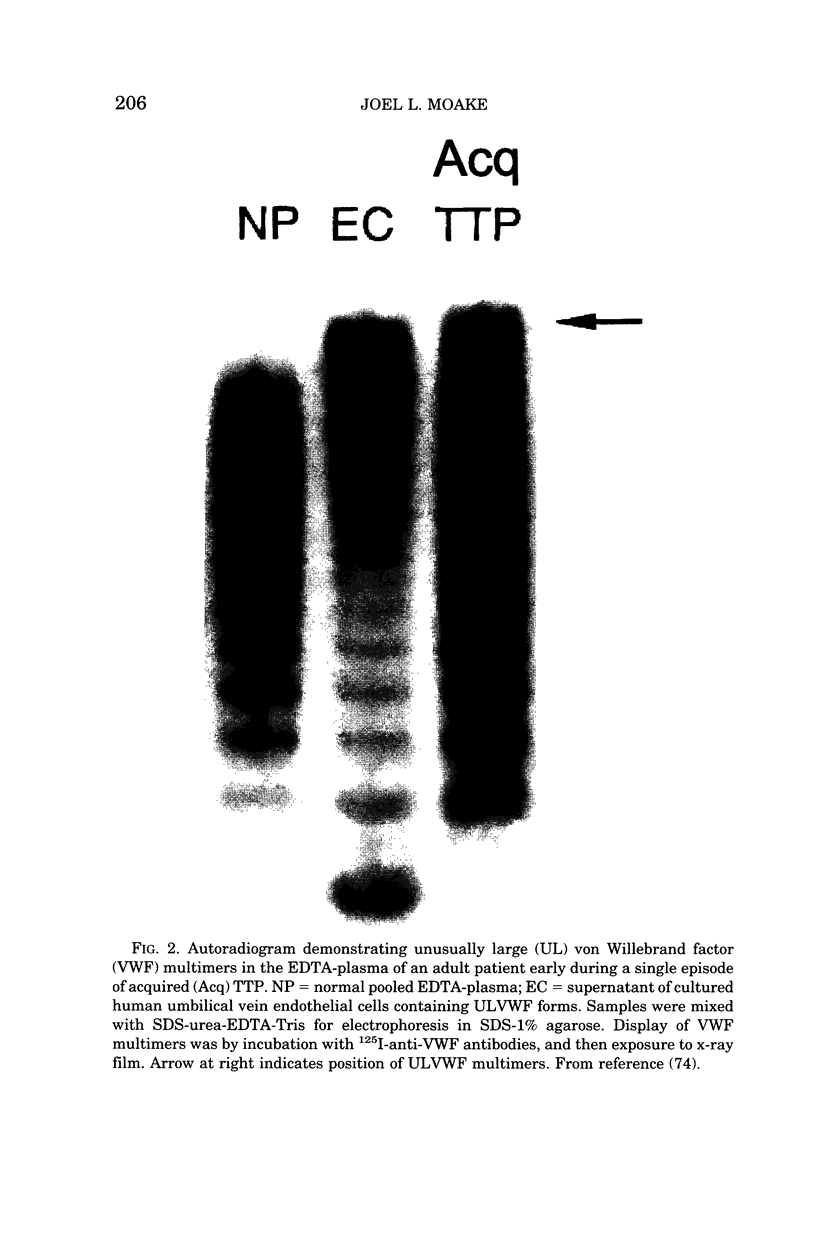











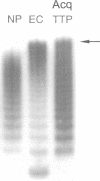
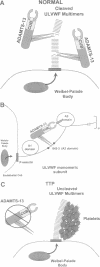
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alevriadou B. R., Moake J. L., Turner N. A., Ruggeri Z. M., Folie B. J., Phillips M. D., Schreiber A. B., Hrinda M. E., McIntire L. V. Real-time analysis of shear-dependent thrombus formation and its blockade by inhibitors of von Willebrand factor binding to platelets. Blood. 1993 Mar 1;81(5):1263–1276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allford S. L., Harrison P., Lawrie A. S., Liesner R., MacKie I. J., Machin S. J. Von Willebrand factor--cleaving protease activity in congenital thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Br J Haematol. 2000 Dec;111(4):1215–1222. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2141.2000.02503.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arya Maneesh, Anvari Bahman, Romo Gabriel M., Cruz Miguel A., Dong Jing-Fei, McIntire Larry V., Moake Joel L., López José A. Ultralarge multimers of von Willebrand factor form spontaneous high-strength bonds with the platelet glycoprotein Ib-IX complex: studies using optical tweezers. Blood. 2002 Jun 1;99(11):3971–3977. doi: 10.1182/blood-2001-11-0060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asada Y., Sumiyoshi A., Hayashi T., Suzumiya J., Kaketani K. Immunohistochemistry of vascular lesion in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura, with special reference to factor VIII related antigen. Thromb Res. 1985 Jun 1;38(5):469–479. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(85)90180-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbot J., Costa E., Guerra M., Barreirinho M. S., Isvarlal P., Robles R., Gerritsen H. E., Lämmle B., Furlan M. Ten years of prophylactic treatment with fresh-frozen plasma in a child with chronic relapsing thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura as a result of a congenital deficiency of von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease. Br J Haematol. 2001 Jun;113(3):649–651. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2141.2001.02808.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell W. R., Braine H. G., Ness P. M., Kickler T. S. Improved survival in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura-hemolytic uremic syndrome. Clinical experience in 108 patients. N Engl J Med. 1991 Aug 8;325(6):398–403. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199108083250605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett C. L., Connors J. M., Carwile J. M., Moake J. L., Bell W. R., Tarantolo S. R., McCarthy L. J., Sarode R., Hatfield A. J., Feldman M. D. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura associated with clopidogrel. N Engl J Med. 2000 Jun 15;342(24):1773–1777. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200006153422402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett C. L., Weinberg P. D., Rozenberg-Ben-Dror K., Yarnold P. R., Kwaan H. C., Green D. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura associated with ticlopidine. A review of 60 cases. Ann Intern Med. 1998 Apr 1;128(7):541–544. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-128-7-199804010-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi Valentina, Robles Rodolfo, Alberio Lorenzo, Furlan Miha, Lämmle Bernhard. Von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease (ADAMTS13) in thrombocytopenic disorders: a severely deficient activity is specific for thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood. 2002 Jul 15;100(2):710–713. doi: 10.1182/blood-2002-02-0344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bork P., Beckmann G. The CUB domain. A widespread module in developmentally regulated proteins. J Mol Biol. 1993 May 20;231(2):539–545. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukowski R. M., Hewlett J. S., Harris J. W., Hoffman G. C., Battle J. D., Jr, Silverblatt E., Yang I. Y. Exchange transfusions in the treatment of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Semin Hematol. 1976 Jul;13(3):219–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukowski R. M., Hewlett J. S., Reimer R. R., Groppe C. W., Weick J. K., Livingston R. B. Therapy of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: an overview. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1981 Winter;7(1):1–8. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1005062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukowski R. M., King J. W., Hewlett J. S. Plasmapheresis in the treatment of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood. 1977 Sep;50(3):413–417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrnes J. J., Khurana M. Treatment of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura with plasma. N Engl J Med. 1977 Dec 22;297(25):1386–1389. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197712222972507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrnes J. J., Moake J. L. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and the haemolytic-uraemic syndrome: evolving concepts of pathogenesis and therapy. Clin Haematol. 1986 May;15(2):413–442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cal Santiago, Obaya Alvaro J., Llamazares María, Garabaya Cecilia, Quesada Víctor, López-Otín Carlos. Cloning, expression analysis, and structural characterization of seven novel human ADAMTSs, a family of metalloproteinases with disintegrin and thrombospondin-1 domains. Gene. 2002 Jan 23;283(1-2):49–62. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(01)00861-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chemnitz Jens, Draube Andreas, Scheid Christof, Staib Peter, Schulz Armin, Diehl Volker, Söhngen Dietmar. Successful treatment of severe thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura with the monoclonal antibody rituximab. Am J Hematol. 2002 Oct;71(2):105–108. doi: 10.1002/ajh.10204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung Dominic W., Fujikawa Kazuo. Processing of von Willebrand factor by ADAMTS-13. Biochemistry. 2002 Sep 17;41(37):11065–11070. doi: 10.1021/bi0204692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. A., Brecher M. E., Bandarenko N. Cellular source of serum lactate dehydrogenase elevation in patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. J Clin Apher. 1998;13(1):16–19. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1098-1101(1998)13:1<16::aid-jca3>3.0.co;2-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowther M. A., Heddle N., Hayward C. P., Warkentin T., Kelton J. G. Splenectomy done during hematologic remission to prevent relapse in patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Ann Intern Med. 1996 Aug 15;125(4):294–296. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-125-4-199608150-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dong Jing-fei, Moake Joel L., Bernardo Aubrey, Fujikawa Kazuo, Ball Chalmette, Nolasco Leticia, López José A., Cruz Miguel A. ADAMTS-13 metalloprotease interacts with the endothelial cell-derived ultra-large von Willebrand factor. J Biol Chem. 2003 May 29;278(32):29633–29639. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M301385200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dong Jing-fei, Moake Joel L., Nolasco Leticia, Bernardo Aubrey, Arceneaux Wendy, Shrimpton Corie N., Schade Alicia J., McIntire Larry V., Fujikawa Kazuo, López José A. ADAMTS-13 rapidly cleaves newly secreted ultralarge von Willebrand factor multimers on the endothelial surface under flowing conditions. Blood. 2002 Jul 25;100(12):4033–4039. doi: 10.1182/blood-2002-05-1401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott Michelle A., Nichols William L., Jr, Plumhoff Elizabeth A., Ansell Stephen M., Dispenzieri Angela, Gastineau Dennis A., Gertz Morie A., Inwards David J., Lacy Martha Q., Micallef Ivana N. M. Posttransplantation thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: a single-center experience and a contemporary review. Mayo Clin Proc. 2003 Apr;78(4):421–430. doi: 10.4065/78.4.421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frangos J. A., Moake J. L., Nolasco L., Phillips M. D., McIntire L. V. Cryosupernatant regulates accumulation of unusually large vWF multimers from endothelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jun;256(6 Pt 2):H1635–H1644. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1989.256.6.H1635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujikawa K., Suzuki H., McMullen B., Chung D. Purification of human von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease and its identification as a new member of the metalloproteinase family. Blood. 2001 Sep 15;98(6):1662–1666. doi: 10.1182/blood.v98.6.1662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furlan M., Lämmle B. Aetiology and pathogenesis of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and haemolytic uraemic syndrome: the role of von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2001 Jun;14(2):437–454. doi: 10.1053/beha.2001.0142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furlan M., Robles R., Galbusera M., Remuzzi G., Kyrle P. A., Brenner B., Krause M., Scharrer I., Aumann V., Mittler U. von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and the hemolytic-uremic syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1998 Nov 26;339(22):1578–1584. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199811263392202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furlan M., Robles R., Morselli B., Sandoz P., Lämmle B. Recovery and half-life of von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease after plasma therapy in patients with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Thromb Haemost. 1999 Jan;81(1):8–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furlan M., Robles R., Solenthaler M., Lämmle B. Acquired deficiency of von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease in a patient with thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood. 1998 Apr 15;91(8):2839–2846. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furlan M., Robles R., Solenthaler M., Wassmer M., Sandoz P., Lämmle B. Deficient activity of von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease in chronic relapsing thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood. 1997 May 1;89(9):3097–3103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
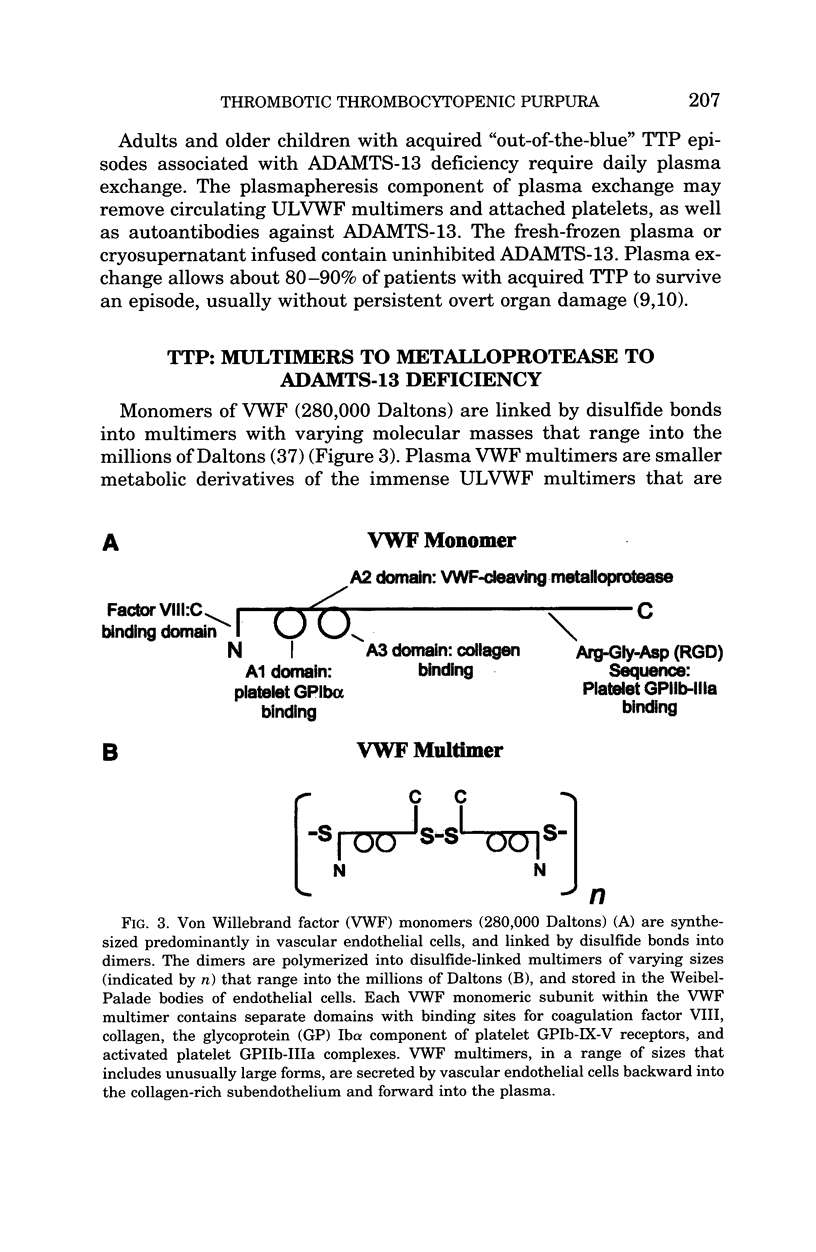
- Gerritsen H. E., Robles R., Lämmle B., Furlan M. Partial amino acid sequence of purified von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease. Blood. 2001 Sep 15;98(6):1654–1661. doi: 10.1182/blood.v98.6.1654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottschall J. L., Elliot W., Lianos E., McFarland J. G., Wolfmeyer K., Aster R. H. Quinine-induced immune thrombocytopenia associated with hemolytic uremic syndrome: a new clinical entity. Blood. 1991 Jan 15;77(2):306–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutterman Lorence A., Kloster Bruce, Tsai Han-Mou. Rituximab therapy for refractory thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2002 May-Jun;28(3):385–391. doi: 10.1006/bcmd.2002.0522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kojouri K., Vesely S. K., George J. N. Quinine-associated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura-hemolytic uremic syndrome: frequency, clinical features, and long-term outcomes. Ann Intern Med. 2001 Dec 18;135(12):1047–1051. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-135-12-200112180-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy G. G., Nichols W. C., Lian E. C., Foroud T., McClintick J. N., McGee B. M., Yang A. Y., Siemieniak D. R., Stark K. R., Gruppo R. Mutations in a member of the ADAMTS gene family cause thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Nature. 2001 Oct 4;413(6855):488–494. doi: 10.1038/35097008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannucci P. M., Canciani M. T., Forza I., Lussana F., Lattuada A., Rossi E. Changes in health and disease of the metalloprotease that cleaves von Willebrand factor. Blood. 2001 Nov 1;98(9):2730–2735. doi: 10.1182/blood.v98.9.2730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMinn J. R., George J. N. Evaluation of women with clinically suspected thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura-hemolytic uremic syndrome during pregnancy. J Clin Apher. 2001;16(4):202–209. doi: 10.1002/jca.10005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moake J. L., Byrnes J. J. Thrombotic microangiopathies associated with drugs and bone marrow transplantation. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 1996 Apr;10(2):485–497. doi: 10.1016/s0889-8588(05)70348-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moake J. L., Byrnes J. J., Troll J. H., Rudy C. K., Hong S. L., Weinstein M. J., Colannino N. M. Effects of fresh-frozen plasma and its cryosupernatant fraction on von Willebrand factor multimeric forms in chronic relapsing thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood. 1985 May;65(5):1232–1236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moake J. L. Insolubilized von Willebrand factor and the initial events in hemostasis. J Lab Clin Med. 1989 Jul;114(1):1–3. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moake J. L., Rudy C. K., Troll J. H., Weinstein M. J., Colannino N. M., Azocar J., Seder R. H., Hong S. L., Deykin D. Unusually large plasma factor VIII:von Willebrand factor multimers in chronic relapsing thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. N Engl J Med. 1982 Dec 2;307(23):1432–1435. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198212023072306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moake J. L., Turner N. A., Stathopoulos N. A., Nolasco L. H., Hellums J. D. Involvement of large plasma von Willebrand factor (vWF) multimers and unusually large vWF forms derived from endothelial cells in shear stress-induced platelet aggregation. J Clin Invest. 1986 Dec;78(6):1456–1461. doi: 10.1172/JCI112736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moake J. L., Turner N. A., Stathopoulos N. A., Nolasco L., Hellums J. D. Shear-induced platelet aggregation can be mediated by vWF released from platelets, as well as by exogenous large or unusually large vWF multimers, requires adenosine diphosphate, and is resistant to aspirin. Blood. 1988 May;71(5):1366–1374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moake J., Chintagumpala M., Turner N., McPherson P., Nolasco L., Steuber C., Santiago-Borrero P., Horowitz M., Pehta J. Solvent/detergent-treated plasma suppresses shear-induced platelet aggregation and prevents episodes of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood. 1994 Jul 15;84(2):490–497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moake Joel L. Thrombotic microangiopathies. N Engl J Med. 2002 Aug 22;347(8):589–600. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra020528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neame P. B. Immunologic and other factors in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP). Semin Thromb Hemost. 1980;6(4):416–429. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1005113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oleksowicz L., Bhagwati N., DeLeon-Fernandez M. Deficient activity of von Willebrand's factor-cleaving protease in patients with disseminated malignancies. Cancer Res. 1999 May 1;59(9):2244–2250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pisciotta A. V., Garthwaite T., Darin J., Aster R. H. Treatment of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura by exchange transfusion. Am J Hematol. 1977;3:73–82. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830030109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaimauer Barbara, Zimmermann Klaus, Völkel Dirk, Antoine Gerhard, Kerschbaumer Randolf, Jenab Pegah, Furlan Miha, Gerritsen Helen, Lämmle Bernhard, Schwarz Hans Peter. Cloning, expression, and functional characterization of the von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease (ADAMTS13). Blood. 2002 Jul 12;100(10):3626–3632. doi: 10.1182/blood-2002-05-1397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiter Rosemarie A., Knöbl Paul, Varadi Katalin, Turecek Peter L. Changes in von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease (ADAMTS13) activity after infusion of desmopressin. Blood. 2002 Sep 19;101(3):946–948. doi: 10.1182/blood-2002-03-0814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rock G. A., Shumak K. H., Buskard N. A., Blanchette V. S., Kelton J. G., Nair R. C., Spasoff R. A. Comparison of plasma exchange with plasma infusion in the treatment of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Canadian Apheresis Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1991 Aug 8;325(6):393–397. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199108083250604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri Z. M. Developing basic and clinical research on von Willebrand factor and von Willebrand disease. Thromb Haemost. 2000 Aug;84(2):147–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh N., Gayowski T., Marino I. R. Hemolytic uremic syndrome in solid-organ transplant recipients. Transpl Int. 1996;9(1):68–75. doi: 10.1007/BF00336815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. E., Damon L. E., Ries C. A., Linker C. A. Thrombotic microangiopathies in the 1980s: clinical features, response to treatment, and the impact of the human immunodeficiency virus epidemic. Blood. 1992 Oct 15;80(8):1890–1895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai H. M., Chandler W. L., Sarode R., Hoffman R., Jelacic S., Habeeb R. L., Watkins S. L., Wong C. S., Williams G. D., Tarr P. I. von Willebrand factor and von Willebrand factor-cleaving metalloprotease activity in Escherichia coli O157:H7-associated hemolytic uremic syndrome. Pediatr Res. 2001 May;49(5):653–659. doi: 10.1203/00006450-200105000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai H. M. High titers of inhibitors of von Willebrand factor-cleaving metalloproteinase in a fatal case of acute thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Am J Hematol. 2000 Nov;65(3):251–255. doi: 10.1002/1096-8652(200011)65:3<251::aid-ajh13>3.0.co;2-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai H. M., Lian E. C. Antibodies to von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease in acute thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. N Engl J Med. 1998 Nov 26;339(22):1585–1594. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199811263392203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai H. M., Rice L., Sarode R., Chow T. W., Moake J. L. Antibody inhibitors to von Willebrand factor metalloproteinase and increased binding of von Willebrand factor to platelets in ticlopidine-associated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Ann Intern Med. 2000 May 16;132(10):794–799. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-132-10-200005160-00005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai H. M., Sussman I. I., Nagel R. L. Shear stress enhances the proteolysis of von Willebrand factor in normal plasma. Blood. 1994 Apr 15;83(8):2171–2179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai Han-Mou, Shulman Keith. Rituximab induces remission of cerebral ischemia caused by thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Eur J Haematol. 2003 Mar;70(3):183–185. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0609.2003.00026.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesely Sara K., George James N., Lämmle Bernhard, Studt Jan-Dirk, Alberio Lorenzo, El-Harake Mayez A., Raskob Gary E. ADAMTS13 activity in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura-hemolytic uremic syndrome: relation to presenting features and clinical outcomes in a prospective cohort of 142 patients. Blood. 2003 Mar 13;102(1):60–68. doi: 10.1182/blood-2003-01-0193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veyradier A., Obert B., Houllier A., Meyer D., Girma J. P. Specific von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease in thrombotic microangiopathies: a study of 111 cases. Blood. 2001 Sep 15;98(6):1765–1772. doi: 10.1182/blood.v98.6.1765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng X., Chung D., Takayama T. K., Majerus E. M., Sadler J. E., Fujikawa K. Structure of von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease (ADAMTS13), a metalloprotease involved in thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. J Biol Chem. 2001 Sep 13;276(44):41059–41063. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C100515200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng Xinglong, Pallera Arnel M., Goodnough Lawrence T., Sadler J. Evan, Blinder Morey A. Remission of chronic thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura after treatment with cyclophosphamide and rituximab. Ann Intern Med. 2003 Jan 21;138(2):105–108. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-138-2-200301210-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Plas R. M., Schiphorst M. E., Huizinga E. G., Hené R. J., Verdonck L. F., Sixma J. J., Fijnheer R. von Willebrand factor proteolysis is deficient in classic, but not in bone marrow transplantation-associated, thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood. 1999 Jun 1;93(11):3798–3802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]