Abstract
Background
Frankia sp. strains, the nitrogen-fixing facultative endosymbionts of actinorhizal plants, have long been proposed to secrete hydrolytic enzymes such as cellulases, pectinases, and proteases that may contribute to plant root penetration and formation of symbiotic root nodules. These or other secreted proteins might logically be involved in the as yet unknown molecular interactions between Frankia and their host plants. We compared the genome-based secretomes of three Frankia strains representing diverse host specificities. Signal peptide detection algorithms were used to predict the individual secretomes of each strain, and the set of secreted proteins shared among the strains, termed the core Frankia secretome. Proteins in the core secretome may be involved in the actinorhizal symbiosis.
Results
The Frankia genomes have conserved Sec (general secretory) and Tat (twin arginine translocase) secretion systems. The potential secretome of each Frankia strain comprised 4–5% of the total proteome, a lower percentage than that found in the genomes of other actinobacteria, legume endosymbionts, and plant pathogens. Hydrolytic enzymes made up only a small fraction of the total number of predicted secreted proteins in each strain. Surprisingly, polysaccharide-degrading enzymes were few in number, especially in strain CcI3, with more esterolytic, lipolytic and proteolytic enzymes having signal peptides. A total of 161 orthologous proteins belong to the core Frankia secretome. Of these, 52 also lack homologs in closely related actinobacteria, and are termed "Frankia-specific." The genes encoding these conserved secreted proteins are often clustered near secretion machinery genes.
Conclusion
The predicted secretomes of Frankia sp. are relatively small and include few hydrolases, which could reflect adaptation to a symbiotic lifestyle. There are no well-conserved secreted polysaccharide-degrading enzymes present in all three Frankia genomes, suggesting that plant cell wall polysaccharide degradation may not be crucial to root infection, or that this degradation varies among strains. We hypothesize that the relative lack of secreted polysaccharide-degrading enzymes in Frankia reflects a strategy used by these bacteria to avoid eliciting host defense responses. The esterases, lipases, and proteases found in the core Frankia secretome might facilitate hyphal penetration through the cell wall, release carbon sources, or modify chemical signals. The core secretome also includes extracellular solute-binding proteins and Frankia-specific hypothetical proteins that may enable the actinorhizal symbiosis.
Background
A variety of plants, called actinorhizal plants, form N2-fixing root nodules when in symbiosis with actinobacteria of the genus Frankia. The molecular interactions governing this symbiosis, such as those involved in signaling between the bacteria and plant, or in penetrating the plant cell wall, are not well characterized, primarily because of the lack of genetic tools for generating Frankia mutants, but also because frankiae grow very slowly [1]. The genome sequences of three Frankia strains have recently become available, representing groups of frankiae having different host specificities. Frankia sp. strain HFPCcI3 (CcI3) is a narrow host range Casuarina isolate, F. alni strain ACN14a (ACN) is a more cosmopolitan Alnus isolate, and Frankia sp. strain EaN1pec (EAN) is a broad host range strain, isolated from Elaeagnus [2]. Although the strains are closely related (97.8–98.9% identity of 16S rRNA genes), their genomes range in size from 5.4 Mbp for CcI3, to 7.5 Mbp for ACN, to 9.0 Mbp for EAN [2]. In addition to the differences in host range and genome size, strains CcI3 and ACN also differ from strain EAN in carbon source usage in culture and in the manner of root infection. EAN can transport and grow on sugars such as fructose, sorbitol, or mannitol using a phosphotransferase system, while CcI3 grows best on pyruvate, and ACN on propionate or acetate [1]. Only EAN can penetrate plant roots intercellularly and via root hair infection, while CcI3 and ACN enter root cells solely through the latter method [1].
An examination of the frankial genomes recently revealed that Frankia strains lack the common nod genes involved in synthesizing signals in legume endosymbionts (Rhizobium and related genera), so an alternative system of chemical signaling between the plant and bacterium to form the root nodule must exist. It is likely that secreted proteins play a role in host-microbe interactions because of the intimate contact between plant and bacterium that occurs within the plant cell. During infection, Frankia hyphae within root cells are encapsulated by plant cell wall material, deposited as the organism penetrates from cell to cell, and consisting of cellulose, pectin, and xylan [3,4]. Cellulases, pectinases, and proteases have been reported in the culture medium of various Frankia strains, and have been proposed to participate in root infection [5-9]. Such proposals are logical since many members of the actinobacteria are nutrient scavengers that secrete enzymes which break down biopolymers and other compounds [10,11]. Acidothermus cellulolyticus, the closest known relative of Frankia, also in the suborder Frankineae, is noted for its cellulolytic ability. More distantly related Streptomyces species secrete chitinases, xylanases, cellulases and proteases into the soil environment [10]. Bacterial and fungal plant pathogens are also known to secrete many hydrolytic enzymes [12,13]. In contrast, legume endosymbionts (Rhizobium and other α-proteobacteria) do not appear to rely on hydrolases during nodulation, though this topic is still a matter of debate [14]. Indeed, it may be counterintuitive for a plant mutualist to secrete enzymes that degrade host tissue, since pectin cell wall fragments have been shown to act as endogenous elicitors of plant defense responses [15]. On the other hand, polysaccharolytic activity reported in Frankia strains, with no observed utilization of breakdown products (e.g. glucose), implies an additional function for these enzymes.
Protein secretion in Gram-positive bacteria is mediated mainly by the general secretory (Sec) and twin arginine translocation (Tat) pathways, and to a lesser extent by ABC (ATP-binding cassette) transporters and other minor pathways such as the ESAT-6 system in mycobacteria [16,17]. Proteins are targeted to both the Sec and Tat secretion systems by means of an N-terminal signal peptide. Both types of signal peptides contain a positively charged N-region, followed by a hydrophobic H-region, and ending with a cleavage site, recognized by signal peptidase I in the Sec system [18]. Tat signal peptides have a longer N-region containing a twin-arginine consensus motif, a less hydrophobic H-region, and "Sec avoidance" residues near the cleavage site [19]. In this work, we used SignalP 3.0 and TATFIND 1.4 to predict the individual secretomes (sets of secreted proteins) of each Frankia strain, as well as the secretome shared by all three strains, which we termed the core Frankia secretome [20-22]. The Frankia secretomes and secretion machinery genes were compared to those of related actinobacteria and other plant-associated bacteria. We reasoned that secreted proteins needed for symbiosis-specific processes are likely to be conserved in the core Frankia secretome, and may lack homologs in closely related actinobacteria. This comparative genomics-based secretome analysis defines proteins potentially involved in the actinorhizal symbiosis.
Results and Discussion
Secretion systems
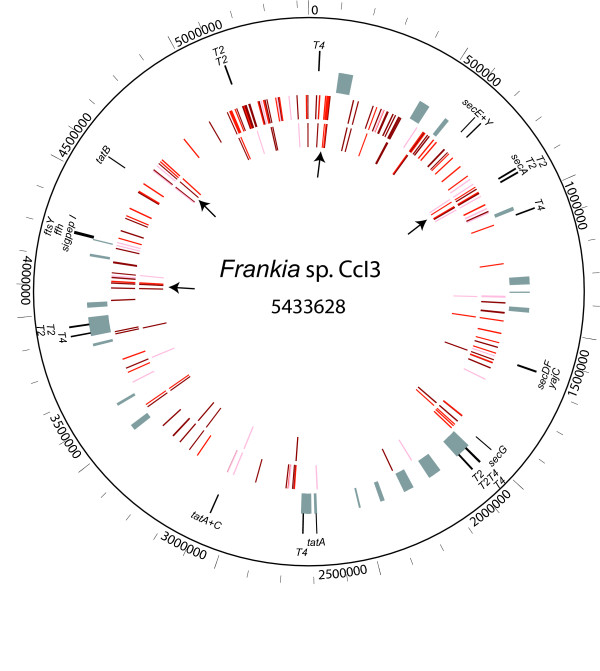
Before predicting the Frankia secretomes, the genomes were scanned for the presence of secretion systems found in other actinobacteria. Genes encoding conserved secretion machinery-related proteins were identified based on the COGs (Clusters of Orthologous Groups) annotations, and are listed in Additional File 1. All genes necessary for the Sec translocation apparatus are present in each Frankia strain. These encode proteins forming the main membrane channel-forming complex, SecYEG, the cytosolic ATPase SecA, the auxiliary proteins SecD, SecF, and YajC, and the chaperones Ffh and FtsY. As in other Gram-positive bacteria, secB is not present [23]. The most closely related homologs to each of these genes are in other actinobacteria. The order and composition of genes surrounding the Sec machinery genes are similar or identical to those in the close actinobacterial relatives Acidothermus cellulolyticus and Kineococcus radiotolerans, and in the more distantly related Streptomyces avermitilis (data not shown). The locations of these genes in the CcI3 genome are depicted in the circular map in Figure 1 (second circle in), along with areas of putative prophage integration (third circle from outside). Genes encoding the twin-arginine translocase (Tat) system, tatA, tatB, and tatC, are also present in the three genomes. In Frankia and in the majority of other sequenced actinobacterial genomes, tatC is present in a single copy, with a tatA directly preceding it, while tatB is located separately from these genes (Figure 1). Each genome has at least one additional copy of tatA.
Figure 1.
Genome map of strain CcI3. Circles, from the outside, show (1) the coordinates in bp, beginning at 0 = dnaA; (2) genes encoding components of the Sec and Tat pathways, and homologs to Type II (T2) and Type IV (T4) secretion proteins; (3) putative prophage regions, consisting of hypothetical proteins bordered by phage integrases; (4) ORFs in the core Frankia secretome; (5) ORFs in the core Frankia-specific secretome. Colors indicate the number of strains in which a signal peptide was predicted: three (dark red), CcI3 and one other strain (medium red), or only ACN and EAN (light red). Arrows indicate clusters of conserved secreted proteins.
Eight genes are annotated as encoding components of a Type II secretion (T2S) system. The closest homologs to these T2S genes are found in other actinobacterial genomes. Gram-negative pathogens secrete toxins via T2S; proteins are translocated to the periplasm by the Sec or Tat system, and then across the outer membrane by the Type II complex [24]. The T2S proteins in Frankia are also similar to the Flp pilus assembly proteins such as the ATPase CpaF, TadA, or TadC. The tad (tight adherence) locus is widespread in bacteria and is involved in adhesion or secretion [25]. The T2S/Flp pilus/Tad homologs in the Frankia genomes occur in operons consisting of two or three genes. There are four of these operons in both the CcI3 and EAN genomes, but only two in the ACN genome. The two operons that are not shared with ACN (Additional File 1) coincide with putative prophages in CcI3 (Figure 1).
The CcI3 and EAN genomes have genes annotated as encoding VirB4 and VirD4 components of the Type IV secretion (T4S) system. Type IV secretory pathways transport macromolecules (proteins or DNA) across the cell envelope in Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. VirB4 and VirD4, located in the cytoplasmic membrane, bind ATP and provide the energy for translocation [26]. The predicted T4S components have low sequence similarity to known T4S proteins, and instead resemble integral membrane proteins with ATP-binding domains. Only one putative VirB4 homolog is conserved among all three strains (CcI3 gi|86738757) and has the highest similarity to an ATP-binding protein from Streptomyces species. CcI3 and EAN each have VirB4- and VirD4-related proteins that are not found in the ACN genome, and most of these are located near phage integrase or excisionase genes.
Based on the observation that genes encoding both the Sec and Tat secretion machinery in Frankia are not only present, but located in conserved regions (in the case of tatA/tatC) in other actinobacterial genomes, it is likely that both of these systems are functional in Frankia. In contrast, it is less clear whether the proteins annotated as "Type II secretion" and "VirB4/D4" homologs constitute significant export pathways in Frankia, as very low sequence similarity is seen between the frankial genes and the known T2S and T4S proteins. These putative secretion machinery genes are not well conserved across the three strains, and appear to be associated with prophage regions in most cases.
Individual Frankia secretomes
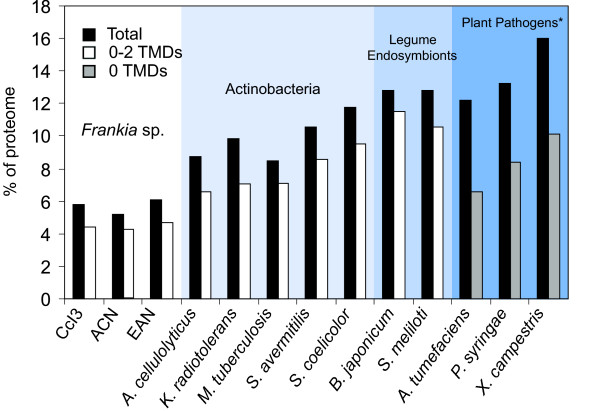
The complete CDS (coding sequence) translations from each frankial genome were analyzed with SignalP 3.0, and then scanned for transmembrane domains with TMHMM v. 2.0 [22,27]. The predicted secretomes for individual strains consist of proteins with signal peptides predicted by both SignalP methods, neural networks (NN) and hidden Markov models (HMM), and containing between zero and two transmembrane (TM) domains. These totals, shown in Table 1, Columns 1–3 (numbers outside parentheses), have been used to estimate the number of secreted proteins in other genome-based secretome studies [28]. The secretomes comprise similar percentages of the proteomes of each strain: 4.4% (197 of 4499 CDS) in CcI3, 4.1% (279 of 6711 CDS) in ACN, and 4.8% (346 of 7191 CDS) in EAN (Table 1, Figure 2). Since the annotation for F. alni strain ACN was performed by MaGe [29] rather than the Joint Genome Institute [30], differences in the annotation of start codons were observed, which may account for differences in signal peptide predictions (see Methods).
Table 1.
Signal peptide-containing proteins in individual and core secretomes. Only sequences containing 0–2 transmembrane domains (TMDs) as predicted by TMHMM are shown.
| Function | CcI3* | ACN* | EAN* | Core secretome† | Core Frankia-specific‡ |
| Cell Wall/Growth | 14 (4) | 13 (6) | 15 (8) | 17 | 6 |
| Hydrolase | 10 (9) | 17 (9) | 21 (6) | 12 | 4 |
| Metabolism | 42 (99) | 55 (159) | 56 (163) | 59 | 7 |
| Regulation | 10 (15) | 13 (19) | 11 (20) | 10 | 2 |
| Solute-binding | 18 (1) | 28 (8) | 62 (12) | 14 | 4 |
| Hypothetical | 103 (110) | 153 (177) | 181 (175) | 49 | 29 |
| Total | 197 (238) | 279 (378) | 346 (384) | 161 | 52 |
* Numbers outside parentheses are predicted to contain signal peptides by both SignalP methods (NN and HMM); numbers inside parentheses are additional proteins predicted to contain a signal peptide by only one method.
† Orthologous proteins present in all strains with a signal peptide predicted in two or three strains
‡ Frankia-specific: when CcI3 sequences from the core secretome list were BLAST searched against four closest actinobacterial relatives, no hits retrieved at an E value cutoff of 10-20
Figure 2.
Comparative secretome sizes. The secretome of each organism is shown as the percentage of coding sequences in the proteome with signal peptides predicted by both SignalP methods (NN & HMM), and containing 0–2 transmembrane domains (TMDs). The genomes of Frankia strains, actinobacteria and legume endosymbionts were analyzed with SignalP 3.0 and TMHMM as described in the Methods. *Data for plant pathogens (analyzed with SignalP, but only reporting proteins with zero TMDs) were adapted from Preston et al., 2005.
Table 1 categorizes the secretome proteins based on annotations from the NCBI database, and a complete list of potentially secreted proteins can be found in Additional File 2. "Cell wall/Growth" includes peptidoglycan-binding proteins and transglycosylases. "Hydrolases" are also listed in Table 2, and are addressed in more detail in the discussion below. "Metabolism," the broadest group, encompasses dehydrogenases, transferases, phosphatases, and enzymes with broadly defined functions. "Regulation" usually refers to sensor histidine kinases, while "solute-binding" refers to extracellular binding of molecules presumably for transport into the cell. Hypothetical proteins accounted for roughly half of the proteins in the individual secretomes.
Table 2.
Hydrolases with signal peptides in one or more strains
| Gene present in three strains | CcI3 gi | ACN gi | EAN gi | |
| Polysaccharolytic | Glycoside hydrolase, family 16 | 86742522 | 111222085 | 158319021† |
| Esterolytic/Lipolytic | Patatin | 86739488 | 111220771‡,111222061† | 158317574, 158312853 |
| Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) depolymerase-like* | 86738795 | 111219601† | 158312237, 158318953 | |
| Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) depolymerase-like* | 86743135 | 111224988 | 158313427, 158312582 | |
| Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) depolymerase-like* | 86739947 | 111221400† | 158314094 | |
| Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) depolymerase-like* | 86742257 | 111225134† | 158313019† | |
| Putative esterase | 86741433 | 111223634†, 111224716† | 158313383, 158315460 | |
| Secretory lipase* | 86738753 | 111219534‡, 111224342 | 158311883† | |
| Proteolytic | Metalloprotease-like protein | 86741105 | 111223246† | 158315133 |
| Peptidase M16-like | 86742474 | 111225385† | 158312786† | |
| Peptidase M22, glycoprotease | 86739340† | 111220592 | 158317749† | |
| Peptidase M23B | 86742263† | 111225140 | 158313012 | |
| Peptidase S1 and S6, chymotrypsin/Hap | 86738792 | 111219598 | 158318956† | |
| Peptidase S1 and S6, chymotrypsin/Hap | 86740691 | 111223367‡ | 158318071 | |
| Peptidase S8 and S53 subtilisin kexin sedolisin | 86742624 | 111225604 | 158312643 | |
| Peptidase S15 | 86742910† | 111224424† | 158315881 | |
| Peptidase S16 lon domain protein | 86742463 | 111225373 | 158312797 | |
| Putative peptidase domain | 86742587† | 111225562 | 158312677 | |
| Hypothetical | Alpha/beta hydrolase fold | 86739338 | 111220590† | 158317752 |
| Alpha/beta hydrolase fold | 86742456 | 111225365† | 158312806† | |
| Alpha/beta hydrolase fold | 86741553 | 111223803 | 158313859† | |
| Hypothetical protein; putative glycosidase* | 86742141 | 111222591 | 158317255 | |
| Hypothetical protein; putative glycosidase* | 86739771 | 111221236 | 158312651† | |
| Hypothetical protein; putative lipase | 86742918 | 111225845 | 158318206 | |
| Hypothetical protein; putative GDSL lipase | 86743055† | 111226008‡ | 158312060 | |
| Hypothetical protein; putative xylanase | 86741387 | 111220334 | 158314619 | |
| Gene present in two strains | ||||
| Polysaccharolytic | Cellulase* | x | 111224344†, 111224345† | 158313493†, 158318914 |
| Glycoside hydrolase, family 3, N-terminal | x | 111220352 | 158317032 | |
| Glucan endo-1,3-beta-D-glucosidase | x | 111221161 | 158318718 | |
| Esterolytic/Lipolytic | Esterase | x | 111221893 | 158313421† |
| Feruloyl esterase* | x | 111221879 | 158315070 | |
| Lipase class 2 | 86739361† | x | 158312565 | |
| Putative carboxylesterase/lipase | x | 111221691 | 158315258† | |
| Putative lipase | x | 111223894, 111223109 | 158314118† | |
| Proteolytic | Peptidase S8 and S53, subtilisin | x | 111224419 | 158314198 |
| Putative protease | 86741028 | x | 158315902 | |
| Gene present in one strain | ||||
| Polysaccharolytic | Arabinogalactan endo-1,4-beta-galactosidase | x | x | 158314089 |
| Glycoside hydrolase, family 26 | 86741945 | x | x | |
| Glycoside hydrolase, family 32 | x | x | 158318776 | |
| Levanase | x | x | 158318763 | |
| Putative glycosidase | x | 111223066 | x | |
| Putative xylanase | x | 111222228 | x | |
| Esterolytic/Lipolytic | Lipolytic enzyme, G-D-S-L | x | 111222700 | x |
| Phospholipase A2 | x | x | 158315136 | |
| Hypothetical | Alpha/beta hydrolase fold | 86741921 | x | x |
* Phylogenetic trees shown in Figure 3. For hypothetical glycosidases, Figure 3(E) shows addtional homologs not listed here.
† Not predicted to contain a signal peptide by SignalP or TATFIND 1.4
‡ Signal peptide predicted after manual inspection/re-annotation of start site region (see Methods)
Table 1 includes some proteins also predicted to contain Tat signal peptides. In CcI3, TATFIND 1.4 predicted 30 Tat signal sequences, and 20 of these were also predicted to have Sec signal peptides. Likewise, 22 of 31 Tat signal sequences in ACN and 48 of 76 in EAN had signal peptides predicted by both TATFIND and SignalP. The results of the TATFIND analysis, including SignalP predictions and Tat signal peptide sequences, can be found in Additional File 3.
Comparison with secretomes from other bacteria
We analyzed seven other bacterial genomes with SignalP and TMHMM: five actinobacterial relatives of Frankia, and two legume endosymbionts, Bradyrhizobium japonicum and Sinorhizobium meliloti. Figure 2 compares the secretomes of each of these, reported as a percentage of the total proteome. Data for three plant pathogen genomes, adapted from Preston et al. (2005), are also included [28]. The secretomes of the two closest relatives of Frankia, Acidothermus cellulolyticus and Kineococcus radiotolerans, comprise higher percentages of the total proteome of each species (6.6% and 7%). Roughly 30% of these secreted proteins are shared with those of Frankia, while another 30% are hypothetical proteins not found in Frankia (using an E value cutoff of 10-20). Notable differences include ten cellulose-degrading enzymes in A. cellulolyticus and 20 extracellular solute-binding proteins for transport of sugars in K. radiotolerans. The secretome of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, making up 7.1% of its proteome, is enriched in lipoproteins and Mycobacterium-specific surface proteins of the PE_PGRS family. The secretomes of the two Streptomyces species make up higher percentages of their proteomes (8.6% and 9.5%), roughly double the percentages seen in Frankia, and contain many potential secreted hydrolytic enzymes (100 in S. avermitilis and 134 in S. coelicolor). The legume symbionts and the plant pathogens analyzed have more than double the percentages of secreted proteins predicted in Frankia (Figure 2). Fewer secreted hydrolases are predicted in legume endosymbionts than in plant pathogens, but both secrete substantially more solute-binding proteins than are found in the Frankia genomes, suggesting a wider range of nutritional sources used. The comparatively small size of the Frankia secretomes may reflect the narrow scope of carbon sources utilized by Frankia strains, especially strains CcI3 and ACN, which have less than half of the solute-binding proteins found in EAN (Table 1, Additional File 2). The secretion of relatively few proteins could also affect its recognition as "friend or foe" by host plants. Unlike the extensive biopolymer-degrading capability observed in Streptomyces, it may be beneficial for Frankia to secrete few degrading enzymes in its mutualistic interactions with plants.
Secretory hydrolases
A major objective of the current study was to screen the Frankia genomes for secreted hydrolytic enzymes, which have been hypothesized to play a role in nodulation. As seen in Table 1, the Frankia genomes have between 10–21 hydrolases with signal peptides predicted by both SignalP methods (NN and HMM), and an additional 6–9 predicted by only one SignalP method. Table 2 lists all hydrolytic enzymes identified in at least one Frankia strain with signal peptides predicted by at least one SignalP method (NN or HMM). Those marked with "‡" had signal peptides predicted only after manual inspection of the N-terminal alignments, and adjustment of the start sites to match those of the other two strains (see Methods). Sequences listed in the same row retrieved one another in a BLAST search using a permissive E value cutoff of 10-5. An "x" in Table 2 indicates the absence of any hits to other frankial sequences at this E value. In many cases, sequences with signal peptides predicted in one strain lack signal peptides in the corresponding proteins in other strains (denoted by †). This may be due to ancestral N-terminal sequences having diverged significantly in each lineage. Alternatively, the similarly annotated proteins within a row may actually only share a conserved domain, but belong to different families. If this is the case, the presence or absence of a signal peptide in one or more strains may indicate distinct ancestral origin, with only superficial (or convergent) similarity to other sequences retrieved in a BLAST search.
Of the secretory hydrolases, lipolytic and esterolytic enzymes had the most signal peptides predicted (Table 2). Lipases and esterases secreted by frankial strains could depolymerize components of plant cell walls, or could modify lipid-based signaling molecules generated by plants in response to stress or pathogen attack [31]. There have been no direct reports of lipase activity in Frankia strains, though whole cell esterase zymograms have been used to distinguish between isolates, and the addition of long chain fatty acids to culture media enhances growth of some strains [32,33]. Lipase activity may be conferred by a conserved secretory lipase (discussed below) or by the putative lipases, one of which (gi|86743055 in CcI3) is similar to a GDSL lipase from Streptomyces rimosus that has demonstrated lipolytic activity [34]. Another possible lipolytic enzyme found in the three strains is annotated as patatin, which is a storage glycoprotein in potato tubers that can act as an acyl hydrolase. Patatin-like proteins are found in many bacterial species, and phospholipase A2 activity has been shown for the patatin homolog ExoU, an exotoxin secreted via Type III secretion by P. aeruginosa [35]. Esterolytic proteins in Frankia could potentially cleave ester linkages in complex plant polysaccharides, liberating compounds for use as carbon sources or signaling molecules. For example, GDSL lipases can act as acetylxylan esterases, and feruloyl esterases cleave ferulic acid from the sugar backbone of pectin [36,37]. The polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) depolymerase-like proteins could degrade polyesters such as suberin, a polyester found in plant root cell walls that consists of lipids and phenolic compounds. The accumulation of suberin in cell walls around Frankia-infected cells has been observed in Casuarina nodules [38].
In contrast to lipases and esterases, polysaccharide-degrading enzymes with signal peptides are less prevalent (Table 2). Strain EAN, which has the largest genome and widest host range, has the most polysaccharolytic enzymes, followed closely by ACN, while CcI3 has the fewest, possessing only general "glycoside hydrolase" genes. Two putative cellulolytic proteins are found in strains ACN and EAN, with a signal peptide predicted only in one EAN sequence. CcI3 lacks both of these cellulase genes. EAN (EaN1pec) has a single pectate lyase gene (gi|158314134, not shown), which is absent from CcI3 and ACN. This protein was not predicted to contain a signal peptide, though it is most similar to a pectate lyase in S. avermitilis that has a predicted Tat signal peptide. Another putative pectin-degrading enzyme found only in strain EAN is an arabinogalactan endo-1,4-beta-galactosidase, which shows highest sequence similarity to this enzyme in Burkholderia cenocepacia (42% identity, E value of 10-64). Frankia strains share a group of hypothetical proteins ("putative glycosidases" in Table 2) with several features indicating that they may act as hydrolases: all share a beta-mannanase (ManB) domain, and several are similar to Glycoside Hydrolase Family 26 or have low hits to the (Trans)-Glycosidase protein superfamily (see Methods). These proteins may potentially interact with plant cell wall polysaccharides, or with glycoproteins or glycolipids on the frankial cell envelope. No clear polysaccharases have signal peptides predicted in all three strains.
Finally, a variety of proteolytic enzymes appear to be secreted by Frankia. Peptidases with clear housekeeping functions in growth and cell wall remodeling are omitted from Table 2. Extracellular peptidases have been detected in culture supernatants of Frankia strains [6,39]. Muller and Benoist [39] described a 1300 kDa proteinase complex, composed of 11 proteinase subunits, from both cell extracts and the extracellular concentrate of Frankia strain BR, a Casuarina isolate. Based on the cleavage specificity of the proteinase subunits, Benoist et al. suggested a role in degrading cell wall proteins such as extensins [7]. The two conserved signal peptide-containing serine proteases belonging to the S1/S6/Hap family may mediate attachment to host cell surfaces, as these are similar to the Haemophilus influenzae adhesin Hap, which binds to the extracellular matrix of human cells [40]. Frankia strains can use peptides and amino acids (and have branched-chain amino acid binding proteins with signal peptides) so the presence of proteases is not unexpected.
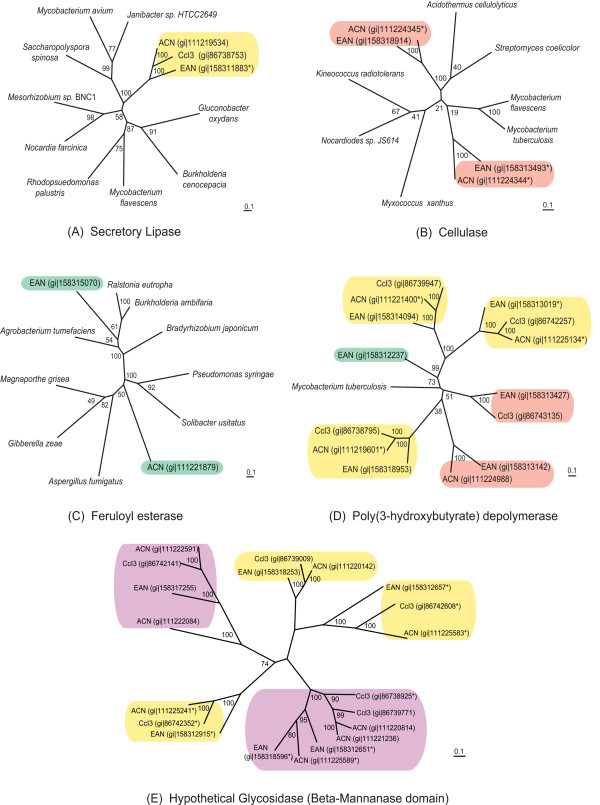
Phylogenetic trees were constructed to trace the origin of selected hydrolytic enzyme genes in the Frankia strains (asterisks in Table 2), and to provide insight on their relevance to the ecology of Frankia. Several patterns become apparent: first, conservation of a gene with a single copy in the three strains that is also present in actinobacterial ancestors. The secretory lipase gene, shown in Figure 3(A), is one of the few examples of this among hydrolases. A second pattern observed is the loss of a hydrolase gene in one or two strains. Losses have occurred most often in the genome of CcI3, which is the smallest of the three and has lost many other genes [2]. As shown in Figure 3(B), two cellulase genes are found in EAN and ACN and in closely related actinobacterial genomes, but have been lost from CcI3. Gene loss may account for the presence of other polysaccharases only in strains ACN and EAN. In contrast, several hydrolases appear to have been acquired separately by one or two Frankia strains. A feruloyl esterase gene is seen in both EAN and ACN, but there is minimal similarity between the sequences, and the tree in Figure 3(C) suggests that these did not originate from a common actinobacterial ancestor, but rather may have been acquired from distantly related soil microorganisms. The fourth notable pattern is that of gene family expansion within the Frankia lineage. The four to six poly-hydroxybutyrate (PHB) depolymerase-like gene families depicted in Figure 3(D) seem to have undergone duplication in a frankial ancestor. The Frankia sequences are more similar to each other than to any other sequences in the database; the outgroup shown belongs to the lipoprotein family LpqC (also in COG3509) of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The expansion and retention of this group of genes points to Frankia-specific function, though interestingly, most of the sequences in strain ACN lack signal peptides, while these are predicted in the other two strains. Another gene family expansion is shown in Figure 3(E), which includes a total of 20 Frankia sequences, ten with signal peptides (see "putative glycosidases" in Table 2), and ten without. While non-Frankia sequences were retrieved in BLAST searches, these did not clearly associate with any Frankia sequences, and so were excluded from this unrooted tree.
Figure 3.
Phylogenetic trees of secreted hydrolytic enzyme genes. Various patterns of gene retention and acquisition are observed in Frankia hydrolase genes, including (A) conservation of an ancestral gene; (B) gene loss in one strain; (C) horizontal acquisition; (D) and (E) gene family expansion (see text). Trees were generated using PhyML (maximum likelihood method). *not predicted to contain a signal peptide by SignalP or TATFIND 1.4.
In summary, esterases, lipases, and proteases are better represented across Frankia strains than polysaccharide-degrading enzymes. The presence of a few more polysaccharases in strain EAN may be a factor in EAN's ability to penetrate plant roots intercellularly via cracks in roots, or may reflect the wider carbon source usage of this strain during saprophytic growth [41]. The patterns of hydrolase gene retention, loss, acquisition, and duplication illustrated in Figure 3 emphasize the divergent life histories of individual strains, a topic addressed on a genome-wide scale by Normand et al. [2].
The core Frankia secretome
Secreted proteins that are essential for the actinorhizal symbiosis are likely to be highly conserved in Frankia strains, and may lack homologs in closely related actinobacteria. To circumscribe this group of proteins, we first identified the core proteome, consisting of orthologous proteins in all three strains (top-scoring reciprocal BLAST hits, in the three bi-directional comparisons, using an E-value threshold of 10-20). At this E value, a total of 2080 sequences belonged to the core proteome. When the sequences of the core proteome (2080 sequences from each genome) were analyzed with SignalP, the signal peptide predictions for these orthologous proteins varied from strain to strain. It was thus necessary to define a limit for including a given protein in the core secretome. We defined the core secretome as proteins within the core proteome that had signal peptides predicted by at least one SignalP method (NN, HMM, or both) and zero to two TM domains, in at least two of the three strains. Of the initial 2080 proteins in the core proteome, 77 were predicted to contain signal peptides in all three strains, and 83 more had signal peptides in two strains; therefore, 161 proteins are estimated to encompass the core Frankia secretome (Table 1, column 4). Notably, only nine hydrolases belong to the core secretome, and these are mainly proteases, esterases, and lipases. The complete listing of proteins in the core secretome can be found in Additional File 4.
To narrow this set of proteins to those highly conserved within the Frankia lineage, the 161 sequences of the core secretome (from each genome) were BLAST searched against genomes of four actinobacterial species closely related to Frankia: Acidothermus cellulolyticus, Kineococcus radiotolerans, Streptomyces avermitilis, and Nocardia farcinica. A total of 52 sequences from the core secretome did not show significant alignment, at an E value cutoff of 10-20, to proteins of these close actinobacterial relatives. These proteins are termed Frankia-specific (see Table 1, column 5), and are listed in Table 3. About half of these sequences, especially the hypothetical proteins, did not retrieve any BLAST hits to actinobacterial proteins at a less stringent E value cutoff of 10-5. Since the sequence alignments have E values very close to zero across the three Frankia strains, it is probable that these proteins carry out novel functions, perhaps governing the interactions with host plants.
Table 3.
The Frankia-specific core secretome
| CcI3 gi | ACN gi | EAN gi | ||
| Cell wall/growth | Lytic transglycosylase, catalytic | 86742160† | 111225025 | 158313119 |
| OmpA/MotB | 86739073 | 111220228 | 158318192 | |
| Peptidoglycan-binding domain 1 | 86741674 | 111224313 | 158314338 | |
| Putative lipoprotein | 86742138 | 111224994 | 158313137 | |
| Septum formation initiator | 86742601 | 111225576 | 158312664 | |
| Transglycosylase-like | 86742920 | 111225850 | 158318320 | |
| Hydrolase | Hypothetical protein; putative glycosidase | 86742141 | 111222591 | 158317255 |
| Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) depolymerase-like | 86739947 | 111221400† | 158314094 | |
| Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) depolymerase-like | 86738795 | 111219601† | 158318953 | |
| Putative signal peptide; putative peptidase domain | 86742587† | 111225562 | 158312677 | |
| Metabolism | GCN5-related N-acetyltransferase | 86743083 | 111226044† | 158312032 |
| K+ transporting ATPase, KdpC subunit | 86741971 | 111224671 | 158312459 | |
| Lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis | 86742615 | 111225592 | 158312648† | |
| Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase, cyclophilin type | 86740087 | 111221586 | 158316890 | |
| Poly-gamma-glutamate biosynthesis protein | 86738783 | 111219578 | 158318982 | |
| Stage II sporulation E | 86739884 | 111221318 | 158317049 | |
| UvrD/REP helicase | 86743179 | 111224714 | 158313386† | |
| Regulation | Protein serine/threonine phosphatases | 86743061 | 111226019 | 158312053 |
| Protein-tyrosine kinase | 86742154 | 111225020 | 158313124† | |
| Solute-binding | ABC-type branched-chain amino acid transport, periplasmic | 86742125 | 111224977 | 158317330 |
| Extracellular ligand-binding receptor | 86741514 | 111223750 | 158314112 | |
| Extracellular solute-binding protein, family 1 | 86739179 | 111220428 | 158317895 | |
| TRAP-type uncharacterized transport system, periplasmic | 86739077 | 111220233 | 158318181 | |
| Hypothetical | Allergen V5/Tpx-1 related | 86743037 | 111225986 | 158312084† |
| Hypothetical protein Francci3_0037 | 86738760† | 111219542 | 158319012 | |
| Hypothetical protein Francci3_0040 | 86738763 | 111219548 | 158319008 | |
| Hypothetical protein Francci3_0066 | 86738789 | 111219591† | 158318965 | |
| Hypothetical protein Francci3_0077 | 86738800 | 111219607 | 158318948 | |
| Hypothetical protein Francci3_0189 | 86738909 | 111224111 | 158318981 | |
| Hypothetical protein Francci3_0265 | 86738982 | 111220095 | 158318303† | |
| Hypothetical protein Francci3_0293 | 86739009 | 111220142 | 158318253 | |
| Hypothetical protein Francci3_0740 | 86739453† | 111220717 | 158317614 | |
| Hypothetical protein Francci3_0760 | 86739473 | 111220756† | 158317589 | |
| Hypothetical protein Francci3_0772 | 86739485 | 111220768 | 158317577† | |
| Hypothetical protein Francci3_0777 | 86739490 | 111220773 | 158317572 | |
| Hypothetical protein Francci3_0789 | 86739502 | 111220806 | 158317543 | |
| Hypothetical protein Francci3_1158 | 86739866† | 111221294 | 158317064 | |
| Hypothetical protein Francci3_1658 | 86740363 | 111223957 | 158313918† | |
| Hypothetical protein Francci3_2782 | 86741470 | 111223676 | 158314336 | |
| Hypothetical protein Francci3_3087 | 86741773 | 111224471 | 158313666 | |
| Hypothetical protein Francci3_3155 | 86741841† | 111224558 | 158313592 | |
| Hypothetical protein Francci3_3200 | 86741886† | 111224609 | 158313544 | |
| Hypothetical protein Francci3_3489 | 86742171 | 111225037 | 158313108 | |
| Hypothetical protein Francci3_3886 | 86742565† | 111225535 | 158312696 | |
| Hypothetical protein Francci3_3888 | 86742567 | 111225539 | 158312694† | |
| Hypothetical protein Francci3_4257 | 86742932 | 111225862 | 158312224† | |
| Hypothetical protein Francci3_4291 | 86742966 | 111225895† | 158312188 | |
| Hypothetical protein Francci3_4326 | 86743001† | 111225939 | 158312147 | |
| Hypothetical protein Francci3_4510 | 86743185 | 111226172 | 158319016 | |
| Kelch repeat protein | 86738890 | 111219845 | 158313864 | |
| Protein of unknown function DUF37 | 86743221 | 111226215 | 158319056 | |
| Protein of unknown function DUF459 | 86742591† | 111225566 | 158312673 | |
| †Not predicted to contain a signal peptide by SignalP or TATFIND 1.4 | ||||
Other proteins listed in Table 3 may have roles in the actinorhizal symbiosis. The proteins listed under "Metabolism" include a peptidylprolyl isomerase, which could assist in modifying the proline-rich proteins of the plant cell wall, or may ensure proper folding of secreted proteins. A peptidylprolyl isomerase (Mip) in Legionella pneumophila, in concert with a serine protease, facilitates entry into lung epithelial cells [42]. The lipopolysaccharide or poly-γ-glutamate biosynthesis proteins may alter cell surface characteristics, contributing to host recognition of the frankial cell envelope. The former has minimal similarity to other proteins in the non-redundant database, while the latter is similar (33% identity, E value of 10-37) to a capsule biosynthesis protein from Bacillus thuringiensis. Twelve solute-binding proteins are found in the core Frankia secreteome. The extracellular solute-binding protein (Family 1) has highly conserved sequence across Frankia, with the next best BLAST hits revealing low sequence similarity to sugar-binding proteins in Mesorhizobium loti and Rhizobium leguminosarium (E values of 10-17). TRAP-type transporters, akin to those in rhizobia, could transport dicarboxylic acids, known carbon sources of some Frankia strains. We propose that these conserved secreted proteins, especially those with little homology to other bacterial proteins, are likely candidates for symbiosis-related functions.
Genome map
Mapping the gene locations of core secretome proteins on the CcI3 chromosome (Figure 1) revealed clustering of conserved secreted proteins, in some cases adjacent to secretion machinery genes. The outer two circles (after the scale) depict the secretion machinery genes, and putative prophage regions, respectively. The third circle in shows the genes encoding the proteins of the core secretome, while the fourth circle in depicts the genes for the proteins in the core Frankia-specific secretome. Colors indicate which strains have signal peptides predicted, as noted in the legend. None of the genes encoding core secretome proteins are located within prophage neighborhoods, and no horizontally transferred "secretion islands" are evident. Clustering of core secretome genes near the origin of replication is seen; this region of the chromosome also shows the most synteny among the three strains, and contains the nif genes required for nitrogen fixation [2]. Several clusters of core secretome genes are located close to secretion machinery genes (arrows, Figure 1). Beginning very close to the origin of replication, one putative secretory region of the Frankia CcI3 chromosome, from roughly 0.035 to 0.096 Mbp, includes the single conserved VirB4-like gene ("T4" in Figure 1). This stretch of 40 ORFs encodes thirteen proteins with signal peptides, four of which are Frankia-specific, as well as an additional nine Frankia-specific proteins (without signal peptides). The secreted proteins include the secretory lipase, the poly-gamma-glutamate biosynthesis protein, the S1/S6/Hap family peptidase, and a PHB depolymerase. In another region, between 0.87 and 0.92 Mbp, the conserved patatin gene is situated several genes downstream of the secA gene, and a few genes upstream of an operon of T2S genes. Downstream of the T2S genes is a conserved hypothetical protein, "Francci3_0789," which has Tat signal peptides predicted in all three strains. This region has five Frankia-specific secreted proteins (out of 40 ORFs), as well as an additional twelve signal peptide-containing proteins and nine Frankia-specific (non-secretory) proteins. Other Frankia-specific hypothetical proteins are clustered in regions near 4.1 Mbp and 4.7 Mbp (Figure 1). Several potential Tat-translocated proteins are found near 4.1 Mbp, and three highly conserved hypothetical proteins (Francci3_3886, Francci3_3889, and Francci3_3891) near 4.7 Mbp are located upstream of a channel protein of the hemolysin III family, which could facilitate protein export. The two peptidylprolyl isomerase genes are located near secretion machinery genes. The cyclophilin-type peptidylprolyl isomerase is located shortly downstream of the operon containing yajC, secD, and secF, while the other (FKBP-type) is found four genes away from the tatA/tatC genes. Two genes encoding proteins with putative Tat signal peptides predicted by TATFIND are roughly fifteen genes away from the tatA/C genes. One of these is a phosphoesterase; the other is annotated as a Dyp-type peroxidase (Additional File 3). Both of these types of proteins were shown to be secreted via the Tat pathway in other bacteria [43,44]. By situating genes in putative secretory regions of the genome, the gene neighborhoods in Figure 1 both highlight regions of interest and support the signal peptide predictions for these sequences.
Conclusion
We screened three Frankia genomes for genes encoding protein secretion machinery and proteins with signal peptides. The protein secretion systems present in Frankia correlate with those found in other actinobacteria, but the predicted secretomes are reduced in size compared to those of other soil bacteria. We propose that this is an adaptation to an endosymbiotic lifestyle, in which Frankia secretes few proteins that might trigger host defenses. The Frankia genomes we examined do not have a conserved set of obvious polysaccharide-hydrolyzing enzymes. This finding challenges the hypothesis that Frankia hydrolyzes plant cell wall polymers during nodulation, though it is possible that the general glycosidases, esterases, or proteases contribute to this function. Genomic evidence suggests that polysaccharases are used to a greater or lesser degree depending on the lifestyle and mode of infection of particular strains, with strain CcI3 having lost secretory hydrolase genes present in the other two strains. The EAN genome also includes four arabinofuranosidases and two rhamnosidases without signal peptides, absent from CcI3 and ACN, which may be used to break down oligosacccharides derived from hemicelluloses. In the absence of plant cell wall degradation, it is likely that Frankia secretes novel classes of effector proteins to communicate with its host, a situation similar to that recently described in the biotrophic plant pathogenic fungus, Ustilago maydis, that is also deficient in cell wall hydrolytic enzymes[45]. The core Frankia secretome represents a conserved set of candidate proteins, including those with hydrolytic, surface-associated, solute-binding, and unknown functions, to assess for involvement in root infection. Mapping the locations of conserved secreted protein genes allowed us to identify genomic "hotspots" containing potentially secreted proteins and other unique frankial proteins. This genome-based Frankia secretome, combined with ongoing proteomics studies, will help navigate the way to a more complete understanding of the actinorhizal symbiosis.
Methods
Sequence analysis
The FASTA amino acid sequences of the three Frankia genomes [CcI3, NCBI RefSeq: NC_007777; ACN14a, NCBI RefSeq: NC_008278; EaN1pec, NCBI RefSeq: NC_009921] and from the Streptomyces avermitilis [GenBank: BA000030], Nocardia farcinica [GenBank: AP006618], Mycobacterium tuberculosis CDC1551 [GenBank: AE000516], Kineococcus radiotolerans [GenBank: CP000750], Acidothermus cellulolyticus [GenBank: CP00481], Bradyrhizobium japonicum [GenBank: BA000040], and Sinorhizobium meliloti [GenBank: AL591688] genomes (including the two S. meliloti plasmids, pSymA [GenBank: AE006469] and pSymB [GenBank: AL591985]) were obtained from the GenBank or NCBI RefSeq FTP sites [46,47]. All sequences were truncated to the first 70 amino acids and analyzed with the SignalP 3.0 program [20]. Sequences predicted to contain a signal peptide by SignalP were analyzed with TMHMM 2.0 [48] to determine the number of transmembrane (TM) domains. The CDS translations of the three Frankia genomes were also searched for the twin-arginine translocation (Tat) sequence motif using TATFIND 1.4 [21]. TATFIND searches for the motif [HAPKRNTGSDQE] RR [APKRNTGSDQE] [IWFLVYMCHAPNT] [ILVMF] within the first 35 amino acids of a sequence (where any of the amino acids in brackets satisfy the match) and scores positive if this motif is followed by hydrophobic stretch of at least 13 amino acids (within 22 downstream residues).
Identification of hydrolytic enzymes
Hydrolytic enzymes were identified with the annotation provided by the Joint Genome Institute (CcI3 and EAN) or MaGe (ACN) [29,30]. To confirm that none of the signal peptide-containing hypothetical proteins were hydrolases, these sequences were searched for conserved domains with the SMART (Simple Modular Architecture Research Tool) program, and analyzed for hits to SCOP (Structural Classification of Proteins) protein superfamilies using the Superfamily 1.69 server [49,50]. The SCOP superfamily analysis led to the identification of four hypothetical proteins with slight similarity (E values between 10-5 and 10-22) to the "(Trans)glycosidase" superfamily (see Table 2 and Figure 3E) and three with hits (E values between 10-8 and 10-27) to the "Pectin lyase-like" superfamily (see Additional File 2). In addition, to confirm that the gene annotation and BLAST searches had not missed cellulase, pectinase, or xylanase genes in the frankial genomes, a PSI-BLAST search was performed [51]. The three genomes were searched using point-specific scoring matrices (PSSMs) of nine conserved hydrolase domains (three Pfam or COG domains for each type of hydrolase listed above) obtained from the NCBI conserved domain database (CDD) FTP site [52]. Only the previously identified polysaccharide-degrading enzymes were retrieved using this method.
For construction of phylogenetic trees, a representative subset of top-scoring BLAST hits was chosen and amino acid sequences were aligned with MUSCLE [53]. To generate trees, PhyML (maximum likelihood method) was used with the JTT substitution matrix and 100 non-parametric bootstrap replicates [54]. Trees were visualized using TreeView [55].
Identification of the core secretome
To find orthologous proteins shared among the three strains, the complete CDSs from each Frankia genome were BLAST searched against those of the other two strains, using an E-value threshold of 10-20 [56]. Using a custom Perl script, we identified the sequences that retrieved each other as the top BLAST hit (orthologs) in all three bi-directional comparisons. The amino acid sequences of these 6240 proteins (2080 from each strain) were then analyzed with SignalP 3.0 and TMHMM 2.0. Of these orthologous sequences, those with signal peptides predicted by one or both SignalP methods (NN or HMM) and having 0–2 transmembrane domains, in two or three of the strains, were considered to belong to the core Frankia secretome.
Manual inspection of start codons
In cases where sequences from two strains had signal peptides predicted but the orthologous sequence from the third did not, the start codon region of that sequence was inspected manually, based on the amino acid sequence alignment with its orthologs. Alignments were viewed with the BLink tool from NCBI [57], and upstream regions were viewed with Artemis through the Frankia alni ACN14a Genoscope website, and the Integrated Microbial Genomes (IMG) website [29,58]. Depending on the conserved start position seen in the N-terminal sequence alignments, and on the presence of a putative Shine-Dalgarno sequence upstream of the start codon, some start sites were manually adjusted and analyzed again with SignalP. A total of 48 sequences in strain ACN were inspected (because CcI3 and EAN had signal peptides in the orthologous sequences); of these, 20 were predicted to contain a signal peptide after manual adjustment. Manual inspection of start codons was also carried out for sequences in the core proteome with a signal peptide predicted in only one strain (by both SignalP methods). Of 104 proteins inspected, only one additional signal peptide was predicted (ACN, gi|111220881). As a control measure, a subset of hydrolases lacking signal peptides was inspected to verify that signal peptides were not missed due to incorrect start codon annotation. After scanning the genome for intracellular hydrolases (of the types listed in Table 2, but not already present in this table), 96 were found in CcI3, 129 in ACN, and 195 in EAN. These were BLAST searched against each of the other genomes, and subgroups were selected in which the start position of the alignment between the query and subject sequences was > 10 amino acids apart. The N-terminal regions of 25 conserved intracellular hydrolases, and 8 hydrolases unique to EAN were inspected, and none of these resulted in new signal peptide predictions.
Authors' contributions
JEM and DRB developed the study, performed the bioinformatics analyses, and wrote the manuscript. LST and PN provided the EaN1pec genome and the ACN14a genomes, respectively, and contributed to the editing of the manuscript.
Supplementary Material
Secretion machinery genes. This table lists the genes encoding secretion machinery components in the three Frankia genomes.
Individual Frankia secretomes. This table lists the proteins in each Frankia genome predicted to contain a signal peptide by both SignalP methods (NN and HMM), and with 0–2 trans-membrane domains predicted by TMHMM.
Tat signal peptides predicted by TATFIND 1.4. This table lists the proteins in each strain predicted to contain a Tat signal peptide by TATFIND 1.4, and shows their N-terminal sequences, including putative Tat motifs.
The core Frankia secretome. This table lists the 161 proteins in the core Frankia secretome, with SignalP predictions listed for each strain.
Acknowledgments
Acknowledgements
We kindly thank Mecky Pohlschröder for supplying TATFIND 1.4, and Pascal LaPierre and Bruce Link for bioinformatics programs. This work was supported by the National Science Foundation Microbial Genome Sequencing Program.
Contributor Information
Juliana E Mastronunzio, Email: juliana.mastronunzio@uconn.edu.
Louis S Tisa, Email: lst@hypatia.unh.edu.
Philippe Normand, Email: normand@biomserv.univ-lyon1.fr.
David R Benson, Email: david.benson@uconn.edu.
References
- Benson DR, Silvester WB. Biology of Frankia strains, actinomycete symbionts of actinorhizal plants. Microbiol Rev. 1993;57:293–319. doi: 10.1128/mr.57.2.293-319.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normand P, Lapierre P, Tisa LS, Gogarten JP, Alloisio N, Bagnarol E, Bassi CA, Berry AM, Bickhart DM, Choisne N, Couloux A, Cournoyer B, Cruveiller S, Daubin V, Demange N, Francino MP, Goltsman E, Huang Y, Kopp OR, Labarre L, Lapidus A, Lavire C, Marechal J, Martinez M, Mastronunzio JE, Mullin BC, Niemann J, Pujic P, Rawnsley T, Rouy Z, Schenowitz C, Sellstedt A, Tavares F, Tomkins JP, Vallenet D, Valverde C, Wall LG, Wang Y, Medigue C, Benson DR. Genome characteristics of facultatively symbiotic Frankia sp. strains reflect host range and host plant biogeography. Genome Res. 2007;17:7–15. doi: 10.1101/gr.5798407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Q, Berry AM. Localization and characterization of pectic polysaccharides in roots and root nodules of Ceanothus spp. during intercellular infection by Frankia. Protoplasma. 1991;163:93–101. doi: 10.1007/BF01323333. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Berg RH. Cellulose and xylans in the interface capsule in symbiotic cells of actinorhizae. Protoplasma. 1990;159:35–43. doi: 10.1007/BF01326633. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Safo-Sampah S, Torrey JG. Polysaccharide-hydrolyzing enzymes of Frankia (Actinomycetales) Plant and Soil. 1988;112:89–97. doi: 10.1007/BF02181757. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Muller A, Benoist P, Diem HG, Schwencke J. Age-dependent changes in extracellular proteins, aminopeptidase and proteinase activities in Frankia isolate BR. J Gen Microbiol. 1991;137:2787–2796. doi: 10.1099/00221287-137-12-2787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist P, Muller A, Diem HG, Schwencke J. High-molecular-mass multicatalytic proteinase complexes produced by the nitrogen-fixing actinomycete Frankia strain BR. J Bacteriol. 1992;174:1495–1504. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.5.1495-1504.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seguin A., Lalonde, M. Detection of pectolytic activity and pel homologous sequences in Frankia. Plant and Soil. 1989;118:221–230. doi: 10.1007/BF02232810. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Igual JM, Velazquez E, Mateos PF, Rodriguez-Barrueco C, Cervantes E, Martinez-Molina E. Cellulase isoenzyme profiles in Frankia strains belonging to different cross-inoculation groups. Plant and Soil. 2001;229:35–39. doi: 10.1023/A:1004835313723. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow M., Williams, S.T., Mordarski, M. Actinomycetes in Biotechnology. San Diego , Academic Press Inc.; 1988. pp. pp. 231–261. [Google Scholar]
- Lykidis A, Mavromatis K, Ivanova N, Anderson I, Land M, DiBartolo G, Martinez M, Lapidus A, Lucas S, Copeland A, Richardson P, Wilson DB, Kyrpides N. Genome sequence and analysis of the soil cellulolytic actinomycete Thermobifida fusca YX. J Bacteriol. 2007;189:2477–2486. doi: 10.1128/JB.01899-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartemann KH, Kirchner O, Engemann J, Grafen I, Eichenlaub R, Burger A. Clavibacter michiganensis subsp. michiganensis: first steps in the understanding of virulence of a Gram-positive phytopathogenic bacterium. J Biotechnol. 2003;106:179–191. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2003.07.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazemi-Pour N, Condemine G, Hugouvieux-Cotte-Pattat N. The secretome of the plant pathogenic bacterium Erwinia chrysanthemi. Proteomics. 2004;4:3177–3186. doi: 10.1002/pmic.200300814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage DJ. Infection and invasion of roots by symbiotic, nitrogen-fixing rhizobia during nodulation of temperate legumes. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2004;68:280–300. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.68.2.280-300.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esquerre-Tugaye MT, Boudart G, Dumas B. Cell wall degrading enzymes, inhibitory proteins, and oligosaccharides participate in the molecular dialogue between plants and pathogens. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2000;38:157–163. doi: 10.1016/S0981-9428(00)00161-3. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Pallen MJ, Chaudhuri RR, Henderson IR. Genomic analysis of secretion systems. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2003;6:519–527. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2003.09.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champion PA, Stanley SA, Champion MM, Brown EJ, Cox JS. C-terminal signal sequence promotes virulence factor secretion in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Science. 2006;313:1632–1636. doi: 10.1126/science.1131167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjalsma H, Antelmann H, Jongbloed JD, Braun PG, Darmon E, Dorenbos R, Dubois JY, Westers H, Zanen G, Quax WJ, Kuipers OP, Bron S, Hecker M, van Dijl JM. Proteomics of protein secretion by Bacillus subtilis: separating the "secrets" of the secretome. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2004;68:207–233. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.68.2.207-233.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berks BC, Sargent F, Palmer T. The Tat protein export pathway. Mol Microbiol. 2000;35:260–274. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2000.01719.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendtsen JD, Nielsen H, von Heijne G, Brunak S. Improved prediction of signal peptides: SignalP 3.0. J Mol Biol. 2004;340:783–795. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2004.05.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dilks K, Rose RW, Hartmann E, Pohlschroder M. Prokaryotic utilization of the twin-arginine translocation pathway: a genomic survey. J Bacteriol. 2003;185:1478–1483. doi: 10.1128/JB.185.4.1478-1483.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SignalP 3.0 Server http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/SignalP/
- Scott JR, Barnett TC. Surface proteins of gram-positive bacteria and how they get there. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2006;60:397–423. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.60.080805.142256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson TL, Abendroth J, Hol WG, Sandkvist M. Type II secretion: from structure to function. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2006;255:175–186. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2006.00102.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kachlany SC, Planet PJ, DeSalle R, Fine DH, Figurski DH. Genes for tight adherence of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans: from plaque to plague to pond scum. Trends Microbiol. 2001;9:429–437. doi: 10.1016/S0966-842X(01)02161-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie PJ. Type IV secretion: the Agrobacterium VirB/D4 and related conjugation systems. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004;1694:219–234. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2004.02.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TMHMM server version 2.0 http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/TMHMM/
- Preston GM, Studholme DJ, Caldelari I. Profiling the secretomes of plant pathogenic Proteobacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2005;29:331–360. doi: 10.1016/j.femsre.2004.12.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MaGe: Magnifying Genomes Microbial Genome Annotation System http://www.genoscope.cns.fr/agc/mage/wwwpkgdb/MageHome/index.php?webpage=mage
- JGI: Joint Genome Institute http://www.jgi.doe.gov/
- Shah J. Lipids, lipases, and lipid-modifying enzymes in plant disease resistance. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2005;43:229–260. doi: 10.1146/annurev.phyto.43.040204.135951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist P, Schwencke J. Native agarose-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis allowing the detection of aminopeptidase, dehydrogenase, and esterase activities at the nanogram level: enzymatic patterns in some Frankia strains. Anal Biochem. 1990;187:337–344. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(90)90466-M. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selim S, Delacour S, Schwencke J. Specific long-chain fatty acids promote optimal growth of Frankia: accumulation and intracellular distribution of palmitic and propionic acid. Arch Microbiol. 1996;165:252–257. doi: 10.1007/s002030050323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vujaklija D, Schroder W, Abramic M, Zou P, Lescic I, Franke P, Pigac J. A novel streptomycete lipase: cloning, sequencing and high-level expression of the Streptomyces rimosus GDS(L)-lipase gene. Arch Microbiol. 2002;178:124–130. doi: 10.1007/s00203-002-0430-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerji S, Flieger A. Patatin-like proteins: a new family of lipolytic enzymes present in bacteria? Microbiology. 2004;150:522–525. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.26957-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akoh CC, Lee GC, Liaw YC, Huang TH, Shaw JF. GDSL family of serine esterases/lipases. Prog Lipid Res. 2004;43:534–552. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2004.09.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathew S, Abraham TE. Ferulic acid: an antioxidant found naturally in plant cell walls and feruloyl esterases involved in its release and their applications. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2004;24:59–83. doi: 10.1080/07388550490491467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg RH. Preliminary evidence for the involvement of suberization in infection of Casuarina. Can J Botany. 1983;61:2910–2918. [Google Scholar]
- Benoist P, Muller A, Diem HG. Coordinate increase in activity of proteinase subunits of the 1300-kDa megaproteinase of Frankia strain BR: role of carbon source depletion and extracellular metabolites. Can J Microbiol. 1993;39:32–39. doi: 10.1139/m93-005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink DL, Green BA, St Geme JW., 3rd The Haemophilus influenzae Hap autotransporter binds to fibronectin, laminin, and collagen IV. Infect Immun. 2002;70:4902–4907. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.9.4902-4907.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankia and Actinorhizal Plants http://web.uconn.edu/mcbstaff/benson/Frankia/FrankiaHome.htm
- Wagner C, Khan AS, Kamphausen T, Schmausser B, Unal C, Lorenz U, Fischer G, Hacker J, Steinert M. Collagen binding protein Mip enables Legionella pneumophila to transmigrate through a barrier of NCI-H292 lung epithelial cells and extracellular matrix. Cell Microbiol. 2007;9:450–462. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2006.00802.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jongbloed JD, Antelmann H, Hecker M, Nijland R, Bron S, Airaksinen U, Pries F, Quax WJ, van Dijl JM, Braun PG. Selective contribution of the twin-arginine translocation pathway to protein secretion in Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:44068–44078. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M203191200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturm A, Schierhorn A, Lindenstrauss U, Lilie H, Bruser T. YcdB from Escherichia coli reveals a novel class of Tat-dependently translocated hemoproteins. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:13972–13978. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M511891200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamper J, Kahmann R, Bolker M, Ma LJ, Brefort T, Saville BJ, Banuett F, Kronstad JW, Gold SE, Muller O, Perlin MH, Wosten HA, de Vries R, Ruiz-Herrera J, Reynaga-Pena CG, Snetselaar K, McCann M, Perez-Martin J, Feldbrugge M, Basse CW, Steinberg G, Ibeas JI, Holloman W, Guzman P, Farman M, Stajich JE, Sentandreu R, Gonzalez-Prieto JM, Kennell JC, Molina L, Schirawski J, Mendoza-Mendoza A, Greilinger D, Munch K, Rossel N, Scherer M, Vranes M, Ladendorf O, Vincon V, Fuchs U, Sandrock B, Meng S, Ho EC, Cahill MJ, Boyce KJ, Klose J, Klosterman SJ, Deelstra HJ, Ortiz-Castellanos L, Li W, Sanchez-Alonso P, Schreier PH, Hauser-Hahn I, Vaupel M, Koopmann E, Friedrich G, Voss H, Schluter T, Margolis J, Platt D, Swimmer C, Gnirke A, Chen F, Vysotskaia V, Mannhaupt G, Guldener U, Munsterkotter M, Haase D, Oesterheld M, Mewes HW, Mauceli EW, DeCaprio D, Wade CM, Butler J, Young S, Jaffe DB, Calvo S, Nusbaum C, Galagan J, Birren BW. Insights from the genome of the biotrophic fungal plant pathogen Ustilago maydis. Nature. 2006;444:97–101. doi: 10.1038/nature05248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GenBank FTP site ftp://ftp.ncbi.nih.gov/genbank/genomes/Bacteria/
- NCBI FTP site ftp://ftp.ncbi.nih.gov/genomes/Bacteria
- Krogh A, Larsson B, von Heijne G, Sonnhammer EL. Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden Markov model: application to complete genomes. J Mol Biol. 2001;305:567–580. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2000.4315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letunic I, Copley RR, Pils B, Pinkert S, Schultz J, Bork P. SMART 5: domains in the context of genomes and networks. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34:D257–60. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkj079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gough J, Karplus K, Hughey R, Chothia C. Assignment of homology to genome sequences using a library of hidden Markov models that represent all proteins of known structure. J Mol Biol. 2001;313:903–919. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2001.5080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997;25:3389–3402. doi: 10.1093/nar/25.17.3389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NCBI CDD FTP site ftp://ftp.ncbi.nih.gov/pub/mmdb/cdd
- Edgar RC. MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004;32:1792–1797. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guindon S, Gascuel O. A simple, fast, and accurate algorithm to estimate large phylogenies by maximum likelihood. Syst Biol. 2003;52:696–704. doi: 10.1080/10635150390235520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page RDM. TREEVIEW: An application to display phylogenetic trees on personal computers. Computer Applications in the Biosciences. 1996;12:357–358. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/12.4.357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215:403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NCBI Resource Guide http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Sitemap/ResourceGuide.html#BLink
- Integrated Microbial Genomes http://img.jgi.doe.gov/cgi-bin/pub/main.cgi
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Secretion machinery genes. This table lists the genes encoding secretion machinery components in the three Frankia genomes.
Individual Frankia secretomes. This table lists the proteins in each Frankia genome predicted to contain a signal peptide by both SignalP methods (NN and HMM), and with 0–2 trans-membrane domains predicted by TMHMM.
Tat signal peptides predicted by TATFIND 1.4. This table lists the proteins in each strain predicted to contain a Tat signal peptide by TATFIND 1.4, and shows their N-terminal sequences, including putative Tat motifs.
The core Frankia secretome. This table lists the 161 proteins in the core Frankia secretome, with SignalP predictions listed for each strain.