Abstract
Extracellular ATP acting on P2X7 receptors opens a channel permeable to small cations, creates an access pathway for the entry of larger molecular weight dyes, and causes cell death. We used whole-cell recording and fluorescence microscopy to measure the time courses of ionic currents, uptake of the propidium dye YO-PRO-1, and membrane disruption, in human embryonic kidney (HEK293) cells expressing the rat P2X7 receptor.
The ATP analogue 2′,3′-O-(benzoyl-4-benzoyl)-ATP (30 μm) induced membrane blebbing within 30-40 s of sustained application; this was 5-10 times slower when extracellular sodium was replaced by larger cations.
Fluorescence of YO-PRO-1 was detectable within 3 s, and the uptake reached a steady rate within 10-20 s; YO-PRO-1 uptake was greatly enhanced by removing extracellular sodium.
Electrophysiological measurements of current reversal potentials with intracellular sodium and extracellular cations of different sizes showed that the ionic channel progressively dilated during 10-20 s to a diameter greater than 1 nm (10 Å). With short agonist applications (3-5 s) the pore dilatation and YO-PRO-1 uptake were reversible and repeatable.
Polyethylene glycols having molecular weights ≥ 5000 blocked the increase in cation permeability, YO-PRO-1 uptake and membrane blebbing.
We conclude that maximum P2X7 receptor activation causes an exponential dilatation of the ion channel with a time constant of 25 s to a final diameter of 3-5 nm from an initial minimum pore diameter of 0.8 nm.
There are currently seven members of the P2X family of subunits for ATP-gated ionotropic receptors, defined on the basis of amino acid sequence deduced from cloned cDNAs (see North & Barnard, 1997). The receptors are multimeric membrane proteins; individual subunits have two transmembrane domains, a cysteine-rich extracellular loop formed by most of the polypeptide chain, and relatively short intracellular N- and C-termini. The P2X7 receptor differs from the others in having a longer C-terminus. Receptors P2X1 through to P2X6 are widely expressed in central and peripheral neurones as well as other excitable cells (Vulchanova et al. 1996, 1997; Collo et al. 1996; Le et al. 1998), but the P2X7 receptor is not neuronal; it is predominantly expressed in antigen-presenting immune cells and epithelia (Rassendren et al. 1997b; Collo et al. 1997; Cario-Toumaniantz et al. 1998).
P2Z is the name given to a subtype of purine receptor by Gordon (1986) which is expressed by antigen-presenting cells such as lymphocytes, mast cells and macrophages. Three consequences of the activation of P2Z receptors have since been widely reported (reviewed by Wiley et al. 1996; Di Virgilio et al. 1996). These are the opening of a cation channel, the creation of a transmembrane pathway sufficiently large to allow the passage of larger molecular weight fluorescent dyes, and cell lysis (Cockcroft & Gomperts, 1979a,b; Dubyak & El-Moatassim, 1993; Di Virgilio, 1995). The most defining features of these actions of ATP are (i) that the effects are much enhanced by removal of divalent cations (which has been interpreted to indicate that ATP4− rather than MgATP is the active species), and (ii) that 2′,3′-O-(benzoyl-4-benzoyl)-ATP (BzATP) is a considerably more potent agonist than ATP itself.
The P2X7 receptor, when expressed in heterologous cells, corresponds in many of its properties to those of P2Z receptors (Surprenant et al. 1996). Thus, HEK293 cells transfected with P2X7 subunit cDNA exhibit inward cation currents, uptake of fluorescent dyes, and cell lysis. Truncation of the receptor by removal of most of the intracellular C-terminal prevents cell lysis, and much reduces dye uptake, but appears not to alter the function of the molecule as an ATP-gated cation channel (Surprenant et al. 1996). The aim of the present work was to make a more complete kinetic study of these three measures of P2X7 receptor activation - cation current, uptake of dye, and cell lysis. Knowledge of their temporal relationships would be helpful in understanding the molecular mechanisms by which they are induced by P2X7 receptor activation.
First, we took a biophysical approach towards measuring the time dependence of the permeability of the cation channel, by measuring the reversal potential of the ATP-induced current with extracellular cations of different size; the largest cation used was N-methyl-D-glucamine (molecular weight 195). Second, we measured the uptake of the propidium analogue YO-PRO-1 (YOPRO) by measuring the change in single cell fluorescence as a function of time after adding BzATP. The YOPRO cation is divalent with a molecular weight of 376. Third, we observed cell lysis directly as membrane blebbing and disruption. We also studied the effects of some polyethylene glycols of various molecular weights on cation currents and YOPRO uptake, because these molecules have been widely used to ‘size’ the permeation path of other large channels (e.g. Krasilnikov et al. 1992; Parsegian et al. 1995a,b;Desai & Rosenberg, 1997).
METHODS
HEK293 cells stably expressing the rat P2X7 receptor (Surprenant et al. 1996) were used in the majority of experiments; some experiments were carried out on HEK293 cells transiently transfected with rat P2X7 receptor cDNA, with co-transfection with enhanced green fluorescent protein cDNA to identify receptor-expressing cells. Methods of stable and transient transfections have been detailed previously (Rassendren et al. 1997b). There were no differences in results obtained from transient or stable expression systems and all results were pooled. Tests of significance were performed using Student's t test; P < 0.005 was considered significant. All experiments were carried out at room temperature (21-23°C).
Electrophysiology
Standard whole-cell recordings were obtained using the EPC-9 patch-clamp system (HEKA, Lambrecht, Germany). Patch pipettes (4-7 MΩ) were filled with (mM): 160 NaCl, 10 Hepes and 11 EGTA; in some experiments the intracellular solution was 154 KCl, 5 NaCl, 10 Hepes and 11 EGTA. Normal extracellular solution contained (mM): 147 NaCl, 2 KCl, 1 MgCl2, 2 CaCl2, 10 Hepes and 12 glucose; ‘low divalent’ solution contained no added MgCl2 and 0.2 mM CaCl2. To measure the permeability to monovalent cations, after the whole-cell configuration was obtained in normal solution the solution was changed to (mM): 154 test cation, 10 Hepes and 12 glucose. Test cations were chloride or hydrochloride salts of 2-methylethanolamine (DEA), Tris, tetraethylammonium (TEA), dimethylamine (DMA), and N-methyl-D-glucamine (NMDG), all from Sigma. To determine anion selectivity, reversal potentials were first measured in 154 mM NMDG/117 mM chloride, and then in solution containing 34.5 mM NMDG/23.4 mM chloride (osmolarity maintained by increasing glucose to 246 mM).
Polyethylene glycols (PEGs) were used at concentrations of 5-20 mM. For PEG 4000 and 6000, NaCl or NMDG in the external solution was decreased to 100 mM to maintain osmolarity; intracellular NaCl was also reduced to 100 mM to maintain bi-ionic conditions. In control experiments for these studies sucrose was used instead of PEG. All solutions were maintained at pH 7.3 and 300-310 mosmol l−1. Dimensions of cations given were estimated using van der Waals radii from energy-minimized models constructed with Desktop Molecular Modeller (Oxford University Press).
ATP and BzATP were applied with a fast-flow U-tube delivery system (Fenwick et al. 1982); the same concentrations were applied in the presence or absence of divalent cations, thus no account has been taken of the active species of ATP (see Virginio et al. 1997). Liquid junction potentials were corrected by use of a salt bridge (3 M KCl) as described by Neher (1992). Unless otherwise stated, membrane potential was held at -60 mV. Currents in the presence of agonist were not corrected for linear leakage because currents in the absence of agonist were < 0.5 % of maximum agonist-induced currents. Series resistance was < 5 MΩ for all experiments; no compensation was applied for currents < 0.5 nA but larger currents were compensated by 75 %. Current-voltage relations were obtained by voltage ramps (0.5-1 s duration) from -90 to 0 mV unless otherwise stated. Results were accepted only if the current and membrane conductance returned to within 2-5 % of control (prior to agonist application) values (e.g. Fig. 3A), thus indicating that the large conductance increase and shift in reversal potential were not due to cell lysis with loss of seal. Following agonist application with the test cation, the solution was rapidly changed back to the normal physiological saline containing MgCl2 and CaCl2. Permeability ratios (PX/PNa) were calculated as described previously (Evans et al. 1996) from:
Figure 3. NMDG permeability increases during P2X7 receptor activation.
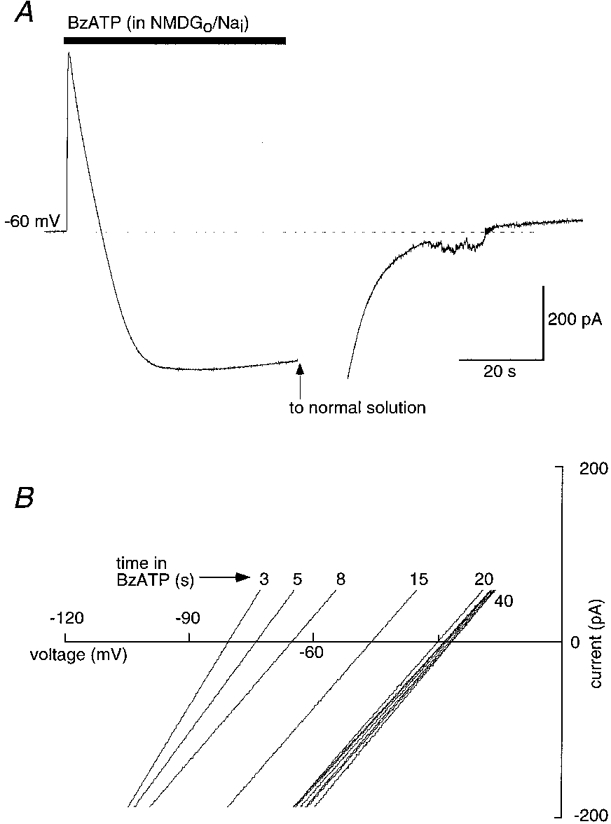
A, whole-cell recording during 50 s application of BzATP (30 μm) in bi-ionic conditions (NMDG outside, sodium inside). At the holding potential of -60 mV, current is initially outward due to net outward Na+ flux but rapidly becomes inward as NMDG permeability increases. B, current-voltage curves constructed from experiments as in A but with ramp voltage commands applied at 2-3 s intervals during BzATP application; reversal potential shifts from -85 mV to a steady value of -28 mV over 20 s.
Values stated in the text and the table are means ±s.e.m. from individual cells, whereas graphs were drawn by averaging the results from all experiments and fitting a single curve to the pooled data.
Single-cell imaging and immunohistochemistry
YOPRO uptake was measured using a Zeiss Axiovert 100 and oil immersion Fluar ×40 objective, and the Photonics monochromator Imaging (TILLionVISION) system (Photonics, Planegg, Germany). YOPRO (1-5 μm, YO-PRO-1 iodide, Molecular Probes) was present in all solutions prior to and during agonist application. Fluorescence was measured from single cells in the field of view (excitation 491 nm/ emission 509 nm); images were captured at 0.2-2 Hz. YOPRO fluorescence from individual cells was averaged; the differentiated signal is presented to indicate the rate of YOPRO uptake into cells. Cell lysis was measured as membrane disruption and the formation of large blebs, visualized with a ×100 Neofluar objective under transmitted light; digital images were captured at 1-2 Hz and subjected to edge-filtering using NIH Image 1.61 software. Time from the onset of agonist application to the first image containing a fully disrupted edge was taken as time to membrane disruption. Data are means ±s.e.m.
For immunohistochemistry, a rat P2X7 receptor cDNA was used that carried a C-terminal epitope (DPGLNEYMPME) cloned into pcDNA3 (Invitrogen) as described previously (Rassendren et al. 1997a). HEK cells were transiently transfected with Lipofectin as previously described (Evans et al. 1996; Rassendren et al. 1997b). Forty-eight hours after transfection, cells were fixed with Zamboni's fixative for 20 min, washed with physiological saline and incubated in donkey serum with or without detergent (2 % Triton X) for 1 h, and then incubated with primary mouse monoclonal anti-EYMPME antibody (BABCO, Berkeley, CA, USA; 1:1000 dilution) for 1 h. Cells were then washed with physiological saline and incubated with the secondary antibody (fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated donkey anti-mouse IgG at 1:100 dilution) for 1 h, washed three times and viewed with the Zeiss Axiovert fluorescence microscope or a Zeiss LSM 410 confocal microscope. These protocols yielded no fluorescence in untransfected, or mock-transfected (with pcDNA3 vector) HEK cells.
RESULTS
Cell lysis during P2X7 receptor activation
Cell lysis due to activation of P2X7 receptors in heterologous expression systems, or P2Z receptors in native cells, is well documented (see Di Virgilio, 1995; Ralevic & Burnstock, 1998). However, its time course has not been reported. We therefore measured the time to membrane disruption in individual HEK cells expressing rat P2X7 receptors in response to application of BzATP at a concentration which is near-maximal for activation of the fast inward current (30 μm: Surprenant et al. 1996). In normal physiological solution, membrane disruption occurred 28-45 s (36 ± 5 s, n = 19) from the beginning of the agonist application (Fig. 1); cell disruption was not significantly faster in magnesium-free solution (28 ± 4 s, Fig. 1D). Replacement of extracellular sodium with NMDG increased the time to membrane disruption by 3- to 5-fold (128 ± 14 s, Fig. 1D) as did replacement with DMA, Tris, TEA, or DEA (data not shown).
Figure 1. Cell lysis in HEK cells expressing rat P2X7 receptor in normal and altered ionic solutions.
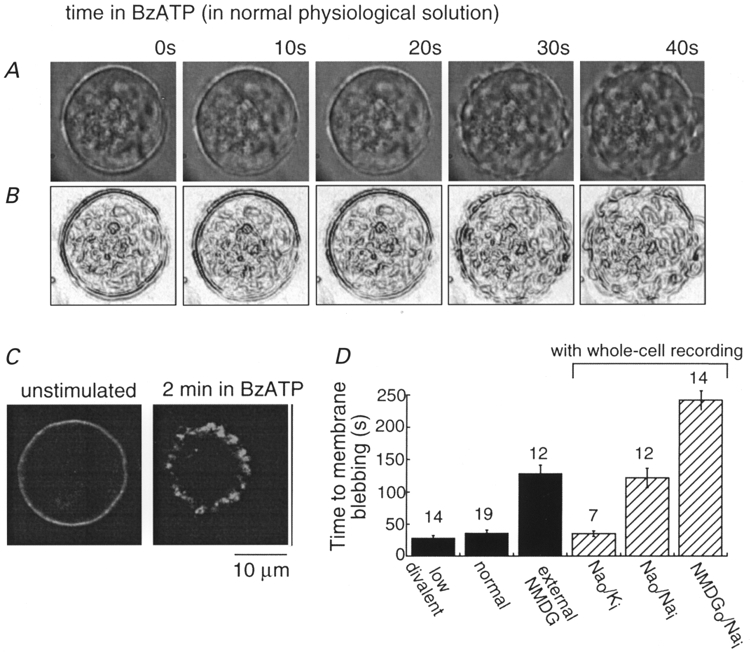
A and B, digital photomicrographs of one cell in normal physiological solution during 40 s application of BzATP (30 μm) at times indicated (A) and after edge-filtering of the image (B); membrane disruption is clearly evident at 30 and 40 s. C, immunohistochemical localization of C-terminal epitope-tagged P2X7 receptor in HEK cells. Cell on left was not exposed to BzATP and was permeabilized with Triton X; cell on right was fixed immediately after 2 min application of BzATP without detergent permeabilization protocol. D, summary of all experiments measuring time to membrane disruption in normal and altered intracellular (via whole-cell recording pipettes) and extracellular solution; numbers above each bar are numbers of cells examined.
In a second series of experiments, we measured the time to membrane disruption in cells from which we also made whole-cell recordings. When the recording pipette contained potassium chloride, the time to membrane disruption was similar to that observed without whole-cell recording in the case of normal extracellular solution (Fig. 1D). However, membrane disruption was greatly retarded when the patch pipette contained sodium chloride in place of potassium chloride (122 ± 15 s, n = 12vs. 35 ± 4 s, n = 7, Fig. 1D). When the external solution contained NMDG in place of sodium, lysis also occurred more slowly if the patch pipette contained sodium chloride (242 ± 21 s, n = 14; Fig. 1D). Thus, extracellular sodium promotes, while intracellular sodium retards, cell disruption during sustained P2X7 receptor activation. In all subsequent electrophysiological experiments, the intracellular solution was sodium chloride; this facilitated calculations of permeability ratios under bi-ionic conditions and allowed measurements of conductance and permeability changes during the sustained 40 s agonist application without danger of cell lysis. The presence of YOPRO (1 μm) in the superfusion fluid did not alter the time to membrane disruption in normal solution (n = 14) or NMDG (n = 9).
Immunohistochemical localization of a C-terminal epitope-tagged rat P2X7 receptor also illustrated the dramatic membrane disruption associated with sustained (2-3 min) agonist application. In cells not exposed to agonist, membrane permeabilization with Triton X revealed P2X7 receptors uniformly distributed at the plasma membrane (Fig. 1C); non-permeabilized cells showed no immunofluorescence. Immunohistochemistry of cells expressing P2X7 receptors after a 2 min application of BzATP revealed gross membrane disarray (Fig. 1C) whether or not the cells had been exposed to detergent.
Uptake of the fluorescent dye YOPRO
Rapid and reversible dye uptake was observed when BzATP was applied in normal physiological saline (Fig. 2A). Cell fluorescence became readily detectable with applications lasting for 5 s, but not when they were less than 3 s. The increase in fluorescence ceased when the brief agonist application was discontinued. With brief (5 s) applications of BzATP repeated at 1 min intervals, the rate of change of fluorescence (indicating the entry of YOPRO in the preceding second) declined to zero after each application; the time constant of decline was 5 ± 0.4 s (n = 19) (Fig. 2A). The rate of YOPRO uptake was greatly increased in the low divalent solution, and it took longer to recover after agonist washout (τ= 12.3 ± 1.4 s, n = 10, Fig. 2A). This transient uptake of YOPRO was not accompanied by evidence of membrane disruption. The rate of YOPRO uptake increased as external sodium was replaced with NMDG (Fig. 2B); this relationship was linear with a slope of 1.8.
Figure 2. YOPRO uptake during activation of P2X7 receptor.
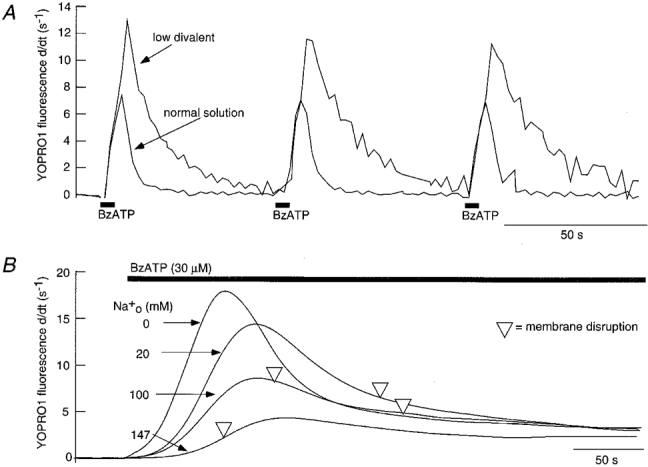
A, rate of YOPRO uptake in response to 5 s application of BzATP at 1 min intervals in normal and low divalent solution as indicated. Traces are the average of 12 cells in field of view; no evidence of cell damage was associated with these brief agonist applications. B, rate of YOPRO uptake increases with decreasing concentration of extracellular sodium; traces are the average of 12-18 cells in field of view. ▿ marks average time of membrane disruption of cells in each of the solutions; note the inverse correlation between YOPRO uptake and cell lysis during P2X7 receptor activation.
Cation permeability increase: pore dilatation
When NMDG was the only external cation, application of BzATP (30 μm) produced an immediate outward current; this indicates that the channel which opens allows sodium to leave the cell more readily than NMDG can enter. However, when the BzATP application was continued for 45-60 s, this outward current declined and became inward within 10 s (Fig. 3A). Reversal potentials were measured at intervals of 2-4 s during this time using ramp voltage commands (Fig. 3B); the reversal potential shifted from -88 ± 1.9 mV (n = 19) at 2 s to a steady-state value of -22 ± 2.4 mV at 20-30 s (Table 1). This corresponds to the permeability ratio (PNMDG/PNa) changing from 0.03 ± 0.002 at t = 2 s to 0.48 ± 0.04 at 40 s (Table 1). If this time-dependent increase in NMDG permeability occurred as a single step transition, then the rate at which it occurred would be independent of the size of the permeant cation used to measure it. Reversal potentials as a function of time were determined for a series of smaller organic cations (Table 1). Figure 4A plots these results; for each cation the time course of reversal potential change was well fitted to a single exponential function, the time constant of which increased as the size of the permeable cation increased (Table 1). These results indicate that the increase in permeability occurs progressively, and that the conducting pore passes through a series of smaller sizes before reaching its NMDG-permeable size.
Table 1.
Summary of permeability change of different-sized monovalent cations with time during P2X7 receptor activation
| Test cation | n | Diameter (nm) | Vrev,2s (mV) | PX/PNa | Vrev, 40s(mV) | PX/PNa | τ (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dimethylamine | 9 | 0.40 | −12 ± 1.5 | 0.62 | 0.9 ± 0.1 | 1.0 | 0.7 ± 0.1 |
| 2-Methylethanolamine | 9 | 0.52 | −37 ± 0.8 | 0.23 | 2.5 ± 2.6 | 1.1 | 3.7 ± 0.8 |
| Tris | 8 | 0.65 | −50 ± 0.9 | 0.14 | −5.3 ± 1.5 | 0.81 | 4.4 ± 0.4 |
| Tetraethylammonium | 7 | 0.72 | −70 ± 0.6 | 0.06 | −8.3 ± 2.4 | 0.72 | 5.9 ± 0.8 |
| N-Methyl-d-glucamine | 18 | 0.76 | −88 ± 1.5 | 0.03 | −22 ± 2.0 | 0.42 | 9.8 ± 1.1 |
Cation ‘diameter’ is estimated as the mean of the two smallest dimensions, calculated as in Methods. Vrev values are reversal potentials measured at 2 s and at steady-state (usually 40 s) during a 40-60 s application of BzATP (30 μm). Time constant (τ) of reversal potential change is from the best single exponential fit. n, number of experiments.
Figure 4. Kinetics of permeability increase.
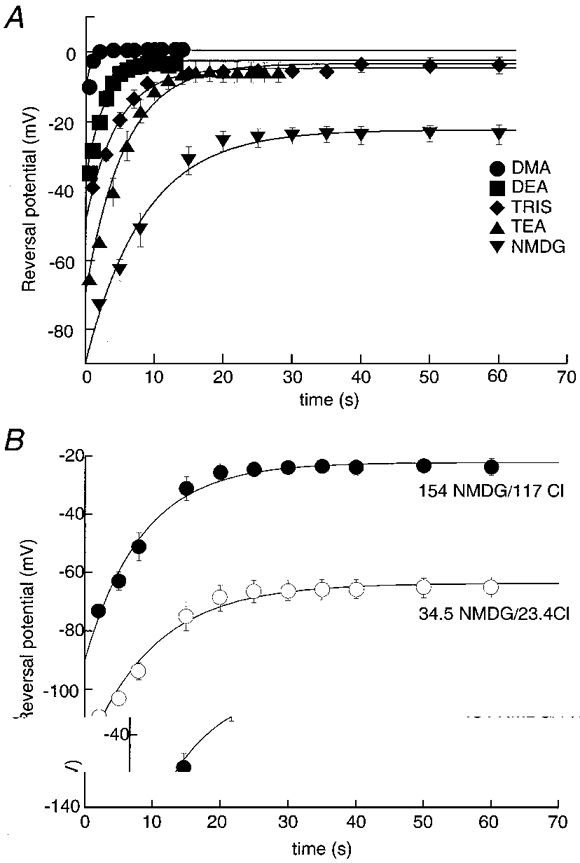
A, time course of permeability increase depends on size of permeant ion. Summary of all results from experiments as illustrated in Fig. 3B with extracellular monovalent cations as indicated. Data points (n = 5-14 for each point) are fitted to a single exponential, the time constants of which increase as a function of the size of the substituted cation. B, reversal potential change with time after BzATP application in standard NMDG/chloride solution (•) and in 5-fold lower NMDG and chloride concentrations (○). Data points for low NMDG/chloride solution are fitted to the exponential function expected if the channel remained cation selective during dilatation.
The conducting pore remained cation selective as it enlarged to reach the NMDG-permeable state. This was shown by comparing the results in the ‘standard’ external NMDG/chloride solution (154 mM NMDG/117 mM chloride) with those in a solution in which both NMDG and chloride concentrations were reduced 5-fold (34.5 mM NMDG/23.4 mM chloride) (see also Tatham & Lindau, 1990). The reversal potential in the low NMDG/chloride solution shifted exponentially from -118 ± 5.3 mV at 2 s to -61 ± 2.7 mV at 40 s (n = 7, Fig. 4B). The time constant of this change was 11.8 ± 1.5 s in the solution with low ion concentrations, which was not significantly different from the control value (Table 1). The theoretical values for the reversal potentials were calculated to be -125 mV and -57 mV at zero and 40 s respectively (using PNMDG/PNa obtained from the standard NMDG solution). The corresponding PNMDG/PNa values in the low NMDG/chloride solution were 0.051 ± 0.01 at 2 s and 0.45 ± 0.05 at 40 s. These values are not different from those measured for the normal NMDG/chloride solution, indicating that the P2X7 receptors remain cation selective throughout the dilatation process.
The rate of increase in NMDG permeability was strongly dependent on the agonist concentration. Little or no change was seen with 0.3 μm BzATP applied for up to 2 min (Fig. 5A), although at later times there was a small but rather variable decline in the NMDG reversal potential; this concentration produced a current in normal physiological saline that was 8-12 % of the maximum current induced by 30 μm BzATP. At 1 and 3 μm, there was a clear delay before the onset of the permeability increase; these concentrations are less than half-maximal (EC50) for inducing inward current in normal external solution (Surprenant et al. 1996). At higher concentrations (30 μm) there was no obvious lag (Fig. 5A). The points in Fig. 5A are reasonably well fitted by a function of the form:
Figure 5. Pore dilatation depends on agonist concentration and divalent ions.
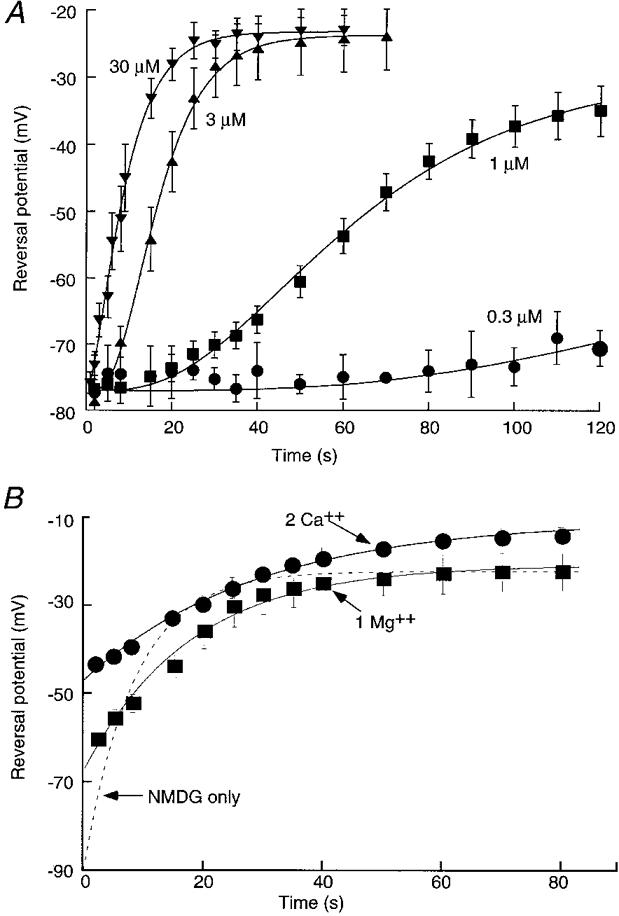
A, concentration dependence of pore dilatation. Reversal potential as a function of time during application of 0.3, 1, 3 and 30 μm BzATP as indicated. Points are fitted by least-squares to eqn (1) in the text. The values for k (μm−1 s−1) and nH are for 0.3 μm: 0.03 and 4.7; for 1 μm: 0.03 and 3.9; for 3 μm: 0.12 and 4.7; and for 30 μm: 0.15 and 1.8. B, addition of calcium (•) or magnesium (▪) decreases rate of change of reversal potential with time in agonist but does not decrease steady-state permeability. Dashed line shows curve from Fig. 4A for comparison. Note that initial values in calcium or magnesium are depolarized with respect to NMDG alone, indicating that both divalent cations permeate the channel.
| (1) |
where Vrev,min and Vrev,max are initial (at 2 s) and final reversal potentials, k is a forward rate constant and [A] is the BzATP concentration. The curves were fitted with nH (Hill coefficient) values of 2-5, suggesting that the forward reaction is driven by the binding of multiple agonist molecules, but that there are also co-operative interactions (see Fig. 5 legend).
External Ca2+ and Mg2+ strongly inhibit the initial currents through P2X7 receptors as well as YOPRO uptake (Surprenant et al. 1996; Virginio et al. 1997; see Di Virgilio, 1995); therefore, we examined the effects of these divalent cations on the change in NMDG permeability. Reversal potentials were measured first in the standard NMDG solution and then after the addition of either 2 mM Ca2+ or 1 mM Mg2+ (Fig. 5B). Both calcium and magnesium slowed down the rate of increase in NMDG permeability, although neither altered the steady-state PNMDG/PNa ratio (calculated values in calcium and magnesium were 0.42 ± 0.05, n = 6, and 0.48 ± 0.06, n = 7, respectively). The time constants were 9.6 ± 1.2 s (n = 13) in control divalent-free solution, 20.5 ± 4.6 s (n = 7) in 1 mM Mg2+, and 32.2 ± 7.5 s (n = 6) in 2 mM Ca2+. Reversals potentials were shifted positively when Ca2+ or Mg2+ were added, indicating that both permeate throughout the duration of agonist application (Fig. 5B).
Effects of polyethylene glycols
NMDG was the largest organic cation readily available for use as a charge carrier; many others which we considered or tried were toxic, or not available in the millimolar concentrations required. We therefore attempted to use polyethylene glycols (PEGs) of various molecular weights, which have been used to size large channels such as alamethicin (diameter ∼2 nm; Bezrukov & Vodyanoy, 1993), the mitochondrial voltage-dependent anion channel (diameter ∼4 nm; Zimmerberg & Parsegian, 1986), and bacterial toxin pores (Moran et al. 1992).
The progressive increase in permeability to NMDG which occurred after adding ATP was cut short by PEG6000. Figure 6A shows the results from reversal potential measurements in control NMDG solution compared with those in NMDG to which had been added PEG6000. In PEG6000 the reversal potential moved positively during the first 5 s, but then it remained at a value of about -60 mV (-61 ± 1.3 mV compared with -25 ± 2 mV in control; n = 4, Fig. 6A). These measurements of reversal potential are necessarily conducted in solutions containing zero external sodium, which would increase the rate of dilatation. We therefore measured the time-dependent conductance increase which occurred after applying agonist, in normal physiological solutions (Tatham & Lindau, 1990). Cells were held at 0 mV and voltage ramps from -40 to 40 mV (1 s duration) were applied at 5-10 s intervals before, during and after BzATP application (Fig. 6B and C). PEG6000 reduced the steady-state conductance increase (Fig. 6C); after 60 s in BzATP the slope conductance was 54 ± 3 nS in control and 23 ± 3 nS in PEG6000 (n = 11). PEG6000 also somewhat slowed the rate at which the conductance increase developed; the exponentials fitted in Fig. 6C have time constants of 24.5 ± 2.6 s for control and 40 ± 3 s for PEG6000.
Figure 6. Effects of PEG6000 on permeability and conductance increase.
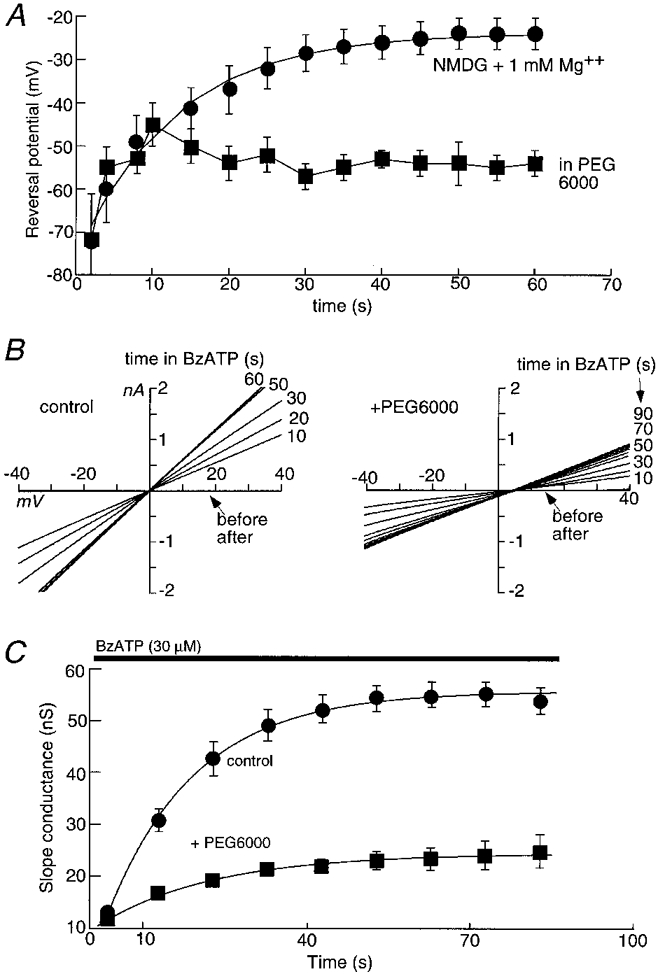
A, NMDG reversal potentials in the absence (•) and presence (▪) of PEG6000; Mg2+ (1 mM) was present in both solutions. Agonist (BzATP, 30 μm) was added at time zero. B, membrane conductance changes with time after BzATP application in normal physiological solution. Current-voltage curves were obtained from one cell during 60-90 s application of BzATP (30 μm) before (left) and after (right) addition of PEG6000. C, summary from all experiments as illustrated in B, where slope conductance is plotted as a function of time in BzATP; n = 9 for each point.
The smaller polyethylene glycols (PEG4000, PEG2000) retarded the entry of YOPRO initially, but after 20-30 s it reached its original rate of entry. The time for the rate of YOPRO entry to reach its half-maximal level was 18 ± 3 s in control solutions, 45 ± 4 s in PEG2000 and 78 ± 6 s in PEG40 000 (n = 11). No uptake of YOPRO was observed in PEG6000 or PEG10 000 even with agonist applications up to 4 min (Fig. 7), nor was there any evidence of cell lysis during this time.
Figure 7. PEG6000 and PEG10 000 prevent YOPRO uptake.
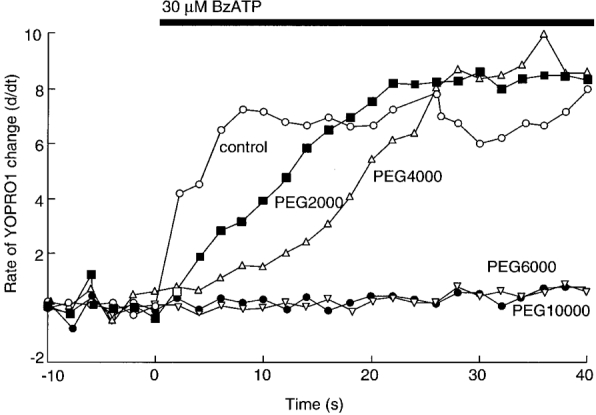
The smaller PEGs initially slow down the rate of YOPRO uptake. Points are the means of 12-42 cells; standard errors of the means are omitted for clarity but are < 12 % for all points. YOPRO uptake experiments were performed in normal physiological saline.
DISCUSSION
Kinetics of pore dilatation
The primary aim of this study was to examine the time course and final size of the dilatation of the P2X7 receptor channel. This is most accurately assessed by reversal potential measurements, using organic cations of a range of sizes. The channel activated by BzATP was initially relatively impermeable to large cations such as NMDG (1.08 nm × 0.87 nm × 0.65 nm), but after 40 s of sustained receptor activation, the permeability increased by about 10-fold (Fig. 3, Table 1; see Surprenant et al. 1996). The time course of this permeability increase was faster for smaller cations (Fig. 3, Table 1) and we interpret this to indicate that the permeation path undergoes a progressive dilatation, rather than a single-step transition from a small size to a large size. Even at its ‘final’ size (see below), the channel remains somewhat selective; it is still about twice as permeable to sodium as to NMDG, and it is essentially impermeable to anions.
When inward currents are elicited by brief applications (1-2 s) of BzATP in cells expressing P2X7 receptors, a dose-response curve is obtained which has a half-maximal concentration (EC50) of about 10 μm (in normal external calcium and magnesium; Surprenant et al. 1996; Virginio et al. 1997). The agonist concentrations which were effective to increase NMDG permeability during prolonged applications were generally similar; the lowest concentration tested (100 nM) evoked a small current in normal solution (about 10 % of maximal) but did not evoke any permeability increase in NMDG solution. Moreover, there was a striking slowing of the onset of the permeability increase when the BzATP concentration was less than 10 μm. On the simplifying assumption that reverse processes can be neglected, the kinetics of development of the NMDG-permeable state conformed reasonably well to a model in which several agonist molecules bind to trigger the permeability increase (Fig. 5 legend). One interpretation of the results is that a singly or doubly liganded receptor might induce the initial (‘channel’) opening, and the binding of further agonist molecules leads to the dilated (‘pore’) state. Other kinetic models are possible, and further experiments would be required to distinguish among them.
One of the limitations in the interpretation of these experiments is that they are necessarily carried out in external solutions lacking sodium, calcium and magnesium. Introduction of calcium or magnesium slowed the rate at which the permeability increased by 2- to 3-fold (Fig. 5B). Independent experiments of two sorts suggest that the rate is also slower when sodium is the main external cation, rather than NMDG. First, simply measuring the cell conductance showed that this increased exponentially with a time constant of about 25 s in 30 μm BzATP, some two to three times slower than the change in NMDG permeability (Fig. 6C). Second, YOPRO entered the cell more rapidly as the external sodium concentration was reduced (Fig. 2B). Moreover, the permeability changes were measured with sodium as the predominant intracellular cation whereas in undisturbed cells this would be potassium. We do not know how this might alter the rate of development of NMDG permeability; we do know that extracellular sodium greatly accelerates membrane blebbing and disruption (see below).
The observations on uptake of YOPRO supplement the measurements of reversal potential in two important ways. First, they are carried out on undisturbed cells. Second, they provide a measure of the uptake of an organic cation which is larger than NMDG. YOPRO is a divalent cation of molecular weight 376; we estimate the dimensions to be 1.68 nm × 0.94 nm × 0.89 nm. The product of the two smallest dimensions is 0.84 nm2, in comparison with 0.57 nm2 for monovalent NMDG. There are disadvantages to the use of YOPRO. We do not understand the details of the kinetics with which it binds to intracellular nucleic acids and becomes visibly fluorescent; moreover, it is also possible that YOPRO becomes readily detectable in the cell as it enters through a small number of quickly dilating channels, whereas the electrophysiological measures of reversal potential would provide a read-out of the average behaviour of all the channels. Nonetheless, the two methods (YOPRO uptake and electrophysiological measures) provide generally concordant evidence that under physiological conditions, at room temperature, activation of the P2X7 receptor results in the immediate opening of a cationic channel which dilates within several seconds to a cross-sectional area at least as great as 6.0 and 9.0 nm2. This process is accelerated by reducing the external sodium concentration, or by removal of external magnesium or calcium.
Although YOPRO uptake and reversal potential measurements provided concordant results for the initial change in channel pore diameter, neither method allowed an estimate of the final size of the pore. Polyethylene glycols have been used to estimate the size of membrane pores because they behave as non-electrolyte spheres in solution. Two main approaches have been used. In the first, the effect of the PEG on single channel conductance is determined, for channels expressed in lipid bilayers: if the conductance is decreased then the polymer is entering the channel (Krasilnikov et al. 1992; Bezrukov & Vodyanoy, 1993). The second approach is osmotic protection: if cell lysis is blocked by a PEG having a larger diameter but not by a PEG having a smaller size, then it might be concluded that the lytic pore allows the smaller but not the larger PEG to permeate (Moran et al. 1992). We found that PEG6000 (and PEG10 000) had four main effects on the action of BzATP: it prevented cell lysis, it prevented YOPRO uptake (Fig. 7), it prevented the large increase in permeability to NMDG (Fig. 6A), and it reduced the slowly developing conductance increase observed in normal solution (Fig. 6C). PEG6000 has a hydrodynamic radius of 2.5 nm (measured by viscosimetry) and a crystal radius of about 1.2 nm (Krasilnikov et al. 1992). The smaller PEGs (2000 and 4000) delayed the onset of YOPRO entry but they did not block it. It is tempting to interpret the experiments with YOPRO (Fig. 7B) to indicate that PEG2000 and PEG4000 lose their ability to block dye uptake because they become able to pass through the pore as it dilates; the pore never reaches a size which allows the passage of PEG6000 (Fig. 7), and the ‘final’ size would lie between these limits. The simple interpretation that PEG2000 and PEG4000 fail to block YOPRO uptake because they permeate the channel would provide an estimate for the diameter of about 4.0 nm, but this would need to be substantiated by direct measurement (perhaps using fluorescently labelled PEGs) before one could make reliable conclusions. In fact, the accuracy of the method of sizing has become somewhat suspect in light of the recent determination of the crystal structure of the Staphylococcus aureusα-haemolysin: the minimum pore diameter of the crystallized protein was 1.6 nm (Song et al. 1996), whereas the minimum diameter estimated with PEG was 2.6 nm (from its hydrodynamic radius; Krasilnikov et al. 1992).
How do these results compare with those obtained for activation of P2Z receptors on native cells? Previous studies on both cloned and native P2X7 receptors have shown significant species differences as well as marked effects of increased temperature (Buisman et al. 1988; Wiley et al. 1996; Virginio et al. 1997); thus, the pertinent comparative studies are those obtained at room temperature in rat tissues. In rat mast cells and macrophages, significant chloride permeability develops during application of ATP (Buisman et al. 1988; Tatham & Lindau, 1990). In our experiments, there was no evidence for the development of any anion permeability at a time when the NMDG permeability had reached a plateau, suggesting that a mechanism distinct from a simple channel dilatation underlies any anion permeability change that may occur. The slow conductance increase in mast cells occurred over tens of seconds, comparable to the present results. Finally, the time course of ethidium uptake into mast cells treated with ATP was broadly comparable to that observed in our experiments.
Pore dilatation and cell lysis
The uptake of membrane-impermeant nucleic acid-binding molecules, such as ethidium, propidium and YOPRO, are standard tools for measuring cell permeabilization; indeed, propidium is often used in fluorescence-activated cell sorters to select and discard permeabilized cells, which are presumed to be dead. Here we show that brief (5 s) activation of P2X7 receptors is sufficient to permeabilize HEK cells because YOPRO uptake is readily observed; this permeabilization is transient, reversible and repeatable for stimulus intervals greater than 1 min.
Previous studies have indicated that agonist concentration- response curves and divalent cation sensitivities are the same for P2X7 receptor-induced cell lysis (measured as visualization of membrane disruption and blebbing) and dye uptake or ionic currents (Rassendren et al. 1997b; Virginio et al. 1997); this has led to the idea that cell lysis directly results from the dilatation of a cell-permeabilizing pore. This is the first study in which membrane disruption has been measured in real time at the single-cell level, and this allows direct comparisons between cell lysis and dye uptake/ionic currents, assuming that membrane disruption adequately reflects cell lysis. We have found three ways in which permeabilization to organic cations including YOPRO, and cell lysis measured as membrane disruption, fail to correlate. First, decreasing extracellular sodium slows membrane disruption by several minutes but increases the rate of pore dilatation measured by either YOPRO or permeability changes. Previous studies in antigen-presenting cells have also found dye uptake during P2X7 receptor activation to be significantly increased by removal of extracellular sodium and concluded that extracellular sodium prevents or slows the cytolytic process (Chen et al. 1994; Wiley et al. 1994; Song & Chueh, 1996). The present study shows the opposite to be true. Second, as discussed above, the ion-conducting pore remains cation selective over the time course of our measurements, and thus does not provide a transmembrane pathway allowing colloid osmotic swelling. Third, microscopic observation of cells activated by P2X7 receptor activation reveals extensive blebbing and membrane disarray unlike that observed after other types of ‘pore-forming’ cell permeabilization methods (Fig. 1C), such as detergents, streptolysin or other antibiotics, and calcium or sodium ionophores (authors'unpublished observations). On the other hand, PEG6000 and PEG10 000, which blocked dye uptake, also blocked cell lysis.
The intracellular C-terminus of the P2X7 receptor is approximately 200 amino acids longer than other P2X receptors; this is required for cell lysis because no lysis occurs in HEK cells expressing a truncated receptor lacking the final 177 residues, although this receptor still functions as a cation-selective ion channel (Surprenant et al. 1996). YOPRO uptake during activation of the truncated receptor is reduced by more than 90 % but is not abolished (Rassendren et al. 1997b). This is consistent with our recent finding that a proportion of cells expressing P2X2 or P2X4 receptors also show rapid and significant uptake of YOPRO when exposed to ATP for several seconds, and that this is accompanied by a progressive increase in permeability to NMDG (Virginio et al. 1999). In fact, the kinetics of that uptake and NMDG permeability increase are very similar to those described for P2X7 receptors in the present paper. However, we have never observed ATP-induced lysis of cells expressing P2X2 or P2X4 receptors. This observation further supports the distinction between YOPRO uptake and cell lysis, and serves to underline how little we understand about the mechanism by which lysis occurs.
In conclusion, we have shown that activation of homomeric rat P2X7 receptors results in a dilatation of a cation-selective channel from its initial diameter (∼ 0.7-0.8 nm) to a size which exceeds 1.0 nm within 10-30 s and may reach 4.0 nm. The rate depends on the ionic composition of the intracellular and extracellular solution. Although activation of this receptor also induces cell lysis, our results suggest that this might not be the immediate result of pore dilatation.
Acknowledgments
We thank Daniele Estoppey for the cell culture.
References
- Bezrukov SM, Vodyanoy I. Probing alamethicin channels with water-soluble polymers: effect on conductance of channel states. Biophysical Journal. 1993;64:16–25. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81336-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buisman HP, Steinberg TH, Fischbarg J, Silverstein SC, Vogelzang SA, Ince C, Ypey DL, Leigh PC. Extracellular ATP induces a large nonselective conductance in macrophage plasma membranes. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA. 1988;85:7988–7992. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cario-Toumaniantz C, Loirand G, Ladoux A, Pacaud P. P2X7 receptor activation-induced contraction and lysis in human saphenous vein smooth muscle. Circulation Research. 1998;83:196–203. doi: 10.1161/01.res.83.2.196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen JR, Jamieson GP, Wiley JS. Extracellular ATP increases NH4+ permeability in human lymphocytes by opening a P2Z purinoceptor operated channel. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 1994;202:1511–1516. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.2102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S, Gomperts BD. ATP induced nucleotide permeability in rat mast cells. Nature. 1979a;279:541–542. doi: 10.1038/279541a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S, Gomperts BD. Activation and inhibition of calcium-dependent histamine secretion by ATP ions applied to rat mast cells. The Journal of Physiology. 1979b;296:229–243. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp013002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collo G, Neidhart S, Kawashima E, Kosco-Vilbois M, North RA, Buell G. Tissue distribution of the P2X7 receptor. Neuropharmacology. 1997;36:1277–1284. doi: 10.1016/s0028-3908(97)00140-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collo G, North RA, Kawashima E, Merlo-Pich E, Neidhart S, Surprenant A, Buell G. Cloning of P2X5 and P2X6 receptors and the distribution and properties of an extended family of ATP-gated ion channels. Journal of Neuroscience. 1996;16:2495–2507. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-08-02495.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desai SA, Rosenberg RL. Pore size of the malaria parasite's nutrient channel. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA. 1997;94:2045–2049. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.5.2045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Virgilio F. The P2Z purinoceptor: an intriguing role in immunity, inflammation and cell death. Immunology Today. 1995;16:524–528. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(95)80045-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Virgilio F, Ferrari D, Falzoni S, Chiozzi P, Munerati M, Steinberg TH, Baricordi OR. P2 Receptors: Localization, Function and Transduction Mechanisms, Ciba Foundation Symposium. Vol. 198. New York: John Wiley & Sons; 1996. P2 receptors in the immune system; pp. 90–302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubyak G, El-Moatassim C. Signal transduction via P2 purinergic receptors for extracellular ATP and other nucleotides. American Journal of Physiology. 1993;265:C577–606. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.265.3.C577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans RJ, Lewis C, Virginio C, Lundstrom K, Buell G, Surprenant A, North RA. Ionic permeability of, and divalent cation effects on, two ATP-gated cation channels (P2X receptors) expressed in mammalian cells. The Journal of Physiology. 1996;497:413–422. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1996.sp021777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenwick EM, Marty A, Neher E. A patch-clamp study of bovine chromaffin cells and of their sensitivity to acetylcholine. The Journal of Physiology. 1982;331:577–597. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon JL. Extracellular ATP: effects, sources and fates. Biochemical Journal. 1996;233:309–319. doi: 10.1042/bj2330309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krasilnikov OV, Sabirov RZ, Ternovsky VI, Merzliak PG, Muratkhodjaev JN. A simple method for the determination of the pore radius of ion channels in planar lipid bilayer membranes. FEMS Immunology and Medical Microbiology. 1992;105:93–100. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1992.tb05891.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le KT, Villeneuve P, Ramjaun AR, McPherson PS, Beaudet A, Seguela P. Sensory presynaptic and widespread somatodendritic immunolocalization of central ionotropic P2X ATP receptors. Neuroscience. 1998;83:144–190. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(97)00365-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran O, Zegarra-Moran O, Virginio C, Gusmani L, Rottini GD. Physical characterization of the pore-forming cytolysine from Gardnerella vaginalis. FEMS Immunology and Medical Microbiology. 1992;105:63–70. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1992.tb05888.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neher E. Correction for liquid junction potentials in patch clamp experiments. Methods in Enzymology. 1992;207:123–130. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(92)07008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North RA, Barnard EA. Nucleotide receptors. Current Opinion in Neurobiology. 1997;7:346–357. doi: 10.1016/s0959-4388(97)80062-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsegian VA, Bezrukov SM, Vodyanoy I. Watching small molecules move: interrogating ionic channels using neutral solutes. Bioscience Reports. 1995a;15:503–514. doi: 10.1007/BF01204353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsegian VA, Rand RP, Rau DC. Macromolecules and water: probing with osmotic stress. Methods in Enzymology. 1995b;259:43–94. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(95)59039-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralevic V, Burnstock G. Receptors for purines and pyrimidines. Pharmacological Reviews. 1998;50:413–492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rassendren F, Buell G, Newbolt A, North RA, Surprenant A. Identification of amino acid residues contributing to the pore of a P2X receptor. EMBO Journal. 1997a;16:3446–3454. doi: 10.1093/emboj/16.12.3446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rassendren F, Buell G, Virginio C, Collo G, North RA, Surprenant A. The permeabilizing ATP receptor, P2X7: cloning and expression of a human cDNA. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1997b;272:5482–5486. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.9.5482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song SL, Chueh SH. Antagonistic effect of Na+ and Mg2+ on P2Z purinoceptor-associated pores in dibutyryl cyclic AMP-differentiated NG108–15 cells. Journal of Neurochemistry. 1996;67:1694–1701. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1996.67041694.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song L, Hobaugh MR, Shustak C, Cheley S, Bayley H, Gouaux JE. Structure of staphylococcal α-hemolysin, a heptameric transmembrane pore. Science. 1996;274:1859–1866. doi: 10.1126/science.274.5294.1859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surprenant A, Rassendren F, Kawashima E, North RA, Buell G. The cytolytic P2Z receptor for extracellular ATP identified as a P2X receptor (P2X7) Science. 1996;272:735–738. doi: 10.1126/science.272.5262.735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatham PER, Lindau M. ATP-induced pore formation in the plasma membrane of rat peritoneal mast cells. Journal of General Physiology. 1990;95:459–476. doi: 10.1085/jgp.95.3.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virginio C, Church D, North RA, Surprenant A. Effects of divalent cations, protons and calmidazolium at the rat P2X7 receptor. Neuropharmacology. 1997;36:1285–1294. doi: 10.1016/s0028-3908(97)00141-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virginio C, MacKenzie A, Rassendren FA, North RA, Surprenant A. Pore dilatation of neuronal P2X receptor channels. Nature Neuroscience. 1999;2:315–321. doi: 10.1038/7225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vulchanova L, Arvidsson U, Riedl M, Wang J, Buell G, Surprenant A, North RA, Elde R. Differential distribution of two ATP-gated ion channels (P2X receptors) determined by immunocytochemistry. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA. 1996;93:8063–8067. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.15.8063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vulchanova L, Riedl MS, Shuster SJ, Buell G, Surprenant A, North RA, Elde R. Immunohistochemical study of the P2X2 and P2X3 receptor subunits in monkey and rat sensory neurons and their central terminal. Neuropharmacology. 1997;36:1229–1242. doi: 10.1016/s0028-3908(97)00126-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley JS, Chen JR, Snook M S, Gargett CE, Jamieson GP. P2 Receptors: Localization, Function and Transduction Mechanisms, Ciba Foundation Symposium. Vol. 198. New York: John Wiley & Sons; 1996. Transduction mechanisms of P2Z receptors; pp. 149–159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley JS, Chen JR, Snook MB, Jamieson GP. The P2Z-purinoceptor of human lymphocytes: actions of nucleotide agonists and irreversible inhibition by oxidized ATP. British Journal of Pharmacology. 1994;112:946–950. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb13172.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerberg J, Parsegian VA. Polymer inaccessible volume changes during opening and closing of a voltage-dependent ionic channel. Nature. 1986;323:36–39. doi: 10.1038/323036a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


