Abstract
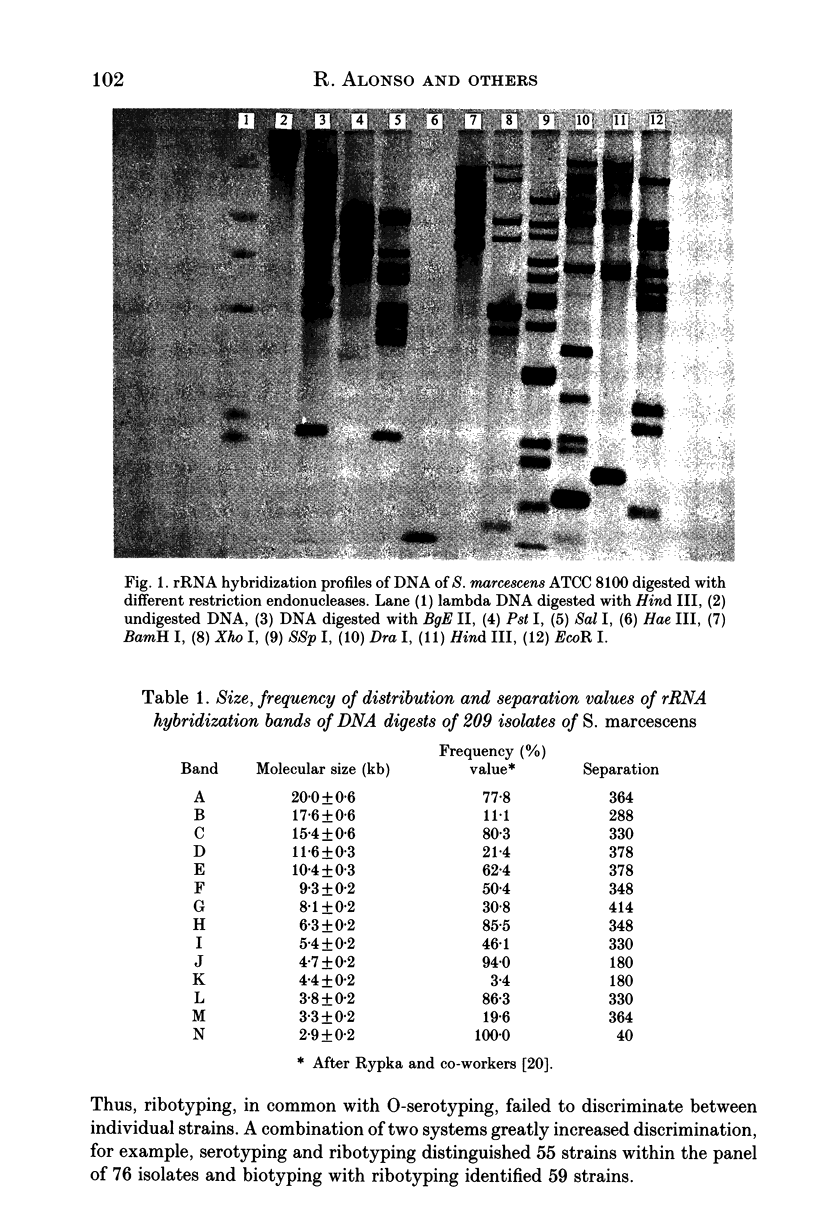
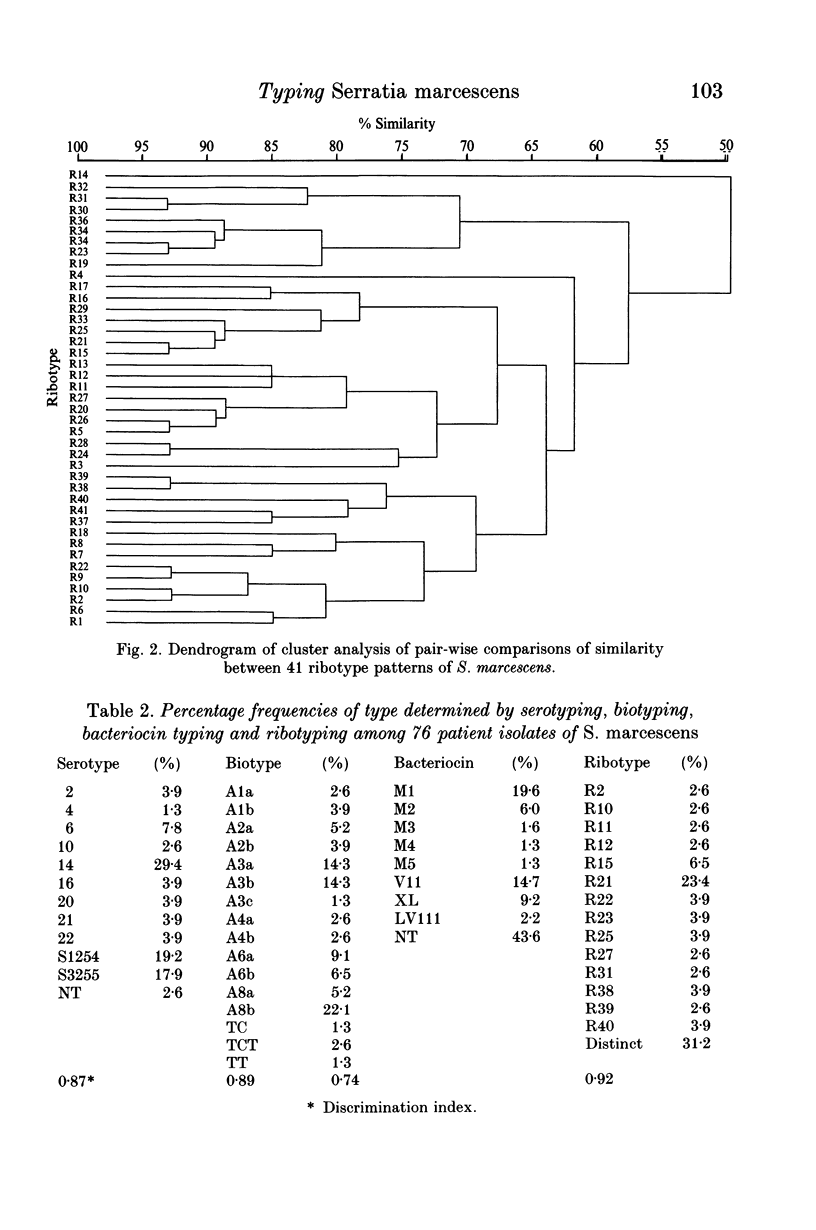
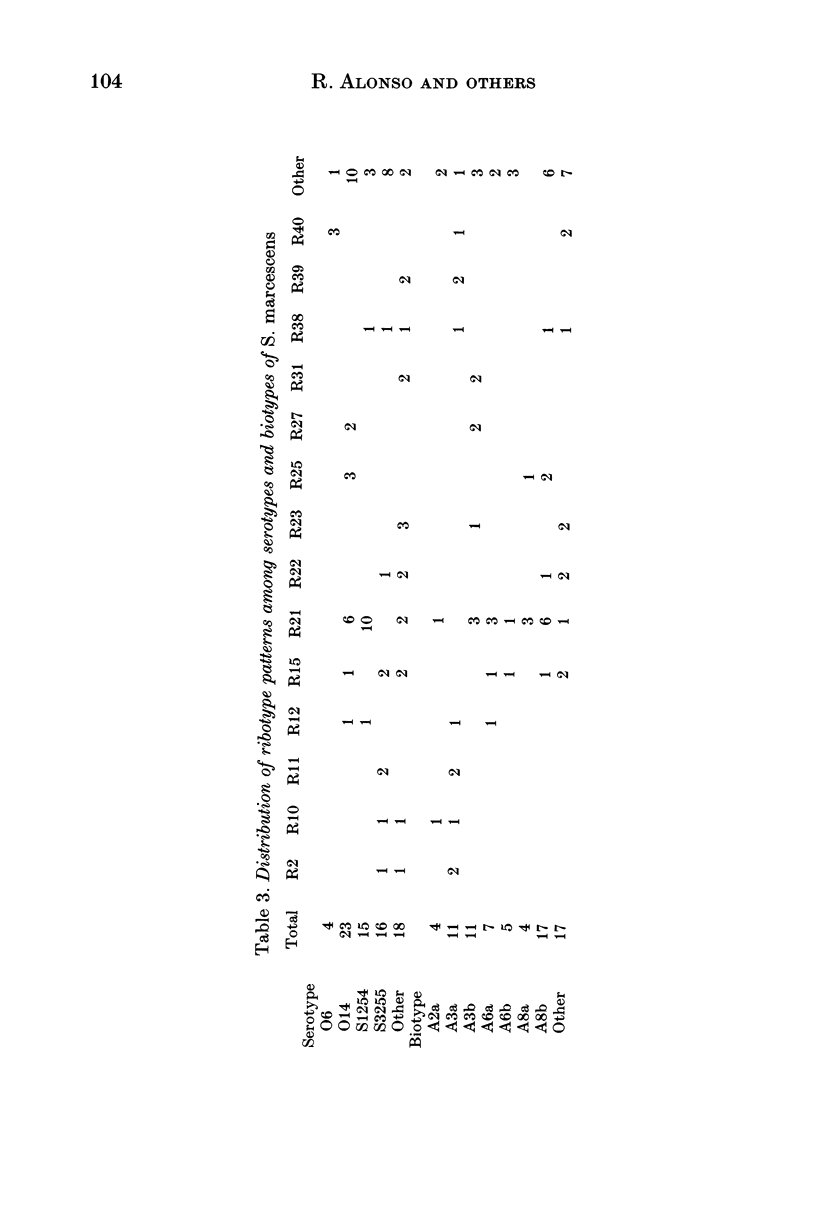
Variations in rDNA gene loci in DNA digests of 209 clinical isolates of Serratia marcescens were determined with an Escherichia coli rRNA probe. Forty-one restriction fragment length polymorphism patterns (ribotypes) were identified, based on the size of 4-14 (mean 7.5) hybridization bands. The patterns differed by more than a single band in 98% of pair-wise comparisons. On a subset of 76 isolates, ribotyping proved to be marginally more discriminating than biotyping (discrimination index 0.92 v. 0.89) followed by serotyping (0.87) and bacteriocin typing (0.74). About one-third of isolates belonged to unique ribotypes and only two ribotypes exceeded 5% in frequency (23.0 and 6.4% respectively). A combination of serotype or biotype with ribotyping defined a similar number of strains, although none of the methods alone was sufficiently discriminatory to identify strains. We conclude that due to the accessibility of biotyping and the lack of commercially available antisera for S. marcescens, the biotype and ribotype together provide reliable markers of strain identity.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alonso R., Nicholson P. S., Pitt T. L. Rapid extraction of high purity chromosomal DNA from Serratia marcescens. Lett Appl Microbiol. 1993 Feb;16(2):77–79. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-765x.1993.tb00348.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bingen E. H., Mariani-Kurkdjian P., Lambert-Zechovsky N. Y., Desjardins P., Denamur E., Aujard Y., Vilmer E., Elion J. Ribotyping provides efficient differentiation of nosocomial Serratia marcescens isolates in a pediatric hospital. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Aug;30(8):2088–2091. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.8.2088-2091.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bollmann R., Halle E., Sokolowska-Köhler W., Grauel E. L., Buchholz P., Klare I., Tschäpe H., Witte W. Nosocomial infections due to Serratia marcescens--clinical findings, antibiotic susceptibility patterns and fine typing. Infection. 1989 Sep-Oct;17(5):294–300. doi: 10.1007/BF01650711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garaizar J., Kaufmann M. E., Pitt T. L. Comparison of ribotyping with conventional methods for the type identification of Enterobacter cloacae. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Jul;29(7):1303–1307. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.7.1303-1307.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gargallo-Viola D. Enzyme polymorphism, prodigiosin production, and plasmid fingerprints in clinical and naturally occurring isolates of Serratia marcescens. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 May;27(5):860–868. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.5.860-868.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaston M. A., Pitt T. L. Improved O-serotyping method for Serratia marcescens. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Dec;27(12):2702–2705. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.12.2702-2705.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimont F., Grimont P. A. Ribosomal ribonucleic acid gene restriction patterns as potential taxonomic tools. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1986 Sep-Oct;137B(2):165–175. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(86)80105-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimont P. A., Grimont F. Biotyping of Serratia marcescens and its use in epidemiological studies. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Jul;8(1):73–83. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.1.73-83.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes B., Costas M., Sloss L. L. Numerical analysis of SDS-PAGE protein patterns of Serratia marcescens: a comparison with other typing methods. Epidemiol Infect. 1990 Aug;105(1):107–117. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800047701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter P. R., Gaston M. A. Numerical index of the discriminatory ability of typing systems: an application of Simpson's index of diversity. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Nov;26(11):2465–2466. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.11.2465-2466.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D., Sackin M. J. Numerical methods in the classification and identification of bacteria with especial reference to the Enterobacteriaceae. Soc Appl Bacteriol Symp Ser. 1980;8:73–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis A. M., Stephenson J. R., Garner J., Afshar F., Tabaqchali S. A hospital outbreak of Serratia marcescens in neurosurgical patients. Epidemiol Infect. 1989 Feb;102(1):69–74. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800029691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis D. A., Hawkey P. M., WattsJA, Speller D. C., Primavesi R. J., Fleming P. J., Pitt T. L. Infection with netilmicin resistant Serratia marcescens in a special care baby unit. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 Dec 3;287(6406):1701–1705. doi: 10.1136/bmj.287.6406.1701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeer A., Low D. E., Penner J., Ng J., Goldman C., Simor A. E. Use of molecular typing to study the epidemiology of Serratia marcescens. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jan;28(1):55–58. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.1.55-58.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakashima A. K., McCarthy M. A., Martone W. J., Anderson R. L. Epidemic septic arthritis caused by Serratia marcescens and associated with a benzalkonium chloride antiseptic. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Jun;25(6):1014–1018. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.6.1014-1018.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitt T. L., Erdman Y. J., Bucher C. The epidemiological type identification of Serratia marcescens from outbreaks of infection in hospitals. J Hyg (Lond) 1980 Apr;84(2):269–283. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400026772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub W. H., Raymond E. A., Startsman T. S. Bacteriocin (Marcescin) typing of clinical isolates of Serratia marcescens. Appl Microbiol. 1971 May;21(5):837–840. doi: 10.1128/am.21.5.837-840.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]