Abstract
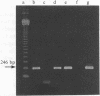
A total of 17 isolates of Vibrio mimicus from patients, 29 from environment and 2 from food was examined for toxigenicity. Sixteen (94%) clinical isolates and one (50%) from food produced TDH-like toxin, whereas none of the environmental isolates did so. The food from which V. mimicus with TDH-like toxin production was isolated, was one which had caused food poisoning. Only one environmental strain produced CT-like toxin, whilst ST-like toxin was not detected from any strains tested.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arita M., Honda T., Miwatani T., Takeda T., Takao T., Shimonishi Y. Purification and characterization of a heat-stable enterotoxin of Vibrio mimicus. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 Mar 15;63(1):105–110. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(91)90536-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury M. A., Aziz K. M., Kay B. A., Rahim Z. Toxin production by Vibrio mimicus strains isolated from human and environmental sources in Bangladesh. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Nov;25(11):2200–2203. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.11.2200-2203.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis B. R., Fanning G. R., Madden J. M., Steigerwalt A. G., Bradford H. B., Jr, Smith H. L., Jr, Brenner D. J. Characterization of biochemically atypical Vibrio cholerae strains and designation of a new pathogenic species, Vibrio mimicus. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Dec;14(6):631–639. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.6.631-639.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean A. G., Ching Y. C., Williams R. G., Harden L. B. Test for Escherichia coli enterotoxin using infant mice: application in a study of diarrhea in children in Honolulu. J Infect Dis. 1972 Apr;125(4):407–411. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.4.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto Y., Kato T., Obara Y., Akiyama S., Takizawa K., Yamai S. In vitro hemolytic characteristic of Vibrio parahaemolyticus: its close correlation with human pathogenicity. J Bacteriol. 1969 Nov;100(2):1147–1149. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.2.1147-1149.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishibuchi M., Fasano A., Russell R. G., Kaper J. B. Enterotoxigenicity of Vibrio parahaemolyticus with and without genes encoding thermostable direct hemolysin. Infect Immun. 1992 Sep;60(9):3539–3545. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.9.3539-3545.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishibuchi M., Khaeomanee-iam V., Honda T., Kaper J. B., Miwatani T. Comparative analysis of the hemolysin genes of Vibrio cholerae non-01, V. mimicus, and V. hollisae that are similar to the tdh gene of V. parahaemolyticus. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 Feb;55(3):251–256. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(90)90004-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishibuchi M., Seidler R. J. Medium-dependent production of extracellular enterotoxins by non-O-1 Vibrio cholerae, Vibrio mimicus, and Vibrio fluvialis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jan;45(1):228–231. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.1.228-231.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oku Y., Uesaka Y., Hirayama T., Takeda Y. Development of a highly sensitive bead-ELISA to detect bacterial protein toxins. Microbiol Immunol. 1988;32(8):807–816. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1988.tb01442.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakazaki R., Tamura K., Kato T., Obara Y., Yamai S. Studies on the enteropathogenic, facultatively halophilic bacterium, Vibrio parahaemolyticus. 3. Enteropathogenicity. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1968 Oct;21(5):325–331. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.21.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shandera W. X., Johnston J. M., Davis B. R., Blake P. A. Disease from infection with Vibrio mimicus, a newly recognized Vibrio species. Clinical characteristics and edipemiology. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Aug;99(2):169–171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spira W. M., Fedorka-Cray P. J. Purification of enterotoxins from Vibrio mimicus that appear to be identical to cholera toxin. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):679–684. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.679-684.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tada J., Ohashi T., Nishimura N., Shirasaki Y., Ozaki H., Fukushima S., Takano J., Nishibuchi M., Takeda Y. Detection of the thermostable direct hemolysin gene (tdh) and the thermostable direct hemolysin-related hemolysin gene (trh) of Vibrio parahaemolyticus by polymerase chain reaction. Mol Cell Probes. 1992 Dec;6(6):477–487. doi: 10.1016/0890-8508(92)90044-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uesaka Y., Otsuka Y., Kashida M., Oku Y., Horigome K., Nair G. B., Pal S. C., Yamasaki S., Takeda Y. Detection of cholera toxin by a highly sensitive bead-enzyme linked immunosorbent assay. Microbiol Immunol. 1992;36(1):43–53. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1992.tb01641.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]